#wild plant
Text
Snake's-head fritillary (Fritillaria meleagris) photos I took today 30/03/2024, area around Smeaton, West Yorkshire


#nature#nature photography#british nature#wild#fritillaries#purple flower#purple floral#purple flowers#purple#wildflora#wildflower photography#wildflower#wildflowers#wild flowers#flower#flowers#flora#flower photography#wild plant#plant#plants#plant photography#botany#botanical#blooms#bloom#fritillary#lily#lilies#liliaceae
173 notes
·
View notes
Text

© Henri Coudoux
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
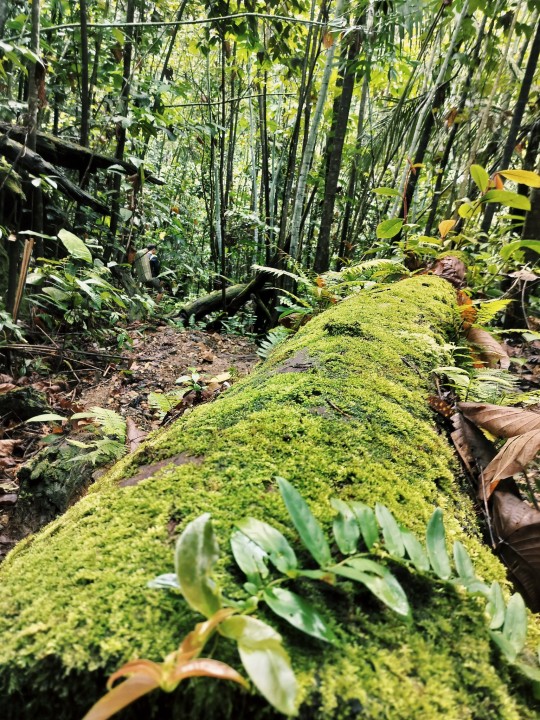
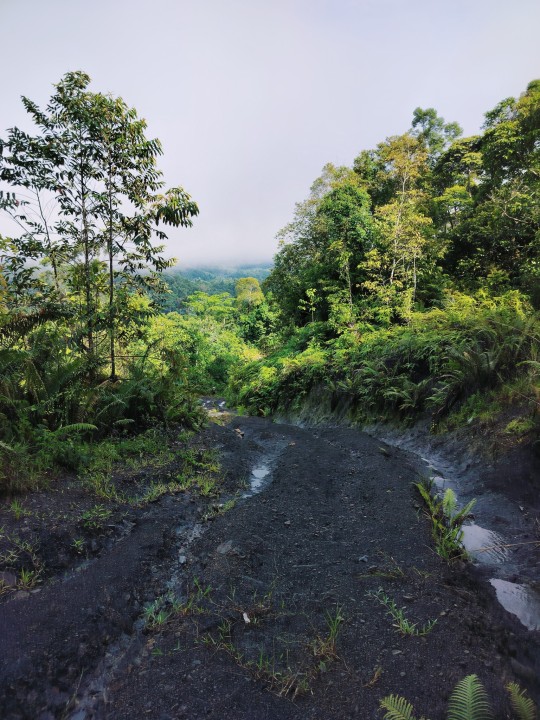




Trip to Baram, July 2023.
#nature#exploring#jungle trekking#jungle#flora#wild plant#scrubs#tropical rainforest#forest#hiking#Baram#Sarawak#Miri#Borneo#landscape#exotic#naturecore
10 notes
·
View notes
Text


Blackberry flowers :-)
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today's Haiku with picture106

at the river bank
Red and white Rukou
pleasing to the eye
河原にて
紅白ルコウ
目の保養
Introduced for appreciation has become a wild plant. Convolvulaceae, a member of the morning glory family, is surprisingly beautiful.
(2022.08.30)
#river bank#rukou#appreciation#wild plant#Convolvulaceae#morning glory#haiku#Today's Haiku with picture
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the Willamette Valley of Oregon, the long study of a butterfly once thought extinct has led to a chain reaction of conservation in a long-cultivated region.
The conservation work, along with helping other species, has been so successful that the Fender’s blue butterfly is slated to be downlisted from Endangered to Threatened on the Endangered Species List—only the second time an insect has made such a recovery.
[Note: "the second time" is as of the article publication in November 2022.]
To live out its nectar-drinking existence in the upland prairie ecosystem in northwest Oregon, Fender’s blue relies on the help of other species, including humans, but also ants, and a particular species of lupine.
After Fender’s blue was rediscovered in the 1980s, 50 years after being declared extinct, scientists realized that the net had to be cast wide to ensure its continued survival; work which is now restoring these upland ecosystems to their pre-colonial state, welcoming indigenous knowledge back onto the land, and spreading the Kincaid lupine around the Willamette Valley.
First collected in 1929 [more like "first formally documented by Western scientists"], Fender’s blue disappeared for decades. By the time it was rediscovered only 3,400 or so were estimated to exist, while much of the Willamette Valley that was its home had been turned over to farming on the lowland prairie, and grazing on the slopes and buttes.

Pictured: Female and male Fender’s blue butterflies.
Now its numbers have quadrupled, largely due to a recovery plan enacted by the Fish and Wildlife Service that targeted the revival at scale of Kincaid’s lupine, a perennial flower of equal rarity. Grown en-masse by inmates of correctional facility programs that teach green-thumb skills for when they rejoin society, these finicky flowers have also exploded in numbers.
[Note: Okay, I looked it up, and this is NOT a new kind of shitty greenwashing prison labor. This is in partnership with the Sustainability in Prisons Project, which honestly sounds like pretty good/genuine organization/program to me. These programs specifically offer incarcerated people college credits and professional training/certifications, and many of the courses are written and/or taught by incarcerated individuals, in addition to the substantial mental health benefits (see x, x, x) associated with contact with nature.]
The lupines needed the kind of upland prairie that’s now hard to find in the valley where they once flourished because of the native Kalapuya people’s regular cultural burning of the meadows.
While it sounds counterintuitive to burn a meadow to increase numbers of flowers and butterflies, grasses and forbs [a.k.a. herbs] become too dense in the absence of such disturbances, while their fine soil building eventually creates ideal terrain for woody shrubs, trees, and thus the end of the grassland altogether.
Fender’s blue caterpillars produce a little bit of nectar, which nearby ants eat. This has led over evolutionary time to a co-dependent relationship, where the ants actively protect the caterpillars. High grasses and woody shrubs however prevent the ants from finding the caterpillars, who are then preyed on by other insects.
Now the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde are being welcomed back onto these prairie landscapes to apply their [traditional burning practices], after the FWS discovered that actively managing the grasslands by removing invasive species and keeping the grass short allowed the lupines to flourish.
By restoring the lupines with sweat and fire, the butterflies have returned. There are now more than 10,000 found on the buttes of the Willamette Valley."
-via Good News Network, November 28, 2022
#butterflies#butterfly#endangered species#conservation#ecosystem restoration#ecosystem#ecology#environment#older news but still v relevant!#fire#fire ecology#indigenous#traditional knowledge#indigenous knowledge#lupine#wild flowers#plants#botany#lepidoptera#lepidopterology#entomology#insects#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
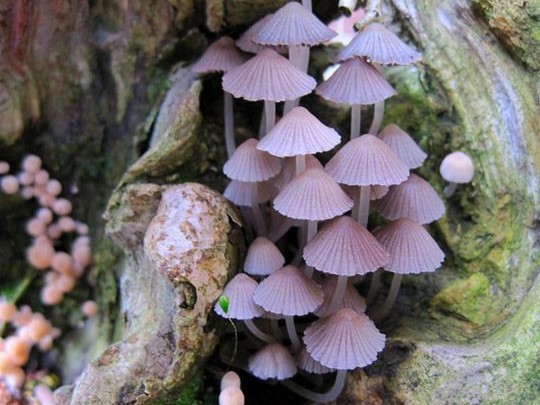

#mushrooms#fungus#fungi#wild fungi#pink mushrooms#forest#trees#landscape#mushroomcore#nature#naturecore#nature aesthetic#landscapes#plants#botany#gardens#gardencore#fairy#fairycore#fairy aesthetic#fairies#faecore#cottage#cottagecore#cottage aesthetic#fairy cottage#cozy cottage#forestcore
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Soulmates In Starlight
Watercolor On Black Paper
2023, 22"x 30"
White Wild Roses
#artists on tumblr#floral#art#flowers#nature#watercolor#plants#artwork#minimalism#painting#wildflowers#roses#rose#white#white flowers#wild roses#botany#garden#plantblr#artblr#contemporary art#cottagecore aesthetic#cottagecore#naturecore
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
ETA: I wrote up a guide on clues that a foraging book was written by AI here!
[Original Tweet source here.]
[RANT AHEAD]
Okay, yeah. This is a very, very, very bad idea. I understand that there is a certain flavor of techbro who has ABSOLUTELY zero problem with this because "AI is the future, bro", and we're supposed to be reading their articles on how to use AI for side hustles and all that.
I get that ID apps have played into people's tendency to want quick and easy answers to everything (I'm not totally opposed to apps, but please read about how an app does not a Master Naturalist make.) But nature identification is serious stuff, ESPECIALLY when you are trying to identify whether something is safe to eat, handle, etc. You have to be absolutely, completely, 100000% sure of your ID, and then you ALSO have to absolutely verify that it is safely handled and consumed by humans.
As a foraging instructor, I cannot emphasize this enough. My classes, which are intended for a general audience, are very heavy on identification skills for this very reason. I have had (a small subsection of) students complain that I wasn't just spending 2-3 hours listing off bunches of edible plants and fungi, and honestly? They can complain all they want. I am doing MY due diligence to make very sure that the people who take my classes are prepared to go out and start identifying species and then figure out their edibility or lack thereof.
Because it isn't enough to be able to say "Oh, that's a dandelion, and I think this might be an oyster mushroom." It's also not enough to say "Well, such-and-such app says this is Queen Anne's lace and not poison hemlock." You HAVE to have incredibly keen observational skills. You HAVE to be patient enough to take thorough observations and run them through multiple forms of verification (field guides, websites, apps, other foragers/naturalists) to make sure you have a rock-solid identification. And then you ALSO have to be willing to read through multiple sources (NOT just Wikipedia) to determine whether that species is safely consumed by humans, and if so if it needs to be prepared in a particular way or if there are inedible/toxic parts that need to be removed.
AND--this phenomenon of AI-generated crapola emphasizes the fact that in addition to all of the above, you HAVE to have critical thinking skills when it comes to assessing your sources. Just because something is printed on a page doesn't mean it's true. You need to look at the quality of the information being presented. You need to look at the author's sources. You need to compare what this person is saying to other books and resources out there, and make sure there's a consensus.
You also need to look at the author themselves and make absolutely sure they are a real person. Find their website. Find their bio. Find their social media. Find any other manners in which they interact with the world, ESPECIALLY outside of the internet. Contact them. Ask questions. Don't be a jerk about it, because we're just people, but do at least make sure that a book you're interested in buying is by a real person. I guarantee you those of us who are serious about teaching this stuff and who are internet-savvy are going to make it very easy to find who we are (within reason), what we're doing, and why.
Because the OP in that Tweet is absolutely right--people are going to get seriously ill or dead if they try using AI-generated field guides. We have such a wealth of information, both on paper/pixels and in the brains of active, experienced foragers, that we can easily learn from the mistakes of people in the past who got poisoned, and avoid their fate. But it does mean that you MUST have the will and ability to be impeccably thorough in your research--and when in doubt, throw it out.
My inbox is always open. I'm easier caught via email than here, but I will answer. You can always ask me stuff about foraging, about nature identification, etc. And if there's a foraging instructor/author/etc. with a website, chances are they're also going to be more than willing to answer questions. I am happy to direct you to online groups on Facebook and elsewhere where you have a whole slew of people to compare notes with. I want people's foraging to be SAFE and FUN. And AI-generated books aren't the way to make that happen.
#foraging#mushroom foraging#plant foraging#mushrooms#edible plants#edible mushrooms#wild foods#food#nature#AI#fungus#fungi#poisonous mushrooms#poisonous plants#botany#mycology#rant
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
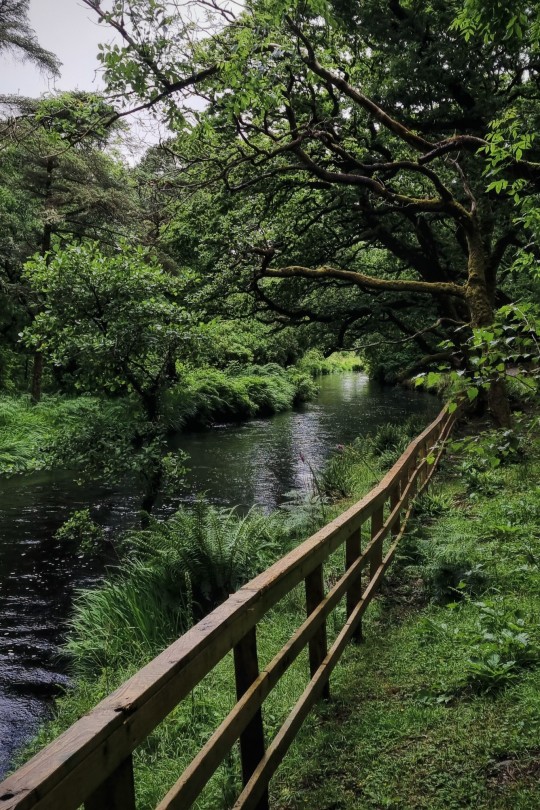
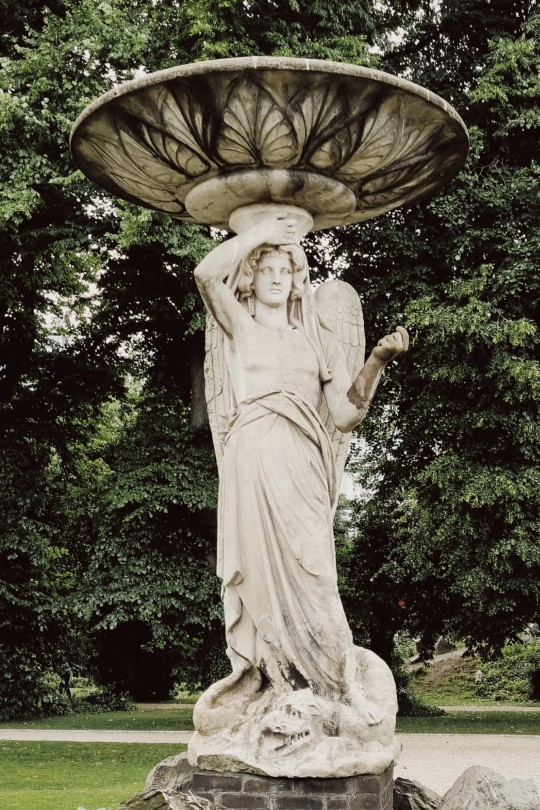
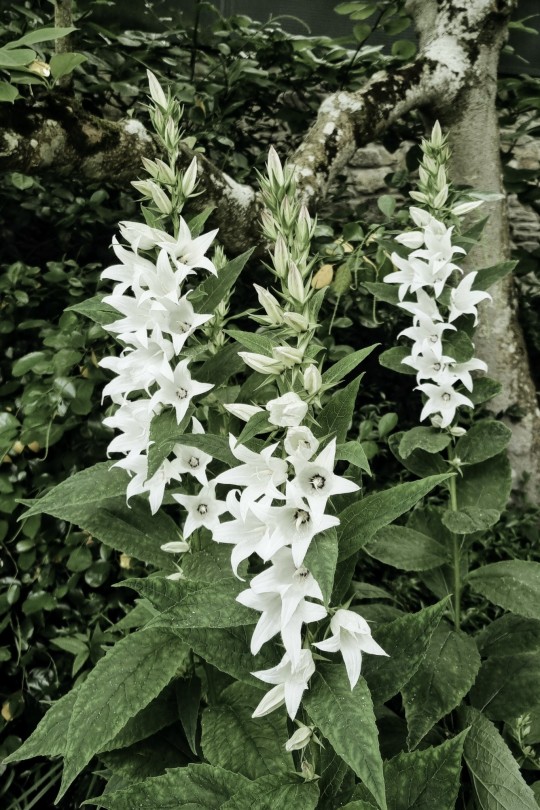
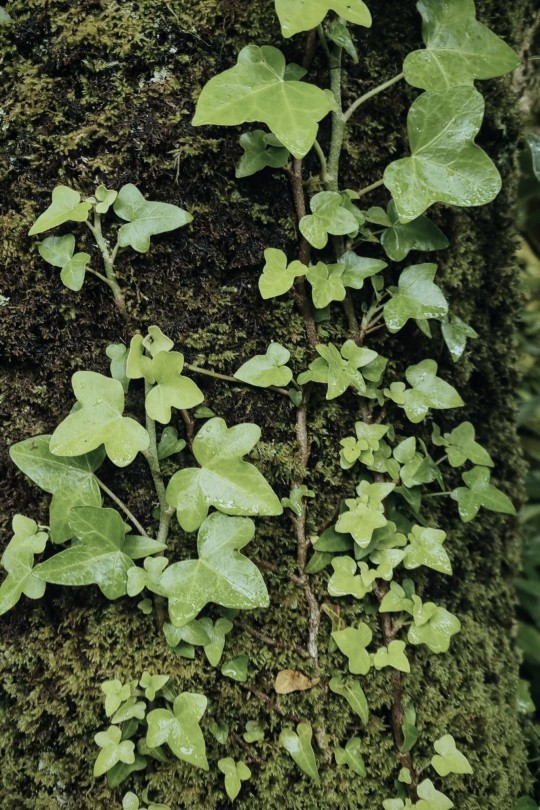




More pics from Ireland because I'll miss it forever 🌾
#nature#green#cottagecore#fairycore#nature photography#photography#ireland#greencore#naturecore#flowers#plants#nature aesthetic#cottagecore aesthetic#cozycore#wild nature#flora#places#goblincore#green witch#witchy aesthetic#europe#ivy
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Marsh marigold (Caltha palustris) wildflower photos I took yesterday 15/04/2024, Stanley, Wakefield, West Yorkshire, UK


#nature#nature photography#british nature#wild#ranunculaceae#yellow flower#yellow flowers#yellow floral#yellow#wild plant#plant#plants#plant photography#wild plants#wildflora#wildflower photography#wildflower#wildflowers#wild flowers#flower#flowers#flower photography#blooms#bloom#flowering plants#blooming#botany#botanical#flora#floral
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

Link and Zelda making dried bouquets at their house in Hateno Village for @byszine 💕🌸
#my art#illustration#artists on tumblr#fan art#mochiwei#digital art#procreate#zelda#tloz#link#Zelink#botw#breath of the wild#dried bouquets#they’re having the time of their lives#Zelda brought in so many plants#zine#zine art#spread
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Wild plant.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
dichotomous plants are so weird man. like they’re not even weird it’s the becoming the dichotomous that’s weird. i went to a talk once about a population of strawberries that were accidentally slowly becoming dichotomous and they didn’t even have sex chromosomes, like they had like a bunch of genes across a bunch of chromosomes that did a little bit of sex but not a lot and it added up to one whole sex kind of but not enough that they had all collectively decided to be one sex or the other, so there was still like, a sizable chunk of the population that was producing flowers of both sexes. like they were microdosing it. taking the sex genes for a spin in the strawberry patch
#the conclusion of the talk was like#what if plants are slowly become more dichotomous over time because it’s more advantageous?#and I was like. that would be interesting but I feel like they would have done it already if it was that good#sex genes are really only as good as the creature or life form you are I think#making the sex genes work for YOU#and for those wild strawberries in the American west. they were just being silly about it you know#and my assumption that having dedicated sex chromosomes that hold the majority but not all sex-related info. turns out that’s kinda weird
1K notes
·
View notes
Text



Flora & Fauna of Hyrule Posters made by WinterZucca
#zelda#nintendo#art#illustration#switch#nintendo switch#breath of the wild#tears of the kingdom#botw#totk#legend of zelda#link#princess zelda#ganon#hyrule#hylian#plants#fungi#bugs#insects#posters#prints#artists#gaming#video games#nature#forestcore#cottagecore#loz
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
Listen here you toe-eyed cabbage. I wasn't born into this world so your fat ass could choke out low-level insults at me. I hope you stub your toe in the dark and have to crawl around your bedroom at 3:47AM in horrific pain after going to the kitchen for a midnight snack of cheese and crackers, you absolute gormless minger.

String identified:
t t- caag. a't t t at a c c t - t at . t t t a a a t ca a at :A c a at gg t t tc a gt ac c a cac, at g g.
Closest match: Glycine soja polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase 2, mitochondrial-like (LOC114411664), mRNA
Common name: Wild soybean
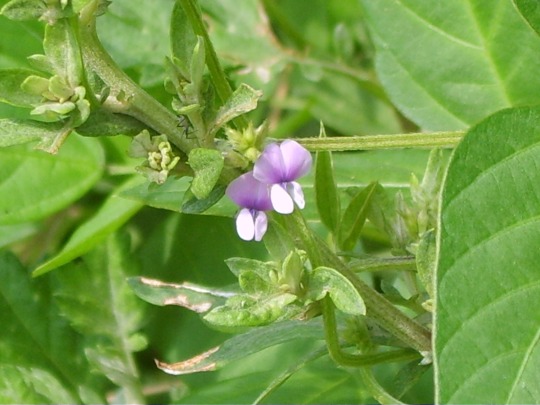

939 notes
·
View notes