#as to whether because it was society imposed
Text
my healing arc will be the story of me mending my relationship with the colour pink
#i used to love pink as a kid#i dont remember the reasons#as to whether because it was society imposed#or just a personal preference#but then overtime when i realised how mainstream pink was#and how overly feminine and girly it was/is#it lost its appeal in my eyes#pink went from being just a colour to the flag bearer of feminity#and as a masc who is too fem passing it felt hurtful to my energy to associate myself with anything pink#i ended up hating pink to judging everyone for loving it and for it's extremely gender imposed overuse#but now when i realise that irrespective of its social or cultural background#pink as a colour has always made me look aliver and brighter and me-er#despite it being only so because of the colour chemistry it has with my physical figure and NOT because pink is my colour or vibe#I've learnt to grow on it and accept it#and that i don't have to conform to gender norms to like a colour for what it is#it provides a fresher perspective looking at things as an artist who understands colours and their significance#now i accept and love whatever pink that works for me as i do with my feminine energy and counterparts#in the end pink is just a colour#bisexual#masc lesbian#pink aesthetic#pinkcore#pink moodboard#pink#pink blog#coquette aesthetic#coquette angel#coquette
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't think there's anything wrong with enjoying kids shows as an adult per se, like that's obviously fine by itself. however I think the fact that there are so many Queers™ that almost exclusively watch shows made for children, and that most of those shows were produced by disney, is indicative of a broader trend of reactionary ideologies in mainstream queer society. often they praise these shows for having "queer representation" in some form, such as a gay couple, usually comprised of young children given who these shows are usually about. of course even these meager scraps of representation are often enough to get a show canceled, but the fact is that for them to even be on children's television in the first place, they must be extremely sanitized. disney in particular is notorious for scrubbing any and all content that any hypothetical evangelical conservative might take issue with from their shows, but this is a problem inherent to children's tv.
I say this not to disparage people who like these shows, but to point out that these shows serve to impose heterosexual norms onto queerness, and it concerns me how many queer people seem to be completely fine with this. why should disney channel and cartoon network get to define what an acceptable level of queerness is? the most radical thing you can expect to see is a same-sex couple briefly kissing. they are wholly sexless and sanitized, stripped away of any challenges to heterosexuality, cissexism, monogamy, and patriarchy. Straight People get the idea that they don't have to worry about queerness, as long as it conforms to their sensibilities and doesn't threaten their dominance.
but worst of all is that queer people themselves approve of this sanitization. I suspect the reason that so many queer people's media landscape revolves entirely around these shows is because they seek acceptance into Straight society, and must prove that they won't rock the boat too much. in doing so, they seek out only portrayals of queerness they consider "safe", and eagerly distance themselves from any form of "degeneracy". queer sexuality, for instance, must be a wholly private endeavor, as it is something shameful. any form of kink that isn't acceptable under wider heterosexual norms is something they must vehemently abhor, and engaging in it must be responded to with violence, whether social, physical, or both.
to be clear, I'm not saying that exclusively watching children's shows causes queer people to be reactionary. on the contrary, I think it's the other way around. queer people who already hold reactionary beliefs flock to these shows because it allows them to see themselves in media while still being able to gain temporary, limited access to the heterosexual project and the privileges doled out to its participants. this is deeply disgraceful. not only is the queer project of assimilating into straightness an inherently harmful one given that it necessitates intentionally throwing queer people who can't assimilate due to being trans, black, disabled, poor, etc under the bus and subjecting them to violence; it's also a fool's errand, given that straight people ultimately still hate the queer people that do try to assimilate and will discard them the moment they stop being a useful tool.
915 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Who’s to Blame for Out-Of-Control Corporate Power?
One man is especially to blame for why corporate power is out of control. And I knew him! He was my professor, then my boss. His name… Robert Bork.
Robert Bork was a notorious conservative who believed the only legitimate purpose of antitrust — that is, anti-monopoly — law is to lower prices for consumers, no matter how big corporations get. His philosophy came to dominate the federal courts and conservative economics.
I met him in 1971, when I took his antitrust class at Yale Law School. He was a large, imposing man, with a red beard and a perpetual scowl. He seemed impatient and bored with me and my classmates, who included Bill Clinton and Hillary Rodham, as we challenged him repeatedly on his antitrust views.
We argued with Bork that ever-expanding corporations had too much power. Not only could they undercut rivals with lower prices and suppress wages, but they were using their spoils to influence our politics with campaign contributions. Wasn’t this cause for greater antitrust enforcement?
He had a retort for everything. Undercutting rival businesses with lower prices was a good thing because consumers like lower prices. Suppressing wages didn’t matter because employees are always free to find better jobs. He argued that courts could not possibly measure political power, so why should that matter?
Even in my mid-20s, I knew this was hogwash.
But Bork’s ideology began to spread. A few years after I took his class, he wrote a book called The Antitrust Paradox summarizing his ideas. The book heavily influenced Ronald Reagan and later helped form a basic tenet of Reaganomics — the bogus theory that says government should get out of the way and allow corporations to do as they please, including growing as big and powerful as they want.
Despite our law school sparring, Bork later gave me a job in the Department of Justice when he was solicitor general for Gerald Ford. Even though we didn’t agree on much, I enjoyed his wry sense of humor. I respected his intellect. Hell, I even came to like him.
Once President Reagan appointed Bork as an appeals court judge, his rulings further dismantled antitrust. And while his later Supreme Court nomination failed, his influence over the courts continued to grow.
Bork’s legacy is the enormous corporate power we see today, whether it’s Ticketmaster and Live Nation consolidating control over live performances, Kroger and Albertsons dominating the grocery market, or Amazon, Google, and Meta taking over the tech world.
It’s not just these high-profile companies either: in most industries, a handful of companies now control more of their markets than they did twenty years ago.
This corporate concentration costs the typical American household an estimated extra $5,000 per year. Companies have been able to jack up prices without losing customers to competitors because there is often no meaningful competition.
And huge corporations also have the power to suppress wages because workers have fewer employers from whom to get better jobs.
And how can we forget the massive flow of money these corporate giants are funneling into politics, rigging our democracy in their favor?
But the tide is beginning to turn under the Biden Administration. The Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission are fighting the monopolization of America in court, and proposing new merger guidelines to protect consumers, workers, and society.
It’s the implementation of the view that I and my law school classmates argued for back in the 1970s — one that sees corporate concentration as a problem that outweighs any theoretical benefits Bork claimed might exist.
Robert Bork would likely regard the Biden administration’s antitrust efforts with the same disdain he had for my arguments in his class all those years ago. But instead of a few outspoken law students, Bork’s philosophy is now being challenged by the full force of the federal government.
The public is waking up to the outsized power corporations wield over our economy and democracy. It’s about time.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
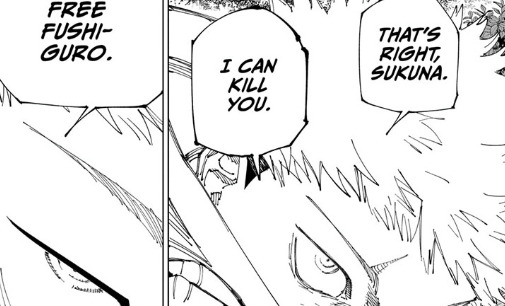

PITY VS. EMPATHY
Jujutsu Kaisen Chapter 265 quickly surpassed Gojo's death chapter as my favorite chapter in the entire manga. It's a high point in both Yuji's character development and the Sukuna fight, a notion most of the fandom agrees with. That being said, it's once again time for me to take a stance contrary to most of the fandom opinion. I was going to make this post two weeks ago but I'm glad I waited, because this week's chapter helps me illustrate my point in the contrasting way Yuji treats Sukuna and Megumi.
As you can probably tell by the title, my hot take of the week is that what Yuji is showing Sukuna isn't true empathy. It's not atn attempt to understand Sukuna's worldview, but rather condescending pity from a place looking down on Sukuna, which is why it infuriates him so much. This is illustrated in Yuji's atual actions this chapter, which is to go at great length to show memories from his past to make Sukuna understand HIM and not the other way around.
Whereas, what Yuji shows Megumi is compassion, because he's not telling Megumi what to feel or imposing his own views on him but rather accepting the fact that Megumi might be suffering too much to keep living on.
I'll explain more under the cut:
Guanyin, Goddess of Mercy
Yuji is, not as far along in his character development as he might seem. I don't want to undervalue his growth, this chapter shows definite progress, and I understand why it would seem that this is the completion of his arc of being a cog in society because he straight up says people don't need roles, and it seems like the manga is quickly coming to a close.

However, sometimes characters words don't exactly match their actions. Sometimes characters aren't self aware. People often call characters multi-layered and complex, but what does that mean exactly? For me, a mutli-layered character is the embodiment of "people are never what they appear to be."
A story has multiple layers when you're not supposed to take everything the author says at face value. Every time you read a story, whether you are aware of it or not you engage in some level of personal interpretation. You're not supposed to automatically accept everything the author feeds you without question. Therefore characters are not exactly what they are stated to be, and good character writing allows room for interpretation for what is going on in a character's head beneath the surface.
In a jungian sense this would be the ice berg model of consciousness. There's the persona, or the ego, which is what the person presents to the world and the people around them. Their own-self conceived image. Then there's the part of the ice berg that submerged, which accounts for all of their internal mechanisms and facets of their personality they aren't aware of. This could range from anything to like, how trauma can affect people's actions without them realizing it, things they are in denial of and don't want to admit to themselves or just like someone who's bossy but not self-aware about that trait until someone else points it out for them.
Everyone's have that friend who you try to call them out on their bad behavior, but no matter how hard you try they just won't admit it. That alone illustrates there's a difference between self-perception, how we view ourselves, behavior - how we actually interact with the world, and pther people's perception of us. Somewhere in between these multiple points of view there exists a vague outline of a person, and personality, whatever "personality" means exactly.
To step away from Jung, in a character writing sense this means a good character's motivations, personality, and actions can be viewed from multiple angles. There is conflict between how Yuji views himself, his actual actions in the story, how other characters might view him, and how he's framed in the story. The first two, Yuji's self-assigned roles, and what his actual actions amount to is a conflict that's run over the entire story.

It starts from chapter three, where Yuji's answer for why he wants to become a sorcerer is that he wants to fulfill his grandfather's dying wish, and Yaga immediately says "Is that what you really believe, or are you just using your grandfather as an excuse?" The story shows us Yaga was right to point out the discord between Yuji's stated motivation and his actual desires because Yuji changes his answer.
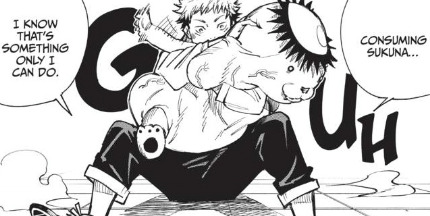
This stated motivation, "To do something that only I can do", or have a role as another way of putting it is Yuji's central motivation for most of the manga. Of course as I said people have multiple layers, so he can also have multiple motivations. Yuji's desire to have a good death, him wanting to be surrounded by people when he dies, his belief that fulfilling his role as a sorcerer will save other people from curses, all of these things are equally true but that one desire to have a role to play in the grand scheme of things is at the center of it.
The role Yuji has chosen is to kill curses so people can have more natural deaths, and also to stop more victims of curses from piling up. He's also resolved from the start to die with Sukuna in his body, to also spare victims of curses Sukuna might attract, and also kill Sukuna for good.
Even these stated motions are challenged right away, and then again continually through the comic.



I'm not going to go over Yuji's entire arc here, but the fact that Yuji is someone constantly interrogated for his motivations and even punished in story for his altruism is a constant pattern in his character arc.
It extends deeper than just the fact that Yuji is a selfless person in a world where selfish people like Mei Mei, and Sukuna get ahead while people like Nanami die young. A world where it is in your best interest to stick out your neck for others.
For me a lot of the harsh consequences Yuji's conflict in the story also centers around the fact that he can never live up to the role that he has assigned himself. Not only is Yuji mistaken in his perception of himself, but the fandom in general is as well, because most people tend to take Yuji's stated desire to guide people to good deaths and save them at face value.
For example, people were excited to point out the Guanyin symbolism directly referenced this chapter, and also the significance of the seal for Yuji's domain.

There is much speculation, but it seems certain that this hand sign is an invocation of Ksitigarbha, a revered bodhisattva in East Asian Buddhism. Ksitigarbha is also known as Jizo Bodhisattva in Japan. His name can be translated as Earth Womb, Earth Matrix, and Earth Store. These translations evoke the image of a vessel, which seems relevant to Yuji's role as Sukuna's vessel.
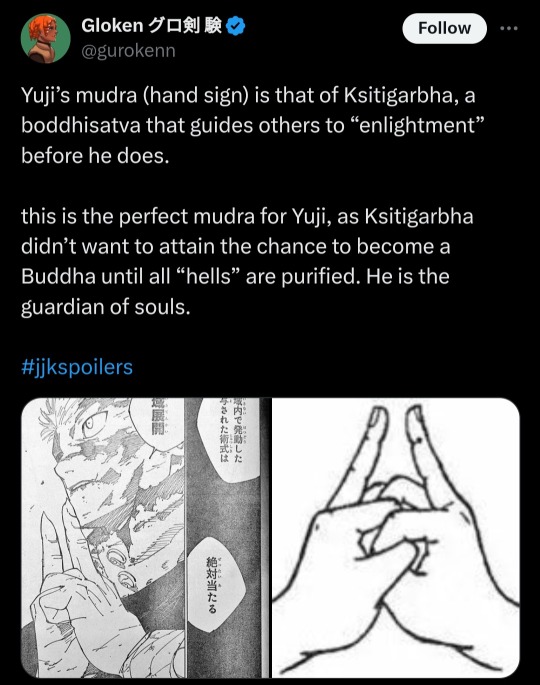
While I agree the symbolism is well suited for Yuji's goals, someone who wished to guide people to a more peaceful death, and also the way Yuji opposes Sukuna right now determined to kill him who lingers in this world as a parasite for a thousand years finally back to the cycle of reincarnation. It even alligns with his desire to try and make Sukuna understand the value in one individual's life by showing him his memories. In that way Yuji is fitting the role of someone guiding others to enlightenment.
However, Yuji is not a bodhivista in the end. He is a normal teenage boy. In fact this is the crux of Yuji's character to me, he is a good kid, but he's not as good as he thinks he is. If anything this is what this chapter goes to great length to demonstrate, that Yuji despite being a science experiment to create the perfect vessel for Sukuna for Kenjaku's 1,000 year plan, had a normal childhood. All of the things Yuji says in this chapter are for the most parts the musing of a normal kid his age.

This isn't me criticizing Yuji. I'm just trying to state the message I believe Gege is getting across in this chapter. It's similiar to the conclusion Yuji himself comes to, the conclusion that the value in life lies in the memories you make on a day to day basis, even if you're not living a life full of adventure.

Yuji's conflict is that he pursues the role of a bodhisvatta, and he holds himself to the standard too of someone who exists to be a sorcerer because by doing his job as a sorcerer people will get saved as a result. However, Yuji as a person will always fall short of this ideal, because ideals by the nature of them being IDEAL and therefore not compatible with reality.
To use an example for another media, it doesn't matter how hard Shirou Emiya strives to save others, or how selfless he tries to be, he will always fall short because the ideal of saving absolutely everyone is impossible. However, in most versions of Fate's story Shirou absolutely refuses to compromise on this and in the future, Shirou will continue to strive towards the ideal of saving everyone until his inability to achieve that ideal and the number of people he's failed to save eventually breaks him.
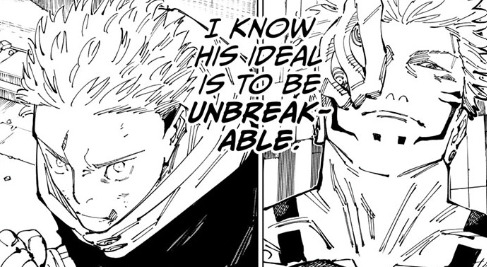
So Yuji may genuinely hold onto an unbreakable ideal, but is his inability to let go of that ideal necessarily a good thing? His ideal might break but what about Yuji as a person? Yuji will in the end always fall short of that ideal because of his humanity, especially since Yuji is the most human character in the story and practically the only one with a normal background.
There's also as I stated above Yuji might not be aware himself of the ways he falls short of his ideal, because he has a flawed self perception. Yuji is getting closer with his revelation in this chapter of looking at reality instead of trying to have a role like a character in the story, but that doesn't mean he's finished (since the story's not finished) or he's become a fully realized character.
One of my favorite quotes from my favorite Yuji video helps describe the point I'm getting at with Yuji's lack of self awareness and the way he sometimes falls short of the savior he sees himself as.



By assigning himself the role as heroes, and the other characters as victims to be saved Yuji sort of condescends to the people he endeavors to save. I describe this as condescending because this way he doesn't see the people he saves as fully fleshed out human beings who are separate individuals from himself.
Yuji is alligned with Higuruma of all people, someone who shares Yuji's savior complex and becomes disillusioned because the people he decided of his own free will to protect as a defense attorney are not perfect victims.
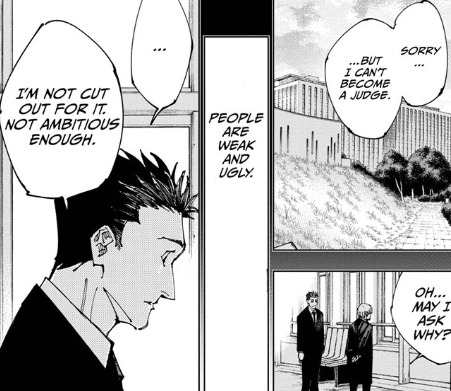
Someone who becomes disillusioned when looking at flaws in other people, and also cannot deal with his own guilt when he too, becomes like the crimminals he once defended after becoming a murderer.
In fact Yuji sees himself in Higuruma's inability to live with his guilt, and only being able to see himself atoning with his death. Yet, despite Yuji seeing himself Yuji also seems uneasy with Higuruma being unable to see one other way forward in life.

Also, remember that Higuruma is a defense attorney. The whole point is he's supposed to defend crimminals even if he knows they did the crime and try to get them off their sentence and win the trial. Therefore at this moment Higuruma has failed to live up to his ideal.
There's another character Yuji is paralleled to constantly, who also shares Yuji's symbolism of being associated with a divine, and benevolent figure.
Geto's ears, his dressing as a monk in a Gojo-gesa, this official art all connect Geto to be Budha and yet it's quite obvious that Geto has failed entirely to live up to his role as the budha.

There's so much symbolism aligning Geto as a divine figure bringing salvation to others, and this corresponds to his original ideal as a sorcerer who belived that sorcerers had an obligation to use their powers to protect others, because in a just society the strong protect the weak.
Geto is an outsider who wasn't born into the Jujutsu World who entered in with an attitude different from most sorcerers by trying to become a sorcerer for altruistic reasons. However, Geto, like Higuruma grows disillusioned when he's confronted with the fact that the people he wants to save are flawed.
However, Geto's ideal was mistaken to begin with because much like Yuji, by distinctly separating people into the weak and the strong, he's separating them into two categories where the former is inherently inferior to the latter. Other people existed to be saved by Geto. He couldn't cope with the fact that the people he wanted to save were people and not victims.
So we finally circle back to chapter 265 where Yuji is attempting to relate to Sukuna and see some humanity in him... or is he?
Yuji shares the same flaw of both Geto, and Higuruma where he sees the people he wants to save as existing in a separate category than himself. So, is what Yuji is offering Sukuna understanding and an attempt to emotionally reach out to him, or is he attempting to show Sukuna the mercy of a conqueror.
Even if Yuji wins the battle and spares Sukuna's life in the end, it won't be Yuji's compassion or empathy that won him the fight. If Yuji wins against Sukuna it's simply because he's stronger. Yuji only feels confident trying to offer Sukuna in the first place because this time he's finally confident he's stronger. It's mercy, offered at a threat with the same time. Yuji, like Geto, is still separating people in categories of strong and weak, he's just showing mercy to someone he now considers weaker than him which is why Sukuna reacted the way he did.
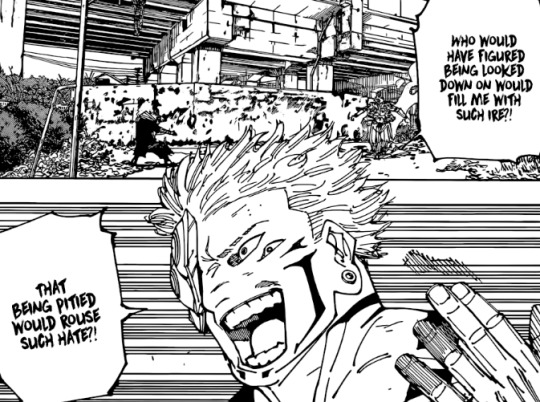

As I said above, Sukuna begins by just assuming that Yuji had just let go of his anger, and was now trying to reach out to him on some other way. He calls him weak for being unable to keep hating his worst enemy, because in Sukuna's world view Yuji should keep hating him and wanting to defeat him with all his strength to the end. Sukuna mistakenly believes for a moment that Yuji is the kind of person who, cannot sustain his anger even towards his worst enemy.

It's when he realizes that Yuji is just showing him simple pity that he snaps. Yuji doesn't care for understanding Sukuna's worldview or seeing the humanity in him, in the same chapter he says he can't forgive people who act like lives are worthless.

To Yuji's credit he admits he doesn't really know which side of the fight is truly human, or whether or not he's right, he admits it's his own personal belief. A lot of Yuji's wisdom this chapter, I'd argue, comes from admitting the things he does not know, and acknowledging that there's no objective truth or "meaning" to the world. However, he still separates people into "good guys, and bad guys".
Yuji isn't actually that interested in considering the perspective of those he considers the "bad guys" he just still had a faint hope that he could somehow convince Sukuna to see worth in his life by sharing memories, therefore convince Sukuna that an individual's life can have value.
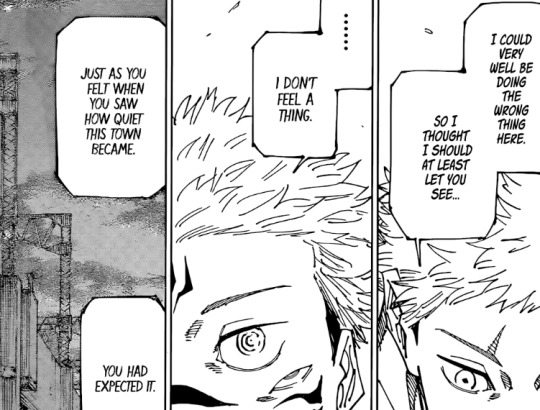
He doesn't want to understand what Sukuna thinks, he wanted to change the way Sukuna thought so it was more like himself. Yuji doesn't ask Sukuna any real questions about himself while exploring his memories. Kind of ironic, because for some reason Sukuna of all people was patiently listening and even engaging Yuji in conversation while he went through the most mundane memories of his childhood.
Irony on top of irony, Yuji's worldview does resemble Sukuna's in some ways. They're supposed to mirror each other after all, Yuji is literally the son of his identical twin brother reincarnated. First and foremost Yuji's offer of mercy isn't really breaking away from Sukuna's ultimate ideal of "Might Makes Right." Yuji isn't seeking some other way of settling this besides fighting Sukuna, he's going to make Sukuna submit because he's stronger.
Maybe there was no hypothetical "third way" for Yuji to put down Sukuna other than fist fighting him into submission. There probably wasn't, Sukuna's pretty up front what he's about, and what he's about is being the strongest and nothing more. He lives and dies by violence, a Sukuna who isn't the strongest is nothing more than a corpse so can that person be reached? However, I just wanted to point out that Yuji wasn't interest in solving this in any way other than a fist fight to begin with. As opposed to say, the way that Takaba handled Kenjaku taking a third route by making Kenjaku feel entertained for the first time in 1,000 years.
In the middle of that fight Takaba even APOLOGIZES to Kenjaku, for saying that it doens't matter if he doesn't understand his audience and he fails to make 1% of them laugh as long as the other 99% of them are laughing and states it's his duty to make everyone laugh otherwise he's failed as a comedian.

Yet, another reason why this is the greatest fight in the manga. Yuta even remarks in the end that Takaba isn't someone who can kill people. Not only does his cursed technique negate most damage to him by turning it into cartoonish antics, but Takaba's comedy is also all about understanding his audience and trying to get his audience to understand him because his comedy began when he clowned around as a kid when he was lonely. All of this to say we've been shown more points of view than just "Might makes Right" and there are characters who've resolved conflicts in other ways. Kenjaku is also, probably as monstrous as Sukuna, and yet Takaba engaged him right from the start by asking him about his motivations and if there was some other way he'd be happy than the merger.
You could argue that maybe Sukuna can't be understood. Characters in the story certainly try to and all they amount to doing is projecting their own ideas onto Sukuna. Yorozu projects her obsession with love onto Sukuna and we get the idea that Sukuna must somehow be lonely at the top, but in the end Gege subverts this expectation by showing us that Sukuna was never lonely, rather characters like Kashimo and Gojo projected their feelings of unresolved loneliness onto him. They are strong, and he is strong, ergo he must feel the same crushing loneliness as them. Gojo himself demosntrates not understanding Sukuna as he expresses regret in the afterlife that he was unable to make Sukuna go all out and that he related to that guy's loneliness only for Sukuna's response to be a very gratified "You cleared my skies."
Sukuna: Others love us for our strength, and we respond to that love.
The twist of that is Kashimo and by extension the audience assume that Sukuna must not understand love, and therefore he's lonely. However, Sukuna all along had his own definition of love, that people express their love and admiration for him by trying to fight him and he receives their love by facing them at his full strength and giving them the chance to prove themselves. Sukuna's habit of toying with his opponents is an extension of this he wants to see them realize their full potential in their fights with him. Sukuna does understand love, he just REJECTS our understanding of love. Sukuna does not think in the way that we do, but that doesn't mean he doesn't have things he values, or is devoid of positive traits. Respect for his opponents, honoring strength, these are all values they're just not Yuji's values.
As stated above, the irony of all this is that Yuji does buy into "Might makes Right" to an extent. To reiterate, following Geto's "the strong exist to protect the weak" still divides people into two categories strong and weak and implies the weak are helpless. A benevolent might makes right, as you might say. Yuji wants to show compassion to the weak, but he also loathes weakness, he loathes himself for being weak.

"There still may be lots of people who are weak like you."
Higuruma even points out the flaw in his mindset, well if you loathe yourself for being weak, then what about other people who are weak do you loathe them too? I think it's no coincidence that Yuji is paralleled not one, but two (Geto, Higuruma) people who tried to use their strength in benevolent ways only to start out loathing the people they were trying to help. I'm not saying that Yuji secretly hates weak people, but his mindset of black and white, weak and strong, a mindset that can't accept the greys of reality is a dangerous mindset to have and Yuji has the potential to become like those two.
However, these parallels exist for us the audience to see just how close Yuji was to repeating the cycle, because it makes it that much more meaningful when Yuji grows in ways that Geto and Higuruma doesn't to move one step forward towards breaking that cycle instead.
Yuji is someone who experiences the same loneliness as Sukuna and Gojo for being the strongest, though to a lesser extent because he wasn't born into the realm of sorcerers. At the start of the manga we're introduced to Yuji a kid who despite being someone friendly to everyone he meets and incredibly social, has a friend group consisting of two friends. Two friends who hang out with him because they need a third member for their occult club. Yuji for the whole manga excluding one exception really only knows how to form relationships based on someone else needing him.
Noritoshi Kamo: Itadori why did you become a Jujutsu Sorcerer?
Itadori Yuji: It just sort of happened. i'm a loner. I wanna help a lot of people so when I die I'll be surrounded by people.
Yuji has also appeared in flashbacks in early culling game as someone who doesn't really understand, or even take notice of weak people. Yuji in Amai Rin's flashback is beating up bullies, a heroic notion, but from the perspective of somone spineless like Amai who was just going along with the bullies so he himself wouldn't be bullied because he didn't have the strength to stand up with them, and wasn't born with the body of an MMA fighter at fifteen, Yuji looks scary.
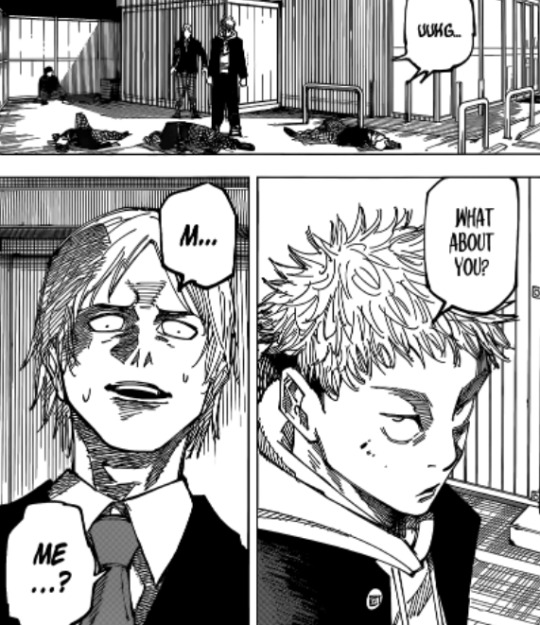

The reason why reducing people to labels like strong and weak is reductive is that humans are complex and contradictory creatures. Let's take Amai Rin for example, an incredibly minor character. In the real world, Amai Rin would be someone as equally complex as Gojo Satoru. Amai Rin a middle school bully would have just as many layers to his personality, inconsistencies, contradictory behavior, different sides of himself as Gojo Satoru himself.
Humans are complex in the first place because we can't see inside their heads, we can only see inside our own heads and know that we're complex and sometimes say things we don't mean, behave differently depending on the situation, do things we're not proud of, but we also usually don't perceive others the same way because we are not inside their heads like our own. Amai Rin is just as complex and multifaceted a human being as Gojo Satoru, he is a person with his own memories and life experiences that shape him, but from Gojo's worldview Amai Rin is a minor character. By reducing him into someone weak, Gojo doesn't care to try understanding him.
So Yuji for the longest time does not try to see the humanity in weak people (except for his big moment with Junpei) he just sees them as people to be saved. Which is why his real moment of progress to me comes the next chapter, with the way he shows empathy to Megumi.
Yuji begins when speaking to Megumi by relating his frustration with his grandfather for not wanting to go through chemo and accepting his own death in old age. Yuji is now mature enough to understand that just because his young body is tough enough to endure chemo, doesn't mean an old man's body can withstand that pain. When he was young Yuji had a very immature viewset of "Well, I can endure it, so why can't they?"

Yuji then compares the situation with his grandfather to Megumi. Yuji wanted his grandfather to keep living, so he couldn't understand why he wouldn't even try the chemo. Yuji wants Megumi to keep living, but he now understand why Megumi wants to give up. Yuji' fe elings of wanting Megumi to live are not more important than Megumi's own feelings of despair and wanting to escape pain.
Yuji is no longer imposing his feelings onto Megumi. Yuji is respecting Megumi's feelings, because in the end he can't FORCE Megumi to live. It has to be Megumi's choice whether he wants to live or not.
Yuji is no longer pushing Megumi away, or acting protective of him, while disregarding his feelings. He has gone from "as long as I'm around you'll suffer" to "I'll be lonely without you." Yuji doesn't ASK Megumi to live even though he wants to, because he knows he can't tell Megumi to keep on living. What Yuji does is just an honest expression of his own feelings. He's sharing his own feelings after listening to Megumi's ideal life with Tsumiki and Yuji, because that's what empathy is, an exchange, a conversation.
People often jokingly use the term "yap sessh" on Twitter, but yeah that's the different between a conversation and a "yap sessh" in the former you actually care what the other person has to say, in a latter it's only about expressing your own opinion.
That's why this panel, is such a perfect contrast with this panel.

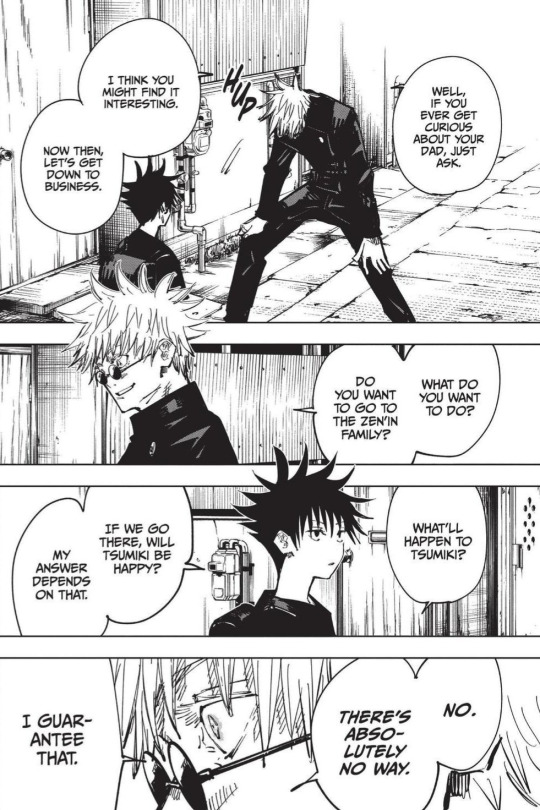
One is Yuji offering Megumi a choice. The other is Gojo taking Megumi's choices away by giving him the false choice of "go to the Zen'in Clan and be a sorcerer and your sister will be abused, or come with me and be a sorcerer." Gojo railroaded Megumi into being a sorcerer and never let him decide for himself if he wanted a normal life. Gojo didn't see Megumi as his own person either, he, just like the Zen'in Clan just saw Megumi as the holder of the Ten Shadows Technique.
This is entirely different to Yuji who respects Megumi's feelings. Yuji expresses that he'll be lonely without Megumi, but that's just laying the cards on the table. In the end Yuji leaves what happens next entirely in Megumi's hands. Yuji cannot tell Megumi to live, even though he wants him to live so badly, he cannot tell Megumi to just get stronger and keep on trucking because he's not Megumi, he's not experiencing Megumi's pain right now.
Yuji does not tell Megumi to live and therefore becomes the first person in Megumi's entire life to give him a choice. This choice is the most important choice of all, a choice we make every day of our lives. The choice of whether we want to keep on living in this world.
Hopefully, Megumi chooses yes.
#jjk meta#megumi fushiguro#yuji itadori#sukuna#ryomen sukuna#geto suguru#higuruma hiromi#itafushi#jjk spoilers#jjk 266#jujutsu kaisen spoilers#jujutsu kaisen 266
493 notes
·
View notes
Text

ANTISEMITIC BIAS
Many antisemites don’t consciously dislike Jews. They might even think highly of Jews. For example, they might believe “positive” stereotypes of Jews, such as that Jews are good at business or good with money. They might have Jewish friends. They might like “some” Jews. But they still cause tremendous damage to the Jewish community.
“Biases” can be defined as “an inclination or prejudice for or against one person or group.”
Unconscious biases are known as implicit biases. We all have implicit biases (whether negative or positive) in the way that we interpret the world around us. Conscious biases (such as, for example, the Nazis outwardly believing that Jews were “the inferior race”) are known as explicit biases.
Because antisemitism is everywhere in our world — in our cultures, our languages, our folklore, our literature, our entertainment, our media, and more — it’s impossible for us not to internalize at least some antisemitic biases. These biases, however, exist on a spectrum: from unconsciously assuming that most Jews are wealthy (implicit bias) to believing the white supremacist conspiracy theory that Jews are enacting a “white genocide” (explicit bias) to everything in between.
Because antisemitism is so old and so deeply embedded into our society and institutions (e.g. religion, language, literature, education, and more), that means that there is a lot of antisemitic bias in our world, most of which you might not even be able to see. But that doesn’t mean it doesn’t exist.
ANTISEMITISM IS A CONSPIRACY ABOUT THE JEWS
Antisemitism can be tricky to spot because it works very differently than every other form of bigotry. While other bigotries see their victims as “inferior,” antisemitism sees Jews as both “inferior” but also “superior” or all-powerful, capable of causing every calamity from wars to natural disasters to diseases to controlling the weather.
Societies project whatever they dislike most onto the Jews. In the Middle Ages, Jews were Christ-killers. In Nazi Germany and McCarthyist America, Jews were communists. In the Soviet Union, Jews were capitalists. In Nazi Germany and during the rise of the scientific racism period, Jews were the inferior race. To white supremacists, Jews are not white. To left-wing anti-Zionists, Jews are white. For centuries in Europe, Jews were untrustworthy foreigners from Palestine. But today among anti-Zionists, Jews are Europeans colonizing Palestine. We are whatever makes us the perfect scapegoat at any given time.
It’s no coincidence, then, that antisemitism tends to surge most when societies are in upheaval. After all, the leaders need someone to blame. Examples of this include the Germans’ blaming Jews for Germany’s suffering post-World War I, as well as the rise of the “Deadly Exchange” conspiracy which blames Israel for police brutality in the United States, following George Floyd’s murder.
Antisemitism moves through conspiracy theories. Most notably, since to the antisemite, Jews are all-powerful, the most prevalent and deeply ingrained antisemitic conspiracies have to do with Jews and wealth and power. In the Middle Ages, for example, Europeans believed that Jews aimed to subvert Christendom. Since the 1920s, antisemitic leaders in the Arab world have rallied their followers behind the conspiracy that Jews intend to destroy Al-Aqsa Mosque and usurp Islamic lands. White supremacists — and far left anti-Zionists — today believe the “Zionist Occupied Government” conspiracy, which accuses Jews of controlling and manipulating the American government for their benefit.
Given the pervasiveness of conspiracies regarding Jews and power, antisemitism is nearly impossible to address without triggering more antisemitism. If an antisemite faces consequences for their actions, antisemites will use this as “proof” that it’s the all-powerful Jews that have imposed these consequences. This makes antisemitism a self-fulfilling prophecy.
BIGOTRY WON'T ALWAYS BE OBVIOUS TO YOU
Most of us want to do the right thing. The problem is that bigotry — whether antisemitism or something else — doesn’t come with a flashing neon sign that says “this is bigoted! Call it out!” Instead, bigotry persists because entire societies convince themselves that their bigoted worldview is somehow justified. This is especially true of antisemitism. Antisemites throughout history have long persecuted Jews under the guise of seeking justice.
For instance, since the Middle Ages, Jews have been periodically persecuted on the accusation that they killed a Christian or Muslim child for ritual purposes. In other words, antisemites were seeking “justice” for these children that the Jews allegedly killed. This antisemitic trope is called “blood libel” and has led to the deaths of millions of Jews. It’s safe to say that these murderous antisemites fully believed that they were doing the “right thing.” Some examples of historic blood libels that have resulted in violence against Jews include the William of Norwich blood libel (1144), the Damascus Affair (1840), and the Kielce Pogrom (1946).
During the Bubonic Plague, Jews were persecuted under the false accusation that they were “poisoning the wells” and sickening the gentile population of Europe. Once again, the persecution of Jews was seen as just.
During the Nuremberg Trials, high-ranking Nazi officers testified that they believed that Jews were a danger to the safety of the German people and the German nation. In other words, they justified their mass extermination of Jew under the guise of “protecting” the people of Germany.
The list goes on and on. Is it possible that today you too have been made to believe that violence against Jews — Zionists, Israelis — is a just cause?
THE NAZI FALLACY
A few years ago, the notorious antisemite Shaun King argued with a Holocaust survivor on Twitter. When accused of antisemitism, he retorted, “I can’t be an antisemite. I fight Nazis every day!” But anyone even remotely familiar with antisemitism or Jewish history will know that Nazis were far from the Jews’ only historic oppressors. You don’t have to be a Nazi to be an antisemite. In fact, most antisemites are not Nazis.Not even close.
Nazism is just one manifestation of antisemitism. It’s a deadly one, certainly, but it’s also far from the only deadly manifestation of antisemitism. Jews have been killed by the thousands — sometimes by the millions — by a multitude of other oppressors. Some, like the Nazis, the KKK, and other white supremacists, are far-right. Others, like the Soviet Union, are far-left. Others are somewhere in the middle, and others oppressed us so long ago that their ideologies long predate the left-right political spectrum as we know it today.
The horrific images of Nazism and the death camps are seared in the world’s collective memory. It’s easy to think that if it doesn’t look like Nazism, if it doesn’t look like Auschwitz, then it’s not actually antisemitism, or perhaps it could be antisemitism, but it’s not serious antisemitism. In reality, though, antisemitism doesn’t go from zero to Auschwitz. Instead, antisemitic tropes, conspiracies, and stereotypes fester and proliferate, operating under new euphemisms and adapting to whatever society they’re in. Many of the same antisemitic conspiracies that drove the Nazis nearly 100 years ago are the exact same conspiracies that are driving “protestors” to violently harass Jews in the streets of New York City today.
For many years before the gas chambers, antisemitism in Germany, which once was home to the most assimilated, well-integrated Jewish community in the Diaspora, proliferated in university lecture halls, justified and explained away in academic language. It wasn’t deadly yet, but it soon would be. When you dismiss any sort of antisemitic rhetoric because it doesn’t mirror the deadliest days of the Nazi regime, what you are actually doing is that you are contributing to the sort of hostile, conspiratorial environment that eventually made the Holocaust possible in the first place.
THE GASLIGHTING
Antisemitism and the gaslighting of Jews go hand in hand. If an antisemite faces consequences for their antisemitism, it simply reinforces their antisemitic beliefs. Because antisemitism always places Jews in the role of oppressor, it’s nearly impossible for Jews to seek accountability or justice without being accused of exaggerating, crying wolf, playing the victim, or otherwise having nefarious intentions.
After the Holocaust, for example, the second in command at the Red Cross, Carl Jacob Burckhardt, decried the Nuremberg Trials, calling them “Jewish revenge.” Others, like the Palestinian newspaper Falastin, did so as well.
Antisemitic bias oftentimes makes it impossible for some people to see Jews as victims. If an antisemite loses their job for espousing antisemitism, they will then blame the “powerful” Jews — or Zionists, or another euphemism — for taking their job. In that way, they turn the victim into the victimizer. This is a classic gaslighting tactic, which creates a catch-22 and is one of the reasons antisemitism can be so hard to combat.
For example, in the lead up to the Holocaust, American isolationists of various political persuasions accused Jews sounding the alarm on the treatment of Jews in Nazi Germany of trying to instigate a war with the Germans.
Sometimes we are even accused of provoking or exaggerating antisemitism for our own benefit. There are a number of conspiracies, for example, that the Zionists worked with the Nazis to instigate the Holocaust to justify the creation of a Jewish state.
An example of the accusation that Jews play the victim is when we are told that we talk about the Holocaust “too much” — contrary to the statistics that demonstrate people are woefully misinformed about the Holocaust — or that we should move on because we “got reparations” (not exactly true, but that’s a different topic).
Then there are the accusations that we brought antisemitism or antisemitic violence onto ourselves — something that we’ve seen on a grand scale following the Hamas massacre on October 7.
WHAT YOU CAN DO
(1) Listen to Jews. I don’t mean just listen to your Jewish friends, or to the Jews you personally agree with. I mean listen to the Jewish community as a whole. Jews don’t often agree on much, but at the end of the day, we are a community, and only the Jewish community can fully describe our own experience.
Don’t listen just to the Jews who validate your views. Listen to the Jews that challenge you. Don’t shut yourself off from learning because it might contradict whatever ideology you follow. Learning is a lifelong process. I promise you you don’t know everything there is to know about antisemitism (I don’t either! I’m always learning). But it’s your responsibility to open yourself up to new information so that you can do better.
(2) if Jews are telling you something is antisemitic, then your first instinct should never be to distrust us.Can Jews weaponize accusations of antisemitism? Sure. Anyone can weaponize anything. Is it likely that that’s what’s happening? No. Antisemitism worldwide has skyrocketed to the highest levels since the end of the Holocaust. It’s a very real threat taking lives. You should take accusations of antisemitism just as seriously as you take accusations of other bigotries…even if initially you don’t see it.
(3) I can’t stress this enough: do your best to educate yourself about antisemitic conspiracies, stereotypes, and tropes throughout history. The euphemisms may change — sometimes we’re “globalists,” other times we’re “Zionists” — but the formula remains the same. To be able to spot antisemitism, you have to learn to spot it. I recommend reading my post “The World’s Oldest Hatred” for more.
Instagram
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
Now that Ram Mandir has been opened can I honestly share what I feel? No, I'm not on the side of the extremist Hinduism nor am I on the leftists I just want to take a neutral stand here.
To everyone saying it's just a political agenda and Modi is using Ram mandir to appease the Hindu vote bank. Yes, and? I think we all (even the Hindus) know what game he's playing here. My house was conflicted yesterday. My mother and nani (grandma) were sobbing on finally getting Ram lalla's darshan yesterday on TV, my nanu (grandpa) wasn't supporting any of it. And I was torn. Torn between celebrating a historic moment and rationalizing whether it even deserved to be celebrated. His return deserved to be celebrated yes but the extreme Hindus who shower flowers with one hand and with the other hand throw stones on innocent Muslims of today who never took away our beloved Ram ji away in the first place. Would Ram ji have wanted this? He would've wanted us to celebrate yes but not at the cost of harming others. I condemn the acts of discrimination against the minor sects of society, everyone who's got to suffer because of this. In Mahabharata too, the minority (Pandavas) had to go through hell but they emerged victorious in the end coz they were right. However, I'd also like to state that it's not that simple here. People calling out Islamophobia, I'm with you. People calling out Hinduphobia, I'm ALSO with you. All lives matter no matter if they are Hindu or Muslim or Christian or Palestinian. "Hinduphobia doesn't exist" It does. Ofc not at the scale of the terrifying Islamophobia in India but it does. In other Islamic etc countries, it does. Just like how Islamophobia exists in countries where Islam folk are in minority. But does that give Hindus a license to endorse and impose themselves any more than the colonizers and invaders did? No.
You can't blame innocent Muslims for what Mughal invaders did centuries ago any more than you can blame Vibhishan for what his own brother Raavan did. But whoever is on the side of wrongdoing no matter their caste, creed or religion is just as much of a criminal like Karna was with Duryodhana even though he was a Pandava by birth.
Yk I've grown up in my remote, countryside hometown where they play azaan in mosques every day morning and evening and kid me since then became so used to it that it would feel like something is missing if I'd not hear it in the background somewhere while swinging around near the trees or while just walking on the terrace and watching the distant sunset. I'm a Hindu but well, that's just personal nostalgia.
Not all muslims are terrorists. Not all Hindus are fascists. But for those who are, I'd let Karma take care of you all.
I stand with humanity.
Jai Shri Ram 🙏
Allahu Akbar 🙏
#desiblr#desi#ram mandir#ayodhya#hinduism#hindublr#islam#islamophobia#hinduphobia#india#hindutva#desi culture#religion#desi aesthetic#desi tag#desi dark academia#desi girl#desi stuff#desi academia#just desi things
308 notes
·
View notes
Photo










October 9th is Psychiatric Survivor Pride Day
“The problems of the ex-patient are more subtle but no less pressing. Many ex-patients try to cope with what has happened to them by pretending that the experience never occurred. However, because the experience of having once been a mental patient teaches you to think of yourself as less than human, this is not a satisfactory solution. People feel emotions. They are justifiably happy or sad, angry, calm, elated, and so forth. As patients, however, we were taught to think of ourselves as permanently crippled, and we tend to react to the normal ups and downs of life as affirmations of our secret deformity. In addition, society imposes penalties upon ex-patients which affect you whether or not you acknowledge your identity. For the rest of your life, you will lie on applications for jobs, schools, and driver's licenses, and worry about being found out. Your friends and acquaintances will be divided into two groups, those who know and those who don't, and it will always be necessary to watch what you say to the latter. Ex-patients are full of anger at what has been done to them, but alone and unorganized this anger is not expressed and is often turned inward against oneself. Our anger is the fuel of our movement, and when we come together, acknowledging our identity to ourselves and to each other, we will have made the first and largest step in striking back at our oppressors.”
— "Mental Patients' Liberation: Why? How?", originally distributed in the early 1970s by Mental Patients' Resistance of Brooklyn, New York


[image ID] Seven photographs from antipsychiatry demonstrations. They are described below, in order of appearance:
1. a picture taken at the National Association for Rights Protection & Advocacy (NARPA) Conference on November 10, 2000 in Sacramento, California. Fifty to sixty people stand around a red sign with white text that reads: NO FORCED TREATMENT EVER.
2. a picture taken on October 9th, 1999 in Toronto, Ontario during a march for Psychiatric Survivor Pride Day. Several people march in a line, including one man at the start of the march playing bagpipes. Behind him is a hand-painted sign being held up that reads: Psychiatric Survivor Pride Day.
3. pictures taken at a demonstration outside the California State Capitol building in Sacramento on February 28th, 2000. The signs in each of these pictures say: Psychiatric drugs can kill!
4. a picture taken at a demonstration outside the American Psychiatric Association's 156th annual meeting in San Fransisco, California. The activist's sign says: PSYCHIATRY IS NOT A MEDICAL PROFESSION: IT IS A TOOL OF OPPRESSION.
5. a picture taken at a demonstration outside the Jacob Javits Center, hosting the American Psychiatric Association's 167th annual meeting in New York City on May 4th, 2014. The picture features an activist wearing a printed t-shirt and is cropped so as not to feature the face of the wearer. The t-shirt says: TO HELL WITH THEIR PROFITS, STOP FORCED DRUGGING OF PSYCHIATRIC INMATES!
6 and 7. pictures taken at a demonstration outside the California State Capitol building in Sacramento on February 28th, 2000. The signs in each of these pictures say: Psychiatric drugs can kill!, STOP expansion of forced treatment, Mental illness is NOT a CRIME, and FORCED MENTAL HEALTH TREATMENT IS INHUMANE.
8. a picture taken at an antipsychiatry demonstration on May 2nd, 1998 in Freedom Plaza, Washington D.C. Two people hold a hand-painted banner-sign that says: BET YOUR ASS WE'RE PARANOID.
9. taken at an antipsychiatry demonstration hosted by the Mental Patients Liberation Alliance during Mad Pride Week in 2000, between July 13th and 16th on the lawn in front of the New York State Capitol Building in Albany. [end of ID]
#antipsychiatry#psychiatric abuse#psychiatric survival#psychiatric survivor pride day#psych abolition
5K notes
·
View notes
Note
Half-doubting if this anon was even a good idea to begin with but, am I a bad communist for being actively hostile against any form of authoritarian concentration of power?
I just don't think any single person could embody the revolution much less serve it on a system built entirely on personalism where we worship the leader instead of the workers themselves. The only role individual people should have on communism is that of thinkers and philosophers, not of absolute rulers.
This may be drawn from a personal bias though, my country was destroyed by a dictatorship that would have gladly shot me and hid my body for being a lesbian and I have developed animosity towards authoritarians that is perhaps unhealthy.
Where do we draw the line to avoid becoming a red painted tyranny? Or am I just not a good communist for my intransigence?
Thank you for your time

I'll break this down into two parts, authority and idolatry
Authority is a value-neutral, metaphysical concept. It is the use of some kind of force to impose a will on others. If you consider yourself a communist, then how do you intend to overthrow capitalism without exerting authority? Engels said it best: «A revolution is certainly the most authoritarian thing there is; it is the act whereby one part of the population imposes its will upon the other part by means of rifles, bayonets and cannon — authoritarian means, if such there be at all». We must come to terms with this, as revolutionary marxists. If we refuse the concept of authority all-together, then all that can happen is that authority is applied against our entire class, for the rest of time. I also live in a first-world country that used to have a fascist dictatorship, and the ~150,000 thousand killed for political reasons, 30,000 disappeared, 500,000 interned in concentration camps, more than 100,000 summary trials, tens of thousands of slaves and the thousands tortured up to the very end can speak to its destructiveness. But it wasn't as simple as "they used authority, therefore all authority (abstractly) is bad". Franco's dictatorship responded to a series of needs that the Spanish and European bourgeoisie had, by the time of their sponsored coup d'etat in 1936, Spain was at the forefront of organization of the working class in Europe, the communist party had hundreds of thousand members if you include their youth wing, and the biggest unions reached the millions, in a country of just under 25 million. Italy, Germany, Austria and Portugal found themselves in a similar resurgence when their fascists took power, in every case financed by their biggest capitalists, national and foreign.
The point I'm getting at is that, if you want to understand class society, you have to go beyond the black-and-white, metaphysical liberal philosophy. Violence can be exerted by multiple classes through their own class organizations, and the character, context and sense of that violence changes accordingly. I'm not saying that all violence committed by workers without exception is wholly good. I'm saying that the relationship each class has with class society modifies the very reasoning and effect of that violence. And no example of violence in history can be really described as senseless. My country's dictatorship did not kill, torture and repress that many people for no reason, the holocaust did not happen because Hitler was an evil entity, and the various proletarian states, past and present, have not exerted their authority senselessly.
In marxist theory there are two very important concepts: the dictatorship of the bourgeoisie (DotB), and the dictatorship of the proletariat (DotP). The DotB is a catch-all term for any state of any form that serves capitalist interests. This is useful because, whether it's a liberal democracy with a strong welfare system, or Pinochet's Chile, they both ultimately serve to protect and expand the interest of the capitalist class. Put another way, the capitalist economy sustains the state and other entities like the media, the military, the government (what we call the suprastructure), while the capitalist economy underneath it all (what we call the infrastructure) maintains its existence. It is a dictatorship because it is one class enacting their own will in their own interests. The DotP is the same concept, but turned on its head. After our class has taken power and has began to build socialism-communism, it is actively enacting their sole will in their own interests. Why would the formerly exploited listen to what their former exploiters want? The proletariat must be able to repress the extant capitalist elements within and the permanently hostile capitalist class without. Dwell on this for a moment. While a DotP fosters democratic mechanisms for its class, the social majority (as all DotP in history have done), it simultaneously exerts its authority on those extraneous to the working class. If you live in a capitalist state, the very same thing is happening, just reversed. The managers of capitalism, i.e. the representatives in liberal democracy, govern for the capitalist class, even representing various sections of that class, while simultaneously repressing or preventing any organization of the working class.
I did not mention Chile as an example for no reason beforehand. When the working class of Chile attempted to build socialism through non-violent means, after the election of Allende (there were many tendencies within Allende's party and among his entire support base but that's beyond this post), they were met with an intervention that did not have any qualms about using violence, kickstarting Pinochet's 17 year long dictatorship, backed by Chilean and USAmerican capitalists, atop the corpses of at least 40,000 executed and/or tortured. Look up the massacre of Estadio Nacional if you're interested, it's where Victor Jara was murdered.
"Authority" in DotP is never as widespread nor as violent, firstly because it doesn't aim to repress the social majority, but rather the small but resourceful capitalist class, and secondly because its "repression" more often than not manifests in our actual goals, which is to build a socialist economy, which would necessarily eliminate the social basis for a capitalist class to exist in the first place. In the USSR, for example, the rich landowner peasants disappeared first an foremost because the structure of land ownership was completely changed, eliminating the source of their power. Any instances of actual violence were mostly against saboteurs during collectivization or during the grain seizures to curb the mass starvation that happened in the cities during the civil war, since no grain made it there. Capitalist authority is meant to keep the mass of working people subservient and exploited, proletarian authority is meant to protect the project of socialism-communism against attacks. It has never been about killing all the rich people, it has been about abolishing the capitalist mode of production and building a new one, one which does not need the oppression of any kind of people to keep functioning.
I recommend the following books if you're interested in sources about "authority" and democracy in DotPs:
The Soviets Expected It, Anna Louise Strong (1941). It is focused on the USSR's lead-up to the fascist invasion, but it contains a few examples from ALS' own, unsupervised, experience with soviet democracy and the general attitude of working people
In North Korea: First Eyewitness Reports, Anna Louise Strong (1949). Same as the previous one, it has a few examples of ALS' unsupervised travels through North Korea before the Korean War that talk about how democracy was set up.
The Triumph of Evil, Austin Murphy (2002). I've said a lot how this author is very annoying about keeping to this useless good vs evil dichotomy when talking about socialism and capitalism, but apart from those sporadic remarks, it's incredibly well researched. It focuses on economic aspects, but chapters 1, 2, especially 3, and 7 all contain analyses on the actual mechanisms of authority that DotP use, taking East Germany as an example. Again though, the author is very annoying as soon as he begins to give his personal opinions on morality.
Stasi State or Socialist Paradise? The German Democratic Republic and What Became of It, Bruni de la Motte and John Green (2015). Pretty self explanatory title, this one goes into more detail about the security apparatus of East Germany. I haven't read this one in full, but it has a dedicated chapter on democracy and the state security service.
Onto idolatry. I promise this part will be shorter.
I've written more in detail about this, but while personality worship is a problem, I don't agree that it leads to the problems you outline. It's undeniable that there have been elements of individual idolatry, but that's neither a reflection of actual power concentration or ever a substitution for the elevation of workers. Leadership in any communist party is always collective, and if it follows Leninist principles of organization even partially, then internal democracy is always guaranteed save for the most extreme of situations. Stalin might have been a popular figure, but the Central Committee he was a part of was not below him, and the periodical Congresses had more authority than the CC or any individual person. ALS mentions how, for example, the 1936 constitution was made. It was a wholly democratic process, more than a hundred thousand suggestions were all recieved and considered by the organs in charge. It was the most progressive constitution in its time, it guaranteed rights many of us still do not have. And that process supposedly happened while the "worship" of Stalin was in full force. Every position in DotPs has some mechanism of recall and accountability, everything is elected and ratified. Can you start a process of recall for any specific member of the state administration in your DotB? In one instance, as ALS says, in the region of Crimea up to half of the elected officials were all recalled in one year.
I keep using the USSR as an example because it's the system I'm most familiar with, but any other DotP you can think of has similar mechanisms and limitations to power. Once again, was there a certain amount of idolatry towards a few individuals? Yes. Was this a harmful vice which created unchecked concentration of power and undue oppression? Most certainly not. Besides this, we're materialists, and we understand that human psychology is largely molded by the underlying material conditions. Focusing on individuals when it comes to these sorts of things is almost inevitable for large groups of people because of how the exploitative economic conditions modify psychological tendencies. It is a remain of liberal ideology for the most part, and it should be fought against. But you can't expect millions of people to change how they view certain processes, changes like those take a lot of time, generations, and education.
I've spent essentially all of my political life within a party structure not very dissimilar from that of Cuba's, the USSR's, China's, the DPRK's, etc, and I can say with full confidence that it is the most democratic and simultaneously productive set of principles you can have in political activity. Compared to liberal democracy, and compared to horizontalist/non-centralized structures, even those employed by anarchists, which I have also experienced, it is still far more democratic and effective at taking into account all input without devolving into a glorified debate club.
I don't think you're a bad communist, having these doubts and talking to other people about it is a very good habit to have. If you still have doubts or want to keep talking about this, feel free to shoot me another ask or a private message :)
#ask#anon#seriousposting#this took quite long to write#I hope you take the time to read it in full anon
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
[C]lass is not an essence but a social classification made by social scientists to explain reality; it is not some inherent nature possessed by the people who are hypothetically divided up according to a scientific assessment of a social reality. In such a context, being conscious of one's membership in a social class, let alone embarking on class struggle, is produced by a mechanism that is based on developing the hypothesis of social classes, which is unified by the concept of class struggle: a revolutionary party. Marx and Engels maintained that the point of a communist party was to organize workers as a class because they understood that the hypothesization of class was in fact a scientific intervention upon the social in much the same way that the hypothesis of the double helix model of genetics, as mentioned above, is an imposition upon crude biological existence.
There are popular strains of first world Marxism (autonomism, communization theories, "left communism") that argue against the above interpretation of class and are thus opposed to the notion that the ultimate meaning of class and class struggle is the business of a party project. My contention, however, is that such an interpretation of class and class struggle, even when it opposes orthodox categories, remains thoroughly economistic because of a reliance on a workerist spontaneity . . .
My position is that class comes into being through a political intervention that declares the meaning of class struggle and intends to impose this meaning upon a conflicted social plane. Such an imposition was also responsible for grasping the foundation of class structure, as analyses such as Marx's Capital demonstrate, but it is not enough to assume that class structure functions abstractly without a lived formation/composition or a political project to determine its conscious articulation as a class for-itself. These class categories are always conflicted, compromised by the detritus of history. To assume that there is a natural unity amongst the entire working class in all social contexts is a grave mistake. Social classes, as we have discussed, are often divided according to interior antagonisms. The point is to accept the fact of this division and locate the most conscious elements of these classes to understand: i) the enemy that is conscious of itself as the ruling class; ii) those who have nothing left to lose but their chains who are also conscious of themselves as a class. Class is thus realized in the crucible of a party project because, whether it be a bourgeois or proletarian party, such projects stamp their cadre with class partisanship.
Thus, class is defined by structure, formation, and consciousness. It is a structure insofar as a mode of production would have no meaning if it did not possess sites of structural occupation that would give it a definition, just as a factory requires pre-existing structural rules that would allow it to function as a factory. It is a formation insofar as the empty structural sites of class are composed of assemblages of real people; the composition is the result of a historical process of formation, the assemblage of multiple identities that are stamped with meaning based on the social context inhabited by the class structure (e.g., a white supremacist society will be a society where the class structure is designed to promote a racist formation). But class is also defined by consciousness, by the awareness of those who inhabit the class structure of their position within this structure, and this consciousness is consummated in a party project. Moreover, since the concept of class is overall a categorical judgment made by social scientists, and since such a judgement is always partisan, it is political inasmuch as it is an economic theory. In this sense the party of a particular class and the ideologues of such a party, call class consciousness into being for-itself. That is, the bourgeois or proletarian subject recognizes themselves as a partisan subject because the meaning of their class consciousness is declared by an organized political faction that provides a line of march. The bourgeois organization or party takes a position on the class structure and proposes a conscious meaning to class formation; the proletarian organization or party expresses a different political line and generates a different conscious meaning.
J. Moufawad-Paul, Politics in Command: A Taxonomy of Economism
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think Mahiru being a literature student is very important to consider when understanding her because Mahiru is a character built around Narrative, well everyone is to some extent (I need to finish that post) but Mahiru especially because she's someone who's main vision of love is influenced by Storytelling.
She sort of subtle but you can see it how she talks about romance, as she says:
Mahiru: [disappointed] I have a pretty poor vocabulary, so I can’t describe it beyond clichéd phrases.
Admitting to only being able to describe love based on commonly repeated ideas in stories and media, soap operas, shoujo manga, films, and so on. The first thing we see Mahiru doing is TIHTBILWY is read.

Mahiru: Yeah, yeah. You’ll deny it at first. I mean, I was like that as well. Before then, I always admired soap operas and shoujo manga because I thought that they depicted a world different from our own.
She's admiring the idealized idea of love rather than the real thing, and you can see that in how she describes it.
Do you really think you know what love is?
If you do, let's just overheat together
Let's have matching pain, this sickness is pretty bad
This idealized idea of a person who can always be there and share in her pain no matter what she does or the circumstances their in.
If they don't then:
Tell me, oh tell me why, won’t you just accept me?
But stories are forms of communication, and stories, especially the highly idealized romance stories Mahiru seems to gravitate towards. Can promote regressive and conservative gender roles and ideas. Ones that Mahiru seems to have accepted she needs to fufill to reach the societal line of acceptability.
Mahiru: Hm? I do~
Cooking, washing, cleaning, I love doing all those sorts of things~
Fufufu, I passed all my self-imposed training to become the perfect wife with flying colours!
Yuno: Wow, incredible…
I don’t know whether to call that old-fashioned or what.
……isn’t it a pain?
TIHTBILWY is presented as a Maganize, it's fundamentally something people buy and subscribe to. Mahiru is very much a character shaped by gendered narratives is society and I think that's interesting.
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
The modern feminism we all see that claims to includes all women while also leaving the most marginalized behind is a recent development. Initially it was only for white women.
When suffragists gathered in Seneca Falls, New York, in July 1848, they advocated for the right of white women to vote. The participants were middle and upper-class white women, a cadre of white men supporters and one African-American male — Frederick Douglass. The esteemed abolitionist had forged a strong working relationship with fellow abolitionists and white women suffragists, including Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony. No Black women attended the convention. None were invited.
According to author Koa Beck, “The goal of white feminism is not to alter the systems that oppress women—patriarchy, capitalism , imperialism—but to succeed within them.” For too long, women from other racial and ethnic backgrounds bought into the false promises of equality.
Now is the time to pull apart the differences between “white feminism” and, as I like to call it, “inclusive feminism,” and hold the former accountable for its inadequacies.
I identify as an inclusive feminist because, in many ways, it allows me to identify with parts of my existence that others do not acknowledge. I face discrimination based on several factors besides my gender identity: skin color, cultural background, accent, religious identity, and even immigration status. My struggles, triumphs, and tribulations result from my efforts to surmount all those inequities, not just my gender. Some may think the term “inclusive feminism” is another phrase in America’s “woke” lexicon. However, it represents my experiences wholly and unapologetically.
I have never felt connected to the ideology of white feminism, which, to me, has exclusively focused on white women and girls. It is less about dismantling broader racial and cultural inequities and more about closing the gaps with preexisting privileged groups—white men versus white women, for example.
White women have benefited tremendously from affirmative action in employment, benefits, education, and more. According to the Economic Policy Institute*, in 2017, “the median annual earnings for full-time, year-round white women workers was just over $46,513. That is 21 percent more than the annual earnings of Black women, whose average salary was $36,735*. Hispanic women earned even less, just $32,002 per year.” Also, looking at men’s income by race tells a story of further advantage for white women. While the acceptance and practice of interracial marriage have increased dramatically, white people are least likely of all racial groups to marry outside their race*. One might conclude that white women marrying white men further increases income disparities between races, given that white men are the highest-earning group in the United States.
White feminism falls into the trap of being performative at times due to its narrow focus on gender alone.
[...]White feminism has also tainted our view of history. For instance, suffragists Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton are typically credited with helping to pass the 19th Amendment, giving women the right to vote. But this version of history conveniently ignores the contributions of BIPOC women, such as African American suffragist and activist Mary Church Terrell, as well as Chinese-born Mabel Ping-Hua Lee and Indigenous activist Gertrude Simmons Bonnin (Zitkála-Šá), to name a few
Time and again, not only have white women in the U.S. leveraged their proximity to white men in order to ground themselves firmly in a society with a clear racial and socioeconomic hierarchy, whether through creating a space within or preserving existing systems of oppression, but they have also imposed or are imposing their version of feminism in other countries around the globe as a blanket solution to women’s liberation.
State wage gaps calculated by National Women’s Law Center (NWLC) are based on 2013-2017 American Community Survey Five-Year Estimates. National wage gap calculated by NWLC is based on 2017 Current Population Survey, Annual Social and Economic Supplement. Earnings are in 2017 dollars. Figures are for full time, year-round workers. ”Lifetime Losses Due to Wage Gap” is what a Black woman would lose, based on today’s wage gap, over a 40-year career. Figures are not adjusted for inflation. Ranks based on unrounded data. “Age at which a Black woman’s career earnings catch up to white, non-Hispanic men’s career earnings at age 60” assumes all workers begin work at age 20. Assuming white, non-Hispanic men have a 40-year career, this is the age at which Black women are able to retire with the same lifetime earnings as their male counterparts.
Wayback link to statistic about white interracial marriage
70 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, sorry if this is intrusive or poorly worded but how do you handle being a lesbian and also a bimbo? Because I've been... not struggling with it but really trying to come to terms with me being a lesbian but also really into kinks that are practically defined by their relation to men and societal roles for them
Oh, you're totally fine! So, the biggest thing to me is that bimbofication and bimbos in general are not defined by their relation to men at all. To me, being a bimbo is about my relationship with my own femininity.
So like, for me... I choose to express it in a hyperfemme, barbie-like way. I wanna be pink and sparkly and get cosmetic surgery and be the best doll I can be. But I'm not doing it for men; I'm doing it for me. And like, I get that society judges anyone that does that but that's because it's a patriarchal society trying to impose its own silly thoughts onto everyone (which is totally rude btw) and act like we all need to play by their rules.
I'm a lesbian because I am attracted to others with strong feminine energy. I'm kinda like, a bimbosexual, if that makes sense. Whether its looks, attitude or both... bimbos are so pretty and hot and yummy to me. How could I not be attracted to them!?
Do you see how like, none of that has anything to do with men at all? I hope it made sense because i feel like I kinda rambled a little. I just really love talking about like bimbo philosophy and stuff!
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
A thing I really love about TBOSAS is its exploration of human nature through the characters, using the ideas of philosophers like Hobbes, Locke, and Rosseau. In fact, it's so important to Suzanne Collins that you make these connections that their most famous works are quoted in the novel's epigraph.
Gaul represents Hobbesian thought in the story, believing humans are hardwired to be cruel, selfish, and willing to kill each other to ensure survival. She tells Snow that the arena is "humanity undressed" and that even Snow, who had the right upbringing and education, quickly becomes a murderer inside the arena (tbosas 243).
It's always been interesting to me that she likens the arena, an environment controlled by the Capitol, to the State of Nature Hobbes writes about.
First of all, the State of Nature is supposed to be a place without any sort of interference, and in an arena, that's just not true; the Capitol controls weapons, food supply, and dangers like mutts. Secondly, the State of Nature was never a real place but more of a thought exercise, but Gaul seems to take this exercise at face value.
In Leviathan, Hobbes says that in the State of Nature, there exists a perpetual state of war, with no moral right or wrong, and to escape this "nasty, brutish, and short" life, humans must create a strong central state to impose order.
Snow's journey in the novel is to decide which worldview he ascribes to, which makes the arrival of Lucy Gray Baird into his life even more important.
Now, Lucy Gray is more in line with Rosseau's view that humans are naturally good, but society is the one that changes that. This is her line of thinking when she tells Snow: "People aren't so bad really[.] It's what the world does to them. Like us, in the arena. We did things in there we'd never have considered if they just left us alone," (tbosas 492).
What I like about TBOSAS is that unlike other prequels centered on the villain, it's not preordained by fate that Snow was meant to be an authoritarian dictator. He has a choice. He meets Lucy Gray when he's leaving childhood, stuck between two forks in the road, and he can choose whether to stay on the right side of the line, as Lucy Gray later mentions. But he decides not to.
He chooses wealth, fame, and power over love and goodness.
It's very telling to me that out in the woods with Lucy Gray, before their relationship quickly sours, he wonders what they should do after they meet their most basic needs. What would they do without books or music? What's the point of survival for its own sake? He even discounts having children with her because he says it would be "too bleak" to condemn a child to such an existence (tbosas 496).
Love is not enough. Not if you subscribe to a worldview where individuals are inherently cruel and if you think control is the only thing preventing chaos. When he turns his gun on Lucy Gray it's the ultimate rejection of her worldview, and his complete turn into Gaul's influence, one where it's every man for himself.
#coriolanus snow#lucy gray baird#the hunger games#the ballad of songbirds and snakes#catching fire#katniss everdeen#peeta mellark#thg#tbosas#i also want to talk about Sejanus bc I think he falls in line with Locke but I didn't want to make this post too long#meta
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
ok i wrote an entire essay on this for class but i keep thinking about it and i really need to get off my chest how utterly devastating it is that antigone truly is doomed by the narrative.
a lot of academics look at her story as an example of athenian literature which opposes the normative gender ideology of their society because antigone is a woman inserting herself into a political sphere with no conventional place for women, especially as it was often held in athenian society that obedience to men was a feminine virtue, which antigone directly subverts by not only standing against creon but doing so publicly.
but, antigone's actions were driven by her will to adhere to the social norm of surviving women in a family performing funerary rites for the deceased men. this isn't really touched upon in sophocles from what i remember, but antigone isn't just determined to complete polynices' funerary rites because he's her brother—the completion of these rites was a position normally held by women of a family, and the responsibilities of daughters to their families wasn't considered extinguished by marriage or any such thing, so even if antigone had been married to haimon by this point the responsibility still would have fallen to her—but she would have felt a duty imposed by the societal norms placed upon women to honour polynices. this therefore obviously creates a conflict — on one hand (μὲν) society expects her to honour her brother's funerary rights, but on the other hand (δὲ) if she does so she's not only publicly disobeying a male authority figure but in a way which threatens to prevent her from marrying and preserving her family line, which was also considered a daughter's responsibility.
in choosing to disobey creon, antigone has been rendered useless as a bride in his eyes, because this rejection of the status quo has resulted in her trespass of the societal boundaries of her gender and she's therefore no longer considered able to serve the expectations of women, so creon declares that she's to die. but if she hadn't disobeyed him, socially she's still failed to uphold the familial responsibilities demanded of her following the normative gender ideology, and so even if no one would have spoken up directly about it because she's followed creon's command, either by wilful perception or subconscious judgment she likely would have been seen as a traitor to her family on some level regardless.
what this means is that not only is antigone truly doomed by the narrative, where her choices render her a servant to social expectations of women whether she outright defies authority or unwillingly defies her womanly responsibilities, but that her entire narrative is ingrained with the very gender ideology that dooms her to begin with.
142 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm curious, what are the main reasons why Dean is your favorite canon bisexual in media? Love your meta and that video btw
Ooooo, anon, thank you for the kind words and for giving me an excuse to talk about my love for bisexual icon Dean Winchester <3
I'm going to be really annoying (sorry) and quote part of my meta first. It summarizes and articulates many of my thoughts on this. And then to further answer your question I'll add a bit under it!
From the very beginning, Dean Winchester has been a character tied to classic elements of American masculinity. He was introduced with a superficial veneer involving those elements, but almost immediately the early episodes provide a look at the complexity of his character underneath it. Over the years, that complexity was further explored, and he came to embody a study in things society would often have us think should be incompatible contrasts: the gruffness and grit of hunting life and its associated masculine iconography, paired with his open and deep emotional care for the world; unabashed love for classic rock, superheroes, and horror movies, as well as unabashed joy connected to TV dramas, chick flicks, and childhood favorites like Scooby-Doo; life on the road with a muscle car, but the desire for a home base with creature comforts he can make his own; motivation to always help people, but the clear longing for balance with personal domesticity and relaxation so he could save not only others but also himself.
As a whole, his character functions as an effective deconstruction of toxic masculinity and stereotypical American heroism. And while much of Dean’s most masculine traits and interests are said to come from his father’s influence, part of his journey is loving those parts of himself on their own merit not because he ever had to but because he wants to. He is not his father, and he redefines those valued parts of his identity so they are his and his alone. He also crucially learns to recognize and joyfully embody that those masculine traits were never all that he had to be, working through and overcoming shame and hesitancy along the way. The result? He’s “good with who he is.”
He and the audience are encouraged to see that there are no rules his identity and interests must subscribe to, on a micro or a macro level. The message is to disregard predetermined destiny or duty. Free will means his life is his to determine, his family can be what he makes of it and how he defines it, and what he needs and wants do not ever have to be mutually exclusive. Dean’s journey is about freedom from outwardly-imposed limitations–whether those limitations come from his father’s example and the God altering his story, or from the pervasive societal ideals and network/executive interference outside of it. Dean can and should contain multitudes, all at once.
In this way, Dean’s story is a powerfully queer narrative that acts as metacommentary. In the fullness of its execution, it is also specifically a deeply bisexual narrative.
The not-so-hidden truth is that Dean is canonically a bisexual man. His story was afforded something that’s rare for most characters and almost nonexistent for queer ones: fifteen years of lengthy, nuanced development.
[...]
Again: Dean’s identity journey is about how he can and does contain the capacity for multitudes, and it’s part of what makes him such a compelling character. He can like “this” and “that.” He can be attracted to women and men. Or, as writer Ben Edlund and director Phil Sgriccia said in a DVD commentary, Dean has “the potential for love in all places.”
I wanted to include the above verbatim because it spells out something specific: Dean's narrative is bisexual in its bones. Supernatural evolved to become a queer text, but the specific ways the show and Dean as a character evolved are very intertwined with and informed by the fact that Dean is a masculine bisexual man. SPN is a story that was not meant to be about being queer, but as it became about freedom through free will, those themes were then leveraged and emphasized in connection to queerness because of Destiel. And by the end, the free will narrative and Dean's journey as a bi man are utterly inseparable, because Dean's fight for true freedom is tied to his love for a man and their untraditional family in a way that higher forces are trying to hinder.
You cannot cut out or edit or remove Dean's bisexuality from the story, or several narratives and plot lines (not just Destiel) would at minimum be misunderstood or at maximum fall apart. And yet, simultaneously? Dean's bisexuality is also far from being the sole important thing about his character because he is written with such nuanced complexities and across so many years of material.
Of course, add onto this the overall unique situation that surrounds Supernatural as a piece of media. People talk at length about how there will never be anything like it again, including me; that's obviously true from multiple different angles and for multiple different reasons, with Destiel being prime amongst them. But a related yet distinctly significant branch of that topic is there will never be another bisexual character who is written and evolves quite like Dean.
Was Dean supposed to be bisexual from the very start, out of the mind of Kripke? Who can know for sure, but probably not. Were certain writers and members of production deliberately putting more queercoding and subtext into Dean's character/story from the very start? Who can know for sure, but potentially yes, and certainly the answer becomes unarguably definitely yes the farther you get into the show. That's part of my love and passion for him too, because all of that is deeply unique and incredibly cool.
Dean's bisexuality evolved in a way that (against all odds) actually feels organic, seamless, and like it's simply a part of his character that's been there all along. The effect when you look at Supernatural as a whole body of work is that Dean's always been bi, and his expressions of and acknowledgements of that part of him ebb and flow depending on situation–which is a very relatable notion for many queer people. And as those writing the show became more committed and certain about that piece of who Dean is, so did he, in nuanced and subtle ways skillfully embedded into his story by design. It's bafflingly, impressively cohesive; gives him an incredibly realistic feel; matches his overall character growth; and rings true to his demographic, age, personality, and experiences.
Dean and his story and the situation(s) surrounding both are simply incomparable, and that will be true forever ¯\_(ツ)_/¯
...also. Well. I simply love him, y'know? For even more reasons unconnected to this. How can you not, right? :')
Thank you for asking, and thanks for reading this bi Dean manifesto!
Putting my video that you mentioned here for anyone who's not watched it:
youtube
My new magnum opus, please stream, etc.
(or watch on Tumblr here)
#bisexual dean winchester#dean is bi#bi dean meta#bi dean winchester#dean winchester is bi#supernatural#spn meta#char writes things#God I LOOOOOVE HIIIIMMMM#dean#anonymous#yes I used like 5 dean is bi tags. I'm valid. leave me alone
296 notes
·
View notes
Text
The extreme of the male culture has become a grotesque caricature of part of the potential inherent in every human being, whether female or male. Why are so many blind to the grotesqueness of the tough, hard, super-balls, insensitive, unemotional male image in John Wayne, James Bond, the Marines, etc.? Or so blind to the grotesqueness of the super-mind, intellect, reasoning, and abstraction removed from any connection with life in the "think tanks" of the Rand Corporation, the academy, the corporations, the Army Corps of Engineers, most scientific research, war games strategies, etc.?
The extreme of the female culture has also become a grotesque caricature of the potential inherent in every human being. Why are so many blind to the grotesqueness of the super-sex goddesses, the sex-object removed from mind and emotion, the motherhood myth, the pettily personal existence which is not allowed to transcend itself into the individual autonomous existence, the enforced delicacy without full feeling and intensity, the sentiment turned into bathos because removed from direct sexual or creative expression, etc.?
The abstractions of male and female are extreme and many people are not molded wholly into either category—there is a great deal of overlap. But no one in the society is allowed to be a whole human being as long as the tyranny of the male and female culture or sex role split exists.
Recently there has been an unfortunate reaction among some women's liberationists and feminists. Some women have begun to call anything which they do not like "male." They seem to think that anything that has been defined as a "male quality" is inherently bad. A woman who is strong or takes initiative is told that she is "acting like a man" or "talking like a man." The crushing of initiative and strength and self-expression in women is now being done by other women in the movement under the guise of "anti-elitism," "anti-male-identification," and "collective self-suppression." It would be a tragedy if women were to make our oppressed state into a virtue and a model of humanity and the new society. We need to sift out what is good in our imposed definition as females and to honestly examine what is stupid and self-destructive. We need also to sift out what is good in what has been defined as male and therefore denied expression in us. We need no more glorification of the oppressed and their "super-soul" and "superior" culture, for that will blind us to our weaknesses and only lead us back into the same mire from which we have been trying to free ourselves.
-Barbara Burris, ‘The Fourth World Manifesto’ in Radical Feminism, Koedt et al (eds.)
27 notes
·
View notes