#Oil | Fatty Acids | Saturated | Unsaturated.
Text
What Happens When You Season a Cast Iron Pan! Here is How Oil and Heat Can Form a Durable Coating.
— By Attabey Rodríguez Benítez | Published: Monday August 1, 2022 | NOVA— PBS

Image Credit: Jack Kennard, Flickr
Ahh, Cast Iron Pans. Love ‘em or Hate ‘em, they’ve been around for hundreds of years. With proper maintenance, they can last long enough to become family heirlooms. A cornerstone of this pan’s upkeep is seasoning, the process of baking oil onto the pan. Contrary to the name, you won’t need salt and pepper, but fat.
To season, you heat the pan covered in fat to scalding temperatures in an oven. What is left behind is a somewhat nonstick surface that not only helps with cooking but protects the pan from rust.
You can use the fat of your choice, but one thing to keep in mind is the smoke point, the temperature at which it starts to smoke. That temperature varies from oil to oil. For example, virgin avocado oil has a smoke point of 520 F, but coconut oil smokes at just 350 F. As soon as that temperature is reached, the seasoning process begins.
There are multiple hypotheses about what’s happening at the molecular level inside that hot oven. The predominant one is that the oil is polymerizing. Fats are made up of different fatty acids, like saturated and unsaturated. When heated, those acids break down into smaller molecules called monomers. And when monomers join together, they form larger molecules called polymers. When this joining happens over and over in an iron skillet, the polymers form a protective layer that keeps water at bay.
A group of researchers from Chongqing University studied this phenomenon in the context of another cast iron cooking tool: the wok. Woks, mainly used in Chinese-style cuisine, are usually round-bottomed. The team hypothesized that the slick surface formed during seasoning is due more to the iron than the oil. To test their hypothesis, the researchers coated a wok with beef tallow and heated it up. As the temperature increased, the fat started to reduce. And the scientists, using X-ray technology, started to see oxygen molecules sneaking into the places where iron was present. With this unexpected guest, iron atoms had to shuffle around to make space, creating small lumps along the surface. The final product is what the team called “iron nanoballs.”
They point out that these nanoballs didn’t make the wok completely nonstick, but rather made the surface conditionally hydrophobic. That means that it repels water when there isn’t much around, but gets wet when there’s a lot of it. The study authors claim this property comes in handy during cooking, because if the pans are completely nonstick, the fat will lump together, causing uneven cooking. If the surface can get wet, it creates an even layer, and the food can cook evenly as the water evaporates, creating less charring.
#Tech & Engineering#Cast Iron Pan#Seasoning#Oil & Heat#Durable Coating#NOVA—PBS#Avocado 🥑 Oil#Coconut 🌴 🥥 Oil#Polymerizing#Oil | Fatty Acids | Saturated | Unsaturated.#Monomers#Polymers#Chongqing University | China 🇨🇳#Hypothesized#Nanoballs | Hydrophobic#Iron Nanoballs#X-ray Technology
0 notes
Text
Fats of land animals typically contain approximately 40% to 50% saturated fatty acids by weight (table 23.5).
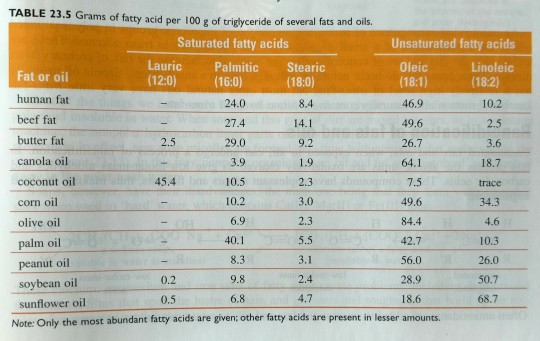
"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#animal fat#land animal#fats#oils#triglycerides#fatty acid#saturated#unsaturated#human fat#beef fat#butter fat#canola oil#coconut oil#corn oil#olive oil#palm oil#peanut oil#soybean oil#sunflower oil#lauric acid#palmitic acid#stearic acid#oleic acid#linoleic acid
0 notes
Text
The Best Natural and Homeopathic Methods to Reduce Fat in the Body
The Best Natural and Homeopathic Methods to Reduce Fat in the Body
This article is about how to reduce fat in the body with natural and homeopathic methods.
The best natural and homeopathic methods to reduce fat in the body are:
– Taking a hot bath for 15-20 minutes.
– Doing some stretches after taking a bath.
– Eating healthy food, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
– Drinking at least 8 glasses of water every day.
– Doing some exercises like…

View On WordPress
#essential fatty acids#fat reduction medicines#fat type#fat-producing foods#fats and oils#how to reduce fat#metabolism boosting exercises#metabolism boosting foods#saturated fat#saturated fats in diet#unsaturated fat#weight loss tips
0 notes
Text
You need to consume unsaturated fats or you'll feel slow, fatigued, and never want to do anything.
You have to learn the healthy fats and eat the healthy fats if you're committed to being vegetarian or vegan. Or you will be tired forever, and not the type of tired where you can push through it, but the type of tired where you feel like you have to stay in bed all day and your heart feels like it's being sucked through a straw.
Fatty acids are what lipids in our bodies are made mostly up of. Fatty acids are responsible for energy storage, brain development, blood clotting, and controlling inflammation. They are necessary for your body to be able to absorb vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K. They are necessary for your body to produce sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Not having enough of these fats can cause muscle pain, night blindness, infertility, easy bruising, dry hair, hair loss, loose teeth, depression and anxiety, and dermatitis (presenting as dry and scaly rashes).
You need unsaturated fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These are good fats. Saturated fats and trans fats are bad, these are what raise your risk of heart attacks and strokes. Diets high in saturated fats might also lead to chronic pain.
35% of your caloric intake should be fats. This can be added to the list on why the diet industry is so cruel. Manufacturers and organizations paired with the pornography and cosmetic industry pushing dieting and beauty norms on women and girls for decades impressed the seriously dangerous and false idea that consuming fats was bad. Denying healthy fats means denying healthy brain development, energy and motivation, better ability to heal from injuries, and preventing depression and anxiety.
Balsamic and olive oil together (and you can add some minced garlic if you like) tastes fantastic with warm bread and can be made in 12 minutes.
Cooking with the oils above instead of butter can also introduce fatty acids in your diet (might not be enough though, you need 1-2 tablespoons a day).
Sometimes if I'm in a hurry I just eat a plain avocado a day.
You can sprinkle chia seeds on yogurt. Add flax seed to smoothies.
Just eat 1/4th of pumpkin seeds too (which are also super high in magnesium). That's basically a handful a day, make it part of your morning routine.
Almonds, walnuts, and pecans are also high in good fats.
121 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which Oil is Good for Health and the Best for Your Heart?
In recent years, there has been growing awareness about the importance of dietary fats in maintaining overall health and well-being. With various types of oils available, it's essential to determine which oil is good for health and particularly beneficial for your heart. This article explores different oils, their health benefits, and helps you find the best oil for heart health.
Understanding Fats and Their Impact on Health
Fats are a crucial part of our diet, but not all fats are created equal. There are three main types of fats: saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats. Understanding these can help you choose the best food oil for heart health.
Saturated Fats: Typically found in animal products and some tropical oils, saturated fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. It’s advisable to limit these in your diet.
Unsaturated Fats: These fats are considered heart-healthy. They are primarily found in plant-based oils, nuts, seeds, and fish. Unsaturated fats can help reduce bad cholesterol levels and provide essential fatty acids.
Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods, trans fats should be avoided as they raise bad cholesterol levels and lower good cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
With this understanding, let's delve into which oil is good for health and specifically beneficial for your heart.
The Best Oils for Heart Health
1. Olive Oil
Olive oil is widely recognized for its health benefits and is often hailed as the best oil for heart health. Rich in monounsaturated fats, olive oil has been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels while raising HDL cholesterol, the "good" cholesterol. It is also packed with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to overall heart health.
2. Avocado Oil
Another excellent option, avocado oil, contains high levels of monounsaturated fats and vitamin E. Studies suggest that avocado oil can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Its mild flavor makes it a versatile choice for various dishes, enhancing both taste and nutritional value.
3. Canola Oil
Canola oil is low in saturated fat and high in unsaturated fats, making it a heart-healthy option. It contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health. Canola oil is often recommended as a cooking oil due to its high smoke point and light flavor.
4. Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil is known for its high content of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Regular consumption of flaxseed oil can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health. It's important to note that flaxseed oil is best used in salad dressings or added to smoothies, as it should not be heated.
5. Walnut Oil
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, walnut oil is another fantastic choice for heart health. It can help reduce inflammation and lower cholesterol levels. The nutty flavor of walnut oil makes it a great addition to dressings and drizzles over cooked dishes.
Oils to Avoid for Heart Health
While it’s essential to know which oil is good for health, it’s equally important to be aware of oils that can negatively impact heart health. Oils high in saturated fats, such as palm oil and coconut oil, should be used sparingly. Additionally, avoid trans fats found in partially hydrogenated oils, commonly used in processed and fried foods.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing the best food oil for heart health can significantly impact your overall well-being. When selecting an oil, consider the following:
Look for Quality: Choose high-quality, extra virgin oils when possible. These oils retain more nutrients and antioxidants compared to refined oils.
Consider Cooking Methods: Different oils have varying smoke points. Choose oils suitable for the cooking method you plan to use. For high-heat cooking, opt for oils like avocado or canola oil.
Balance Your Fats: Incorporate a variety of healthy fats into your diet. This not only enhances flavor but also provides a range of health benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining which oil is good for health and specifically the best oil for heart health involves understanding the types of fats and their effects on your body. Oils like olive, avocado, canola, flaxseed, and walnut oil are excellent choices that contribute positively to heart health. By making informed decisions about the oils you use, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
When looking for the best food oil for heart health, remember that moderation is key, and combining various healthy oils in your diet can yield the best results. Make the switch today, and enjoy a heart-healthy lifestyle!
0 notes
Text
6 Foods Good for Liver Detox

Why liver detox?
Based on a 2020 study that was published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology, between 25% and 30% of Indians overall have NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease). This is in line with results from additional research showing an elevated prevalence of the condition. NAFLD is more common in men than women, with an estimated prevalence of 40% in men and 26% in women. A healthy liver is very crucial for holistic health.
Here you can track down the 6 foods good for liver detox that will help you in liver detoxification:
Also Read: 6 Ways to Detox Your Liver at Home
Apple and liver health
You must have heard of “an apple a day keeps the liver at bay.” It is because Apple have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties as it are rich fiber and other nutrients. It supports metabolism and with its high hydration properties, it flushes out all toxins in the body, supporting gut health. Vitamin C and potassium in apples are involved in metabolic processes that can aid in liver health.
When life gives you lemons, make a lemonade
When life gives you lemons, give your liver a boost. Lemon plays a crucial role in detox diet. Start your day with warm lemon water; this can help kick start your metabolism. You can add salads or make smoothies to boost the flavor that will complement Vitamin C for your body. Lemons stimulates digestive enzymes and further reduce oxidative stress. Maintaining a balance between free radicals and antioxidants is crucial for protecting liver health and function.
Why olive oil?
One of the components of Olive oil, hydroxytyrosol, has been shown to reduce negative effects of fatty liver disease. It supports insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammation, and enhances fat metabolism. Olive oils have monosaturated fats, whereas the other oils are rich in omega 6 fatty acids and saturated fats. Monosaturated fats improve the lipid profile and other liver-related conditions.
Liver’s best friend (Garlic)
When it comes to liver health, garlic acts as an ally in the kitchen. Consuming raw garlic is one of the most effective way to support your liver health. It reduces fat accumulation and supports immune function. The antioxidants in garlic, including selenium and vitamin C, help neutralize harmful free radicals in the liver. Through its rich content in sulfur, it stimulates liver enzymes and promotes detoxification.
Nuts to boost liver’s roots
Nuts can fortify and support the basis of liver function, Nuts like walnuts, cashews, almonds, and brazil nuts are rich in omega 3 fatty acids, vitamin E, magnesium, and zinc that can promote healthy weight, healthy digestion, support immunity and reduce liver’s burden. The unsaturated fats present in nuts can prevent NAFLD.
Avocados
Avocados are an excellent source of glutathione, which protects liver health, guards the liver from unwanted toxins, and strengthens the liver's cleansing function. It is also rich in Vitamin B6 and Vitamin C, which act as antioxidants, reversing oxidative damage to protect liver.
Also Read: Say No to Fatty Liver
TAKEAWAY
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” Other than the food mentioned above, one can incorporate watermelon, banana, salmon, pumpkin, tomato, tuna, mung beans, papaya, and grapes into nutrition plan. What you eat and how you move determines your gut health. Chronic oxidative stress is linked to various liver conditions like NAFLD, Alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis, and liver cirrhosis. Balancing your diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while staying hydrated and exercising regularly can support liver health and overall well-being.
#fitliver#liver#healthcare#health & fitness#healthylifestyle#benefits#health and wellness#wellness#nutrition
0 notes
Text
This article is originally published on Freedom from Diabetes website, available here.
The Janmashtami prasad- Panjiri is made with several nutritious ingredients, including ghee, dry fruits, coriander seeds, lotus seeds, almonds, cardamon, and some powdered sugar—which we will replace with stevia, so as to retain the sweet component without spiking Blood Sugar Levels (BSL). The seeds are added to replace grains, which are proscribed during fasts—again, this has health benefits, especially for diabetics.

Ingredients for janmashtami Parsad-Panjiri
Desiccated coconut flour- 3/4 cup
Coconut oil can help in reducing waist circumference, lowering insulin resistance, and improving levels of HDL cholesterol. In addition, coconuts contain many beneficial nutrients. Coconut is rich in dietary fiber, which helps lower cholesterol levels and the risk of developing a cardiac disease.
Coriander seeds- 1 cup
Coriander contains bio-active components, flavonoids, and phenolic acids.
Melon seeds- 5 tsp
Watermelon seeds are high in zinc, which is an important nutrient for building immunity. Zinc is also essential for the digestive system and nervous systems.
Coconut ghee- 7 tbsp
Ghee is the current darling of the health-food crowd, and while it does have many undeniable positives, the fact that it is an animal product, and thus, high in saturated fat outweighs the perceived benefits.
Lotus seeds- 1 cup
The entire lotus plant can be consumed: the root stalks (rhizome) as food, seed as medicine, thalamus (the thick part of the stem near the flower) as fruit, leaves are used as a plate (thali), stalks can be pickled, petals provide color, and tender leaves are eater as a vegetable.
Almonds, diced and roasted- 3 tbsp
Nuts contain vegetable protein, unsaturated fatty acids, fiber, phytosterols (cholesterol-lowering elements), phenolic compounds (potent antioxidants), calcium, magnesium, potassium, and Vitamins like folic acid, niacin, and B6.
Cardamom- 3 1/2 tsp
Cardamom is commonly used as a spice to flavor a number of dishes. In addition to its culinary properties, it is also a potent antioxidant and used in traditional medicinal preparations to regulate BP.
Stevia 6-8 drops
Stevia is a much healthier alternative—it contains no carbohydrates, calories, or artificial ingredients.
Janmashtami Parsad- Panjiri recipe
Dry roast the coconut flour on a low flame until it turns a rich golden hue.
Add the coconut ghee, coriander seeds, and cardamom pods and continue roasting until the ghee is absorbed into the flour and the 3. Flour releases the aroma of the spices.
4.Now add diced and roasted almonds, lotus seeds, and shelled melon seeds, and stir the mixture until everything is roasted perfectly.
Finally, add the stevia and turn off the flame.
Your Panjiri Prasad is ready!
To know more about this, please visit our Article.
Also please connect with me on my website, Facebook page, and YouTube if you want to stay in touch or give me any feedback!
#Janmashtami prasad benefits#Panjiri health benefits#Benefits of Panjiri for health#Healthy prasad for Janmashtami#Panjiri nutritional value#Panjiri for Janmashtami#Traditional Panjiri benefits#Panjeri recipe for Janmashtami#Panjiri and health benefits#Janmashtami prasad Panjiri benefits
0 notes
Text
Healthy Fat: is Butter Better?

Saturated fats, like those found in butter, may not be as harmful as once thought and can be part of a healthy diet.
Copper deficiency is linked to various heart disease risk factors, including high cholesterol and oxidative stress.
Unhealthy fats, particularly trans fats found in processed foods, are detrimental to heart health.
A balanced diet with the right types of fats and nutrient-rich foods is important for overall wellness.
The debate over whether butter and other saturated fats are harmful or beneficial has been ongoing for years.
Recent research has shed new light on the topic, highlighting the importance of understanding the different types of fats and their impact on health.
Understanding Fats

Types of Fats
Fats can be categorized into three main types: saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats. Each type of fat affects the body differently, making it important to understand their unique properties and health implications.
The Role of Fats in the Diet
Fats are essential for storing energy, maintaining cell structure, and producing hormones. They also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
Saturated Fats: Not as Harmful as Once Thought
Recent research indicates that saturated fats, such as those found in butter, may not be as harmful as previously believed.
These studies suggest that moderate consumption of saturated fats can be part of a healthy diet without significantly increasing the risk of heart disease.
Nutritional Benefits of Butter
Butter is not only a source of saturated fat but also contains essential vitamins and minerals. It is rich in vitamin A, which is crucial for vision, immune function, and skin health.
Additionally, butter contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which has been linked to various health benefits, including improved metabolism and reduced body fat.
Copper Deficiency and Heart Health

The Link Between Copper Deficiency and Heart Disease
Copper plays a key role in maintaining heart health. It is essential for producing red blood cells, maintaining healthy blood vessels, and supporting the immune system.
A deficiency in copper can lead to various heart disease risk factors, including high cholesterol and oxidative stress.
Ensuring adequate copper intake is vital for overall cardiovascular health.
The Dangers of Trans Fats
Trans fats, commonly found in processed foods, are detrimental to heart health. These fats increase so-called ‘bad cholesterol’ (LDL) and decrease good cholesterol (HDL), leading to a higher risk of heart disease.
Avoiding foods with trans fats and choosing healthier fat options is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart.
Adding Healthy Fats to Your Diet
Healthy fats are important for overall wellness. Focus on sources like butter, fatty cuts of meat, eggs, and full-fat dairy products.
These foods provide essential fatty acids and other nutrients that support heart health, brain function, and overall well-being.
The Science-backed Benefits of Natural Fats
Recent research has highlighted the importance of including healthy fats in our diet. Here are some examples of valuable dietary fats, and their benefits:
Cod liver oil: High in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and D; supports heart health, brain function, and immune system.
Tallow: Rich in saturated fats and fat-soluble vitamins; can help protect the liver, brain, and nerves.
Ghee: Source of medium-chain triglycerides and butyrate; supports digestive and immune health.
Butter: Contains health-promoting CLAs, vitamins, and minerals; associated with improved metabolism and immune function.
Olive oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants; may reduce cardiovascular disease risk and inflammation.
Avocado oil: Good source of monounsaturated fats, vitamin E, and antioxidants; may help lower bad cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Practical Tips for a Heart-Healthy Diet

Carbohydrates contribute to weight gain, increased blood sugar levels, and a higher risk of heart disease.
Reducing carbohydrate intake can help manage these risks and improve overall health.
Monitor Copper Intake:
Ensure your diet includes copper-rich foods like shellfish, organ meats, and beef liver to prevent deficiency and support heart health.
Enjoy Healthy Fats:
Choose nutrient-dense sources
Cod liver oil: High in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and D; supports heart health, brain function, and immune system.
Tallow: Rich in saturated fats and fat-soluble vitamins; can help protect the liver, brain, and nerves.
Ghee: Source of medium-chain triglycerides and butyrate; supports digestive and immune health.
Butter: Contains health-promoting CLAs, vitamins, and minerals; associated with improved metabolism and immune function.
Moderate Dairy Fats: Include full-fat A2 dairy products like cheese, yogurt, and cream in your diet.
Selective Plant-Based Fats: Include small amounts if you need more variety.
Olive oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants; may reduce cardiovascular disease risk and inflammation.
Avocado oil: Good source of monounsaturated fats, vitamin E, and antioxidants; may help lower bad cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Eliminate Processed Foods: Steer clear of foods high in trans fats and refined carbohydrates.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of different fats and the importance of copper in heart health can help make better dietary choices. While butter and other saturated fats may not be as harmful as once thought, balancing them with other nutrient-dense foods and avoiding unhealthy fats is key to maintaining a healthy heart.
FAQs
What are the differences between saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats? Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and found in animal products. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and found in certain plant-based oils and fish. Trans fats are artificially created and found in processed foods.
Is butter really bad for your heart? Recent studies suggest that moderate consumption of butter may not be as harmful as previously believed, especially when balanced with other healthy fats.
How does copper deficiency affect heart health? Copper deficiency can increase cholesterol, oxidative stress, and inflammation, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
What are the best sources of healthy fats? Healthy fats can be found in animal-based products like butter, ghee, and fatty cuts of meat, as well as in small amounts of nuts, seeds, and avocados.
How can I reduce unhealthy fats in my diet? Avoid processed foods high in trans fats and focus on whole, unprocessed foods rich in beneficial animal fats.Research
Albrink, M.J., Lavietes, P.H., & Man, E.B. (1963). Vascular disease and serum lipids in diabetes mellitus: Observations over thirty years (1931-1961). Ann Intern Med, 58, 305-323.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14011776/
Allen, F.M., Stillman, E., & Fitz, R. (1919). Total dietary regulation in the treatment of diabetes. Monograph 11. Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.
Banting, F.G., & Best, C.H. (1922). The internal secretion of the pancreas. J Lab Clin Med, 7, 465–480.
Baker, S., 2019. The carnivore diet. Victory Belt Publishing.
Broom GM, Shaw IC, Rucklidge JJ. The ketogenic diet as a potential treatment and prevention strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Nutrition. 2019 Apr;60:118-121.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30554068/
Brinkworth GD, Buckley JD, Noakes M, Clifton PM, Wilson CJ. Long-term effects of a very low-carbohydrate diet and a low-fat diet on mood and cognitive function. Arch Intern Med. 2009 Nov 09;169(20):1873-80.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19901139/
Byrne P, Demasi M, Jones M, Smith SM, O’Brien KK, DuBroff R. Evaluating the Association Between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Reduction and Relative and Absolute Effects of Statin Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(5):474–481. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0134
Choi YJ, Jeon SM, Shin S. Impact of a Ketogenic Diet on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Obesity or Overweight and with or without Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 06;12(7).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32640608/
Dhillon KK, Gupta S. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Feb 6, 2023. Biochemistry, Ketogenesis.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493179/
Gardner CD, Landry MJ, Perelman D, Petlura C, Durand LR, Aronica L, Crimarco A, Cunanan KM, Chang A, Dant CC, Robinson JL, Kim SH. Effect of a ketogenic diet versus Mediterranean diet on glycated hemoglobin in individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The interventional Keto-Med randomized crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Sep 02;116(3):640-652.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35641199/
Grotto D, Zied E. The Standard American Diet and its relationship to the health status of Americans. Nutr Clin Pract. 2010 Dec;25(6):603-12.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21139124/
Guzel O, Uysal U, Arslan N. Efficacy and tolerability of olive oil-based ketogenic diet in children with drug-resistant epilepsy: A single center experience from Turkey. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2019 Jan;23(1):143-151.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30497921/
Hernández F. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis: A teaching view. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100016.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8289105/
Krebs HA. Gluconeogenesis. Expos Annu Biochim Med. 1965;26:13-30.
Micha R, Peñalvo JL, Cudhea F, Imamura F, Rehm CD, Mozaffarian D. Association Between Dietary Factors and Mortality From Heart Disease, Stroke, and Type 2 Diabetes in the United States. JAMA. 2017 Mar 07;317(9):912-924.
O'Neill B, Raggi P. The ketogenic diet: Pros and cons. Atherosclerosis. 2020 Jan;292:119-126.
Oh R, Gilani B, Uppaluri KR. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Aug 17, 2023. Low-Carbohydrate Diet
Phillips MCL, Murtagh DKJ, Gilbertson LJ, Asztely FJS, Lynch CDP. Low-fat versus ketogenic diet in Parkinson's disease: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Mov Disord. 2018 Aug;33(8):1306-1314.
Roehl K, Falco-Walter J, Ouyang B, Balabanov A. Modified ketogenic diets in adults with refractory epilepsy: Efficacious improvements in seizure frequency, seizure severity, and quality of life. Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Apr;93:113-118.
Rodell A, Rasmussen LJ, Bergersen LH, Singh KK, Gjedde A. Natural selection of mitochondria during somatic lifetime promotes healthy aging. Front Neuroenergetics. 2013;5:7.
Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JE, Ludwig DS, Willett W, Hu FB. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015 Dec;3(12):968-79.
Włodarek D. Role of Ketogenic Diets in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease). Nutrients. 2019 Jan 15;11(1).
Zhu H, Bi D, Zhang Y, Kong C, Du J, Wu X, Wei Q, Qin H. Ketogenic diet for human diseases: the underlying mechanisms and potential for clinical implementations. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jan 17;7(1):11.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35034957/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Nutrition Basics: Understanding Macronutrients and Micronutrients
Proper nutrition is the foundation of good health. Understanding the roles of macronutrients and micronutrients in your diet can help you make informed choices that support your overall well-being. Here’s a guide to the basics of macronutrients and micronutrients and their importance in your diet.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients your body needs in larger amounts to provide energy and support growth, metabolism, and other bodily functions. There are three main macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels your brain, muscles, and other tissues.
Sources: Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats), fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products.
Simple Carbohydrates: Found in sugary foods like candies and sodas. They are quickly digested and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
Complex Carbohydrates: Found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. They are digested more slowly, providing a steady release of energy.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function.
Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Amino Acids: Proteins are made up of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids, nine of which are essential, meaning they must be obtained from the diet.
Fats
Fats provide a concentrated source of energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
Sources: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish, and dairy products.
Saturated Fats: Found in animal products and some tropical oils. Should be consumed in moderation as excessive intake can raise cholesterol levels.
Unsaturated Fats: Found in plant oils, nuts, seeds, and fish. These are considered heart-healthy fats.
Trans Fats: Found in some processed foods. Should be avoided as they can increase the risk of heart disease.
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals required in smaller amounts but are crucial for various bodily functions, including growth, disease prevention, and overall health.
Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds that support numerous bodily functions, including energy production, immune function, and blood clotting.
Water-Soluble Vitamins: Include Vitamin C and the B-vitamins. These are not stored in the body and need to be consumed regularly.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Include Vitamins A, D, E, and K. These are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver.
Minerals
Minerals are inorganic elements that support processes such as bone formation, heart function, and fluid balance.
Macro Minerals: Needed in larger amounts. Include calcium, potassium, magnesium, and sodium.
Trace Minerals: Needed in smaller amounts. Include iron, zinc, copper, and selenium.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Balanced Diet: A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods ensures you get a mix of macronutrients and micronutrients. Eating a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats helps meet your nutritional needs.
Nutrient Density: Focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide more vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds relative to their calorie content. Examples include leafy greens, berries, nuts, and seeds.
Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating and to ensure you're getting the right amount of nutrients without excessive calories.
Hydration: Water is also essential for health. It supports digestion, nutrient transport, and temperature regulation. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Conclusion
Understanding the roles of macronutrients and micronutrients is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. By focusing on a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, you can support your body’s functions and overall well-being. What dietary changes have made a positive impact on your health? Share your experiences and tips in the comments!
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Rich Tradition of Buffalo Ghee: A Nutritional Powerhouse
Buffalo ghee, a staple in many traditional kitchens, is gaining popularity worldwide due to its rich flavor and numerous health benefits. This article delves into the history, production, benefits, and uses of buffalo ghee, providing a comprehensive guide for those looking to incorporate this nutritious fat into their diet.

buffalo ghee
What is Buffalo Ghee?
The Origins of Buffalo Ghee
Buffalo ghee is a type of clarified butter made from buffalo milk. It has been a crucial component of Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines for centuries. Unlike cow ghee, buffalo ghee is known for its white color and slightly different nutritional profile. It is produced by simmering butter made from buffalo milk until the water content evaporates, leaving behind pure butterfat.
Nutritional Profile
Buffalo ghee is rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins A, D, E, and K, and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). It is known for its high fat content, which makes it an excellent source of energy. The fat profile of buffalo ghee includes both saturated and unsaturated fats, which are beneficial for various bodily functions.
Health Benefits of Buffalo Ghee
Rich Source of Healthy Fats
Buffalo ghee is a fantastic source of healthy fats. These fats are crucial for maintaining healthy skin, supporting brain function, and providing long-lasting energy. Unlike many processed fats, buffalo ghee contains medium-chain fatty acids that are easier to digest and can be quickly converted into energy.
Supports Digestive Health
Ghee, including buffalo ghee, has been used in Ayurvedic medicine to support digestive health. It aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and minerals, improves gut health, and can even help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. The butyrate in ghee is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to support a healthy gut lining.
Enhances Immunity
The high levels of antioxidants in buffalo ghee help boost the immune system. Vitamin A, in particular, plays a crucial role in maintaining immune function. Regular consumption of buffalo ghee can help enhance your body's defense mechanisms, making it more resilient against infections and diseases.
Culinary Uses of Buffalo Ghee
Cooking and Frying
Buffalo ghee's high smoke point makes it ideal for cooking and frying. Unlike many oils, it does not break down into harmful compounds when heated to high temperatures. This makes it a safer and healthier option for frying and sautéing.
Baking
Buffalo ghee can also be used in baking to replace butter or other oils. It imparts a unique flavor and enhances the nutritional profile of baked goods. Its rich, creamy texture makes it perfect for pastries, cookies, and cakes.
Traditional Dishes
In many cultures, buffalo ghee is used to prepare traditional dishes. In India, it is a key ingredient in recipes like biryani, dal, and various sweets. Its unique taste and aroma add depth and richness to these dishes, making them more flavorful and satisfying.
Buffalo Ghee vs. Cow Ghee
Nutritional Differences
While both buffalo and cow ghee offer numerous health benefits, there are some differences in their nutritional profiles. Buffalo ghee generally contains more fat, which results in a higher calorie content. It also has higher levels of CLA and certain vitamins. However, both types of ghee are nutritious and can be included in a balanced diet.
Flavor and Texture
Buffalo ghee has a distinct flavor and texture compared to cow ghee. It is typically thicker and has a richer, creamier taste. This makes it a preferred choice for those who enjoy a more robust flavor in their cooking.
How to Make Buffalo Ghee at Home
Ingredients and Equipment
Buffalo butter (preferably organic and grass-fed)
Heavy-bottomed saucepan
Cheesecloth or fine strainer
Glass jar for storage
Steps to Prepare
Melt the Butter: Place the buffalo butter in a heavy-bottomed saucepan and melt it over medium heat.
Simmer: Reduce the heat and let the butter simmer. As it simmers, the water will evaporate, and the milk solids will separate from the fat.
Skim the Foam: Occasionally skim off the foam that forms on the surface.
Strain: Once the milk solids turn golden brown and settle at the bottom, remove the pan from the heat. Strain the liquid ghee through cheesecloth into a glass jar.
Cool and Store: Allow the ghee to cool completely before sealing the jar. Store it in a cool, dark place.
FAQs About Buffalo Ghee
Is Buffalo Ghee Healthier Than Cow Ghee?
Both buffalo and cow ghee have their unique health benefits. Buffalo ghee contains more fat and certain vitamins, while cow ghee has a slightly different fatty acid profile. The choice between the two often comes down to personal preference and dietary needs.
Can Buffalo Ghee Be Used for Weight Loss?
While ghee is high in calories, it can support weight loss when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Its healthy fats can help keep you satiated and provide steady energy, which may reduce overall calorie intake.
How Long Does Buffalo Ghee Last?
Buffalo ghee has a long shelf life and can last up to a year when stored properly.
Is Buffalo Ghee Lactose-Free?
Ghee, including buffalo ghee, is almost entirely lactose-free because the milk solids are removed during the clarification process.
Conclusion
Buffalo ghee is a versatile and nutritious fat that offers numerous health benefits. Its rich flavor, high smoke point, and impressive nutritional profile make it a valuable addition to any kitchen. Whether used for cooking, baking, or enhancing traditional dishes, buffalo ghee can elevate your culinary creations while supporting overall health. Embrace the tradition of buffalo ghee and enjoy its many benefits as part of a balanced and wholesome diet.
0 notes
Text
Table 23.4 gives common names and structural formulae for the most abundant fatty acids.


"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#fatty acid#animal fat#vegetable oil#biological membrane#crisco#olive oil#canola oil#saturated#unsaturated#lauric acid#myristic acid#palmitic acid#stearic acid#arachidic acid#palmitoleic acid#oleic acid#linoleic acid#linolenic acid#arachidonic acid#hydrocarbons
0 notes
Text
#Buy Hydrogenated Coconut Oil#Buy Hydrogenated Coconut Oil for sale#buy Hydrogenated Coconut Oil online#Hydrogenated Coconut Oil#Hydrogenated Coconut Oil online#Hydrogenated Coconut Oil online for sale#Order Hydrogenated Coconut Oil#Order Hydrogenated Coconut Oil for sale#Order Hydrogenated Coconut Oil near me#Order Hydrogenated Coconut Oil online
0 notes
Text
What are the Ingredients in Vezlay Veg Meat?
In recent years, plant-based meat substitutes have become increasingly popular as people seek healthier and more sustainable food options. Among the various alternatives available in the market, Vezlay Veg Meat stands out for its unique blend of ingredients and remarkable nutritional profile. In this article, we delve into the specific ingredients that make it a preferred choice for many, highlighting its health benefits, versatility, and why you should consider buying it from Catchy Court.
Understanding Vezlay Veg Meat
This is a plant-based meat alternative crafted to mimic the taste, texture, and nutritional benefits of traditional meat. It caters to vegetarians, vegans, and anyone looking to reduce their meat consumption without compromising on taste or nutrition.
Primary Ingredients in Vezlay Veg Meat
1. Soy Protein
Soy protein is the primary ingredient in this. It is derived from soybeans, which are rich in high-quality protein. Soy protein provides all the essential amino acids needed for human health, making it an excellent meat substitute. Moreover, soy protein is known for its benefits in reducing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health.
2. Wheat Gluten
Also known as seitan, wheat gluten is another critical component of it. Wheat gluten is made from the protein portion of wheat and has a chewy, meat-like texture. It is a complete protein source, offering various essential nutrients such as iron and selenium. Additionally, it is low in carbohydrates and fat, making it a healthy alternative to traditional meat.
3. Pea Protein
Pea protein is a high-quality, plant-based protein derived from yellow peas. It is easily digestible and hypoallergenic, making it suitable for those with soy or gluten allergies. Pea protein is rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) that support muscle growth and recovery. Its inclusion in this enhances the product’s nutritional profile and texture.
4. Natural Flavors
To ensure that it closely resembles the taste of real meat, natural flavors are incorporated. These flavors are derived from various plant sources and are carefully selected to provide an authentic meat-like taste without the use of artificial additives or preservatives.
5. Vegetable Oils
Vegetable oils, such as canola or sunflower oil, are used in Vezlay Veg Meat to provide the necessary fat content. These oils are rich in healthy unsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for brain health and overall well-being.
6. Seasonings and Spices
A blend of seasonings and spices is added to Vezlay Veg Meat to enhance its flavor. These may include ingredients like garlic, onion, paprika, black pepper, and more. The precise combination of these seasonings gives its distinctive taste, making it a versatile ingredient for various dishes.
Health Benefits of Vezlay Veg Meat

1. High in Protein
Vezlay Veg Meat is an excellent source of protein, providing a substantial amount of this essential macronutrient. Protein is crucial for building and repairing tissues, maintaining muscle mass, and supporting metabolic functions.
2. Low in Saturated Fat
Compared to traditional meat, Vezlay Veg Meat contains significantly lower levels of saturated fat. High saturated fat intake is linked to increased cholesterol levels and a higher risk of heart disease. By choosing it, you can enjoy a heart-healthy diet without sacrificing flavor.
3. Rich in Fiber
Including plant-based ingredients such as soy and peas makes it a good source of dietary fiber. Fiber aids in digestion helps regulate blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can assist in weight management.
4. Cholesterol-Free
This is free from cholesterol and is only found in animal-based products. Consuming a diet low in cholesterol can help reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
5. Packed with Vitamins and Minerals
This is fortified with essential vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and zinc. These nutrients are vital in various bodily functions, including oxygen transport, bone health, and immune system support.
Culinary Uses of Vezlay Veg Meat
1. Versatile in Cooking
This can be used in various dishes, making it a versatile addition to your kitchen. It can be grilled, sautéed, stir-fried, or baked like traditional meat. Its ability to absorb flavors makes it an excellent choice for marinades and sauces.
2. Perfect for Traditional and Modern Recipes
Whether you’re preparing a traditional Indian curry, a hearty stew, or a modern vegan burger, It fits perfectly into a wide range of recipes. Its meat-like texture and flavor make it an ideal substitute for any dish that calls for meat.
3. Convenient and Quick
It offers convenience and quick preparation for those with a busy lifestyle. It is available in ready-to-cook forms, allowing you to prepare delicious and nutritious meals quickly.
Why Buy Veg Meat from Catchy Court?

1. Quality Assurance
Catchy Court is committed to providing high-quality products to its customers. When you buy Buy Veg Meat from Catchy Court, you can be assured of its freshness, authenticity, and adherence to quality standards.
2. Easy Accessibility
Catchy Court makes it easy for you to purchase Buy Veg Meat online. With a user-friendly interface and reliable delivery service, you can enjoy the convenience of having your favorite plant-based meat substitute delivered to your doorstep.
3. Competitive Pricing
Catchy Court offers it competitively, ensuring you get the best value for your money. Additionally, periodic discounts and promotions make it even more affordable to incorporate this healthy alternative into your diet.
4. Customer Support
Catchy Court provides excellent customer support to address any queries or concerns you may have about your purchase. Their dedicated team is always ready to assist you, ensuring a seamless shopping experience.
Conclusion
Vezlay Veg Meat is a nutritious and delicious plant-based meat alternative that offers numerous health benefits and versatile culinary uses. By buying Vezlay Foods Products from Catchy Court, you can enjoy high-quality, convenient, and affordable plant-based meat substitutes delivered right to your door.
#vezlay foods#food#vezlay#buy now#order now#vezlay foods products#vezlay veg chicken#vezlay veg meat#catchy court product#food products
0 notes
Text
The Golden Elixir: Exploring the Benefits of West African Red Palm Oil
West African red palm oil, known for its vibrant color and rich nutritional profile, has been a staple in the diets and cultures of West African communities for centuries. Extracted from the fruit of the oil palm tree, this oil is celebrated not just for its culinary uses but also for its myriad health benefits. Let's delve into the reasons why West African red palm oil is considered a golden elixir.

Vitamin E and Carotenoids
West African red palm oil is one of the richest sources of tocotrienols, a form of vitamin E with potent antioxidant properties. Tocotrienols help protect the body's cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are linked to chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. Additionally, the oil's deep red hue comes from its high concentration of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A.
Essential Fatty Acids
This oil is also packed with essential fatty acids, particularly oleic acid and linoleic acid. These fatty acids are vital for brain health, reducing inflammation, and maintaining healthy skin. Unlike other oils that may contain unhealthy trans fats, red palm oil offers a healthy balance of saturated and unsaturated fats.
Heart Health
Contrary to the belief that all saturated fats are harmful, the saturated fats in red palm oil can support heart health. Studies have shown that red palm oil can help reduce bad LDL cholesterol and increase good HDL cholesterol, thereby lowering the risk of heart disease. The presence of tocotrienols further enhances this benefit by preventing the oxidation of cholesterol, a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis.
Boosting Immune Function
The high levels of beta-carotene and vitamin E in West African red palm oil play a crucial role in strengthening the immune system. Vitamin A, derived from beta-carotene, is essential for maintaining the health of mucous membranes in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, which act as the body's first line of defense against pathogens.
Skin and Hair Health
Red palm oil is a beauty secret that West African women have cherished for generations. Its rich content of vitamins A and E, along with fatty acids, makes it an excellent natural moisturizer. Applied topically, it helps to nourish the skin, reduce signs of aging, and promote a healthy, glowing complexion. For hair, red palm oil can combat dryness, reduce breakage, and add a natural shine.
Cooking and Flavoring
Red palm oil has a high smoke point, making it suitable for frying, sautéing, and baking. It imparts a rich, earthy flavor and a striking color to dishes, making it a favorite in traditional West African recipes such as stews, soups, and sauces.
Nutrient Retention
One of the key advantages of cooking with West African red palm oil is its stability at high temperatures. Unlike some oils that lose their nutritional value when heated, red palm oil retains its beneficial compounds, ensuring that you get the maximum health benefits from your meals.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fats: The Good, The Bad and the Essential for High-Perforance Athletes

Introduction
In the world of elite sports, especially for pre-pubescent and pubescent teenagers on the developmental track, nutrition plays a pivotal role. Among the various nutrients, fats often get a bad rap. However, not all fats are created equal. For high-performance athletes, understanding the different types of fats, their benefits, and their potential downsides is crucial. This knowledge can help them achieve and maintain optimal performance, particularly during these critical stages of growth and development. Moreover, fats are not just about physical performance—they also play a significant role in mental health, anxiety, and mental fatigue, which are vital aspects for athletes training at intense levels.
The Good Fats
Good fats, also known as healthy fats, include unsaturated fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats are essential for several bodily functions and can significantly benefit athletes.
Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats are found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats help:
Reduce inflammation, which is crucial for recovery after intense training sessions.
Maintain healthy cholesterol levels, supporting cardiovascular health.
Provide a steady source of energy, essential for prolonged physical activity.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), walnuts, and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for athletes:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Reduce Inflammation: This helps in quicker recovery and less muscle soreness.
Improve Cardiovascular Health: Vital for endurance and stamina.
Support Brain Health: Essential for cognitive function, which can enhance focus and decision-making during competitions.
Enhance Mental Health: Omega-3s are known to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, helping athletes maintain a positive mindset.
The Bad Fats
Bad fats refer primarily to trans fats and excessive saturated fats. These fats can negatively impact an athlete's health and performance.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are artificially created through hydrogenation and are commonly found in processed foods, baked goods, and fried items. They can:
Increase bad cholesterol (LDL) levels while lowering good cholesterol (HDL) levels.
Lead to inflammation, negatively affecting recovery and overall health.
Increase the risk of heart disease, which can compromise an athlete's stamina and endurance.
Saturated Fats
While not all saturated fats are harmful, excessive consumption can pose risks. Saturated fats are found in animal products like red meat, butter, and full-fat dairy. High intake can:
Raise cholesterol levels, potentially leading to cardiovascular issues.
Contribute to weight gain if not balanced with other nutrients and physical activity.
The Essential Fats for High-Performance Athletes
For athletes, particularly pre-pubescent and pubescent teenagers, incorporating essential fats into their diet is critical. These fats support growth, development, and performance.
Importance for Physical Health
Energy Production: Fats are a dense source of energy, providing 9 calories per gram. This energy is crucial for endurance sports and intense training sessions.
Hormone Production: Fats are necessary for the production of hormones, including those that regulate growth and metabolism.
Cell Membrane Integrity: Fats are a vital component of cell membranes, aiding in nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
Importance for Mental Health
Brain Health: Essential fatty acids like omega-3s are crucial for brain development and function. They support cognitive processes, memory, and focus.
Mental Fatigue: A well-balanced diet with adequate fats can help prevent mental fatigue, allowing athletes to maintain high levels of concentration during training and competition.
Anxiety and Mood: Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. For young athletes, managing mental health is as important as physical health, given the pressures of high-level training and competition.
What to Include in the Diet
Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide a mix of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats, they are great for heart health and energy.
Olive Oil: A healthy alternative for cooking, providing monounsaturated fats.
Dark Chocolate: In moderation, dark chocolate can be a good source of healthy fats and antioxidants.
What to Avoid
Processed Foods: These often contain trans fats, which are detrimental to health and performance.
Fried Foods: High in unhealthy fats and can lead to weight gain and inflammation.
Excessive Red Meat: While it can be part of a balanced diet, consuming it in large quantities can increase saturated fat intake.
Conclusion
For high-performance athletes, especially those in their developmental years, understanding the role of fats in their diet is essential. Good fats support physical health, enhance performance, and are crucial for mental well-being. By focusing on healthy sources of fats and avoiding the bad ones, athletes can ensure they are fueling their bodies and minds for optimal performance and long-term success.
#sports#coaching#gymnastics#mental health#sports training#elite coaching#mental wellbeing#healthy living#kiserspeaks#healthy diet#teaching high performance#high performance coaching#periodized high performance training#high performance training#high performance#high performance mindset#elite sports#elite training#elite gymnastics#elite#the elite#elite mindset#good fats#bad fats#essential fats#essential oils
0 notes
Text
The Benefits of Organic Soybean Oil: A Healthy Choice for Your Kitchen
Organic soybean oil is gaining popularity as a staple in kitchens around the world. Praised for its versatility and health benefits, this oil is an excellent option for those seeking healthier alternatives to traditional cooking oils. This article explores the benefits of organic soybean oil, examining its nutritional profile, cooking properties, environmental advantages, and more.

Understanding Organic Soybean Oil
What Is Organic Soybean Oil?
Organic soybean oil is derived from the seeds of the soybean plant (Glycine max) and produced through organic farming practices. Unlike conventional soybean oil, which may be extracted using harmful chemicals and pesticides, organic soybean oil is harvested from non-GMO seeds and processed without artificial additives.
Historical Context
Soybeans have been cultivated for thousands of years, particularly in Asia. Initially used for various purposes, including as a source of protein and fermentation, soybeans have since gained popularity in Western cuisine, particularly as a cooking oil due to their numerous health benefits and culinary versatility.
Nutritional Profile of Organic Soybean Oil
Rich in Healthy Fats
Organic soybean oil primarily consists of polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These essential fats are crucial for maintaining heart health, supporting brain function, and promoting healthy skin. The ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in soybean oil is considered beneficial for dietary balance.
Source of Vitamin E
Organic soybean oil is an excellent source of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant. Vitamin E helps combat oxidative stress, supports immune function, and promotes skin health. Incorporating soybean oil into your diet can contribute to overall well-being and provide necessary nutrients.
Cholesterol-Free
Unlike animal fats, organic soybean oil is cholesterol-free, making it a heart-healthy option. Using soybean oil in place of saturated fats can help lower bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Culinary Uses of Organic Soybean Oil
Versatility in Cooking
Organic soybean oil has a high smoke point, making it suitable for various cooking methods, including frying, sautéing, and baking. This oil's light flavor does not overpower dishes, allowing the natural flavors of ingredients to shine through.
Salad Dressings and Marinades
Due to its mild taste, organic soybean oil makes an excellent base for salad dressings and marinades. It can be easily blended with vinegar, herbs, and spices, creating flavorful dressings without overwhelming the palate.
Baking
When it comes to baking, organic soybean oil can serve as a healthier substitute for butter or margarine. It can help achieve moist and tender baked goods, from cakes to cookies, while reducing overall saturated fat content.
Health Benefits of Organic Soybean Oil
Heart Health
Incorporating organic soybean oil into your diet may provide significant heart health benefits. The high content of polyunsaturated fats supports cardiovascular function and may help lower blood pressure. Studies suggest that replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The omega-3 fatty acids found in organic soybean oil possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can help alleviate chronic inflammation in the body. Consuming an adequate amount of omega-3s is essential for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of inflammatory diseases.
Supports Brain Health
The essential fatty acids in organic soybean oil play a critical role in brain health. Omega-3 fatty acids are known to support cognitive function, memory, and mood regulation. Including soybean oil in a balanced diet may contribute to overall brain health, especially as one ages.
Environmental Benefits of Organic Soybean Oil
Organic Farming Practices
Choosing organic soybean oil supports environmentally friendly farming practices that avoid synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming promotes healthier soil and biodiversity, making it a sustainable choice for both consumers and the planet.
Soil Health and Preservation
Organic farming methods prioritize soil health through crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage. These practices help preserve soil quality and prevent erosion, leading to better long-term agricultural sustainability.
Reduced Chemical Exposure
By opting for organic soybean oil, consumers help reduce chemical exposure not only for themselves but also for farming communities. Organic farming minimizes the use of harmful substances that can affect water systems, wildlife, and farmworkers' health.
Selecting Quality Organic Soybean Oil
Certifications and Labels
When choosing organic soybean oil, look for certifications such as USDA Organic, which guarantees the oil is produced according to strict organic standards. Additionally, labels indicating cold-pressed or expeller-pressed extraction methods may signify a higher-quality product.
Storage and Shelf Life
To maintain freshness, store organic soybean oil in a cool, dark place, away from direct sunlight. Proper storage can help prolong the shelf life of the oil, allowing you to enjoy its benefits for an extended period.
Common Misconceptions About Soybean Oil
Concerns About GMOs
One common misconception is that all soybean oil is genetically modified. Organic soybean oil, however, is made from non-GMO soybeans and adheres to strict organic standards. Consumers can choose organic soybean oil with confidence, knowing it is free from genetically modified organisms.
Saturated Fat Debate
Another misunderstanding involves the discussion surrounding fats. While some oils are high in saturated fats, organic soybean oil provides a heart-healthy alternative due to its high levels of unsaturated fats. Understanding the difference between fat types is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Cooking Tips with Organic Soybean Oil
Using for High-Temperature Cooking
Due to its high smoke point (around 450°F or 232°C), organic soybean oil is ideal for frying and sautéing. Avoid overheating the oil to retain its nutritional benefits and prevent the formation of harmful compounds.
Infusing Flavor
For added flavor in dishes, consider infusing organic soybean oil with herbs, spices, or garlic. This technique enhances the oil's flavor while still allowing for versatile usage in various recipes.
Balancing with Other Oils
While organic soybean oil is a great choice, consider mixing it with other oils like olive or avocado oil to reap the varied benefits of different fats. Blending oils can provide a more complex flavor profile and varied health benefits.
The Role of Organic Soybean Oil in a Balanced Diet
Moderation Is Key
Incorporating organic soybean oil into a balanced diet is beneficial, but moderation is essential. While it offers several health advantages, it's vital to consume a variety of fats to ensure a well-rounded intake of nutrients.
Part of a Plant-Based Diet
Organic soybean oil fits well into plant-based diets, providing essential fatty acids that may be less prevalent in certain plant foods. Using it in conjunction with a variety of fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes can enhance overall health.
Conclusion
Organic soybean oil is a healthy, versatile, and environmentally friendly choice for cooking. Its rich nutritional profile, including essential fatty acids and vitamin E, makes it a valuable addition to any kitchen. By incorporating organic soybean oil, you can enjoy its health benefits while supporting sustainable farming practices.With its high smoke point and mild flavor, organic soybean oil lends itself to various culinary applications, from frying and baking to salad dressings. Dispelling misconceptions about its origin and fat content, consumers can confidently choose this oil as a staple in their kitchens.As awareness about health and environmental issues grows, organic soybean oil is likely to become an even more popular choice among food enthusiasts. By embracing this natural cooking oil, you not only enhance your meals but also contribute to a healthier planet and a healthier lifestyle.
0 notes