#Science of Intelligence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🔍 Wie lernen wir am besten – allein oder in der Gruppe? Forschende vom @maxplanckgesellschaft @scienceofintelligences & @universitaet.tuebingen haben das beliebte Game #Minecraft 🧱 genutzt, um soziales Lernen zu erforschen. 💡 Fazit: Wer flexibel zwischen eigenem Ausprobieren & dem Beobachten anderer wechselt, lernt am effektivsten. Adaptives Lernen schlägt starre Strategien – selbst im virtuellen Dschungel. 🌱🎮 👁 Mit Blickverfolgung & KI-Modellen wurde analysiert, wie sich Menschen in einer digitalen Nahrungssuche verhalten. Die Studie zeigt: Soziales Lernen ist komplex, dynamisch & ein Schlüssel unserer Intelligenz. 🎥 Einblicke ins Experiment gibt’s auf YouTube: Link in Bio oder 👉 https://youtu.be/wyk7RbmHiok #SozialesLernen #MinecraftStudy #LernenMitMinecraft #ScienceCommunication #Wissenschaft #Forschung #Neuroscience #Kognitionswissenschaft #MaxPlanck #MPIB #ScienceOfIntelligence #AIandLearning #CollectiveIntelligence #LernenVerstehen #Bildungsforschung #WissenschaftErklärt

View On WordPress
#adaptives Lernen#Bildungsforschung#Blickverfolgung#digitale Bildung#Entscheidungsfindung#Experiment#Forschung#Gruppendynamik#immersive Forschung#individuelle Lernstrategien#Informationsverarbeitung#innovative Forschung#KI#Kognitionswissenschaft#kollektive Intelligenz#Künstliche Intelligenz#Lernen mit Minecraft#Lernverhalten#Max-Planck-Institut#Minecraft#Nature Communications#Neuroscience#Science of Intelligence#soziale Intelligenz#soziale Interaktion#soziale Lernstrategien#Soziales Lernen#Videospiel#virtuelle Umgebung#Wissenschaft
0 notes
Text

Self-Awareness by Katsuhiro Õtomo
#artificial intelligence#self awareness#android#futurism#cyberpunk#technology#science fiction#robots#reflection#mirror#sci fi#art#transhumanism#drawing#cyborg#robot#singularity#m. c. escher
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ethics and Intelligence
Zărnescu, Narcis (2024), Ethics and Intelligence, Intelligence Info, 3:4, pag, Abstract Is there a Science of Intelligence? The answer is affirmative, as evidenced by the numerous academic projects launched by universities worldwide, including those in Europe, the United States, Japan, and China. In an era of globalized strategic intelligence and expanding secret services, fueled by the digital…
0 notes
Text





More Stowaway AU
Pacifica dynamics with each Grunkle. Happy late Father’s Day and birthday to the grunks!
#Pacifica Northwest#Stanley Pines#Stanford Pines#Stan Pines#Gravity Falls#Stowaway AU#my art#doodles#there’s much more lovecraftian ass monsters and pirate specters than I’ve depicted I just really like making jokes about the dynamics#i love Paz and Stan beefing but like now it’s with love#Ford and Pacifica though that was a surprising discovery bc before I’d always have their relationship as positive neutral#maybe Paz a little tinyyyy bit scared of him bc he is Dipper coded but once he finds out about her paranormal connections he might#unintentionally treat her more science experiment and anomaly more than like a person which is very NOT a Dipper thing so Paz is freaked#but like in the Stowaway AU ok some of that happens but I think the more Ford gets to know her as a bullheaded but intelligent kid who’s#eager to impress he sees a bit of himself AND his brother within her personality and she’s had to go through so much shit but she’s still#here and talking her shit and she’s surprisingly interested in history and so intuitive and REALLY into paranormal shit like even if its not#all the cryptid and science shit he likes they find something to really bond over#and then everything else is just like hey! this kid is cool#and then in the middle of the night one day he’s like ‘Stanley I think I’m ready to be a father.’ and Stan goes BWUH?????
2K notes
·
View notes
Text



You guys wanna see a science Lego set? Well, here's Lego DNA!
With a scientifically accurate DNA model, and a historically accurate lab + 5 scientists!
Aims: to promote science to kids and honor Rosalind Franklin.
Less than 600 votes needed to reach 10K when it will be considered as a real official Lego set to be sold worldwide!
If you like it, please support here and share with your friends: https://ideas.lego.com/projects/c92cd95b-49e7-46ec-b844-ac6482c51139
More details below!











#chemistry #science #biology #design #diy #education #nature #environmental science #molecular biology #stem #women in stem #research #laboratory #women scientists #school #university #college #students #learning #lego art #lego photography #afol #lego sets #lego ideas #lego builds #lego moc #rosalind franklin #james watson #francis crick #university student
#biology#chemistry#college#afol#science#design#diy#education#nature#environmental science#environment#stem#women in stem#stemblr#stem student#stem academia#biochemistry#phd#university#universidad#lego art#lego moc#moc#lego photography#lego minifigures#molecular biology#molecules#research#knowledge#intelligence
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Elephants call out to each other using individual names that they invent for their fellow pachyderms, a study said on Monday. While dolphins and parrots have been observed addressing each other by mimicking the sound of others from their species, elephants are the first non-human animals known to use names that do not involve imitation, the researchers suggested. For the new study, a team of international researchers used an artificial intelligence algorithm to analyse the calls of two wild herds of African savannah elephants in Kenya. The research "not only shows that elephants use specific vocalisations for each individual, but that they recognise and react to a call addressed to them while ignoring those addressed to others," lead study author Michael Pardo said. "This indicates that elephants can determine whether a call was intended for them just by hearing the call, even when out of its original context," the behavioural ecologist at Colorado State University said in a statement.
Continue Reading.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

get weird get weird get weird get weird. kiss your sophont friend now
#they're both sapient. they are both intelligent enough to understand taxes and science and yaoi#specbio#finished this AGES AND AAAGES ago but never got around to posting it#alien#speculative biology#queer art#weirdfur#alien art#alien species#alien OC#artists on tumblr#specevo#sophont#sophonts#based on that one artwork of a centaur and his rider kissing
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
"There was an exchange on Twitter a while back where someone said, ‘What is artificial intelligence?' And someone else said, 'A poor choice of words in 1954'," he says. "And, you know, they’re right. I think that if we had chosen a different phrase for it, back in the '50s, we might have avoided a lot of the confusion that we're having now." So if he had to invent a term, what would it be? His answer is instant: applied statistics. "It's genuinely amazing that...these sorts of things can be extracted from a statistical analysis of a large body of text," he says. But, in his view, that doesn't make the tools intelligent. Applied statistics is a far more precise descriptor, "but no one wants to use that term, because it's not as sexy".
'The machines we have now are not conscious', Lunch with the FT, Ted Chiang, by Madhumita Murgia, 3 June/4 June 2023
#quote#Ted Chiang#AI#artificial intelligence#technology#ChatGPT#Madhumita Murgia#intelligence#consciousness#sentience#scifi#science fiction#Chiang#statistics#applied statistics#terminology#language#digital#computers
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
New crow ability dropped
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In the 1750s, an Italian farmer digging a well stumbled upon a lavish villa in the ruins of Herculaneum. Inside was a sprawling library with hundreds of scrolls, untouched since Mount Vesuvius’ eruption in 79 C.E. Some of them were still neatly tucked away on the shelves.
This staggering discovery was the only complete library from antiquity ever found. But when 18th-century scholars tried to unroll the charred papyrus, the scrolls crumbled to pieces. They became resigned to the fact that the text hidden inside wouldn’t be revealed during their lifetimes.
In recent years, however, researchers realized that they were living in the generation that would finally solve the puzzle. Using artificial intelligence, they’ve developed methods to peer inside the Herculaneum scrolls without damaging them, revealing short passages of ancient text.
This month, researchers announced a new breakthrough. While analyzing a scroll known as PHerc. 172, they determined its title: On Vices. Based on other works, they think the full title is On Vices and Their Opposite Virtues and in Whom They Are and About What.
“We are thrilled to share that the written title of this scroll has been recovered from deep inside its carbonized folds of papyrus,” the Vesuvius Challenge, which is leading efforts to decipher the scrolls, says in a statement. “This is the first time the title of a still-rolled Herculaneum scroll has ever been recovered noninvasively.”
On Vices was written by Philodemus, a Greek philosopher who lived in Herculaneum more than a century before Vesuvius’ eruption. Born around 110 B.C.E., Philodemus studied at a school in Athens founded several centuries earlier by the influential philosopher Epicurus, who believed in achieving happiness by pursuing certain specific forms of pleasure.
“This will be a great opportunity to learn more about Philodemus’ ethical views and to get a better view of the On Vices as a whole,” Michael McOsker, a papyrologist at University College London who is working with the Vesuvius Challenge, tells CNN’s Catherine Nicholls.
When it launched in 2023, the Vesuvius Challenge offered more than $1 million in prize money to citizen scientists around the world who could use A.I. to help decipher scans of the Herculaneum scrolls.
Spearheaded by Brent Seales, a computer scientist at the University of Kentucky, the team scanned several of the scrolls and uploaded the data for anyone to use. To earn the prize money, participants competed to be the first to reach a series of milestones.
Reading the papyrus involves solving several difficult problems. After the rolled-up scrolls are scanned, their many layers need to be separated out and flattened into two-dimensional segments. At that point, the carbon-based ink usually isn’t visible in the scans, so machine-learning models are necessary to identify the inked sections.
In late 2023, a computer science student revealed the first word on an unopened scroll: “porphyras,” an ancient Greek term for “purple.” Months later, participants worked out 2,000 characters of text, which discussed pleasures such as music and food.
But PHerc. 172 is different from these earlier scrolls. When researchers scanned it last summer, they realized that some of the ink was visible in the images. They aren’t sure why this scroll is so much more legible, though they hypothesize it’s because the ink contains a denser contaminant such as lead, according to the University of Oxford’s Bodleian Libraries, which houses the scroll.
In early May, the Vesuvius Challenge announced that contestants Marcel Roth and Micha Nowak, computer scientists at Germany’s University of Würzburg, would receive $60,000 for deciphering the title. Sean Johnson, a researcher with the Vesuvius Challenge, had independently identified the title around the same time.
Researchers are anticipating many more breakthroughs on the horizon. In the past three months alone, they’ve already scanned dozens of new scrolls.
“The pace is ramping up very quickly,” McOsker tells the Guardian’s Ian Sample. “All of the technological progress that’s been made on this has been in the last three to five years—and on the timescales of classicists, that’s unbelievable.”"
-via Smithsonian, May 16, 2025
#I've been following this project for a couple of years now it's honestly super exciting#we are going to read scrolls that were charred shut in antiquity!!! that people thought could never be read#because they could never be unrolled#no one was read these words in 2000 years!!!!#until now!!!!!#archeology#ai#herculaneum#pompeii#vesuvius#citizen science#classics#classical studies#classical literature#ancient rome#artificial intelligence#roman history#ancient history#philosophy#epicurus#epicurean#good news#hope
596 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rationing Insulin.
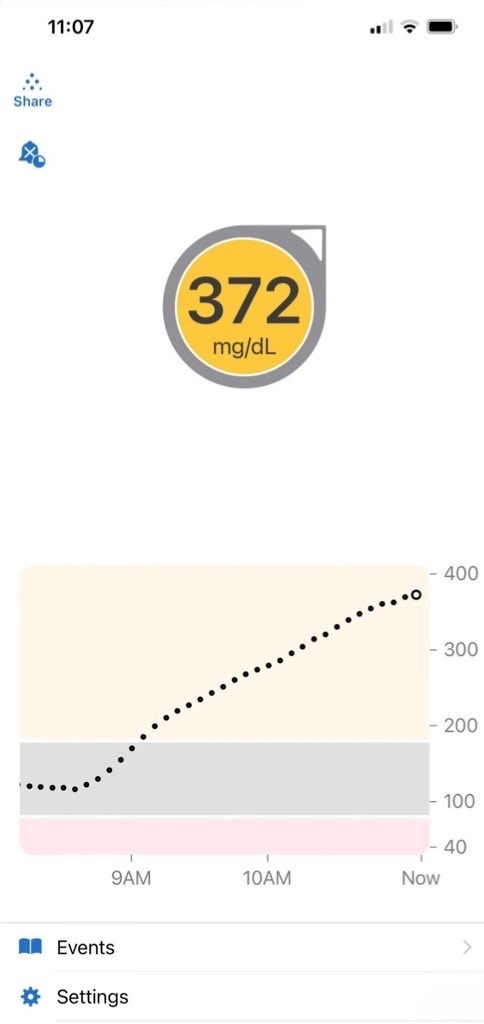
Blood sugar reading this morning. The average blood sugar reading should be between 60mg/dl - 100mg/dl. I am terrified of not being able to administer my insulin simply because I was too poor to afford it. I am strongly in need of community help.
CA: $HushEmu
I am happy to announce I raised $33 🎉 I only need $417 to get my prescription

#antiques#archaeology#artificial intelligence#biology#code#chemistry#college#computer science#classic car#conservation#entomology#environment#equestrian#etsy#ferrari#fishing#charity#geography#halloween#anthropology
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
why neuroscience is cool
space & the brain are like the two final frontiers
we know just enough to know we know nothing
there are radically new theories all. the. time. and even just in my research assistant work i've been able to meet with, talk to, and work with the people making them
it's such a philosophical science
potential to do a lot of good in fighting neurological diseases
things like BCI (brain computer interface) and OI (organoid intelligence) are soooooo new and anyone's game - motivation to study hard and be successful so i can take back my field from elon musk
machine learning is going to rapidly increase neuroscience progress i promise you. we get so caught up in AI stealing jobs but yes please steal my job of manually analyzing fMRI scans please i would much prefer to work on the science PLUS computational simulations will soon >>> animal testing to make all drug testing safer and more ethical !! we love ethical AI <3
collab with...everyone under the sun - psychologists, philosophers, ethicists, physicists, molecular biologists, chemists, drug development, machine learning, traditional computing, business, history, education, literally try to name a field we don't work with
it's the brain eeeeee
#my motivation to study so i can be a cool neuroscientist#science#women in stem#academia#stem#stemblr#studyblr#neuroscience#stem romanticism#brain#psychology#machine learning#AI#brain computer interface#organoid intelligence#motivation#positivity#science positivity#cogsci#cognitive science
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Robot Who Dreams" by Phillipe Caza

#android#robots#science fiction#isaac asimov#art#artificial intelligence#futurism#transhumanism#dreams#sci fi#cyberpunk#robot#androids#cyborg#singularity#technology#space#dream
7K notes
·
View notes
Text

Your summer reading list: An Introduction to Cybernetics. W. Ross Ashby - 1963.
#vintage illustration#vintage books#books#reading lists#book covers#paperbacks#vintage paperbacks#books and reading#summer reading#nonfiction#non fiction#science#science books#the sciences#cybernetics#robotics#automation#tech#technology#artificial intelligence#ai
304 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tool Use by New World Halichoeres Wrasses
Juliette Tariel-Adam, Jaqueline G. Toledo, C. E. O’Brien, et al.
ABSTRACT
A diverse array of animals has evolved the ability to use tools (e.g., primates, parrots, octopus, crabs, and wasps), but the factors leading to tool use evolution are poorly understood. Fishes could provide insight into these factors via comparison of ecological and morphological differences between tool-using and non-tool-using species. Anvil use is one example of tool use by fish: the fish holds a hard-shelled prey item in its mouth and strikes it onto a hard surface (anvil) to open it. To date, anvil use has been described in 26 of the > 550 described wrasse/Labridae species. Through a community science program called Fish Tool Use, 16 new observations of anvil use were collected in five species of a monophyletic group of wrasses called the New World Halichoeres. These new observations provide the first evidence of anvil use by Halichoeres brasiliensis, H. poeyi and H. radiatus, and the first video evidence of anvil use by H. garnoti and H. bivittatus. They extend the geographic range of known anvil use by wrasses to a new region, the western Atlantic, making this behaviour even more widespread than previously reported. Video analysis revealed that wrasses are flexible in their anvil use: They did not have a preferred side of their body, they cracked open a diverse array of prey on a variety of anvil types, and often used many anvils and striking points for the same prey item. More observations are needed to determine the evolutionary origin of anvil use behaviour, its ecological drivers, costs, and benefits.
Read the paper here:
Tool use by New World Halichoeres wrasses | Coral Reefs
#animal intelligence#animals#nature#ichthyology#fish#bony fish#wrasse#labridae#labriformes#ocean#science
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
Insects and Other Animals Have Consciousness, Experts Declare
A group of prominent biologists and philosophers announced a new consensus: There’s “a realistic possibility” that insects, octopuses, crustaceans, fish and other overlooked animals experience consciousness.
In 2022, researchers at the Bee Sensory and Behavioral Ecology Lab at Queen Mary University of London observed bumblebees doing something remarkable: The diminutive, fuzzy creatures were engaging in activity that could only be described as play. Given small wooden balls, the bees pushed them around and rotated them. The behavior had no obvious connection to mating or survival, nor was it rewarded by the scientists. It was, apparently, just for fun. The study on playful bees is part of a body of research that a group of prominent scholars of animal minds cited today, buttressing a new declaration that extends scientific support for consciousness to a wider suite of animals than has been formally acknowledged before. For decades, there’s been a broad agreement among scientists that animals similar to us — the great apes, for example — have conscious experience, even if their consciousness differs from our own. In recent years, however, researchers have begun to acknowledge that consciousness may also be widespread among animals that are very different from us, including invertebrates with completely different and far simpler nervous systems...
Read more: https://www.quantamagazine.org/insects-and-other-animals-have-consciousness-experts-declare-20240419
#philosophy#science#animal intelligence#animal minds#animals#nature#animal welfare#vegan#vegetarian#politics#animal emotions
808 notes
·
View notes