#and are far more complex and variable
Text
to be honest kitten, non homogeneous second order linear differential equations are making daddy want to kill herself
#its like okay I get how to solve it i GUESS#but why tf does it work#also not a fan of just guessing the form of the particular integral#wdym you just guess...based on fucking what...#no proof in the textbook either what if I killed myself#I miss separation of variables method 💔 it was so elegant and classy to my mind#on the whole though I have to say I enjoyed further pure a lot#except for the vectors bullshit it was good#and the complex numbers and trig bit is so nice#yeah so far further maths has been way better than regular maths#you don't have to remember as much useless nonsense#also looking forward to learning more mechanics next year😈#further maths and physics is actually such a godly combination#same thing for like 25% of it..
1 note
·
View note
Note
Hey!!! You made a "how to draw wings" sheet, but— how on Earth do you draw horse!?!? The bane of every artists existence
Yeahhh horses are hard. They have lots of little nuances on top of complex anatomy and weird ass shapes (literally and figuratively). Drawing them requires lots and lots of practice. And this is like...entire art book levels of subject matter but here are a few tricks that I've picked up over time -
Key body shapes - shoulder, barrel, hip
I won't go too far into this one because Ken Hultgren does a much better job in his book The Art of Animal Drawing. But TL;DR - a horse's body has three main masses - the shoulder, the barrel, and the hip. Each one is tricky to draw on it's own since they're all weird shapes, but it's helpful to me to break a horse body down into simpler terms.
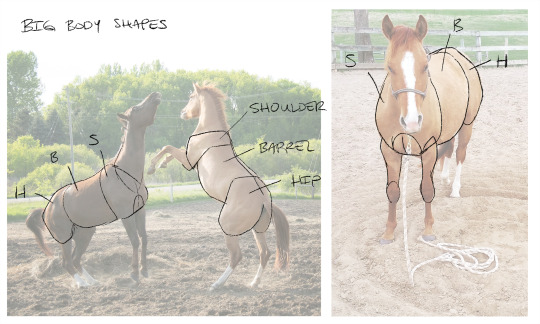
Key muscle masses
When I draw horses, I like to emphasis curves vs straights. Horses have that built in naturally as their body is often either "pure muscle" or "pure bone". There's some really nice details at the intersections of body parts, like at the front elbow and behind the ears along the neck (aka the "poll") where there's highly definable muscle groups that can help with visual clarity.

Fun fact, young horses grow hip-first. The horse in the photo above is 8 years old. That same horse at 4 years is below. Cracks me up how much taller his hip was at the time.
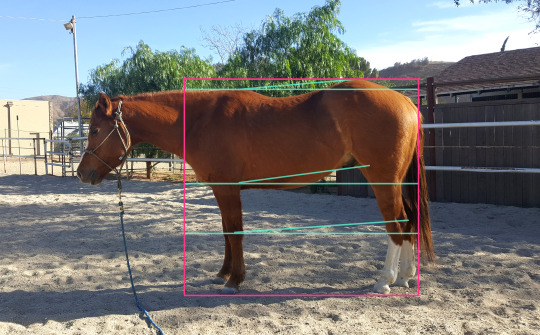
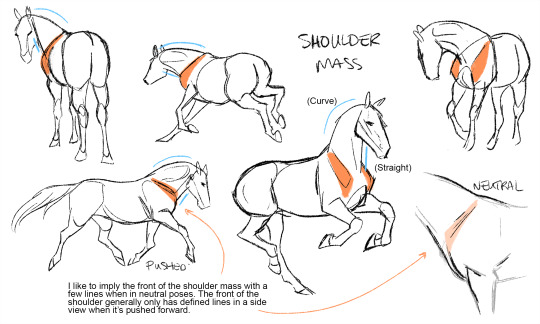
Ok so the muscles on the front legs combined with the shoulder mass is a fave combo of mine. The shoulder mass itself is something that I've found that is particularly horse-ish. For me, it's a pretty big visual signifier - almost more important than the neck. You can show a lot of tension/action in the body with the shoulder depending how you simplify it. Horses use their shoulders A LOT (too much if you ask any dressage rider or reiner), so emphasizing the shoulder can make a horse more expressive.
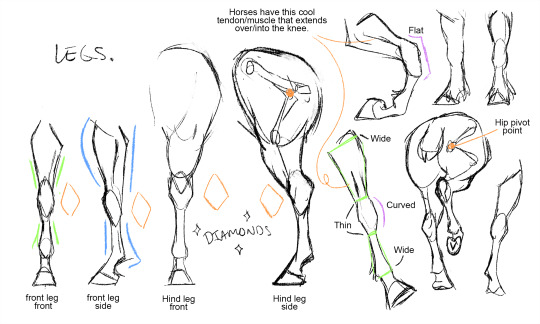
Legs. Oh heavens, the legs.
Yeah ok so again, Hultgren goes into fantastic detail on legs and hooves (I still follow how he simplifies hooves to this day my gosh that guy is a genius), but I often break them down like this for quick sketching. Are horse's legs realistically this emphasized? No, but I like the visual language; believable but expressive. This can apply to any size/shape from arabians to drafts.
And finally...
A few head details -
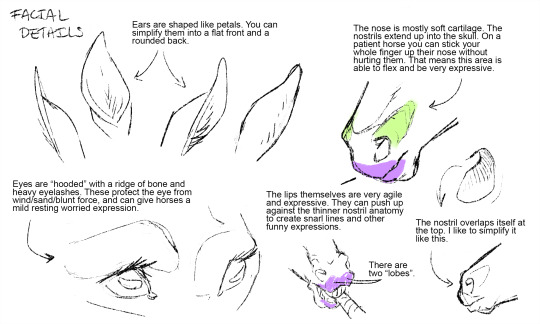
Overall horses have SO many variables. The fun part about that is that they're highly customizable and able to be endlessly stylized. The tough part is that they're hard to draw strictly because of all of the little things to keep track of to make sure the horse reads as "horse".
And so because third time's the charm, Ken Hultgren's Art of Animal Drawing really is one of the best I've seen for breaking down, simplifying, and applying horse anatomy to active drawings.
But most of all, the more you draw horses the easier they'll be.
–
Discord | Patreon | Art Prints
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Barbara Gordon's Coding & Computer Cram School is a popular YouTube series. Tucker Foley is a star student.
Barbara Gordon's Cram School posts free online courses for both coding and computer engineering. Think Crash Course in terms of entertainment, but college lecture in terms of depth. Hundreds of thousands of viewers flock to it— students who missed a class, people looking to add new skills to a resume, even simple hobbyists. It’s a project Barbara’s proud of.
Sometimes, when she wants to relax, she’ll even hop in the comments and spend an afternoon troubleshooting a viewer’s project with them.
User “Fryer-Tuck” has especially interesting ones. Barbara finds herself seeking out his comments, checking in on whatever this crazy kid is making next. An app for collecting GPS pings and assembling them on a map in real-time, an algorithm that connects geographic points to predict something’s movement taking a hundred other variables into account, simplified versions of incredibly complex homemade programs so they can run on incredibly limited CPU’s.
(Barbara wants to buy the kid a PC. It seems he’s got natural talent, but he keeps making reference to a PDA. Talk about 90’s! This guy’s hardware probably predates his birth.)
She chats with him more and more, switching to less public PM threads, and eventually, he opens up. His latest project, though, is not something Barbara has personal experience with.
FT: so if you found, hypothetically, a mysterious glowing substance that affects tech in weird and wacky ways that could totally have potential but might be vaguely sentient/otherworldly…. what would you do and how would you experiment with it. safely, of course. and hypothetically
BG: I’d make sure all my tests were in disposable devices and quarantined programs to keep it from infecting my important stuff. Dare I ask… how weird and wacky is it?
FT: uhhh. theoretically, a person composed of this substance once used it to enter a video game. like physical body, into the computer, onto the screen? moving around and talking and fighting enemies within the game?
FT: its been experimented with before, but not on any tech with a brain. just basic shields and blasters and stuff, its an energy source. also was put in a car once
FT: i wanna see how it affects software, yk? bc i already know it can. mess around and see how far i can push it
BG: […]
FT: … barbara?
BG: Sorry, thinking. Would you mind sharing more details? You said “blasters?”
Honestly. Kid genius with access to some truly wacky materials and even wackier weapons, she needs to start a file on him before he full sends to either hero or villain.
[OR: Tucker is a self-taught hacker, but if he were to credit a teacher, he'd name Barbara Gordon's Coding & Computer Cram School! He's even caught the attention of Dr. Gordon herself. She's full of sage advice, and with how she preaches the value of a good VPN, he's sure she's not pro-government. Maybe she'll help him as he studies the many applications of ecto-tech!]
#she does end up sending tucker a PC lol#and after she learns he has experience supporting a superhero team maybe pushes his name forward to WEs outreach program for r&d potentials#picks him up by the scruff and says MY coding buddy#also fun fact she had a phd in library science at one point. i like that about her i think we should talk about it a little more#also tucker was making a ghost reporting & tracking app for amity parkers#dpxdc#dcxdp#barbara gordon#tucker foley#prompt#kipwrite
579 notes
·
View notes
Text


❀ ゚. ༄ ┊ 𝐓𝐄𝐍𝐃𝐈𝐍𝐆 𝐓𝐎 𝐓𝐇𝐄𝐈𝐑 𝐈𝐍𝐉𝐔𝐑𝐈𝐄𝐒 ( 𝐩𝐭. 𝐢𝐯 ) ;

characters : wriothesley • neuvillette
fandom : genshin impact
╰┈ pt i. • pt. ii • pt. iii


↬ wriothesley ࿐ ࿔
wriothesley is far too familiar with getting injured on the job. it's nothing new, not really-- what's work if he doesn't get a little roughened up, anyway? it's certainly not a big deal ( to him, at least ).
he'll admit that some days are worse than others, but he's got too much to do, too much to protect. he can't afford to let anyone take him down. so all in all? he'll be fine. end of story.
you, on the other hand? he's not really sure. he's warned you from time to time that he's bound to run into trouble here and there; the fortress is not a place of innocence, after all, and you are both all too aware of that.
still, that doesn't stop you from mentally combusting every time he walks through the door, cuts and bruises all across his body. unfortunately, tonight is no different, even if his injury ( if anyone can even consider it to be one ) is a small cut on his cheek.
"jail. jail for a thousand years."
it's three in the morning, and yeah, he's a little sleep deprived, so he's not really sure if he heard you correctly. he blinks a few times, brows knit ever so slightly as he tries to register your words.
huh.
he's far more used to a lecture, but he'll take this instead.
"a thousand years?" he grins, though the amusement fades slightly as you use a washcloth to wipe the blood away. "that's a little cruel. seriously, do you think you could survive that long without seeing me?"
"guess we'll see."
he lets out a chuckle, though he sees through your annoyance. it may be a simple cut to him, but to you, it runs deeper and he knows that. he chooses to keep his silence instead of continuing the banter, only watching you carefully as you study him in search of other injuries you may have missed.
"i miss you when i'm gone for a thousand minutes." he leans in, closes that small distance between you two. "don't send me away." he murmurs. "i won't survive."
you don't say anything for a long while, a small sigh escaping through parted lips. it's his unique way of asking for forgiveness; of course you'll grant it. but you're just as stubborn as he is, so you don't quite give him the satisfaction or peace of mind that he expects.
you kiss him for a moment too short, then speak.
"how many hours is a thousand minutes?"
↬ neuvillette ࿐ ࿔
neuvillette is not accustomed to the woes of human emotion. it is a fickle thing, he muses, and the nature of one's heart is a complexity he wishes to understand with ease. he tries, but there are so many variables and constants that even the ludex of fontaine cannot grasp it.
he is, admittedly, always a little doubtful of himself when it comes to such interactions. he is careful in his approach-- certainly not wary, but careful in the means of not causing offense. he is learning with time, after all, and though he has learned much through experience and through you, there is much he still remains naive to.
but this-- this, he understands : the silence that weighs heavy in the air, the lack of words so often spoken when you are together, the way your eyes won't meet his. your gaze is focused elsewhere as you throw all concentration into putting away the antiseptic and spare bandages, carefully organizing the supply kit in the most optimal manner in case of emergency. he is not sure how long you spend rearranging it, but surely it is a means of distraction to distance yourself from your feelings.
"thank you." neuvillette speaks up after a long while, notices how you pause at his gratitude. your body tenses up for the slightest moment, but you are quick to force yourself to relax.
"you're welcome."
he is unsure of how to proceed at this point. it is not often that he gets injured; such occasion is truly rare, but it is not something always in his control. he understands you are worried. he understands that you are afraid, that you might be angry. he wishes to speak, but when he hears that little sniffle, he freezes.
"please, look at me."
you listen. when he looks at you, there is something strange that stirs in his heart-- something so softly devastating at the sight of your sorrow. he hesitates, wonders if he will do the right thing to comfort you.
his hand cups your cheek, thumb wiping away the tear that trails down your face. there is the gentle curve of the lips-- a subtle reassurance, quiet in its nature, but deeply resonant.
"do not waste your tears on me." he tells you, gentle. "i'm alright. so long as the tides continue to turn, i will be here."
he presses a kiss to your forehead, smile growing ever so faintly as your tears continue to fall. it is something that cannot be helped; he knows this more than anyone, this weeping dragon. he pulls you into his arms, and until the tears are no longer shed, he will not let you go.
#genshin impact#genshin impact x reader#favoniuslibrary#wriothesley x reader#neuvillette#fyi i skimmed through wriothesley's wiki for like 5 mins. if he's ooc .......No He's Not#.: writing#.: multi#only 2 characters bc i am a lil sleepy and wanted to get smth out :^)
611 notes
·
View notes
Text
The thing is. Not gonna put this on fox’s post bc it’s a tangent. Anyway the thing is Ed and Stede are kinda codependent? What they are, though, is a) two animals who have pair bonded and b) ed seems to have more of an actual clinical depiction of codependency.
The big thing about codependency is that it’s not actually “one partner keeps the other partner good and pure and keeps them from being Mean and Bad.🥺” Codependency’s whole thing is control. It’s a saviour complex. And THE THING IS? It doesn’t work. You cannot “save” a person from being themself, from engaging in their addiction, from hurting themself. They need to make the executive decision to change, the codependent person cannot do that for them. Thus it becomes a cycle. Try to save -> see that they’re not doing what you want -> get angry/upset/punish yourself for not succeeding/sink with them -> rinse and repeat.
Izzy? Now HE is codependent on Ed. You can be codependent on someone who is perfectly fine. He tries to control Ed’s every move, doesn’t succeed, and inevitably gets angry. If you pick up an on god actual textbook, or like any Melody Beattie book, you will see that he is the very definition of codependency.
Cycling back to Ed, though. I do think he’s codependent. You don’t kill your alcoholic father to protect your mother. We don’t mysteriously never see his mother again and know that he went to sea at a young age for no reason. He tried to save her, it backfired. A woman telling her child that they’ll never have better because god decided they’d be miserable is not ready to be saved, is not ready to get out of an abusive situation.
Then, of course, there’s Jack. Jack is eternally getting Ed to do shit for him. To help him because he’s so helpless uwu or whatever. A douchebag who can’t seem to take care of himself and is on the hunt for someone to cater to him??? Mmm yummy! A codependent’s dream! In the episode, he caters to Jack’s every whim, makes excuses for him, and finally does the “sinking with him” thing when he inevitably pushes too far. This is partly because of Jack’s manipulation, partly because that’s what Ed’s family situation had been.
Now that we’ve established all of that, back to my original point: you don’t stop being codependent just because you get into a healthy relationship. I’m certain that a small part of the breakup era sads was that yet again he’d done something huge, sacrificed something big, and his efforts had gone wholly unwanted, just like what he’d done for his mom. And then there’s that fear. Ed knows the power that people he loves have over him. He knows how he acts in love! He knows how much it hurt when Stede left him! It makes sense, then, that he would run away when he sees Stede doing something he’s not too keen on (going full pirate party animal when Ed doesn’t want to be a pirate anymore). It’s fantastic that he’s running away though! He’s not doing shit he doesn’t want to do to humor Stede like he did with Jack. He’s not trying to force Stede to change directions. He’s not trying to control the situation! He’s seeing that he’s freaking out and he’s removing himself. Albeit poorly, but this is a step closer to being able to actually communicate things. He realizes he’s the variable he can change in dynamics.
So to close up, yeah the relationship is maybe a little codependent but not in the way people seem like to say? It’s codependent in that Ed has codependency issues and those will inevitably crop up in any deeply intimate relationship you’re in. It doesn’t mean you shouldn’t be in a relationship. It doesn’t mean that the relationship is bad or unhealthy. It just means you’re a human person with shit to work on.
112 notes
·
View notes
Note
Any news on ch 2 being released, the date? Also do you find it easier now that you're workin to chapter 2 in comparasion when u started ch1
It shall be done when it is done. We speculated on release dates before, but the simple fact is that since we're a hobby group working on this on our free time, we don't know for sure how long it'll take. When we know, we will be yelling about it very excitedly!!
As for difficulty, some parts are easier and some parts are harder. We have a lot of frameworks in place, yay! There's a set of base assets that we can work with, also yay! That does make work easier for us.
But from a writing perspective, we have the challenge that Chapter 1 starts the player at zero and there's only so far the player can diverge from that point in terms of variables and affection levels with the LIs. But now we have to start Chapter 2 aware of the many variables already in place and writing around them while adding more. Obscura doesn't have much hard branching, thank goodness, but the complexity still compounds over time just due to remembering and accounting for variables in place.
Just as a small example, characters remember how you did on your first heist with Keir in Chapter 1 and they do comment on it. If you fumbled an arm signal, Griff will have something to say about that in a conversation later on. If you were perfect and got away without a chase scene, the characters will acknowledge that Vesper is a natural at this kind of work. Stuff like that builds up and it's incredibly fun to write, but it does mean there's more work this time around.
90 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi! do you have any ideas on how to reward a dog who doesn't have any strong motivators? Treats are the only thing that work but he doesn't really care if there is something else he wants, doesnt care for toys, pets are ignored. I just have no idea what other rewards could be used
Id take a good look at Why the dogs motivation seems to be lacking, what environment it tanks in, and ensure to keep an eye out for things like stressors, overstimulation, fear, met needs, and other variables that may impact a dog’s comfort taking treats or exhibiting play behaviour. Things like illness or pain should also be considered as a factor for a lack of motivation (schedule their annual and take a good look at their behaviour and their movement- do they sit sloppy, pop hip often, hunch back, etc. these can all be more overlooked signs of pain!). Breed can also be a factor as some are more self motivated than people pleasing so their motivation tends to just look a bit different!
I'd also be curious to know if this dog has always been disinterested or if this has cropped up over time. A common factor for decreasing motivation is the fact that training itself has become unfun. Usually as a result of asking too much of the dog too fast, not paying them adequately for the work they're doing, working in far too complicated settings, too many competing reinforcers, getting frustrated during the session, using rewards to lure a dog towards feared things or simply having training sessions run on for too long where the dog then ends sessions feeling bored or tired. This can cause even the most active dog to become averse to training as a whole which can present itself as an aversion or lack of interest in many common rewards.
Additionally see what sorts of environments the dog is comfortable being rewarded in, perhaps they take treats okay in a certain room of the home but not outside. This can give us a lot of info and allow us to start in an environment they can succeed in and gradually shift to other environments with more complex challenges (like the competing reinforcers you mentioned)
Reinforcers can be Anything the dog actually wants. The sky is really the limit here. I can stick a treat in every dogs mouth and it’s not going to help anything if the dog itself doesn’t find that treat rewarding. Some options might be:
Treats- experiment with different types and textures. Smelly cheeses, hotdog, and sausage are common high value snacks that can help increase motivation in difficult situations but all dogs are different and some might find a satisfying crunch of a crispy biscuit more rewarding. Try new things and see what they gravitate towards. Additionally watch the way you deliver the reward, a common mistake is to push the treat in towards the dog's nose- this can be off-putting as you add spatial pressure which over time can cause a dog to refuse to take treats altogether. Instead try to offer the treat a distance away from their nose so they step towards it to take it (also watch for things like the way you hold your hand, some dogs may find a hand looming down with the treat threatening while a hand held below nose level with the palm up to be nicer to take treats from). You can also deliver treats in more engaging ways instead of just handing it to them. Toss it in the air for them to catch, roll it along the floor to chase, scatter a few pieces in grass, have them chase and follow the hand for a bit prior to releasing the treat. Make getting the treats a whole Experience!
Toys- rubber toys, canvas, biting, chasing, squeakers, tug. There's a ton of options. Not all dogs like playing in the middle of training as it breaks their focus but others live for it. While not for every dog I will say that playing is a good measure for a dog's comfort. If, for example, you can play tug indoors and have a fun time but the dog is unable to play tug at all outdoors that tells us the dog doesn't feel comfortable enough to exhibit that behaviour. That's information we can use!
Petting- Not my favourite thing to use, affection isn't really something you want to be bargaining off in exchange for favours but it has its uses. A fearful dog may love some pets to help comfort them and reduce that fear response, some affection can also go a long way in just grounding your dog and keeping a training session light and fun. A bit of a social fun break. There's definitely some dogs that can appreciate a pet as a reinforcer and they can work in a pinch if other reinforcers aren't available.
Sniffs- Not something you want to overuse as sniffing is a fundamental part of how dogs explore the world but an excellent way to shift to self reinforcing fundamentals like loose leash walking. Most dogs love a good sniff, your hound types especially, and you can use that to your advantage as you ask for a behaviour and then release them to go snuffle away. Sniffing is also a calming behaviour that can reduce heart rate and build confidence in their environment which can reduce issues like not taking treats outdoors in the first place.
Speed- A lot of dogs find human walking paces slow and frustrating (a common cause for leash pulling) so you may find that in outdoor environments you can reward your dog by simply jogging for a short burst. The speed is fun and enticing and as such can often become quite the powerful reward.
Personal play + Volume - Whether this be the opportunity to howl and bark or you getting loud and excited with them. Sometimes a dog may not be interested in toys but they may be interested in your engagement. This might be baby talking to them in a happy tone or fully getting down on their level to wrestle and bop around or perhaps running away and having them chase you. A different way to initiate play for those disinterested in toys.
Premack's Principle - When you are dealing with competing reinforcers most people will find they lose this battle where whatever you have is not as valuable as what the dog actually wants (chasing a squirrel perhaps). In many cases you cannot fight instinct and genetics with a piece of cheese. At least not without prepwork. This is where Premack's Principle comes in to play, where a dog is able to do a less desirable behaviour (ignoring the squirrel) in exchange for a more desirable behaviour (getting to go chase the squirrel). You can use the thing you're struggling with to reinforce what you'd rather see. Another example may be having your dog a distance away from other dogs, waiting for eye contact and then releasing them to go greet the dog. Over time this could cause an exciteable greeter to offer frequent eye contact to you whenever they spot a dog in anticipation of getting to go greet the other dog which is a nice alternative to barking or pulling. Practically everything your dog would Rather Be Doing you can use as a reward for what You would rather they be doing.
I'd also take a look in to "engagement games" online, there should be a load of force free resources out there for ways to make yourself more engaging and fun which can really help in encouraging a dog to be more excited to train. Strong foundations in how they view interacting with you and training as a whole can really go a long way in impacting motivators and training results.
There's a whole lot more to consider and a ton of more complex things that could be at play but without knowing your dog personally I'll leave this here for you to ponder and play with!
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
ART NOUVEAU
Art Nouveau appears at the end of the 19th century and spreads widely across Europe and the United States. It draws inspiration from the Japanese, Oriental, Byzantine and Celtic arts as well as Impressionism. The peculiarities of the style are highlighted decoration and strong interest in the ornament and curve line. Stylised floral motifs and human images combined with asymmetric compositions are used. The emotional suggestions that are inherent in style are: refinement, elegancy, spirituality, variability, expressiveness, romance, love, tenderness, nostalgia, dreaminess.

.

Origin of Art Nouveau.
On the one hand, it is the English Arts and Crafts movement from the middle of the nineteenth century and headed by William Morris. The basis of this movement is Morris's idea of affirming the value of handmade handicrafts against the industrial products. His followers replace cheap mass production with quality handmade items. They stem from the beauty of natural forms, the tradition of old medieval styles and folklore.
On the other hand, the ideas of Art Nouveau are also based on the works of Augustus Pugin, who seeks reforming society through the plastic forms of Gothic, which he considers to be the bearer of Christian values.The artists and designers of the 1990s developed the ideas of Puigin and Morris and enriched them with new forms and materials. This also determines the aesthetic basis of the new style. The materials used for everyday use are very high quality.
It has been assumed that all forms of plastic visualisation are equally valuable (until this moment it is believed that such activities are under the artist's dignity.)
The essence of Art Nouveau is that the art shape is particularly important, it is even more important than the content and even the most prosaic content can be represented in a highly artistic shape.
Another important aesthetic feature is the appearance of the female figure. Portraits of women are common in this style. The most common image is just a woman as a center of composition, in the way that the figure is an integral part of the ornament in the whole.

The art of posters is also developing in Paris.The emblem of this art becomes Alphonse Mucha. He designs theatrical posters and settings, but also made designs multiple packaging and patterns for mass consumption. Frequently used in them are stylised images of women whose long hair has been turned into complex decorative ornaments.

Like many of his peers Toulouse Lautrec follows the principles of Japanese engraving, which is based on the flat construction of the shapes, the exaggerated facial expressions and the strong theatrical compositions. The objects of his inspiration are dancers, actresses, singers, courtesans. He works a lot in the field of poster and advertising, raising this genre to the level of real art.

Gustav Klimt is the leading figure of the Vienna Secession. His works are very decorative and filled with erotism. Again, the woman is his main inspiration and is elevated to a cult.

In conclusion, Art Nouveau is one of the last attempts to create a common style in plastic arts, architecture, interior and furniture design, poster, book design, and more.

The aim of the architect, the artist, the designer is the creation of a synthetically complete work of art that enters the private life of man through the items that surrounds him. That's why this style is cosmopolitan.
As far as Art Nouveau artists and designers are concerned, it can be said that they develop and enrich the ideas of Pugin and Morris, and because of everything listed above we can define their work as a top-class art.
78 notes
·
View notes
Note
PLEASE EXPLAIN SEERS OBSCURA VS NORMAL SEERS i cant for the life of me remember the difference & the specs for both and its driving me crazy

I’m too lazy to make slides for this one (and too excited bc I love seers) THIS IS WHY IVE REWATCHED EVERY MORGAN AUDIO FIFTY TIMES… ahem anyways.

Seers Vs Seer Obscura
Seers are already a very complicated race. They branch off from vampires, can be latents, can use any sort of magic, and can hide their cores cleverly from any other race… and they are very, very rare. Very.
Although they can “see the future”, they can only see every see all variables in situation, mathematics and quantity. Probability machines. NOT SET IN STONE.
(Example: Morgan’s listener (seer obscura) hid their core and covered it with an illusionary aura, meaning nobody knew they were a seer. Seers are all talented at this.)

Seer Obscura are EVEN MORE RARE.
(The last Seer that the department had record of was waaay back in the early 1800s.)
Secondly, it’s hard to see any (if any at all, which is said to be impossible) future that a Seer Obscura is in. Their presence literally obscures and deforms the way the other seers and themselves see the future.

Morgan explains the way Seer Obscuras futures and any futures they are involved in by using a “radio frequency” type of analysis. The closer you get to the Seer Obscura in the future you’re searching, the more static it all becomes.
The only difference so far is that Seer Obscuras quite literally fry the futures (or the visions) of themselves and people in their lives.
(These were talked about in better depth in Morgan’s third audio.)

Think about it like this.
Let’s say you, a Seer Obscura, wanted to see the future of… maybe a stranger. You’d be able to see all the future of theirs that you’d like because you aren’t an active member in their future.
Now let’s take this same scenario but instead of a stranger, it was your friend/partner. A lot of their future would be staticky and unreadable for both you and other seers because of your “interference.”

Other:
Sight can not be learned. Either you are born with the ability to see the future or you can’t at all. Not even demons can.
The inversion shifter the timeline in all. Everything seen from before that point about the future became invalid.
There are places that are obscured as well. For example: death & Aria itself.
They can learn any magic at any level.
Any race can be Obscuras, actually. The title of obscura only means that you interfered with the timeline. Seer Obscuras are just waaaaaaay more rare and complex. For all we know, David could be a Shifter Obscura.
The soldality: (may have misspelt it.)
A group of seers who live publicly known for the race that they are, which is rare because seers tend to be in hiding. They are protected by the department. They all watch the time streams and predict what the future would be. The most of them believe that there is a for certain known outcome.
(The “known outcome” does not take account of those places and people who are obscured, making this group… a bit invalid in that place)
#redacted audio#redacted asmr#redactedverse#moronkyne#morons addition#redacted morgan kyne#redacted seer obscura
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m thinking about how, from the point that the release of Odium is set in motion, Szeth is killing lots of kings and nobility. A lot of them. It’s pretty brutal and one of those things the text doesn’t really want to spend long with for its brutality. But, while researching for something else, I saw this exchange with Szeth and Taravangian that stuck out to me:

“The world would have been able to stand against the enemy if you hadn’t made me murder half their monarchs”
No it wouldn’t have. Gavilar was a power hungry piece of shit willing to do anything to achieve immortality. If Gavilar had stood to face Odium he could never have done what Dalinar did. He would have turned Champion.
“No! We killed to save the world.”
If any of the powerful leaders of the world were alive to face Odium, we’d have had a much stronger alliance against the world. He would have tempted them with ease.
Instead we were left mostly with people who could recognize the dire situation and do what was right even if it wasn’t easy. For the Alethi it took Dalinar. For the Azir, it took a street urchin. For Jah Keved… it took a more complex series of actions to neutralize them, since allying would have never occurred ultimately. Consider how obvious Taravangian makes the betrayal of the Jah Keved troops. Enough that Dalinar positions against them before they’ve even switched sides.
Everything Taravangian has done was to weaken any and every pawn Odium could have had at his disposal. Put him on the backfoot and force him down a series of choices. Without the Diagram, Odium had every way to win. With it, he’s far more limited.
The problem is that limited isn’t enough—he could still pull it off, which is why Renarin, as an unknown variable, is key.
Renarin pushed the warcamp, namely Dalinar, into action with his cryptic warnings. If that hadn’t occurred, they wouldn’t have been paranoid enough for Szeth’s encounter. Dalinar would have likely fallen and Urithiru never found.
Following that, Renarin, his spren, and the connection to Sja-Anat provided another key turn point; the spren that alerted Odium to Taravangian’s meddling.

…

Without Renarin’s meddling and Odium interrupting, Szeth would have killed Taravangian. There would have been no ascension, and Rayse would still yet live. Maybe not be able to secure a full victory, but what really is the time Wit secured with the contest?
We need Taravangian in control of Odium for something and I think only Cultivation really knows why.
#stormlight archive#cosmere#the stormlight archive#kowt spoilers#wat spoilers#kowt speculation#taravangian#odium#szeth son son vallano#renarin kholin
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
player!killer and anomaly!dust
since these ideas have been invading my brain lately, i feel like i need to ramble about the toxic (doomed) kist potential they have.
imagine the game world of dusttale trying to correct itself ever since the anomaly/virus that is killer entered it. so things in the world start to glitch and don't make sense. a character repeats their lines over and over without stopping. shortcuts stop working properly. character stats inexplicably get messed up. goners start appearing to warn dust and killer about the end of the world. it's nearing its doomed timeline trajectory, and yet dust will not give up trying to salvage his universe. in his mind, there's one surefire way to get everything back to normal: exterminate the virus that is killer.
dust and killer (and the goners and the almagamates) are not affected by the glitches because they are anomalies, glitches detached from the world already. to killer, this means enlightenment and freedom. he doesn't understand dust's attachment to the underground, his dogmatic beliefs about justice and the greater good for the monsters. doesn't dust want to ascend to be something "real", rather than the npcs that the rest of the monsters are? doesn't he want to escape from the control of the player? why would he want to obey to the whims of a dying, boring, constricting world anyway? if dust can't see it, then killer will make him see.
the thing is, dust is a difficult monster to persuade. sure, killer can kill him again and again (chances are 50/50 on who will win anyway). but dust always bounces back, more vindicated in his retaliation and belief that killer needs to be gone. the thing is, when you want to break someone down, you need to be the thing they fear the most. killer is already that, isn't he? he's a future of a sans, of dust's own past. this is what dust could have become. killer is what dust has become - a sans doing the work of the no-mercy player.
"aren't you bored of doing the same thing over and over again? aren't you crazy from repeating all these useless cycles only to reach the same conclusion again and again?... oh wait, you already are!"
and dust - what can he say to all that? is it true? is it not? who cares - the only satisfaction he can have is wiping that smirk off that face. killer knows intimately beings like dust - not only because they were the same person at some point, but also because dust is a control freak with a savior complex as well as survivor's guilt. deep down inside, dust cannot fathom losing. he has poured too much, sacrificed too much, to get this far. and he won't stop - not until he reaches his happy ending, which will never come. so he'll forever be stuck down here, repeating his worst nightmares again and again in a hell of his own making.
the only variable in dust's life is killer. gradually, dust treats killing other monsters as a job - an important yet thankless job that someone has to do. the only kill in which he feels something is of his brother... and killer. with killer, dust is filled with something - maybe it's joy, maybe it's hate, it's hard to tell when apathy is his usual state.
and the thing is, the opposite of love isn't hate. it's the lack of love - it's apathy. he feels something for killer - an attachment, an obsession, a possessiveness. "only i get to kill him", "he's my kill", that's what dust thinks. he rationalizes that thinking of course - killer reminds of him too much of himself, the person he hates the most. but there's that fear every time he kills killer - fear that killer will never come back, leaving dust with his empty broken world and voices in his head. and he fears killer will know it, somehow.
for killer, it's always a game to see who's the winner and who's the loser. it's a struggle for control, with the controller and the controlled. and with the player gone, dust should belong to him now. an eternal playmate, after everyone else has disappeared from his life. and like, it's totally therapeutic to beat up and mess with the guy who reminds you of yourself, right? totally not a self-esteem issue waiting to be explored or anything at all. it's funny how much they match. "look, we both wear red!" exclaims killer as he points to his own red soul and dust's red iris. determination pulls them together, and determination will break one of them in the end, and it's not going to be him. he'll persevere once this world rots away, while dust will be trapped by his own volition.
maybe, just maybe, he'll whisk dust away once the end comes. and they'll find another playground to re-enact their play again. killer will take and take and take, until all they are is dust.
Oh, I will ruin you
It's a habit - I can't help it
I will only break your pretty things
I will only wring you dry of everything
And if you're fine with that
If you're fine with that
#hell yeah toxic dust strikes again#cw toxic relationship#dust sans#murder sans#killer sans#kist#love affair#utmv#undertale au#sanshipping#sanscest#Spotify
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
i think i followed you Back In The Day, seven years and seven blogs ago, for something related to mass effect (zaeed? maybe? who could say) and it's wild to come back to this site years later and find you thriving, surviving, growing-- playing ffxiv! love that game. curious how you'll feel about some side characters in shadowbringers, but i won't spoil which ones.
i do have real questions, though; writing tools. not pens or software, but personal structure tools and/or guidance. what does a beat sheet look like, for you? do you have a favored way of outlining or note-taking on your own thoughts when putting a story together?
and... i'm really curious how you hold a big story together in your head while you work on it in pieces, especially for something like dangerous crowns. there's this larger story i've been chasing around for a while, and I can't quite wrap my head around how to write the political/espionage plot for it without feeling like i've actually written a children's pantomime. the best i've got so far is "research real life events and use those as my outline" but after a point it becomes hard to keep track of all the variables of who knows what about whom, who is planning x when y, etc, etc. the characters don't need to know all that-- and may never know some things-- but i feel like /I/ need to understand what's happening on the macro level so i can move the world around them appropriately.
short version: how do YOU wrap your head around writing complex plots?
hey, anon! i started endwalker this week after a long... uh... glamour detour, so don't worry about spoiling things. i spoil myself for a lot of stories on purpose anyway. let's just say i've been attached to one too many characters who got killed.
anyway. writing. i've always handled plots the same way: clear documentation. if i don't note it down, i'm not going to remember it. i've used the same table outline since around 2014. it varies in detail for different projects, but the core format stays. i know it's kicking around in my blog archive somewhere, but it's worth reposting once in a while because people like to ask about it. here's what it looks like, featuring plot points cribbed from an endeavour episode:

i used this format for an outline at work a while back, and the team found it easy to follow, which was a big day for my ego. keeping track of plot structure is even more chaotic at work because we have multiple writers who all need to stay on the same page. we have very meticulous notes on what the player should know at which point, when we're introducing new information, and what we know, but shouldn't tell. we're also not above leaving notes like "this character has to convey X," "this character has to learn Y here," or "this is a clue that they're planning Z." it can be super on-the-nose. all that matters is that it makes sense to you. because you're right - if you get too lost, you can write yourself into logic holes of tremendous proportions. ask me how i know!
[as a sidenote, researching real-life events as a starting point has really grown on me in the past few years. my lead on coh3 had me do it. he said we were dealing with real people's history, so we couldn't be cheap or play fastball - we had to be accurate to pay it respect. even if you're not writing historical fiction, it just gives you insight into how people behave.]
i would argue that the plot of dangerous crowns is actually not that complicated, maybe to its detriment. there's kind of a genre struggle going on. at voltage, we were taught romance fans came for the relationship beats and valued them above all else. in fact, leadership told us players got irritated - which meant less sales - when the plot was too complex and took time away from the making out. political thriller fans, by contrast, expect relentless twists, high stakes, and harsh consequences, and sometimes see the relationships as superfluous.
but whatever. the point is, when you look at dangerous crowns' structure, it's a pearl necklace: a chain of anchoring events. the "pearl" scenes are where Big Plot happens. they're the reason you want to write the story, and probably the ones you have the most vivid daydreams about. the scenes in between are the string. not flashy, but important because they connect the pearls. they build tension and add logic, cohesion, and context. take the opera and hector's failed assassination. those are pearl scenes. that's a burst of drama i really wanted the story to build up to. i also had other flashbulb visions. livia by the fountain questioning herself, marcus' macbeth moment, the temple riot, things like that. so the question was, how could i believably travel between these pearl scenes? how could i make these big showcase moments connect smoothly?
if you're having trouble holding the story together in your head, i would ask, "what are your pearls?" what are the anchor points? outline those. it might not look like a necklace yet, but you'll sort of see it taking shape. and then, once you can see where your heart's-desire milestones are, you'll have a clearer idea of what can't fire until you set it up first. two other neat things can happen here. you could find the rhythm of your pacing, or realize you have a lot more plot meat than you thought you did. even if you don't, you have some road. and if you can't think of the string, sometimes you just have to start writing the pearls and see what comes to you.
good luck!!
89 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hiii I'm not sure if your requests are still open but 🧑🦲🧑🦲 can you do angst x reader 🧑🦲🧑🦲 like a songfic or something with 'The Scientist' by Coldplay 🧑🦲🧑🦲 (with senku ofc) 🧑🦲🧑🦲 preferably set before everyone was petrified 🧑🦲🧑🦲🧑🦲 ty ♡
the emojis in this request made me laugh THANK YOU for your request! i love love songfics.

Senku Ishigami is first and foremost a scientist. He, like all scientists, considers, observes and acts logically. He doesn’t do illogical as a man of science. Giving into illogical nonsense is just…well, illogical.
So when he first considers his romantic feelings for you, he does so from a logical perspective.
You spend a lot of time together, you share common interests, and beyond that, you were a caring, kind and passionate person. You and Senku clicked, and it made sense why.
However, Senku found himself thinking about how logical it was to be involved with you romantically; as a couple, you and Senku didn’t make sense at all.
Senku was reserved about his feelings outside of his typical enthusiasm over science and deadpan when it came to certain people, while you were the opposite. And so the two of you clashed horribly when it came to intimacy.
How was it that two people could be so similar yet so different?
Throughout your possibly (mostly likely- Senku’s still considering) illogical romance, Senku was cold toward your affection, which hurt you greatly. All you wanted to do was be close with your boyfriend. You wanted to be by his side, get to know him on a more personal level, but Senku’s lack of reciprocation of your affection only saddened, and over time, offended you.
You grasped at straws for any sort of affection you could manage out of him. Weren’t boyfriends meant to spend time with you? Ask you about your day? Be vulnerable and open and affectionate?
Each attempt at vulnerability with Senku led to the man of logic falling short, casually dismissing your efforts and resuming his talk about something science related. You did your best to be patient. These new levels of intimacy and trust took time to build. Each time, however, your heart grew heavier and heavier when your boyfriend made no sign of budging from his usual emotionally reserved nature.
And so, eventually, you stopped putting in the effort.
You started mimicking him near the end of your relationship. You distanced yourself emotionally, and you spent a lot of the time you’d usually spent with Senku on a science gadget to focus on your own interests.
He just doesn’t care, you would think sadly to yourself. We just don’t work.
And so eventually, the two of you broke things off.
Your friends were encouraging and insistent, however. “Every relationship has some roadblocks,” your friend Yuzuriha tried to reason empathically after you had vented your frustration and sadness to her, “you two just need to work together. You love each other a lot.” Somehow your friend saw something that you just couldn’t.
“How could you be so cold toward Y/N, Senku? I thought you liked each other.” Taiju had asked with all the genuinity in the world, but something about the question made Senku suppress a shudder. “I guess it makes sense. You aren’t into the whole romance thing.”
Senku isn’t a tin man with a missing heart no matter how much it may seem that way, however. His feelings for you were genuine, he wouldn’t have been in a relationship with you if they weren’t. He had approached your relationship as if it were a complex puzzle, when in reality, science and logic just didn’t fit in this equation. He had been looking at it all wrong.
To be logical didn’t simply mean to look at the cold hard facts. It certainly didn’t mean disregarding emotion from the equation all together. If anything, it was an important variable. He had a bad habit of getting so caught up in himself that he tended to forget such important details. But at this point, he was too late. He had realized his mistake far too soon, and now you were gone to him.
He’s lost another important variable- one that makes the whole equation fall apart. He spends a lot of time reflecting, and the entire time he knows, logically speaking, that the two of you weren’t meant to last for various reasons. Yet still, he realizes that he'd been trying to approach something that's illogical logically. His relationship with you wasn’t science, and he was a fool for ever thinking there was anything to compare. It isn't some complex formula or even some video game.
Did he really need to have a logical reason for liking, loving a person? Enjoying their company, admiring and cherishing them?
You didn’t want to take it too personally, however. Friends were what the two of you were better off as.
Yet over 3700 years pass and Senku finds that he has an overwhelming desire to start over. His heart, embarrassingly, yearns for something more. To try it all again, to repair his mistakes. It’s only enhanced the more time he spends around your brilliant mind, witnessing your kindness and empathy over and over, especially when it's most needed during troubling times.
He turns away when he feels guilt bloom in his chest. His attentive eyes can see from your lingering stares and wide smiles that you too would want a do-over.
The cycle of going through the motions would rinse and repeat to the point of exhaustion; this was Senku’s biggest fear, that this hypothesis would be proven true. He hoped that this was a theory he could disprove.
#i feel my senku characterisation has collapsed a bit :( been a while since ive seen my guy#this has been rotting for literal months in my drive#i forced myself to finish SOMETHING#writing has just not been clicking#dr stone angst#dr stone x reader#dr stone oneshot#dr stone imagines#senku ishigami x reader#senku x reader#senku ishigami oneshot#senku ishigami angst
142 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transgender people don't owe you an explanation about their bodies
This is a thing I believe should be said. I don't usually write about being LGBT+ or anything related to that, but for other trans people's sake, I will put it out here and hopefully reach out to those who need it.
Being transgender means your gender identity doesn't match the sex you are assigned at birth. Meaning, if a baby was born and they were immediately assigned as being male, then eventually this baby realised they're actually a girl. This person is transgender.
If someone is assigned female at birth, then eventually realises they actually don't identify as a woman nor a man. Then this person is also transgender.
One of the few cases in which these lines might get blurry is if the person was assigned male, then realises their gender is actually woman and man. They wouldn't be wrong to say they are both cis and trans.
This is without mentioning the complexities that comes with being intersex, gender non-comforming, drag queen/drag king, salmacian, crossdresser and many other variations that will affect the specific ways some transgender people experience their genders.
Regardless of these variables, one thing is a fact though, I honestly can't believe I have to say that in 2024, nobody is entitled to know about our bodies. Not a single person, except ourselves.
Oh, you mean, you know it isn't polite to ask about a trans person's genitals, right? Well, the issue is actually a lot more complex than that.
Probably the most talked about issue related to it is about sexual partners. If a cis man happens to have a sexual interaction with a trans woman, then decides to take her to a one way trip to the afterlife in an unimaginable traumatic and painful way... Then that's on him. He's a transphobe and a criminal. He isn't a victim in this situation.
"Oh, but did she disclose that she was trans?"
I mean, not everyone is going to disclose the way their genitals are different or some not very pleasant traits of their bodies, yet they don't die because of that. Especially not in such humiliating ways and have a bunch of people who weren't there claiming this was the victim's fault.
Honestly, the only reason I even suggest that trans people tell their partners is for their own safety and there's literary no guarantee even that will help since some people use this as an excuse to commit hate crimes. You know, not even our sexual partners are entitled to know our medical history. Not a single person needs to know about our biology, unless we need them to know.
That means, people who would literary put us in danger (accidentally or not) if they didn't know, such as sexual partners and doctors. Even these cases are best to be analysed in each context if that'd be a good idea. (A sexual partner online that has no plans of meeting up the transgender person will be more likely to be transphobic if they know this information, but if they were going to meet in person, then it would be safer for the trans partner to disclose it for their own safety.)
Frankly, if a person decides to cut contact with every single family member, friend and acquaintance who met them before transitioning, moving far away, making up a completely different story about being cisgender and living as their gender while taking their whole process to the grave... That's their right. If this is what would make them happy, they should be allowed to go for it.
"But what about the trans women/trans men invading lesbian/gay spaces?"
If they are lesbian/gay women/men, then they are at the absolutely right space. (Or generally attracted to the same gender.) Attempts of forcing people out of gendered spaces that they belong to means you do not see trans women as real women nor trans men as real. That is transphobia and entitlement to trans people's bodies.
"What about intersex people? They don't want you to use them as arguments for nonbinary existence nor as ways to keep yourself being stealth."
Nonbinary people could still exist even if being intersex wasn't a thing since sex =/= gender. Besides, intersex bodies do show that sex isn't limited by male and female just like nonbinary shows that gender isn't just man or woman.
Also, the whole thing about "pretending to be intersex" as a trans stealth person being intersexism is literary something new. At least from what I've seen in trans spaces, we aren't even doing that. We are actually claiming to have hormonal imbalance (that has causes not related to being intersex at times) that makes us not have the expected hormones for men/males or women/females, which is absolutely correct. Many trans women cannot produce the expected amount of estrogen for women and tend to have higher levels of testosterone as well. Doing hormonal therapy for this is something that even cis women do, especially if they happen to have PCOS. The fact that she's not disclosing her transness doesn't mean she's taking up the space that belongs to intersex people.
Just like how some pre or non-op trans men who have visible chests aren't taking up intersex spaces by saying he has gynecomastia, since this condition can also happen if someone takes risperidone as a side effect. Cis men who have such condition may opt for surgery that often comes with the very same scars you see with top surgery made for trans men/transmasculine people/nonbinary folks. If a person needs or wants to be stealth about it, they are allowed to say they had excess growth of breast tissue that made them uncomfortable and not have to specify they were actually dealing with gender dysphoria. That's private information nobody has any business knowing.
While many things have changed and progress has been made for trans people to be open about their transness, some of us don't want to deal with the discrimination that comes with such visibility and that doesn't make us liars nor monsters. Sometimes we need to do so because it's what makes us happy and our gender dysphoria can destroy this if others know about our past, even if they live in a trans positive environment.
We do not owe our bodies to anyone.
We do not owe letting other people know of the medical procedures we went or go through.
We do not owe our current or past sex characteristics to anyone.
If you do not support trans people who cannot or don't want to pass, then you are a transphobe.
If you do not support trans people who do pass and are open about being transgender, then you are a transphobe.
If you do not support trans people who are stealth and have to hide or change parts of their story to keep being seen as equal towards their cisgender peers, then you are a transphobe.
If you do not support trans people occupying gender-specific spaces that match their gender identities even if it goes against the sex they were assigned at birth, then you are a transphobe.
If you do not support trans people who cannot come out or get gender-affirming care for any reason, then you are a transphobe.
If you do not support trans people who don't want to do any gender affirming procedures or hormonal therapy, then you are a transphobe.
We do not owe you our medical history, our social changes, our document changes nor the lack of these. If we share this information with you, don't expect that from other trans people. We are individual and we are allowed to disclose or not about ourselves.
If you cannot treat trans people as the gender they are, then you are a transphobe. The sex we were assigned at birth doesn't have to be part of our social interactions and as long as society keeps separating us from the groups we belong to, we will have to keep this information private. Sometimes we have to do so because we get gender dysphoria over being forced to disclose our sex assigned to us at birth.
I'm nonbinary, but my goal is to get to a point people would look at me and assume I was assigned male at birth. No, I'm not talking about being seen as a man, I'm literary talking about being assumed to have been born with sex characteristics assumed to belong only to men and be out as nonbinary if safe to do so.
I honestly don't see anything wrong with my transition goals since they literary won't have any negative consequences to the people around me. My family mouring a "girl" doesn't count. They wouldn't have to do so if our society didn't demonize us or if they didn't have such limited views of what a woman or a man can do/be.
I had to deconstruct the ideas I had of what being a man or woman meant, so will they if they plan on having a good relationship with me. That's just how it is. The fact is that we always existed in society and we will keep existing even if you try to make us go extinct. We don't owe you information about our bodies and never will.
#lgbt#lgbtq community#lgbtq#lgbtqia#transgender#nonbinary#trans women are real women#trans men are real men
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, I think the fandom is chilled out enough at this point to discuss in good faith and maturity how Edelgard has a tendency to rationalize working with people she hates while making enemies with people she likes/loves. I think this is a bad habit, but certainly one developed as a survival mechanism.
Just, imagine being Claude von Reigan staring at the Spare Or Kill bar over your head thinking "Duke Aegir gets house arrest and I get exile or execution??? Life is not fair." Or Dimitri thinking about how exile is not even an option for him, but Thales is still breathing. It is hilarious, in a tragic way.
Welcome to the Expanded Universe of Insane Edelgard Analysis where all of you who read my little analysis on Edelgard and Faith are going to get a completely inversed statement on Edelgard! So, to disclaimer, Edelgard is certainly more idealistic than cynical, although she would likely argue she is a realist (LOL), but she certainly has tendencies to dip into fatalism and such as. Edelgard thinks violence is inveitable, she sees a continent that Seiros reforged with violence, that was broken earlier by Nemesis's violence, and has been subverted by the violence of TWSITD and the nobility. Edelgard is willing to take up the tools of her enemies because she thinks this is the only way to play the game (how metatextual of her). She is driven by her ideals to win this game and make something better of it at the end, but it is still a grim reality to just accept as inevitable.
I think it boils down to Edelgard's dislike of losing control over things. Edelgard is working with people she hates, but they are people she has known for over half her life. She knows how they think, what makes them tick, what they want, all of that jazz. At this point, their naked self interest and penchant for atrocity do not surprise her (often, at least). Claude and Dimitri might seem like good people, Edelgard might be able to work with them, but in her mind her course was set years ago and she cannot go jeopardizing or even altering her plans on unknown variables. Edelgard does not know how they think, she often assumes the worst of them when they offer her any kind of laurel because assuming the worst has worked for her so far. This is not to say what she did was right, by the by, just to understand what she was thinking. Because "I will court the favour of Adrestia's nobility (who I hate) and secretly cooperate with TWSITD (who I hate even more), but I will not work with Claude or Dimitri (who annoy me sometimes, but are clearly not evil)" is a chain of thought that requires a complex answer and an interesting one at that. I think it is reasonable to say that not making an alliance with Claude or Dimitri (we are operating strictly with Three Houses, I adore Three Hopes, but what is going on there would make this all the more complicated) was a miscalculation, at least. A miscalculation that led to a continental war, but hey this is what they mean by the games of mice and men.
It is just so tragic, I think, that Edelgard was prepared for a world choked with evil, expected corruption and cruelty wherever she looked, and there was so much of it, but what she was unprepared for was a few sparks of good outside her own. If the odds were more against her, if Claude and Dimitri were not there, if there really was no one else willing to change Fódlan besides Edelgard, I think she might have had a better chance of victory than in the canon sequence of events. Edelgard really did not account for being in a Fire Emblem game where the power of friendship is real and it can kill your enemies (or you, if you make enemies of your friends). It is really funny, in a really heartbreaking way.
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trying to make sense of Umineko while playing it for the first time, essay post-Ep1: The Beatrice lies in the details
0. On games, interactivity, roulette, and chess, or: how to lose at Umineko
Umineko no Naku Koro ni, commonly translated as Umineko: When they cry, also translated as Umineko: When the seagulls cry, also abbreviated as Umineko, also subtitled (I think?) Rondo of the Witch and Reasoning, is a visual novel series originally released between 2007 and 2010 by the group 07th Expansion, under the influential authorship of Ryukishi07, also abbreviated Ryukishi in fandom discussions. Umineko might best be classified as a story[i]. As far as the medium goes, Umineko has, as far as I understand, existed in form of an online visual novel, a PS3 game, a manga, a downloadable visual novel, and an anime, if not more. And yet, as I experience Umineko, I have paid for it and downloaded it from Steam, as well as having installed a massive and wonderful total conversion mod on top of it. The question of “what is a game” is an esoteric one, one that renders “is Umineko a game” absurdly unanswerable. But while categorizing Umineko as a game or not a game is difficult, it is easy to see that Umineko has a loaded allegorical relationship to game(s).
In Episode 1 of Umineko, Legend of the Golden Witch (to be called Ep1 from now on), two different games are brought to the table regularly, both as metaphors and games characters play: chess and roulette. Chess and roulette are very different games, almost diametrically opposite. Chess is a game in which every move can be calculated, at least in theory. While such computers are yet to be created, a computer with sufficient capacity of calculating could simulate every possible chess game, always know a certain path to victory. Humans are incapable of knowing every single possible chess game at once. Humans playing chess at a high level memorize and execute cyclical patterns and try to guide their opponent(s) into patterns and cycles they are unfamiliar with. Despite having no randomness involved, despite seeming predetermined every time, chess is a fascinating and very human game to play. And, indeed, a lot of the humans (and witches) in Umineko Ep1 play chess. When Ushiromiya Kinzo asks his resident doctor and old friend how long he still has to live in the prelude, the doctor points to a chess game they are playing to establish a metaphor. When trying to solve the death of his parents as a crime, Ushiromiya Battler turns to chess and the repeating idea of “spinning around the chessboard” to find the culprit. Who plays chess against whom and with what level of skill is a motive and allegorical theme repeated over and over and over again in Umineko Ep1.
While no character in Umineko Ep1 plays an actual game of roulette, roulette is also a repeated motive in this story. Roulette is random or not random depending on a complex philosophical debate around determinism – but on a well-designed roulette table, no human or computer is able to tell the outcome of a spin of the wheel. To many minor factors, like air flow, friction of minute surfaces, gravitational pulls, and rotational momentum make roulette highly random. In Umineko Ep1, the so-called demon’s roulette is a repeated motive pertaining to the potentially supernatural violence that characters are subjected to as the deaths and murders commence, as well as an allegory for capitalism. One character in Umineko Ep1, a child servant by the name of Kanon, wants to withdraw from this seemingly randomized violence of the demon’s roulette by explaining that he will become the unforeseen variable in this roulette game, the Zero, neither red nor black on the roulette wheel, and therefore a gamble to bet on. I do not know a lot about roulette, but if I recall correctly, the Zero is part of roulette not as a game-breaking but game-enabling mechanism; through the Zero, the house has a statistical edge on a longer and longer series of roulette games.
Be that is it may, both games are referenced and loaded with meaning in Umineko Ep1. Chess, not random and a clash of human minds, versus roulette, totally random, a game of chance without reason; this opens a spectrum through which to categorize any other game. Some characters as well as some of the menus in Umineko Ep1, particularly Lady Bernkastel in the second-order frame narrative, urge the players/readers/player-readers to treat Umineko as a game of chess, one with pieces, invalid and valid, better and worse moves. This framing of Umineko as a chess-like game implies that Umineko could be solved. The question is what it means to solve Umineko. Umineko happens. It happens to the player-reader. The player-reader cannot change the story on any level of the story. Sure, in the first-order and second-order frame narratives, the player-reader can choose to turn the descriptions of characters in the menu that functions as a dramatis personae to their respective dead or alive states, which reflects what happens when the dramatis personae updates during the happenings of the embedded narrative. But toggling states in the dramatis personae doesn’t change anything; the player-reader but sees different text describing characters. Beatrice’s entry into the dramatis personae in the first-order and second-order frame narratives even taunts the player-reader with their powerlessness, the inability to interact, when you try to set Beatrice’s entry to dead. If Umineko is a game, it is not played within the mechanics of the software. Umineko is, if even playable in the first place, played metatextually. Presenting itself on the outset as a murder mystery, solving Umineko means unravelling its mysteries as it progresses. There is no apparent win-or-lose condition to Umineko.
And yet, one does not simply commit to a story as massive and complex as Umineko without prior knowledge of it. I got into Umineko because of @siphonophorus/Ozaawa’s obsession with it. Ozaawa is a cherished discord friend, who has had Beatrice as their profile picture ever since I can remember. I had started Umineko Ep1 with multiple spoilers in mind, such as: “There is a long time loop”, “Beatrice is really queer”, “people die and get resurrected over and over again”, “magic somehow is and isn’t real at the same time”, and “the narrative structure is a mess”. But the most intriguing piece of knowledge is as follows: “you can solve a lot Umineko from very early on”. Apparently someone in the fandom named pochapal had solved large pieces of the puzzle very very early on in the course of the story. Now, since Umineko urges you to treat it as chess, there is an analogy that immediately sprung to my mind: There are ways to checkmate someone in chess in the least possible amount of moves, a common one of these strategies being called a scholar’s mate. Four moves by the player controlling the white pieces lead, under ideal circumstances, to a checkmate and victory. Without knowing the solution to Umineko, you can meaningfully solve Umineko in a (relatively) short amount of story. I call this idea Umineko’s scholar’s mate. I want to explore this possibility, one of the primary reasons why I am writing this essay and plan on writing more of them in the future; to solve as much as I think I can after every episode. Writing this essay is me playing Umineko (I think). There is however a massive problem to me being obsessed with Umineko’s scholar’s mate; namely, that I suck absolute ass at chess and detective/murder mysteries. I am also rather mediocre at literary analysis, and cannot call myself a literary scholar in a great capacity. Congratulations to pochapal for doing Umineko’s scholar’s mate or at least coming close to that, I will not be able to reproduce that achievement. I have invested roughly 31 hours into Ep1 and I still do not know where to start solving the epitaph or who was killed how by whom. I am a historian, and that is about the range of my expertise. I almost did not write this essay and had been moving into Ep2 for roughly thirty minutes before a dumb joke I made on Discord lead to a lot of pieces clicking into place and me being able to synthesize a stable, if a bit tangential reading of Ep1 (more on that serendipitous accident in section 3 of this essay).
All in all, I am obsessed with this story to an extreme level and my brain is constantly trying to crack its mysteries. I invite you to join me on this journey, a delayed live-commentary of my first play-readthrough of Umineko. That being said, given the nature of my approach to play-reading Umineko, I’d like to avoid spoilers for Episodes I have yet to read as much as possible, and I’d hope anyone reading this will respect that wish.
Content warning: Umineko is a horror story that deals with a lot of systems of violence in gruesome detail. So much violence in fact that I fear the content warning in itself could be triggering. The full content warning will be found under the Read More.
Umineko Ep1 contains in varying degrees of alluding, mentioning, and describing: extreme gore, murder, suicide, sexual assault, patriarchal violence, class violence, child labour, grooming, familial violence, intergenerational violence and intergenerational trauma, child abuse, misogyny, psychological horror, colonialism, imperialism, and fascism.
1. On Umineko Ep1, or: Synopsis
The story of Umineko Ep1 unfolds in stages. The first stage to unlock is the embedded narrative of Ep1. It opens with a prelude on the island of Rokkenjima, a fictional, circular island with a circumference of roughly ten kilometres that is part of the real-life volcanic Izu Archipelago of Japan[ii], a short amount of time before Saturday, the 4th of October 1986. A conversation between Ushiromiya Kinzo, patriarch over the ultrawealthy Ushiromiya family and man who bought himself into the title of “owner of Rokkenjima”, and Doctor Nanjo, his attending physician and long-term friend, unfolds in Kinzo’s study in his mansion. Nanjo reveals to Kinzo that the latter is dying and has not much time left, explaining to Kinzo that he might want to settle his affairs. Kinzo reacts, in the presence of a disturbed Nanjo and the much more calm and collected head servant Genji, with at outburst of anger, revealing an obsession with a woman named Beatrice.
On the morning of Saturday, the 4th of October 1986, members of the Ushiromiya family assemble on a nearby airport. Among those assembled are Kinzo’s second oldest child, Eva, her husband, Hideyoshi, and their child, George, as well Rudolf, Kinzo’s third child, Rudolf’s second wife Kyrie, and Rudolf’s son out of his first marriage, Battler, and lastly, Kinzo’s fourth and youngest child, Rosa, as well as Rosa’s daughter, Maria. These seven travel per airplane to nearby Niijima, where they meet up with Jessica, the daughter of Kinzo’s oldest son, and Kumasawa, one of the servants at Rokkenjima. They take a boat to Rokkenjima, arriving around 10:30 AM.
On Rokkenjima, the weather starts to show signs of getting worse. Traversing through the Ushiromiya family estate, the only part of the island that is inhabited by humans, they meet Godha, the ambitious and renowned private cook, and Kanon, a teenager and servant at the household, currently struggling to do heavy labour in the elaborate rose garden. The new arrivals settle into the guesthouse, separated from the main mansion by the rose garden. In the mansion, the final set of characters of importance to the story get introduced. Sayo, working under the servant name of Shannon, another young servant of the household, Krauss, Kinzo’s first child and heir-apparent to the Ushiromiya head family, and Natsuhi, Krauss’ wife and Jessica’s mother.[iii]
The children, i. e. the cousins, staying at the guesthouse, do some catching-up on their lives, while the parents, i. e. the siblings, discuss at the mansion. Between 12:00 PM and 1:30PM, the family and Nanjo assemble in the dining room of the mansion for lunch. Waiting in vain for Kinzo’s attendance, they proceed to eat without him. At around 1:30 PM, the parents withdraw to discuss finances and inheritance politics. Knowing that Kinzo is close to death, the question of who gets which part of the vast family fortune takes centre stage in their discussion. Accusing Krauss of embezzling some of Kinzo’s private fortune, namely the vast amount of it stored in a supposed ten tons of gold, Eva, Hideyoshi, Kyrie, and Rudolf (and Rosa to some degree) open with an offensive, demanding immediate compensation by Krauss. Denying the existence of the gold and shutting Natsuhi out of the conversation, Krauss counters, revealing that Rudolf is in desperate need of money because he is embroiled in legal battles in the United States, Hideyoshi and Eva are in need of money to support the shaky expansion of their business, and Rosa needs money for her fledgling business. Their talks ultimately end in a draw. Krauss later reveals to a distressed Natsuhi that the gold actually exists, showing a bar as proof.[iv]
Meanwhile, the children roam the mansion and later head down to the beach. They discuss a portrait hanging in the main staircase area, one that Battler had not seen since the last time he had been at Rokkenjima many years ago. The portrait supposedly shows the mystery woman, Beatrice, and has an epitaph underneath. Beatrice is known as the witch of the island, a myth Battler denounces as a fairy tale. The epitaph takes the form of a riddle, forecasting much death and tasking the readers with finding the hidden gold. On the beach, the children try to solve the riddle, also reminiscing on Kinzo’s biography and the history of the family fortune. While the Ushiromiya family had lost most of its wealth, means of production, and members in the Great Kantō earthquake of 1923, Kinzo rose to inherit the title of head of the family. By 1950, Kinzo had (re)established the family as one of the wealthiest of the country, having successfully gambled a lot of capital of mysterious origin on the Korean War. The children wonder if this mysterious starter capital might have been the gold, and if Beatrice might have been a mysterious financier that gave Kinzo this money. Maria, autistic child hyperfocused on the occult and dark magic, insists that Beatrice is a witch and had produced the gold using a “philosopher’s stone”.[v]
In the meantime, a massive storm that had been brewing for a while turns into first rainfall. At around 6:00 PM, Maria is still missing after having been hit in the face multiple times by Rosa a couple of hours earlier as a supposed disciplinary measure. The family goes searching for Maria. She is found in the rose garden, holding an umbrella, still looking for a singular rose plant she had taken a liking to when they first arrived at the island, scared that something might happen to the plant in the storm. Going on to look for whoever had handed Maria the umbrella to properly thank them, Maria insists that the umbrella had been handed to her by Beatrice. Furthermore, Beatrice, according to Maria’s description, had handed her a letter, to be read to the family. The letter, supposedly written by Beatrice herself, reminds them to solve the riddle of the epitaph, lest Beatrice collect what is owed to her according to a mysterious contract between Kinzo and her. Distressing over the letter, the adults continue to fight each other with words, up until midnight for some of them. In the meantime, George and Sayo, secretly involved with each other, meet up in the rose garden. George proposes to Sayo.
On the next day, at around 6:00 AM on the 5th of October, the machinery of the household springs to life again, while the storm still rages on. Preparing the breakfast is impossible, however, due to Godha being missing. As more of the guests and residents of the mansion and guesthouse wake up, it turns out that not only Godha is missing, but Sayo, Krauss, Rudolf, Kyrie, and Rosa as well. After Kanon discovers occult symbols written out in blood on the shutter of the rose garden storehouse, several characters rush to open it. Inside the storehouse are the corpses of all six that are missing, mutilated, especially in their faces.[vi] The family attempts to contact the police, but the telephones have failed in the storm, similarly, boats are no option.
Retreating to the mansion, they find the dining room covered in blood. Fearing for their lives, the survivors hole up in the parlor of the mansion at around 9 AM. Afterwards, they find Kinzo missing from his study. Everyone soon falls into suspicion of each other, suspecting a murderer in their midst, but also unable to rule out other parties, namely Beatrice, being involved. Especially Eva and Natsuhi begin fighting, while Natsuhi carries Kinzo’s rifle, the only known firearm on the island. In the meantime, the children, with the help of Maria, try to discuss the occult implications of the murders, and a new letter that had been found. At some point, despite Natsuhi’s reservations, Eva and Hideyoshi retreat to their guest rooms in the mansion.
At 7 PM, the servants discover the door to Eva and Hideyoshi’s room to be painted in blood. Prying the door open, they find the corpses of Eva and Hideyoshi, with strange spikes lodged into their foreheads.[vii] Smelling a strange smell coming from the boiler room in the basement, Kanon runs there. Challenging Beatrice, which he assigns to the darkness in the corner of the room, he tries to harm her, leading only to him being mortally wounded.[viii] It is difficult to decipher his final words, I personally do not understand if he had anticipated or at least accepted the potential of his death in that action. When everyone else catches up with him, it quickly becomes apparent that the smell is coming from the boiler, in which Kinzo’s charred corpse is found.[ix] The survivors retreat to Kinzo’s study, judging it to be the safest room in the mansion.
At around 8 PM, George, Battler, Jessica, and Natsuhi look at the smaller portrait of Beatrice on the wall of the study, when suddenly, another letter by Beatrice appears, in which Beatrice gleefully celebrates her victory. Suspecting those who had not looked at the portrait to contain Beatrice or at least a collaborator, Natsuhi sends out Nanjo, Genji, Maria, and Kumasawa.
At around 11:30 PM, the phone in the study rings, revealing a singing Maria. Sensing that she might have send the four others to their doom, Natsuhi goes looking for them. Their corpses are found in the parlor, safe for Maria, who stands to a wall, singing.[x] Natsuhi runs out to the main hall, when the clock strikes midnight. She challenges the darkness, Beatrice, to a duel, which leads to her being shot with the rifle she is carrying.[xi] The children arrive in the main hall to see a woman standing, half-shrouded in the dark, who Maria identifies as Beatrice, running towards her.
The next bit of story unfolds in the epilogue, written in the style of a historiographical account. The police arrive the next day, finding everyone dead, except the children, whose corpses could not be fully identified in the gore.[xii] An urban legend spawns from these two days at Rokkenjima. Some years later, a notebook fragment lodged inside a wine bottle washes ashore at a beach. It is a fragment of Maria’s diary, reporting on the events of the days, concluding in a cry not for help, but for the someone to solve the mystery at hand.
Concluding this embedded narrative, a new chapter called the Tea Party unlocks in the game’s menu. In the Tea Party, the first-order frame narrative unfolds, in a domain only labelled Purgatorio in the opening slide.[xiii] Kanon, Sayo, George, Jessica, Maria, and Battler converse about the events of the first Episode, fully aware that they are characters in a story. Most of them either believed in magic previously or now concede that magic must have been the murder weapon. Battler, however, resists this reading of events. Beatrice appears, superficially amused by Battler’s antics. Transporting them to the scene of Hideyoshi’s and Eva’s murder, she demonstrates supposedly magic mastery over so-called demonic stakes, with which she murders Hideyoshi and Eva again. Battler still does not concede, vowing to uncover what practical tricks Beatrice uses for her murders. The other children and young adults begin violently unravelling into piles of gore[xiv], as Beatrice magic keeping them alive supposedly fails as Battler is unable to believe in that magic. In her dying words, Jessica urges Battler to resist believing in magic.
Concluding the Tea Party, another chapter unlocks in the game’s menu. In this second-order frame narrative, in some ill-defined realm of witches, Beatrice hosts a witch named Bernkastel in her domain, inviting her to watch another game. While Beatrice is absent for a short while, Bernkastel turns her eyes and attention to the play-reader, giving, out of a self-reported pity for the play-reader, cryptic clues to playing/reading/observing Umineko. This concludes Ep1.
2. On apples falling from family trees, or: cyclical systems of violence
2.1 What the actual fuck, Battler: Rudolf, Rosa, parental violence, masculinity, and the patriarchy
The first thing that one can easily observe when reading Umineko Ep1 is that violence happens cyclically, on multiple levels. The violence Umineko examines is incredibly complex, with multiple threads interwoven into a singular system of power. A very fitting way to try to unravel these threads from one another (at least to some degree) is looking at the branches of the family tree placing allegorical emphasis on different aspects of that violence.
Much sooner than when the shutter is raised on the rose garden storehouse, Umineko Ep1 reaffirms that it is a horror game; more precisely, every third time[xv] Battler opens his mouth. For play-readers who get lulled into a false sense of security by the mundane family conversations at the airport, the harbour at Niijima reminds them of its horror when Battler makes jokes about sexually assaulting his cousin, Jessica. Later, he makes a joke about making Maria, his nine-year old cousin, promise that he can touch her breasts once he has grown up. This joke causes concern by George and Jessica. When Battler only shortly after sets out to touch Sayo’s breasts, Sayo does not resist, until she is directly ordered to do so. The characters around him barely acknowledge Battler’s insistence on semi-seriously performing symbolic acts of sexualized violence, only the joke with Maria leads to Jessica slapping Battler in the face, and the dynamic returns to friendly as quickly as it escalated. This absence of consequences for his violence stands for two things: How fundamental and normalized misogyny and the patriarchy are in the family, and that Battler is his father’s son. Indeed, that Battler mirrors in speech what his father enacts in material reality also stands as a pars pro toto for the fact that children in Umineko perpetuate the violence of their parents, with only minor variation per generation.
The extent of Rudolf’s patriarchal and sexualized violence is cloaked in hushes and whispers in Ep1, but the outline of his actions clings to his character. In his introduction at the airport, Kyrie and Battler joke about Kyrie being the only woman capable of holding Rudolf in his reigns; a metaphor of taming wild horses that seems to be close to common social narratives around particularly sexually violent men. Battler had left the family behind for about six years, angry at Rudolf for what Rudolf did to Battler’s mother, a mystery as of now. After the death of Battler’s mother, it took Rudolf not long to marry his former advisor-secretary Kyrie. Kinzo laments about his children and mentions Rudolf’s inability to control his lust. With a father like that, Battler’s sticking to mostly spoken jokes about misogynistic violence measures the distance the apple ultimately managed to fall from the tree.
That violence is an inheritance in the Ushiromiya family is very evident. This includes physical abuse. Rosa’s beating of Maria, for Maria speaking in a way perfectly normal for an autistic nine-year old, is one example of this. Indeed, this very overt act of parental violence also happens in the context of Maria searching for a singular, slightly wilting rose in the rose garden that she had taken a liking to. Engaging in improper speech patterns (read: making noises instead of using a sophisticated, class-appropriated lexicon) and showing compassion, things that all children engage in in some degree because (I cannot stress this enough) humans are born ultimately compassionate and playful, are met with extreme violence to be eradicated. The kind of adult growing up from such a childhood has to invest a lot of emotional energy in unravelling that violence and the trauma it causes. Those used to violence have a choice to either counter this violence by difficult means and heal, or perpetuate the same kind of violence. It is evident Rosa picked up her parenting methods from Kinzo, who is noted to have hit Krauss often and loudly as a child.
As violence is carried mostly undisturbed from generation to generation, misogyny becomes an integral aspect of the mechanism of violence. Battler notes that the Ushiromiya family places a special emphasis on blood relations, perhaps more than other families, but that focus on blood still includes the patriarchy to a large degree, just in an uncommon variation. Indeed, in parts of Ep1 focusing on Natsuhi, it becomes clear that especially women marrying into this family structure are seen as little more than means to produce heirs.
2.2 Class dismissed: Eva versus Natsuhi, the mansion, Gothic horror, and servants
Upon marrying into the Ushiromiya family, Natsuhi was expected to give birth to an heir to the head family as soon as possible. Indeed, she becomes reduced to her womb, in an incredibly dehumanizing fashion. Still, within the rigid social structure of the mansion, she is the host, the one every servant first turns to. When a servant is unable to perform their labour and present a perfect household, Natsuhi pays in social capital. As the connecting tissue between the servant class and the ultrarich family, as the outsider womb that failed for the longest time, as the silenced and excluded player in the parents’ game of inheritance splitting, Natsuhi takes a fringe position. She is a fulcrum of violence, both recipient and exacter of it. Nominally member of the uppermost class, and a woman, she should find herself on similar station to Eva.
And yet, in the incredibly weird and fully obscene tension between Eva and Natsuhi, Eva manages to mobilize class and blood relations to gain an advantage over Natsuhi. Eva managed to place Hideyoshi into the family registry, maintaining her family name despite that not being common, and upstages Natsuhi in fulfilling the role and purpose of a woman in this family structure, by birthing an heir faster than Natsuhi. Eva envies Krauss and wants to gain his level of power. George is Eva’s ambition grown into flesh, not a son but a pawn and argument, her project to produce a human more fit to the title of heir to the head family than Jessica. Indeed, Eva fully modelled George into that role, and most of the family agrees that he would make a better heir than Jessica. Natsuhi, maintaining a modicum of humanity and compassion despite the family around her, does not manage to exert the same level of violent force upon her daughter Jessica, leading to Jessica being labelled a failure, and Natsuhi in turn as well. Eva goes as far as calling Natsuhi a “lowly maidservant”. Natsuhi’s ambiguous state in the family comes also to be expressed in her not being allowed to bear the family crest, a one-winged eagle. While the servants and all (blood) family members are allowed to carry it on their clothes, Natsuhi is not afforded that status. Belittled over decades, torn from her old family and forced to cut all ties, reduced to a womb, called a failure time and time again, Natsuhi jumps at the opportunity when Kinzo tells her she is allowed to carry the one-winged eagle in her heart. Her desperation to become a full-fledged member of the family comes to a close when she, as the only surviving parent, calls herself heir to the family in her duel with Beatrice. This quest, to become full participant in the violent machinery of the family structure, fails, and she dies by the firearm so closely linked with the head of the family. And yet, the situation of the servants is markedly worse than Natsuhi’s.
While Natsuhi is dehumanized by being reduced to a walking womb, the servants are not even afforded a distant connection to flesh and blood, being reduced to furniture. It is a mantra beaten into them, one they repeat again and again to deny their own agency, to be “nothing but furniture”. The way the servants navigate this lack of agency varies. Genji consigns himself to collected and veiled pride; being most trusted by Kinzo, moreso than Kinzo even trusts his own children. Godha, not unlike Natsuhi, tries to integrate himself into this power structure, but unlike Natsuhi, he is not tied down by regret, pain, and a modicum of humanity. He steals what little social capital is afforded to the servants for himself, assigning them much less prestigious tasks. And yet, he ends up destroyed in the same machinery of power he tried to kiss up to, being one of the first to die. Kumasawa withdraws herself from difficult labour, and tells stories and lies and uses a semblance of a jester’s freedom to protect the young servants as best as she can. Sayo freezes in inaction and despair. And Kanon, the youngest, reacts ultimately in an outburst of righteous anger. One must note the degree of violence of class that is enacted upon mere children. In an act veiled in the narrative of philanthropy, Kinzo recruits little children from orphanages to work at the household. This is praised as a chance for them to make money, and to raise in social status. In reality, Kanon’s introduction, in which he fails at performing incredibly hard labour in the garden, shows that Kinzo employs child labour to upkeep his machinery of family as enshrined by the building of the mansion. Once again, violence is exerted upon children to force them into a new generation of this cycle.
The mansion itself is a symbol that can be read in multiple ways, two of which are yet to follow; but it is a very evident expression of power. The ability to buy the rights to an entire island and build a massive mansion complex on it, one large enough to fit a miniature version of itself – Kinzo’s study being called a mansion inside a mansion at some point – is of course an expression of class. Elaborate rooms in the upper floors assigned to be only walked by the high and mighty, and the utilities assigned down below to be only visited by the servants – the structure of the mansion uses its walls to create and reinforce borders and delineations between the classes. These borders only fall, servants walking main rooms and the rich seeing the utilities up close, when Rokkenjima’s violence becomes unable to be narrated away as actual blood and gore runs through its halls.
A potentially supernatural murder series inside a western style mansion could be read as a marker of genre, even – but Umineko Ep1 resists strict allegiance to a singular genre. It toys with the elements of Gothic horror – of which the mansion as a stage and ordering device is a central one – but also transcends it. The origins of Gothic horror in the late 19th century, from what little I know about literary history, do treat their servants as actually nothing more than furniture, barely mentioned if all, not counted as human. Umineko’s supposed furniture cries, curses, bleeds, resists, gives in, dreams of love, stands together and aside. Umineko’s servants navigate class and agency, and that navigation takes centre stage multiple times, their inability to throw their own humanity and compassion away underlining and inverting the parents’ demand to ignore notions of compassion and humanity. But the mansion, particularly its position on an island otherwise uninhabited by humans, takes on multiple roles at once.
2.3 Pecunia non olet: Krauss, resource extraction, ecology, and the storm
The mansion and its surrounding area are an exception to the typical structure of Rokkenjima. Rokkenjima is densely inhabited and brimming with life, but not of the human variety. It is marked by a dense forest, and its cliffs are home to the black-tailed gulls who mark the text’s title – they are the Umineko, a common seabird found across many Pacific coasts, particularly in East Asia. The absence of their distinctive cry upon the visitor’s arrival on the island is remarked upon in the text, and it is one of the many early indicators of the impending tempest that entraps the island for two days. As the gulls notice changes to the wind patterns, humidity, and air pressure, they instinctually withdraw to safer locations to sit out the storm. Once they cry again, the storm has passed.
The mundane black-tailed gulls are in several ways a counterpart and mirror to the seemingly majestic one-winged eagle. Whereas the gulls have (probably) existed on Rokkenjima since its distinct geo-ecological formation as an island, the one-winged eagle specifically as the symbol of the Ushiromiya family has rested on Rokkenjima only since Kinzo manoeuvred himself into de-facto legal possession of the island. As Battler remarks at some point:
“Buying an entire island is not something that you can ordinarily do today. However, Grandfather was clever. He contacted the GHQ and applied for the establishment of a marine resource base. He acquired this island as a business property, then tossed that project aside and claimed it as his own plot of land. [...] Later, Tokyo made difficulties by telling Kinzo to return the land, but the pushy GHQ intervened. Grandfather, with considerable skill and good luck, managed to weather the stormy seas of that period, obtaining a vast fortune and his own island. [...] A mansion was built on the island soon after. [...] Grandfather, with his love of the Western style, made this once uninhabited island a canvas upon which he could realize his dreams to his heart’s content. He now had the Western mansion of his dreams, overflowing with emotion and atmosphere, and a beautiful garden featuring all sorts of roses. And he had a private beach where nobody other than himself would ever be permitted to leave a footprint.”
There is a lot – a lot – going on this passage, and I will come back to it in section 2.4, but for now, there is one focus point: The island is described by Battler as having been previously uninhabited. This draws, at minimum, a line in which a distinct human presence is conflated with the state of being uninhabited. Rokkenjima, before Kinzo’s arrival, so the narrative spun by Battler, exists as a social and ecological terra nullius, this “empty canvas”, into which Kinzo inscribed his personal vision. This passage continually reaffirms the notion that land can be viewed through the lens of ownership – which far from a neutral idea.
By turning the land into something that can be “obtained”, “bought”, and “claimed” by a singular individual, its ecology is exposed to the logics of neoliberalism. And, indeed, Kinzo’s eldest, the designated heir to the financial empire, Krauss, doubles down on this process. The guest house is a symbol of Krauss trying to extract monetary value from the idea of land ownership: He plans on turning the island into a vacation resort for well-paying customers. As Rudolf comments on Krauss’ plan:
“You were brilliant when you saw that using this island only as a place to live was a waste. I think it was a pretty good plan to turn it into a resort that could use the prospect of marine sports, fishing, honeymoons and the like to attract customers. If I were the oldest son, I’m sure I’d have strained my brain looking for a way to make profit off this island.”
Later, Rudolf adds:
“I’ll bet you want to liquidate but can’t. After all, there’s no reason for anyone to buy such an extravagant hotel on an isolated, empty island without any established sightseeing routes.”
An island existing on its own, as an ecologically closed system by itself, is an impossibility under capitalism. Value must be extracted from everything, even the fact of land and ecology itself, else, it is, as Kinzo’s children seem to unanimously agree, a “waste”. Rokkenjima, so full with dense forestry and filled to the brink with life is “empty” because humans cannot make more money out of it. Establishing sightseeing routes, cutting through the ecology to maximize human access – and human profit – to and from it, is the only way not to “waste” it. The black-tailed gull is not granted any meaningful connection or presence on the island. And yet, on the morning of the 6th of October, the skies clear, and the black-tailed gulls cry again, alive and present on the island, whereas those who previously so proudly wore the one-winged eagle lie slaughtered into piles of blood and gore across the mansion and garden.
Kinzo’s fortune – not coincidentally – is maintained through having invested his money during the Fifties into the iron and steel industry, key actors in material resource extraction and environmental devastation, also given the connection of the steel and coal industries. The influence the economic system has on the ecology is marked by resource extraction. When it is a tropical thunderstorm that entraps the Ushiromiya family on this island it previously called its possession, forcing everyone to meet their violent demise, there is a certain comedic catharsis to it – thunderstorms, their increasing likelihood and extremeness, are a direct result of the economic mechanisms that marked the Ushiromiya ascension to power. For all their money, the Ushiromiyas cannot escape the storm. By exploiting nature they rise, by being unable to control such a large natural event they fall.
The theme of the Ushiromiyas’ fall repeats in the ecology, not only being found in the fauna but also in the flora. The rose garden is part of Krauss’ “development” of the land as well as Kinzo’s self-inscription onto the island. It is a model of making sense of nature – whereas the Ushiromiyas describe the forest of Rokkenjima as uninviting, dark, and imposing, the rose garden is a source of respite, admiration, and a stage upon which their control is played out. But the garden is far from a fitting presence on the island – it is noted multiple times that the yearly thunderstorms devastate the garden, leading to it requiring major repair and replanting every time. Rokkenjima is not a natural habitat for roses – and yet, as a mark of pride and possession of nature, it has to be repeatedly reinstated on it. And yet, after the storm passes, the trees of Rokkenjima still stand, whereas the roses of the Ushiromiyas have been scattered and largely destroyed. It is just as fitting to underline the Ushiromiyas’ relationship to the ecology around them that Maria’s concern for the well-being of a singular rose – an entirely positive process in which two organisms interact in a caring and gentle way – is seen as childish and absurd, whereas establishing a rose garden on Rokkenjima in the first place is seen as logical and meaningful.
Turning from the text to the real world, there is an actual and vast touristic network spanning the Izu islands. There is reason to assume that Krauss’ plans might have been fruitful if it were not for his face being separated from the rest of his body. Then again, the Izu islands also feature a long history of hotel ruins and closed tourist resorts – a very interesting example being the Hachijō-jima Royal Hotel, a project very similar to Krauss’, just some decades prior. Also featuring a sizable hotel complex in the Western style, it is now an abandoned ruin, having closed in 2006 (see Lowe, 2016). More importantly, the Japanese government used to advertise this hotel as the “Hawaii [sic!] of Japan”, a marketing pitch that, according to David Lowe, saw success at the time (2016). Let us put a pin on the mobilization of an image of Hawai’i by Japanese government actors, and turn from the branches of this rotten family tree to its roots and finally fire Chekhov's Winchester M1894.
2.4 How to get away with fascism: Kinzo, imperialism, occultism, cowboys, the nonexistent philosopher’s stone, and (hi)storytelling
This reading of the Ushiromiya family so far has purposefully taken individual members to underline larger system, but of course, this choosing-of-focus is an artificial fragmentation. Eva’s ambition overlaps with Krauss’ neoliberalism. Rudolf’s misogyny overlaps with Eva’s attempts to push Natsuhi down. Rosa’s explicit violence against Maria overlaps with Eva’s implicit violence against George. I cherry-picked aspects of their violence that seemed to stick out as an illustration, but they all orbit around the same centre of gravity, the source of it all: Kinzo.
Multiple times in Ep1, the Ushiromiya family history gets narrated, specifically, surrounding Kinzo’s financial decisions. Every time, the story starts at the Great Kantō Earthquake of 1923[xvi], and ends around 1950, with the start of the Korean War. During the earthquake, the family is said to have lost their means of production, having been industrialists beforehand, and having lost several members, leading to Kinzo’s unlikely ascension to the head of the family. Kinzo is said to have acquired some starter capital in the form of a massive amount of gold before 1950, very early going all in on some form of Korean War bonds, being called Korean War Demands in the text. Kinzo is in these descriptions universally praised for his cunning, willingness to take risks, cooperation with the West, and seemingly inhuman foresight. Let’s reexamine this story again: A Japanese former industrialist rebuilds his family’s fortune between 1923 and roughly 1950, by acquiring gold of mysterious origins in between that timeframe. In the text, the adults speculate that Beatrice might have been a mysterious widowed financier willing to support Kinzo, whereas Maria insists that Beatrice used black magic – the philosopher’s stone, specifically – to create gold out of nothing. But this story of the family fortune is painfully familiar to me as a historian capable of speaking and reading German. Now, class, can anyone tell me what might have happened in these less than three decades that a sufficiently violent man could have used to make a small fortune out of nothing?
When I commented in the Discord chat that I use to ramble about Umineko on exactly that fact after the first time the financial history of the family was narrated, and called Kinzo a fascist, Ozaawa confirmed my conclusion. The Ushiromiya family gold – the source of it all, Kinzo’s great legacy – stems from fascist sources. The mysteriously lacking narration of the company history for the Thirties and Forties aside, there is another factor to consider to point towards this conclusion as early as the middle point of Ep1. When Krauss shows Natsuhi an actual bar of the family’s gold reserves, Natsuhi notices the absence of a note of the forge/bank that is customary for high-quality gold bars. All that the gold bars show is a one-winged eagle. Now, of course you can think of the philosopher’s stone all you want, and deliberate how gold bars created from magic might look – but unmarked gold acquired in the Thirties and Forties could be explained by much less magical origins. The eagle itself is a symbol mobilized by many fascists the world over – its role as a symbol for the Ushiromiya family hints further towards the origins of that fortune.
The supposed mystery of the gold’s origin only becomes less mysterious when considering what means of gaining wealth are fully accepted as legitimate parts of the family history. The Korean War Demands – some way of profiting of the Korean War – are seen as a masterful stroke by Kinzo. That the Korean War was an incredibly bloody proxy war between the US-American and Soviet Empires, one fought with a land and population as collateral that had been violently occupied by Imperial Japan for decades prior, makes no difference. Kinzo’s war profiteering in 1950 is a socially acceptable form of imperialism, whereas the source of the gold is not. That Kinzo simply changed which imperialists to support between 1940 and 1950 does not change that he is profiteering of it in some capacity or another. His supposed cunning as a businessman is nothing more than a keen understanding of which empire will win and lose in which conflict combined with a willingness to turn the blood spilled by imperialism into gold.
Speaking of spilling blood, the murders of Rokkenjima are, as elaborated in the introduction, called “the demon’s roulette” in the text on multiple occasions, referring to some obscure black magic ritual. Magic and the occult are, so it is said by several people at multiple times in the text, bound by the logic of miracles. Kinzo explains it as such to Kanon:
“In other words, magic is a game. It is not the case that the one who performs the best becomes the victor. The victor performs the best because he has been granted magic. [...] Of course. I made it difficult. ...But you must try to solve it as well. That will form the seed that summons the miracle of my magic. If every one attempts it and everyone fails, that will be that. However, if the miracles come together and give birth to magical power, it will happen! [...] That is why you must attempt it too. Everyone must attempt it. And in so doing, they will give strength to my magic!! Do you understand?!”
Kinzo’s magic trick requires unfaltering belief in the riddle of the epitaph. Everyone, no matter of which background, can solve the riddle of the epitaph, a riddle that promises those who solve it wealth in the form of gold, and everyone must attempt to do so. The neoliberal credo is that everyone must use their own cunning and skill to strive for wealth, and that everyone can ascend to wealth when they are cunning enough. The demon’s roulette, as a pars pro toto for black magic and the occult, operates noticeably in parallel to the logics of capitalism. The occult as explained by Kinzo, in this reading of Ep1, therefore becomes a mirror to imperialist capitalism – capable of withdrawing it from the narratives that cloak it and obscure its violence, the demon’s roulette embodies and demonstrates the violence necessary to operate imperialist capitalism. It is easy for the characters to think of the gold as a distant, clean commodity and bargaining chip. It is easy for me to describe that the text alludes to the origins of the gold in fascism and imperialism. But when Battler breaks down in tears at the sight of his parent’s disfigured and defaced corpses, when the blood and gore of everyone mixes so much that class distinctions break down just as much as the bodies, when the eldest and most powerful man and the youngest, abused servant both lie in death and dead in the same room, the demon’s roulette unveils what stands behind the Ushiromiya wealth: blood. Rudolf’s negotiation with Krauss features the only mention of roulette in the text that I noticed that is not the demon’s roulette:
“The iron rule of the money roulette is that you bet against the loser.”
The demon’s roulette is the money roulette. Capitalism and imperialism operate like the occult in the embedded narrative of Ep1 does, just with one being more socially accepted than the other. Just as the violence of the occult fails and falls apart when people’s belief in it shakes, so does capitalism.
In the end, the family tree planted by Kinzo bears the fruits he has ultimately sown. Is not Eva as manipulative and emotionally violent as him? Does his obsession with Beatrice not speak the same language as Rudolf’s misogyny? Is Krauss’ money-making not just as random and based on chance as his? Does Rosa not beat her own child like he beat his? When Kinzo laments how horrible his children are, is he clairvoyant enough for that to be self-hatred? The violence that marks the Ushiromiya family stems from imperialism and fascism and capitalism in all their entanglements, made manifest in the structure of the family and mansion.
A perfect illustration of this is the symbol of the Winchester M1894. It is a gun featured in western Westerns, a motive that keeps reappearing. Being the actual gun used in filming some Western[xvii], Kinzo had it bought and retrofitted to his liking. Kinzo, so is reaffirmed many, many times in the text, is obsessed with the West. His ability to schmooze up to the GHQ is just one example of this. Kinzo, the Japanese imperialist, being close to the West, is yet another pars pro toto; Japanese imperialism has historically grown in close proximity to Western imperialism. With the end of the Shogunate and the beginning of the Meiji restoration, the idea of industrialization and restructuring of society after the western model laid the ideological groundwork for building imperial Japan; particularly, the contact point of the Pacific brought Japan into connection with the United States, extending its Empire by the annexation of the Kingdom of Hawai’i. That Japanese government agents used the idea of the US tourist industry in Hawai’i – an inextricable part of imperial control and domination – to promote a hotel resort on an actual island close to where Rokkenjima would be in the real world, ties Krauss’ island development project back to Kinzo and Kinzo’s obsession with the West. He has a western-style mansion, a western-style rose garden, his children have western-style names, and he has a western-style Western rifle. The idea of the cowboy in the genre of the Western is one inherently tied to US myths of westward expansion and manifest destiny. If the rifle then symbolizes the cowboy, and one questions the context of the genre where the cowboy is the protagonist, it becomes a tool of violent colonial inscription. Rokkenjima becomes Kinzo’s colonial playground, one which he violently claims and violently maintains while wielding the cowboy’s gun, one modified to his liking. It is western imperialism with a small twist, retrofitted for the logics and specific situation at play in Rokkenjima. Natsuhi dies, claiming the rifle and the title of head of the family, shot by the instrument of imperialism she could, in the end, not wield properly.
When Battler wishes for the seagulls to cry, he envisions the police showing up at that point, solving the murders logically, restoring sense and meaning and order as it was before. But the murders unsettle the dynamics of the Ushiromiya family, in a way that cannot be undone. They reveal the deeper violence at play, embody that blood and gore which was previously obscured. One can doubt that the police can restore the status quo that Battler dreams of, as the state, of which the police are central actors and agents, is linked to the very imperialism that sits at the core of these murders. And indeed, as the epilogue of the embedded narrative reveals, the police do not do anything of meaning in reaction to the murders. Ep1, in this reading, becomes a story of the violence of imperialist capitalism crashing down on the family it once uplifted. All of this is a nice reading, but that is a story that does not necessitate magic being real. This reading is missing one integral piece: Beatrice, the sexy, sexy ominous demonic presence of the horror story that is Ep1, exists.
3. On Divine Comedies and Worldly Tragedies, or: how did I almost miss this
So far, I have not really said anything that is not obvious from even a superficial reading of Ep1. It does not take much attention to figure out that the Ushiromiya family is deeply fucked up. It does not take much attention to figure out that Kinzo is a disturbingly violent man. The entire second segment of this essay is simply a close reading of something that sits at the surface of Umineko Ep1. Sure, I did that little trick of understanding early on that there is imperialism and fascism at play here – but I can be far from the only one who picked up on that as soon as it was placed down in the text. This essay, for the longest time, was just that second segment, that close reading of the family violence – and I wondered if that even was enough to publish it. It was missing something grander, some reason to give me a seat at the table of those scholars who understand Umineko from early on. Missing that element, that link to make a more complex reading of Ep1 work, I simply gave up. I started Episode 2, broken-hearted, and followed it until it is implied early on that George will be sent into an arranged marriage. And all along I was making jokes about Umineko to the admin of the Discord server where I ramble about Umineko – she has not read the story, but enjoys my commentary on it. I made a joke about the frame narratives being nestled, like wooden dolls – and then I wanted to double down on that joke by referencing the well-known movie Shrek (2001) by saying something along the lines of “or like ogres and onions”. But I felt I needed some other joke, something a bit more weird than a simple and well-known Shrek meme, to mask my devastation at being unable to solve Ep1. And so I said: “Or like the layers of hell in the Divine Comedy. Didn't Beatrice call herself a guide through purgatory in the tea party? Is she the Virgil to my Dante?[xviii]”. The exact line I am referencing is spoken by Beatrice, when explaining the murders of Eva and Hideyoshi in the first-order frame narrative:
“Come, arise, children. I am the guide of Purgatory. Forgive the deadly sins and hold the Seven Stakes.”
A sentence I had glossed over when I first read the tea party, one seemingly inconspicuous. But it had lodged itself into my brain and become the basis of aforementioned joke. My joke, made simply because I was momentarily tired of Shrek memes, had been closer to the truth of it all than I could have ever imagined. It took me twenty-nine minutes to see it, to realize it. I came back to the Discord chat, typing in all caps. Beatrice exists. Boy, does Beatrice ever exist. Beatrice is (not only) the guide of Purgatory. Beatrice is the guide of Heaven. Beatrice is a literary figure that has existed for seven centuries.
3.1 14th century Italian poetry, in your Umineko? It’s more likely than you think
The Divine Comedy, originally the Commedia and then the Divina Commedia, is a long poetic text by exiled and grumpy Florentine author Durante Alighieri, better known as Dante Alighieri, written in the early 14th century. Its narrative is divided into three parts. In Inferno, the Dante of the narrative descends through the centre of the Earth. He receives help in navigating Hell, which is located in the centre of the Earth, by the Roman poet Virgil, who knows the rules and dangers of the nine circles and centre of Hell. Each circle of hell features a specific punishment for sinners. In Purgatorio, Virgil and Dante emerge on the other side of the Earth onto a sole, circular island in the pacific. This island, marked by a mountain, is also subdivided into nine rings and one centre. Souls who wish to enter heaven have to ascend through the rings up the mountain to find themselves in the Garden of Eden atop the mountain. Here, Dante meets a woman named Beatrice. In Paradiso, Beatrice guides Dante through the celestial heavens. The heavens are inhabited by the most virtuous of souls and divine beings. They are also subdivided into nine parts, plus God in their outermost layer. Upon Dante reaching God under Beatrice’s guidance, the story ends, as Dante is imbued with fundamental understanding of God.
Under the eurocentric lens of western academia, the Divine Comedy is considered to stand among the most important works of world literature. It is also considered one of the, if not the foremost entries into the Italian literary canon[xix]. It, that much is certain, played an important role in formalizing the Italian language, and had introduced a very detailed description of hell and demons, something unprecedented given that western church canon[xx] had avoided giving clear descriptions of hell. The tropes established in the Divine Comedy regarding the structure and functioning of hell have received an incredibly extensive reception over the centuries, being integral pieces of the collective imagining of hell and demons, and referenced in much contemporary media. I hold very little knowledge of contemporary Japanese media, but I know that the Devil May Cry franchise has been very successful and in some connection to the Divine Comedy since 2001.
The Divine Comedy features a very extensive range of appearing figures, symbols, metaphors, and narrative systems. From real life figures living and dead to themes spanning such questions as the implications of a round Earth (see Schlingen 2021, p. 386) and human bodiedness in connection to human emotions (see Howie 2021), there is a lot one can take out of the Divine Comedy. And indeed, one can read Umineko Ep1 alongside – or perhaps against – the Divine Comedy. The opening slide of the first-order frame narrative reveals that it is set in Umineko’s Purgatorio – whatever that may mean. This setting of the tea party, and the sentence in which Beatrice describes herself as the guide of Purgatory, are direct hints at a connection between the Divine Comedy and Umineko Ep1. And yet, the most meaningful connection between the Divine Comedy and Umineko Ep1 is much more simple. As Lady Bernkastel explains to the player-reader in the second-order frame narrative:
“First of all, about that girl. She does have the name Beatrice, but that doesn’t necessarily mean she is ‘one individual woman’.”
That begs the question: How many individual women is Beatrice, exactly?
3.2 Into the Beatriceverse
Beatrice Portinari is a Florentine woman that was married to a man named Simone de Bardi in 1287 (see Lewis 2001, p. 72). She died in the summer of 1290 (see Mazotta 2000, p. 18). Her father, a banker named Folco Portinari, died on the 31st of December 1289 (see Lewis 2001, p. 77). That much is something we can say with relative certainty. Church recordings in central Italy were thorough when it came to deaths, births, and marriages. Anything else we know about Beatrice Portinari – well, it is complicated. The most extensive account of Beatrice Portinari’s life was written by Dante Alighieri in the 1290s, the Vita Nuova. Dante Alighieri reports extensively on his lifelong obsession with Beatrice Portinari, a woman he spoke to merely a handful of times, at least to his own accord (regarding the number of direct interactions see Lewis 2001). If we trust Dante to tell the truth, they were about the same age, setting her birth at around 1265, and indicating that she was 25 at the time of her death. Dante’s infatuation with Beatrice Portinari lead him to engineer social situations in which he might be able to see her. The Vita Nuova holds little information on anything Beatrice Portinari ever did out her own accord. We know nothing reliable about her interests, likes and dislikes, or emotions. Most what we know about her life is delivered to us through the eyes and words of a man who held a deeply one-sided obsession with her. If the Vita Nuova was simply the ramblings of an obsessed, grieving poet, Beatrice Portinari might have been drifted out of our collective memory.
But the Vita Nuova is not the only time Dante wrote (about) Beatrice Portinari. Divine Comedy Beatrice is one of the central figures of that poetic work, likely a direct reference to the real-life Beatrice Portinari. Divine Comedy Beatrice is the one who starts the events of the story; Virgil appears before Dante in the name of Divine Comedy Beatrice, who wishes to see Divine Comedy Dante guided to the heavens. It is in constantly referencing Divine Comedy Beatrice that Divine Comedy Dante keeps a focus through hell and purgatory. Divine Comedy Beatrice takes on the role of an angelic being guiding Divine Comedy Dante to God (see Kirkpatrick 1990, p. 101), and performs “the priestly roles of confessor, teacher, interpreter of Scripture, and spiritual guide” (Waller 2021, p. 702). These two Beatrices – Beatrice Portinari and Divine Comedy Beatrice – stand in a complicated relationship. Feminist critiques of Dante taking possession of the memory of Beatrice Portinari and puppeteering it for his own purposes have existed for a long time. To cite a longer passage from Kirkpatrick 1990, p. 101:
“Beatrice has been cited more than once as evidence that the selflessness that the lover attributes to an ideal lady is not so much a manifestation of spiritual nobility as a covert sentence of death. [...] Whether as the selfless object of courtly love or as an angelic being, the lady dies insofar as the historical woman becomes a cipher on which the patriarchal will of the writer - be he courtly poet or God - can exert itself.”
We do not know what Beatrice Portinari thinks of the long poetic text written after her death by a man she barely knew in which he wields the image of her. What we know is that centuries after her death, Dante’s obsession with her is still idealized. His writings are regarded by many as the height of romantic poetry, and allusions to Divine Comedy Beatrice run throughout western literature[xxi]. I agree with the point Kirkpatrick is making, but would maybe extend it by the semantic question if we are faced with a “death sentence” of the historical woman or her unwilling entrapment in a “literary immortality” that robs her of all agency and personhood. In the end, though, both these terms describe the same act of violence.
These two Beatrices, as well as the relationship between the two, are certainly figures at play in Umineko Ep1. We can count the extratextual number of Beatrices as two, which leaves us with the question of how many Beatrices we are dealing with in Umineko Ep1. There is a woman named Beatrice which Kinzo met sometime in the Thirties or Forties, a woman that died at some point in the past, as Genji explains when the survivors barricade themselves in Kinzo’s study. I would like to title this Beatrice “Umineko’s Historical Beatrice” for the time being. We know little about Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, just as we know little about Beatrice Portinari. Kinzo’s entanglement in Japanese imperialism and with the axis powers would certainly leave him with a plethora of opportunities to exert totalizing power over quite a number of women. Then, there is “Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice”. Kinzo weaves a narrative around Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, just like Dante did around Beatrice Portinari. The resulting woman, Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice, is one he mobilizes as an excuse for his obsession with the occult. It is difficult to tell at this point if Kinzo made that mysterious contract with Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, or if the contract is part of the narrative of Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice. Then, there is Golden Witch Beatrice – a myth, whispered by the servants and Maria in awe, fear, and distant hope for liberation, a myth of a second master of Rokkenjima, one who assumes control when Kinzo sleeps, but also haunts the mansion in perhaps some level of agency. There is the Mystery Financier Beatrice, an explanation the adults and Battler come up with for the letters and for Kinzo’s gold and for the murders, a very human, if hypothetical woman – Mystery Financier Beatrice is closely related to Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice, perhaps by intention of Kinzo. Both Mystery Financier Beatrice and Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice are removed from any actual agency or self-hood, they are stories told and speculated upon. Then, there is Arisen Beatrice – a woman, in the flesh, who we only catch a glimpse of at the end of the embedded narrative, who greets the surviving children, primarily Maria. And lastly, there is Eternal Witch Beatrice, the witch who we see in the second-order frame narrative and, as I assume, the same Beatrice we encounter in the first-order frame narrative.
Now, take this list with a grain of salt. These Beatrices do overlap and may even sometimes be the same person. There is plenty reason to assume that Arisen Beatrice and Eternal Witch Beatrice are the same, as much as there is plenty reason to assume that there is a strong overlap between Golden Witch Beatrice and Eternal Witch Beatrice. Perhaps Arisen Beatrice and Umineko’s Historical Beatrice somehow are the same figure – Lady Bernkastel mentions that she was mortal once, implying that one can ascend to being a witch from a state of mortality. But, ultimately, I mark these Beatrices as distinct because just as much as Beatrice Portinari and Divine Comedy Beatrice, they have the capacity to stand in relationship to one another, and they have vastly different agencies, roles, and limitations when compared to each other. Every single one of these Beatrices is commanded by different forces, used and presented and (figuratively and literally) painted by different people, sometimes by her own, sometimes by individual others, sometimes by collective others. Close attention needs to be paid at how these eight-ish Beatrices, two extratextual and six-ish intratextual, are played out in very different ways. And, as I theorize is integral for understanding Umineko Ep1 – the very relationship between Beatrice Portinari and Divine Comedy Beatrice mirrors the relationship between Umineko’s Historical Beatrice and Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice intentionally. When the survivors retreat to the study, and Genji recounts the story of Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice, the first reaction that the listeners have is understanding and empathy for Kinzo. It is only when realizing that the murders happening around them are closely tied to Kinzo’s obsession with and hope for a resurrection of Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice that they realize that Kinzo had gone too far. In Kinzo, so my reading, Umineko Ep1 satirizes Dante Alighieri. Eternal Witch Beatrice lashing out can be read as a symbolic act of intertextual retribution for the textual violence and entrapment Beatrice Portinari has suffered, just as much as it could be a retribution for the suffering Umineko’s Historical Beatrice had endured. Umineko, so I further theorize, can be read as an inverse Divine Comedy – a Worldly Tragedy, if you will. Let me further illustrate this point by turning our attention to round islands in the Pacific.
3.3 Rokkenjima is other people: Reverse-engineering hell and the omnipresence of guides
Rokkenjima is an interesting stage for the violence of Ep1 to play out. As elaborated in sections 2.3 and 2.4, Rokkenjima can be read through an ecocritical and postcolonial lens, as an ecosystem upon which Krauss exerts capitalist logics and as a space which Kinzo uses as a miniature colony. But reading Umineko as a critical parody of the Divine Comedy, we also gain access to another understanding of Rokkenjima; as a twisted mixture of hell and purgatory. Hell and purgatory in the Divine Comedy have different, more specifically opposite, spatial structures. Divine Comedy Dante goes through hell by descending, going down each ring, narrower and lower than the one before. Reversely, he ascends purgatory by going up each ring, narrower and higher up than the one before, before reaching Eden – and Divine Comedy Beatrice – at the top. Such spatial trajectories also get mentioned in Umineko Ep1, but ultimately and immediately deconstructed. When the visitors arrive on the island, Battler comments upon the sloping path one has to take up from the landing pier to the mansion complex:
“A serpentine, twisting path led through a dim forest. It ran a bit uphill. I’d guess the path was made all twisty so the slope wouldn’t seem too steep, but personally, I’d have been happier if they’d had the guts to make some stairs in a straight line ......No doubt they made the path twist on purpose, to put on airs of distance and importance...”
One might read this path guests of Rokkenjima ascend through as part of the microcolonial architecture that is such an integral part of Kinzo’s and Krauss’ laying-claim to the island. One might also read Battler’s alternative as an expression of that same architectural hubris, as a disregard for the geological and structural reality of that stretch of Rokkenjima, because it remains to be questioned how intrusive a set of straight stairs[xxii] might have been in the context of the local landscape. But this spatiality may also be read in conjunction with the very first lines of Inferno:
“In the middle of the journey of our life, I came to myself in a dark wood, for the straight way was lost.” (Alighieri/Turner 1320/1996, p. 27)
This entry of Divine Comedy Dante towards his journey into hell mirrors Battler’s monologue in a couple of ways. Whereas the difficulty of the paths in the Divine Comedy represent the theological difficulty of salvation, difficulties through which Divine Comedy Dante has to be lead by Divine Comedy Beatrice as the representation of perfected christian belief, Rokkenjima’s meandering paths, at least for now, represent both a nuisance to the characters and their unknowing physically ascent into a hell that will unfold around them soon. Whereas at the top of the winding path in Purgatorio, the Garden Eden awaits with Divine Comedy Beatrice ready to appear and take Divine Comedy Dante to the heavens, at top of the winding path in Umineko Ep1, the rose garden awaits with Golden Witch Beatrice ready to appear and murder everyone.
But this inversion and reconfiguration of spatiality is more than a singular instance of a mirror and parody of the Divine Comedy. Whereas Divine Comedy Dante has Virgil and then Divine Comedy Beatrice to explain to him all the minutiae and idiosyncrasies that govern the realms of the Divine Comedy, there is a distinct lack of a singular, final, authoritative voice explaining the idiosyncrasies of Umineko Ep1. This is not because guidance is absent in Umineko Ep1, rather the opposite: The omnipresence of contradicting, incomplete, and biased guides is what makes Umineko Ep1 so impassable on every narrative and metanarrative level. Battler seemingly guides the play-reader through most of the embedded narrative, but how much competence can one expect from a guide that uses the first moment of introspection the narrative provides to him to whine about how difficult it is to be a child born into unfathomable intergenerational wealth? What ability does Battler have to introduce us to the women of the embedded narrative when the first thing he does on multiple occasions is to joke about harassing them or come very close to actually doing it? When the Ushiromiya adults take over with the narration, how trustworthy are they? Can we believe the ultrarich capitalist to give us a proper account of how the servant’s social space functions? Can we trust the violent imperialist Kinzo to properly explain the functionings and logics of the occult to us? Umineko Ep1 is littered with instances of people speaking for other people, trying to explain what the true meaning of someone else’s words and actions and emotions is. The closest the player-reader comes to gaining a guide through Umineko Ep1 is only after having traversed the story, when Lady Bernkastel gently removes the fourth wall, turns it around, and fixes it in place again. But according to her own report, Lady Bernkastel uses the player-reader as a piece in a game to deal with her boredom; a move made out of pity and amusement. Is she the ultimate authoritative voice which may guide the player-reader through the narrative?
From the constant discussions of murder mystery novels in the embedded narrative, to the murder victims discussing the implications their deaths have on the genre in the first-order frame narrative, to the outright obliteration of the fourth wall in the second-order frame narrative: Umineko Ep1 brims with metanarrative commentary. By presenting us with a plethora of guides through this strange hell-purgatory of Rokkenjima and making each of them untrustworthy in the same moment, Umineko Ep1 engages in a permanent suspension of suspension of disbelief. The player-reader is supposed to engage with Umineko as a fictionalized narrative while remaining very aware that it functions as such. If my reading is to stand any ground, this is where the concept and figure of the witch begins to unravel.
3.4 Darkness, witches, angels, and the absence of a god: How to decipher Golden/Eternal Witch Beatrice as an anti-Beatrice
Reading Umineko as a parody and commentary on the Divine Comedy means that a lot of the motives and symbols of Umineko become very legible from the start, courtesy of the extensive symbolic lexicon employed by the Divine Comedy.Unfortunately, one of the most important symbolic figures of Umineko, the Witch, has no meaningful direct equivalent in the Divine Comedy. If we approach the witches in Umineko Ep1, we gain pitifully little information on what they are. The dramatis personae of the second-order frame narrative informs the player-reader when trying to set Eternal Witch Beatrice’s entry to dead that she can theoretically be destroyed, but not by means accessible to the player-reader. One of Lady Bernkastel’s lines implies that witches start off mortal but ascend to witchhood at some point and then are immortal. When Lady Bernkastel talks about what Eternal Witch Beatrice is, she says the following:
“Get what I mean? In other words, she’s not some Human. Her existence is a personification of the rules of this world. To beat her, you have to expose the rules of this world and unravel them.”
The key to witchhood, then, is closely linked with understanding the truth(s) of Umineko. Witches are also incapable of being harmed by material means (see Kanon’s and Natsuhi’s failed attempts to lash out at Golden Witch/Arisen Beatrice). They exist in a sort of immaterial, half-immortal state, in which they are closely linked to immaterial ideas and truth(s). You know which group of figures in the Divine Comedy exists in a sort of immaterial, half-immortal state, in which they are closely linked to immaterial ideas and truth? That’s right, you have read the title of this subsection: Angels. Alison Cornish explains the theological nature of angels, as interpreted by Dante and introduced into the Divine Comedy, as follows:
“Angels differ essentially from human beings in that they are separated substances—separated, that is, from matter [...] This separated state makes them purer and better receptors of intellectual substance. They are “intelligences” who feed on intellectual fare, namely, truth, and what Dante repeatedly calls the “bread of angels,” to which they have direct access but to which the philosophically inclined may also aspire” (p. 38)
I am not saying that witchhood in Umineko translates one-to-one into the notion of the angelic in the Divine Comedy. But there is no denying that the two direct allusions to Dante that Ryukishi07 placed in the first-order frame narrative are meant to create meaning, and the criticism of Dante’s obsession with Beatrice Portinari through Kinzo’s obsession with Umineko’s Historical Beatrice cannot be a coincidental reading. I also know from being slightly spoiled by Ozaawa that there will be a character named Virgilia later on, and I look forward to seeing what Ryukishi07 does with that character. My point in all of this is that those two texts clearly enter into a dialogue, and that dialogue allows me to use established readings of the Divine Comedy to unravel Umineko. Dante’s angels and Ryukishi07’s witches can be seen as entering a dialogue with one another.
Just as Dante places Divine Comedy Beatrice in close proximity to the angelic (see Cornish 2000, p. 37), Kinzo allows for Kinzo’s Portraitized Beatrice to be regarded as being in close proximity to witchcraft. Both Dante’s angels and Ryukishi07’s witches are complex allegorical figures that fulfill many roles and objectives at once. Whereas Divine Comedy Beatrice in her quasi-angelic state is identified with (reflecting) light as the central motive to stand for God (see Cornish 2000, p. 39), Golden Witch/Arisen Beatrice is associated with darkness. Both when she interacts with Kanon and Natsuhi, and when Sayo observes Golden Witch Beatrice way earlier in the story, the Beatrices stand cloaked in darkness to the point that the darkness becomes them, reciprocally personified. Golden Witch Beatrice is said to be the master of Rokkenjima at night, when the island is cloaked in darkness. Divine Comedy Dante can only ascend through purgatory during the day, when God’s light graces the island. If Divine Comedy Beatrice glows bright and is the light as she – like an angel – reflects God and God’s truth, Golden Witch Beatrice commands and laughs from the darkness in the absence of a God, and stands for a much more wordly truth, that of Kinzo’s violence.
Given that Lady Bernkastel tells us that Eternal Witch Beatrice is a personification of the rules of this world, and that this world of Umineko is deeply metanarrative, I propose a very theoretical early reading of what witches are in Umineko: Witches are allegorical representations of the fundamental forces and properties of a narrative. Eternal Witch Beatrice, so the second-order frame narrative, has the power to kill someone eternally, without fail, and yet fail does not exists in the realm of witches. I cannot explain every aspect of what is said in the second-order frame narrative through this reading, but: Let us reexamine the idea of narrative entrapment in immortality/death that has been explained in subsection 3.2 through the examination of the relationship between Beatrice Portinari and Divine Comedy. Is that constant denial of agency by assuming complete control over someone’s memory not a (metaphorical) way of killing someone over and over, given that death can be seen as the greatest possible loss of agency an individual can suffer through? Eternal Witch Beatrice's power, as explained in the second-order frame narrative, is one she has reappropriated from the abuser(s) of her namesake(s), namely, Dante and Kinzo, now wielding it as her own. In that sense, I find it fascinating how the epilogue of the embedded narrative stresses that the murders that have happened on Rokkenjima turn into an urban legend afterwards. The most important legacy the Ushiromiyas leave behind, the thing that they will always be associated with, is the mystery of their deaths that left them a puddle of gore on the grounds of Rokkenjima. Every time this urban legend is repeated again, the deaths repeat, and the Ushiromiyas are denied agency by becoming reduced to a singular aspect of their memory. If we read Eternal Witch Beatrice’s power as such, then the Rokkenjima murders become the ultimate act of retribution against Kinzo, one that forces him into the same fate as he forced upon Umineko’s Historical Beatrice.
We can further examine the figures of Beatrices in Umineko Ep1 through the lens of the Divine Comedy, as some miscellaneous symbols and points also connect. Kinzo wishes for nothing more than to see “Beatrice’s smile” again before he dies, a point he makes clear in the prologue/first scene and constantly repeats. Divine Comedy Dante is constantly reminded of his path to heaven and salvation when thinking about Divine Comedy Beatrice’s smile, and it is this smile she shows him when he arrives at the summit of purgatory (see the commentary in the translation by Turner 1990, p. 558). Divine Comedy Beatrice’s smile becomes a mark of salvation and the path to God. When Kinzo cries and shouts about “Beatrice’s smile”, it becomes a symbol of that absence of a divine presence, and, as he will not see “Beatrice’s smile” again, he does not find salvation, but death. Indeed, Umineko Ep1 seems to mock the christianized logics of punishment and salvation at multiple turns. The stakes that Eternal Witch Beatrice commands are ascribed to demons that stand for sins more or less appropriate for the people killed by the individual stakes.[xxiii] When finding the corpses of his deeply violent, mysogynistic father and the woman that enabled him at many turns, Battler wonders what they had ever done to deserve such a punishment. He repeats later that no one deserves such a fate. And, as Eternal Witch Beatrice makes clear in the first-order frame narrative, the stakes and the forces that wield them are supposed to forgive the sins – by killing the sinners. In this inherent violence, the Rokkenjima murders withdraw from the logics of christian salvation, just as much as Arisen Beatrice denies Kinzo her smile. There is no salvation, only death. Eternal Witch Beatrice does not seek out salvation for the Ushiromiyas (except Maria), she seeks revenge in the form of blood.
Another symbol to decipher is that of the butterflies. Golden Witch Beatrice is said to appear in the form of golden, glistening butterflies. Butterflies indeed appear in the Divine Comedy, namely, in a metaphorical role in the in Purgatorio.
“O proud Christians, woeful wretches, who sick in the mind's vision, place trust in backward steps, do you not see that we are worms born to form the angelic butterfly which flies to justice without shields? How is it that your spirit soars so high, when you are as imperfect insects, like the larva lacking its full formation?” (Alighieri 1320, as translated in Singleton 2019, p. 60-61)
Here, as explained in Turner’s commentary on his translation of Purgatorio, the butterfly is used in its capacity as an analogy for metamorphosis, a literary tradition reaching back to antiquity. More specifically, Turner further explains, it stands for “spiritual change as metamorphosis” (p. 171).[xxiv] It stands as a warning against pride (Singleton 2019, p. 61). In Dante’s usage, the butterfly stands for a yet-to-be-completed angelic spiritual transformation that is hindered by pride. In contrast, one could read the butterflies of Golden/Eternal Witch Beatrice as meaning that she has already undergone a transformation – not towards an angelic state, but towards witchhood, Umineko’s likely answer to Dante’s angels.[xxv] If Golden/Eternal Witch Beatrice is the swarm of butterflies, she has already metamorphosized; moved by a spiteful pride and wrath against the man who harmed Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, she has transformed by a logic completely opposite to that presented in the Divine Comedy. Once again, Umineko’s register of motives opposes its Divine Comedy counterparts in full force.
The last motive that I want to look towards in its interactions with (or rather against) the Divine Comedy is that of the “Golden Land”. In the Divine Comedy, the exact wording of “Golden Land” is never used, but it explicitly leans on the long-standing motive of the “Golden World” – one that is in Dante’s usage intrinsically tied to the idea of political order and stability acting as justice under the Roman Empire, as Robin Kirkpatrick explains (1990, p. 112-113). In other words, the logics of the Divine Comedy entangle ideas of political hierarchies, rule/ruling, spiritual ascension, justice, and Christianity under the concept of the “Golden World”.[xxvi] It is, also remarkably, situated partially on top of the mountain that is purgatory; the Garden Eden being a part and aspect of this concept (compare Kirkpatrick 1990, p. 112). The political order that houses and props up the mansion complex of Rokkenjima, Kinzo’s private and privatized Garden Eden, is completely unsettled and exposed as unjust by the forces that govern Eternal Witch Beatrice’s Golden Land. As Kirkpatrick once again elaborates:
“In canto XXVII of the Purgatorio, Virgil performs a verbal coronation in which Dante is declared to be at last free, upright, and whole, and thus fit to enter the Golden World.” (1990, p. 113)
Character’s aptitude for entering the “Golden Land” in Umineko Ep1 is indeed a topic brought up, but Dante’s equivalent – Kinzo – is made unfit to enter the “Golden Land” by death quite early on. Whereas Dante’s elaborated and detailed “Golden World” is a symbolic stabilization of spiritual and political practice at the time, Umineko Ep1’s is a vague threat and promise at the same time, one that symbolically destabilizes the ideological and political practice on Rokkenjima. In short, the ambiguous and so far not fully explained register of motives, symbols, and ideas surrounding Eternal Witch Beatrice stands as a rejection of Divine Comedy Beatrice and the literary trope Divine Comedy Beatrice became over the centuries.
3.5 Ave Maria: A short tangent on the role of motherhood and Christianity in Umineko Ep1
Not only the figure(s) of Beatrice(s) unravel through a closer reading of Umineko Ep1 alongside the Divine Comedy. If you are like me, you might have wondered early on what is going on not only with so many of the names being western, but also christian in origin, not even mentioning the crosses littering the outfits worn by several of the Ushiromiyas. One example that comes to mind, that unravels rather neatly, is Eva. Eva, the non-anglicized form of Eve, stands as a crude parody Christianity's human progenitor, first ever mother. Eva is the second human, if you so will, that Kinzo “created”, and is marked by a constant wrath for being locked out of first place. Through being the first to prolong the bloodline, she outperforms Natsuhi in the violently misogynistic structure of the family. Just as Eve makes Adam bite the apple, Hideyoshi merely follows Eva’s quest for the gold. In other words, Eva, a woman wielding misogyny against another woman, mirrors the foundational misogynistic trope of Christianity in name and in some of her relations to other characters.
But even more pronounced is the concentration on the concept of motherhood in Maria and her proximity to Beatrice – both in the Divine Comedy and Umineko Ep1. Mary is but the anglicized form of Maria, patron saint of motherhood, and one of the principal divine figures in catholicism. In the Divine Comedy, Divine Comedy Beatrice's closeness to Mary in the celestial rose, the symbolic seat of saints, underscores her exemplary nature as a pious woman and her allegorical role as divine wisdom and divine truth (for an explanation of this more analysis of Divine Comedy Beatrice and the celestial rose, see Singleton 2019, p. 61). In Umineko Ep1, it is Maria's closeness to Golden/Eternal Witch Beatrice that receives thematic meaning, when we read Beatrice as a marker of the worldly absence of the divine, as I have proposed, Maria's proximity to Beatrice means she is closest among all the characters to understanding the truth of the violence at hand. Whereas in catholicism, Mary is a symbol of divine grace in motherhood, Maria is the inverse, a symbol of the worldly pain in daughterhood. Mary nurtures Jesus, Maria is harmed by Rosa. Even the name Rosa reinforces Maria as an inversion of Mary. Roses have a long symbolic tradition in catholicism to refer to Mary, which is the reason a rosary is called a rosary, as the Latin word for rose garden. Which is the place in which the physical violence of Rosa against Maria takes place.
4. Recurrence, (in)justice, punishment, rage, catharsis, and torment through narrative (im)mortality: Trying to estimate the central themes of Umineko via Ep1
All this being said and analyzed, this leaves us with the question that started this essay, the question I directed at Umineko Ep1: What the fuck is going on here? In the introduction, I explained that I am interested in how much of Umineko you can solve within the information presented in Ep1, or as I named it, Umineko’s scholar’s mate. I also said that I am bad at murder mysteries and that I have no idea what is going on in the epitaph. Now, it has been a while since I started writing this essay, almost two months, and in the meantime, I have acquired the Answers Arc of Umineko on steam. And there, I was presented with a sentence that made things particularly interesting; it said something along the lines of “this will answer most of your questions, but you still have to solve the epitaph by yourself”. Now, I do not know if I read this sentence, this spoiler correctly; but to me, it implies that the canon text will never provide a singular, clear answer on what the epitaph riddle means.
The classical murder mystery systematically opens up several questions for the reader/viewer/player to answer, only to answer them all at the end, in an elegant fashion, perhaps to shine light on the clever detective character. Umineko Ep1 withdraws rather openly from the murder mystery genre. The logics by which a murder mystery novel operates are brought up even in the embedded narrative, where characters seem to be mostly oblivious to the fact that they exist within a story. Operating within these logics, something that Battler calls Game Theory in remembrance of a lesson Kyrie once gave him on chess, Battler tries to solve the story of Ep1 by rational means, and fails spectacularly[xxvii]. In the first-order frame narrative, i. e. the tea party, George concedes that magic must be real and at play, and that this story, which he then consciously recognizes as a story, can not be a classical murder mystery novel. Here is the thing: There is violence at play in Umineko Ep1, a lot of it, and they story tasks the player-reader with uncovering and understanding it; but, as I propose, the player-reader is not (entirely) supposed to solve the murders of the 4th and 5th of October 1986. The violence represented in the murder mystery genre is localized, individual; even in the most brutal crime novels, you have a couple dozen victims at best. When the seagulls cry (again), about 18-ish people lay dead in the embedded narrative. So far, this follows that general system of the murder mystery genre. But even with those 18-ish victims are difficult to fully keep apart; the murders happen in stages, people die in small numbers, one or only a handful at a time, and yet the player-reader has trouble following along. The fact that the number of victims alone is difficult to reconstruct points (intentionally, as I suppose in this reading) to the fact that the underlying violence of Umineko Ep1 cannot be represented in the murder mystery genre. Kinzo ascended to his position of head of the family, sole ruler of Rokkenjima, and multimillionaire by participating in imperialist-fascist projects. The estimated number of deaths associated with the Second Sino-Japanese war is around one order of magnitude larger than the number of words in the entirety of Umineko. In other words, listing but the name of every victim structurally connected with the historical violence in Ep1 would exceed the limits of the text itself. The logics of the traditional murder mystery genre (treating death and murder as localized and individual exceptions to a larger sense of peace and order) are fully incapable of adequately representing genocide, a mode of violence in which murder and death become collective, embedded, and structural.
Umineko Ep1 – and by my suggestion, all of Umineko – then becomes a tale of (meta)narrative violence, or how narratives can be mobilized in support and even creation of material, actualized violence. Multiple times, characters puppeteer the narrative of progress; Battler’s answer to the question how the murders might have happened if it were not for magic is to refer to technological progress. Multiple times, characters affirm the narrative that “modern times” are more logical, enlightened, progressed. All this they do while standing on a family fortune built on blood. It is the narrative of progress upon which the neoliberal ideology that builds up the family rests, an excuse, distraction, denial of the true origin of their status. Whereas Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, a woman harmed to no end by Kinzo, exists, the philosopher’s stone does not. The underlying implication of the epitaph is an alibi, a lie, a myth; Kinzo mobilizes the idea of the witch and magic to deny what he has truly done to acquire the gold. Maybe he has bought into his lies so much already that he has partially started to believe them himself.
The clues that the game lays out in the main menu might then be read as much more allegorical than to be taken at face value. The technical specifications of the Winchester M1894, like its fire rate and ammo capacity, might be less relevant to solving Umineko. It seems, at least to me so far, far more relevant to read the Winchester M1894 as a symbol for colonization and colonial inscription. In that, the detailed contents of the epitaph might become irrelevant to solving Umineko, and thus the epitaph has to be regarded as a clue in form of an analogy, an analogy for the lie of neoliberalism that anyone could gain fortune, an analogy for the nonsensical and empty narratives neoliberalism props up, an analogy for the Game Theory employed by capitalism. Perhaps the future episodes will reveal that trying to solve the epitaph at face value is a losing game. Indeed, maybe, its purpose is to create losers to its supposed game, because it might be this analogy for capitalism itself. As Jack Halberstam put it in 2011:
“Failure, of course, goes hand in hand with capitalism. A market economy must have winners and losers, gamblers and risk takers, con men and dupes; capitalism, as Scott Sandage argues in his book Born Losers: A History of Failure in America (2005), requires that everyone live in a system that equates success with profit and links failure to the inability to accumulate wealth even as profit for some means certain losses for others.” (p. 88)
In that sense, people losing to the epitaph is a necessary component to the money roulette as well as the demon’s roulette. I have no certain idea why Kinzo has put up the epitaph in the first place. Perhaps he genuinely believes he has cracked a dark magic code. Maybe he believes it. Maybe he does not. All I know for certain is that I will not solve the epitaph any time soon; perhaps that is the entire point of it, perhaps not.
Eternal Witch Beatrice claws her way out of (and then back into) several narratives, within the text and outside of it. She is vengeance personified, an answer for Beatrice Portinari and Umineko’s Historical Beatrice, women eternally entrapped in narratives created and maintained by men many times more powerful than them. Both Kinzo and Dante puppeteer their respective narratives of Beatrices to create and maintain their legacy. And in both instances, this violence repeats and echoes in recurrence. Violent systems of control are more likely to transform and stay nearly as violent than they are to dissolve. The Ushiromiya children repeat the sins of their parents, and their parents repeat the sins of their father. Like the musical format of the Rondo that one of the subtitles of Umineko mentions, this violence is going to be picked up again and again and again in future Episodes. Every time, it will be varied a little bit. Move back to the 3rd of October and change a couple of factors, and the violence that is the Ushiromiya family is likely to resurface again, just in a different iteration. No matter which iteration of chess moves one looks at, the players will likely aim to reduce the other’s material advantage and number of pieces; the Ushiromiyas are destined to destroy each other over and over and over again in the gamified violence of imperialist and colonial capitalism. This violence repeats synchronically and diachronically; who even needs a magical time loop when imperialism and the patriarchy and capitalism are so cyclical in nature?
Ultimately, though, I know that Umineko is a hopeful story. Ozaawa told me that the central sentence they see in Umineko is “without love, it cannot be seen”. I do not know the context in which this sentence appears, but there is a thematic equivalent in Ep1, namely, a challenge Kyrie places into the logics of Game Theory:
“Events in the world of humans are normally full of noise. Aren’t human emotions that way? Even if the exact same thing occurs more than once, there’s no guarantee that humans will always act in a predictable fashion.”
Whereas the world of witches – the realm of narratives and their powerful implications – operates on strange but fixed rules and semi-random but calculable probabilities, humans have the capacity to defy odds. Whereas it is likely that systems of violence permute throughout generations, there is always hope to be had that the human heart can ultimately defy these systems. The chance of breaking the cycle is always non-zero. That being explained, I love Eternal Witch Beatrice.[xxviii] Her struggle to defy all the narrative entanglements she was and is trapped in, her incredibly human feelings, her desire for autonomy and agency, are to me the core of the story, and what motivated me to write these thousands upon thousands of words.
5. On chess openings, or: What I still can’t explain
Here is the thing: All of this is a lot, many thousand words in fact, of speculation and half-baked theorizing. This is a reading, not the reading; I can’t even begin to fathom what this story is once the player-reader completes it. Even if I am to be right and the epitaph does not solve in a singular, meaningful, truthful way, there are still so many things I can not explain. Maybe I am completely wrong on many, if not all accounts. It would be awfully convenient for the lesbian that is bad at murder mysteries if solving Umineko under the classical logics of murder mysteries is intentionally impossible; perhaps I have misunderstood so much that I have deluded myself into thinking that such is a valid reading. I still hope this essay is an entertaining practice in trying to closely read Ep1 of Umineko without knowing all too much about the future episodes.
After finishing Ep1 for the first time, I formulated some questions I could not answer, but that I thought important to answer:
- What was the role of Rokkenjima between 1923 and 1945?
- What is the original contract made between Kinzo and Beatrice somewhere in this time? Does it even exist?
- What kind of interest can Beatrice collect on the gold when Kinzo got it from collaborating with imperialist fascism or even engaging in it?
I think they still hold value to ask, though some answers I have already partially established. And, I think this should be added:
- Why did Rudolf rightfully report in advance that he would die during the night?
- What is a witch?
And, this is still a burning question of mine: How did pochapal solve much of this story very early on? What the fuck is even going on?
6. Citations
Alighieri, D. (1996). Divine Comedy: Inferno (R. Turner, Trans.). Oxford UP. (Original work published around 1320).
Cornish, A. (2000). Angels. In R. Lansing (Ed.) Dante Encyclopedia (1st ed., pp. 37-45).
Halberstam, J. (2011). The Queer Art of Failure. Duke UP.
Howie, C. (2021). Bodies on Fire. In M. Gragnolati et al (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Dante (pp. 494–509). Oxford UP.
Kirkpatrick, R. (1990). Dante' s Beatrice and the Politics of Singularity. Texas Studies in Literature and Language 32(1), 101-119.
Lewis, R. W. B. (2001). Dante's Beatrice and the New Life of Poetry. New England Review 22(2), 69-80.
Lowe, D. (2016, April 17). The Rise and Unravelling of the Hachijo Royal Hotel. Ridgelineimages. https://ridgelineimages.com/haikyo/unravelling-of-the-hachijo-royal-hotel/.
Mazzotta, G. (2000). Alighieri, Dante. In R. Lansing (Ed.) Dante Encyclopedia (1st ed., pp. 15-20).
Schlingen, B. D. (2021). The East. In M. Gragnolati et al (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Dante (pp. 383–398). Oxford UP.
Singleton, C.S. (2019). Journey to Beatrice. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins UP doi:10.1353/book.68489.
Waller, M. (2021). A Decolonial Feminist Dante: Imperial Historiography and Gender. In M. Gragnolati et al (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Dante (pp. 701–718). Oxford UP.
7. End notes
[i] Citation needed.
[ii] This overly detailed descriptions is not setting up a point I want to make way later, do not worry about it.
[iii] For anyone still confused, here is the dramatis personae broken down in non-linear order: Kinzo is the head of the family. Krauss is Kinzo’s eldest child, Krauss’ wife is Natsuhi, and their one child together is the teenager Jessica. Eva is Kinzo’s second child, she married Hideyoshi, and they had one son, George, a young adult, together. Rudolf is Kinzo’s third child, he had a son named Battler, 18 years old, and later married Kyrie, his former secretary. Kinzo’s youngest child is Rosa, her child with an unknown person is the nine-year old Maria. The servants are Genji, trusted head servant, Godha, renowned cook and newest member of the servants, Kumasawa, an old woman and long-time servant at the household, Kanon, barely a child, and Sayo, another very young servant. Doctor Nanjo hangs out on the island as well.
[iv] This overly detailed descriptions is not setting up a point I want to make way later, do not worry about it.
[v] This overly detailed descriptions is not setting up a point I want to make way later, do not worry about it.
[vi] Death count: 6.
[vii] Death count: 8.
[viii] Death count: 9.
[ix] Death count: 10.
[x] Death count: 13.
[xi] Death count: 14.
[xii] Death count: Everyone? 14-18?
[xiii] This overly detailed descriptions is not setting up a point I want to make way later, do not worry about it.
[xiv] Death count: Who knows.
[xv] Slight hyperbole.
[xvi] Which in Battler’s internal monologue narration gets placed as follows: “The Great Kanto Earthquake happened in Taisho 13 (1924) [...]”. Now, Taishō 13 is 1924, that much is correct, but the one major earthquake of the era I could identify is firmly located in September 1923, indeed being called the Great Kantō earthquake in many sources. This could mean several things; perhaps I am bad at research, perhaps the translation made a mistake somehow, perhaps it took Kinzo a year to assume the position of the head of the family after the earthquake, or maybe this is intentional by the author to make the reader question Battler’s authority in narrating the past.
[xvii] Frankly I forgot which one. Sorry :(
[xviii] The well-read observer might now think “Kassandra how the fuck did you instantly remember Virgil as a character of the Divine Comedy but not Beatrice”, to which I would like to respond with one of Patrick Star’s most famous aphorisms: The inner machinations of my mind are indeed an enigma.
[xix] “Literary canon”, not to be confused with “literary Kanon”.
[xx] “Western church canon”, not to be confused with “western church Kanon”.
[xxi] I personally remember reading Dan Brown‘s Inferno as a teenager, where in typical Dan Brown fashion, the woman becomes an object to be taken by the wisdom of the middle-aged academic white man; and I am pretty certain the idea of her being “a Beatrice” runs throughout the text as much as allusions to Dante and his work.
[xxii] “Straight stairs”, not be confused with “gay stares”, which is what I do whenever Eternal Witch Beatrice is onscreen.
[xxiii] Eva got killed by the stake of Asmodeous, who stands for lust. The last time Eva is seen alive is when she is very very horny towards Hideyoshi. Hideyoshi, a capitalist invested in the food distribution business, is killed by the stake of Beelzebub, the demon responsible for gluttony. Kinzo, the ultrarich capitalist, is killed by the stake of Mammon, the demon of greed. Kanon dies wrathful, lashing out at the darkness, and is killed by the stake of Satan, demon of wrath. Genji, proud of his servant role and the trust Kinzo places in him, is killed by the stake of Lucifer, demon of pride. Doctor Nanjo, a man who reacted to all the death and blood around him by freezing in place and barely reacting at all, is killed by the stake of Belphegor, who stands for sloth. Kumasawa dies by the stake of Leviathan, who stands for envy – I am unable to fully decipher that one. Maybe she felt excessive envy for the safety that those who were barricaded in the study found themselves in.
[xxiv] You might be wondering why I am using one translation while using another translation’s commentary to analyze the quote. The answer is simple; I liked the one translation more from its poetic execution.
[xxv] The butterfly as a symbol for Eternal Witch Beatrice also takes on another role; I cannot quote this enough, as stated by Ozaawa 2023: “Beato trans.”
[xxvi] This is so tangential I dare not even put it in the main text, but Dante’s fascination with the Roman empire might tie back into his political support of the Holy Roman empire and the figure of the Holy Roman emperor, a political entity that claimed to be a direct heir to the Roman empire. The imperial symbol of the Holy Roman empire and emperors is the two-headed, two-winged eagle. In my deliberations on the symbolic implications on the One-Winged (and one-headed) Eagle, I have yet to resolve a direct connection to any real world symbol, and the Holy Roman empire is the closest node of possible connection my brain can come up with. However, I assume that it is completely unrelated.
[xxvii] Failing spectacularly is kind of Battler’s entire modus operandi, if you think about it.
[xxviii] And not just because its t4t. But also because it is t4t.
#kassandra plays umineko#umineko spoilers#umineko#I appreciate all the kind words in the comments and reblogs and DMs :) thank you all
96 notes
·
View notes