#high quality low cost living
Text

No spend activities
Breaking the cycle of always buying things, being in malls and having to spend money to be happy is one of the best things we can do to set ourselves free from the blind consumerism that society is drowning in.
#free#free range human#happiness#high quality low cost living#blind consumerism#joy#nature#love#wisdom#priceless#empathy
1 note
·
View note
Text
On Cosplay, Fast Fashion, & Waste
Fast fashion and disposable outfits in cosplay community spaces give me anxiety. Seeing people openly talk about throwing their "trashed" cosplay away after a single con makes me sad. Some costumes are crafted with such low durability that they fall apart beyond repair if you look at them the wrong way. I've met a ton of other cosplayers whose idea of "cosplay repair" ends with a stapler and some hot glue.
I never ever ever ever want to shame people for not knowing something. Crafting is hard. Making a low-quality costume isn't a sin or a crime. If you're new and still learning and don't really know what you're doing yet, that's fine! No harm, no foul, no bruise.
The cosplayers who do make me grouchy, however, are the ones who are unwilling to try. The ones who are flippant about throwing away a cosplay without trying to mend it, repurpose it, reuse it, or pass it along. The ones who intentionally make a costume just durable enough to last a single day, then toss it in the trash with zero thought.
My sewing and costuming experience started when I joined the ren faire, and I had to make my costumes sturdy enough to survive multiple weeks of heavy use, with the durability and freedom of movement to allow sword fighting on the living chessboard. I was taught how to shop for inexpensive fabrics and materials, but use high-quality, long-lasting techniques so that my costumes didn't disintegrate after a single day of performing. I have made extremely durable, cost-effective costumes out of bedsheets and thrift store fabric, as have many of my friends.
That experience has carried over into my cosplay. I am not happy with a costume unless it can go through three consecutive days of stage combat and high-intensity walking around outside in the heat, go through the washer and dryer, and come out completely unscathed.
Again, I never want to needlessly shit on other people's cosplay. Cosplay gatekeeping sucks and is no fun for anyone. At the same time, fast fashion is just as rampant in cosplay as it is everywhere else, and it sucks to see how wasteful it is.
You can make things durable even with cheap materials. Stop making flimsy costumes that you're just going to toss. Stop making piles and piles of waste. Please stop buying fabric just to slap a costume together with glue and throw it in the trash. If you are going to invest time and money into making something by hand, make it durable and comfy and worth the effort.
Even if you only want to personally wear it once, you can sell it, give it away, trade it, do something other than toss it in the trash. Show some love to your costumes, show some love to the planet, pick one action you can take to make your cosplay a little less wasteful. Being obsessed with the myth of a "personal carbon footprint" isn't helpful, but we as cosplayers should try to at least make things that'll last longer than 24 hours.
I understand that sewing can be incredibly intimidating, but basic stitching really isn't that complicated if you have a guide and the right tools. I personally need assistive devices for sewing thanks to my hand tremors and tendonitis, but those tools do exist, and can make things easier for both disabled and newbie sewists. I use rotary cutters instead of scissors, I keep a supply of needle threaders on hand, I have multiple little gadgets that help me sew in a straight line so my shaking hands don't screw everything up. There are tons of tools available, tons of tutorials online, and if you're interested in learning, there's a whole world out there to explore.
If you don't want to do all the crafting yourself, that's totally fine, but if you are going to hand-make your costume, you should try and make it durable. It's better for the planet and it's way less stressful to go to an event when you know your costume won't fall apart on the con floor.
If you have zero idea where to start, here are some books with crafting techniques I've found very useful, both in cosplay and regular household sewing I do for my family:
Make, Sew and Mend: Traditional Techniques to Sustainably Maintain and Refashion Your Clothes, by Bernadette Banner (who also has an incredible YouTube channel)
Cosplay Fabric FX: Painting, Dyeing & Weathering Costumes Like a Pro, by Julianna Franchini
Creative Cosplay: Selecting & Sewing Costumes Way Beyond Basic, by Amanda Haas
Level Up! Creative Cosplay: Costume Design & Creation, SFX Makeup, LED Basics & More, by Amanda Haas
464 notes
·
View notes
Text
Better failure for social media
Content moderation is fundamentally about making social media work better, but there are two other considerations that determine how social media fails: end-to-end (E2E), and freedom of exit. These are much neglected, and that’s a pity, because how a system fails is every bit as important as how it works.
Of course, commercial social media sites don’t want to be good, they want to be profitable. The unique dynamics of social media allow the companies to uncouple quality from profit, and more’s the pity.
Social media grows thanks to network effects — you join Twitter to hang out with the people who are there, and then other people join to hang out with you. The more users Twitter accumulates, the more users it can accumulate. But social media sites stay big thanks to high switching costs: the more you have to give up to leave a social media site, the harder it is to go:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
Nature bequeaths some in-built switching costs on social media, primarily the coordination problem of reaching consensus on where you and the people in your community should go next. The more friends you share a social media platform with, the higher these costs are. If you’ve ever tried to get ten friends to agree on where to go for dinner, you know how this works. Now imagine trying to get all your friends to agree on where to go for dinner, for the rest of their lives!
But these costs aren’t insurmountable. Network effects, after all, are a double-edged sword. Some users are above-average draws for others, and if a critical mass of these important nodes in the network map depart for a new service — like, say, Mastodon — that service becomes the presumptive successor to the existing giants.
When that happens — when Mastodon becomes “the place we’ll all go when Twitter finally becomes unbearable” — the downsides of network effects kick in and the double-edged sword begins to carve away at a service’s user-base. It’s one thing to argue about which restaurant we should go to tonight, it’s another to ask whether we should join our friends at the new restaurant where they’re already eating.
Social media sites who want to keep their users’ business walk a fine line: they can simply treat those users well, showing them the things they ask to see, not spying on them, paying to police their service to reduce harassment, etc. But these are costly choices: if you show users the things they ask to see, you can’t charge businesses to show them things they don’t want to see. If you don’t spy on users, you can’t sell targeting services to people who want to force them to look at things they’re uninterested in. Every moderator you pay to reduce harassment draws a salary at the expense of your shareholders, and every catastrophe that moderator prevents is a catastrophe you can’t turn into monetizable attention as gawking users flock to it.
So social media sites are always trying to optimize their mistreatment of users, mistreating them (and thus profiting from them) right up to the point where they are ready to switch, but without actually pushing them over the edge.
One way to keep dissatisfied users from leaving is by extracting a penalty from them for their disloyalty. You can lock in their data, their social relationships, or, if they’re “creators” (and disproportionately likely to be key network nodes whose defection to a rival triggers mass departures from their fans), you can take their audiences hostage.
The dominant social media firms all practice a low-grade, tacit form of hostage-taking. Facebook downranks content that links to other sites on the internet. Instagram prohibits links in posts, limiting creators to “Links in bio.” Tiktok doesn’t even allow links. All of this serves as a brake on high-follower users who seek to migrate their audiences to better platforms.
But these strategies are unstable. When a platform becomes worse for users (say, because it mandates nonconsensual surveillance and ramps up advertising), they may actively seek out other places on which to follow each other, and the creators they enjoy. When a rival platform emerges as the presumptive successor to an incumbent, users no longer face the friction of knowing which rival they should resettle to.
When platforms’ enshittification strategies overshoot this way, users flee in droves, and then it’s time for the desperate platform managers to abandon the pretense of providing a public square. Yesterday, Elon Musk’s Twitter rolled out a policy prohibiting users from posting links to rival platforms:
https://web.archive.org/web/20221218173806/https://help.twitter.com/en/rules-and-policies/social-platforms-policy
This policy was explicitly aimed at preventing users from telling each other where they could be found after they leave Twitter:
https://web.archive.org/web/20221219015355/https://twitter.com/TwitterSupport/status/1604531261791522817
This, in turn, was a response to many users posting regular messages explaining why they were leaving Twitter and how they could be found on other platforms. In particular, Twitter management was concerned with departures by high-follower users like Taylor Lorenz, who was retroactively punished for violating the policy, though it didn’t exist when she violated it:
https://deadline.com/2022/12/washington-post-journalist-taylor-lorenz-suspended-twitter-1235202034/
As Elon Musk wrote last spring: “The acid test for two competing socioeconomic systems is which side needs to build a wall to keep people from escaping? That’s the bad one!”
https://twitter.com/elonmusk/status/1533616384747442176
This isn’t particularly insightful. It’s obvious that any system that requires high walls and punishments to stay in business isn’t serving its users, whose presence is attributable to coercion, not fulfillment. Of course, the people who operate these systems have all manner of rationalizations for them.
The Berlin Wall, we were told, wasn’t there to keep East Germans in — rather, it was there to keep the teeming hordes clamoring to live in the workers’ paradise out. In the same way, platforms will claim that they’re not blocking outlinks or sideloading because they want to prevent users from defecting to a competitor, but rather, to protect those users from external threats.
This rationalization quickly wears thin, and then new ones step in. For example, you might claim that telling your friends that you’re leaving and asking them to meet you elsewhere is like “giv[ing] a talk for a corporation [and] promot[ing] other corporations”:
https://mobile.twitter.com/mayemusk/status/1604550452447690752
Or you might claim that it’s like “running Wendy’s ads [on] McDonalds property,” rather than turning to your friends and saying, “The food at McDonalds sucks, let’s go eat at Wendy’s instead”:
https://twitter.com/doctorow/status/1604559316237037568
The truth is that any service that won’t let you leave isn’t in the business of serving you, it’s in the business of harming you. The only reason to build a wall around your service — to impose any switching costs on users- is so that you can fuck them over without risking their departure.
The platforms want to be Anatevka, and we the villagers of Fiddler On the Roof, stuck plodding the muddy, Cossack-haunted roads by the threat of losing all our friends if we try to leave:
https://doctorow.medium.com/how-to-leave-dying-social-media-platforms-9fc550fe5abf
That’s where freedom of exit comes in. The public should have the right to leave, and companies should not be permitted to make that departure burdensome. Any burdens we permit companies to impose is an invitation to abuse of their users.
This is why governments are handing down new interoperability mandates: the EU’s Digital Markets Act forces the largest companies to offer APIs so that smaller rivals can plug into them and let users walkaway from Big Tech into new kinds of platforms — small businesses, co-ops, nonprofits, hobby sites — that treat them better. These small players are overwhelmingly part of the fediverse: the federated social media sites that allow users to connect to one another irrespective of which server or service they use.
The creators of these platforms have pledged themselves to freedom of exit. Mastodon ships with a “Move Followers” and “Move Following” feature that lets you quit one server and set up shop on another, without losing any of the accounts you follow or the accounts that follow you:
https://codingitwrong.com/2022/10/10/migrating-a-mastodon-account.html
This feature is as yet obscure, because the exodus to Mastodon is still young. Users who flocked to servers without knowing much about their managers have, by and large, not yet run into problems with the site operators. The early trickle of horror stories about petty authoritarianism from Mastodon sysops conspicuously fail to mention that if the management of a particular instance turns tyrant, you can click two links, export your whole social graph, sign up for a rival, click two more links and be back at it.
This feature will become more prominent, because there is nothing about running a Mastodon server that means that you are good at running a Mastodon server. Elon Musk isn’t an evil genius — he’s an ordinary mediocrity who lucked into a lot of power and very little accountability. Some Mastodon operators will have Musk-like tendencies that they will unleash on their users, and the difference will be that those users can click two links and move elsewhere. Bye-eee!
Freedom of exit isn’t just a matter of the human right of movement, it’s also a labor issue. Online creators constitute a serious draw for social media services. All things being equal, these services would rather coerce creators’ participation — by holding their audiences hostage — than persuade creators to remain by offering them an honest chance to ply their trade.
Platforms have a variety of strategies for chaining creators to their services: in addition to making it harder for creators to coordinate with their audiences in a mass departure, platforms can use DRM, as Audible does, to prevent creators’ customers from moving the media they purchase to a rival’s app or player.
Then there’s “freedom of reach”: platforms routinely and deceptively conflate recommending a creator’s work with showing that creator’s work to the people who explicitly asked to see it.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
When you follow or subscribe to a feed, that is not a “signal” to be mixed into the recommendation system. It’s an order: “Show me this.” Not “Show me things like this.”
Show.
Me.
This.
But there’s no money in showing people the things they tell you they want to see. If Amazon showed shoppers the products they searched for, they couldn’t earn $31b/year on an “ad business” that fills the first six screens of results with rival products who’ve paid to be displayed over the product you’re seeking:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
If Spotify played you the albums you searched for, it couldn’t redirect you to playlists artists have to shell out payola to be included on:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/09/12/streaming-doesnt-pay/#stunt-publishing
And if you only see what you ask for, then product managers whose KPI is whether they entice you to “discover” something else won’t get a bonus every time you fatfinger a part of your screen that navigates you away from the thing you specifically requested:
https://doctorow.medium.com/the-fatfinger-economy-7c7b3b54925c
Musk, meanwhile, has announced that you won’t see messages from the people you follow unless they pay for Twitter Blue:
https://www.wired.com/story/what-is-twitter-blue/
And also that you will be nonconsensually opted into seeing more “recommended” content from people you don’t follow (but who can be extorted out of payola for the privilege):
https://www.socialmediatoday.com/news/Twitter-Expands-Content-Recommendations/637697/
Musk sees Twitter as a publisher, not a social media site:
https://twitter.com/elonmusk/status/1604588904828600320
Which is why he’s so indifferent to the collateral damage from this payola/hostage scam. Yes, Twitter is a place where famous and semi-famous people talk to their audiences, but it is primarily a place where those audiences talk to each other — that is, a public square.
This is the Facebook death-spiral: charging to people to follow to reach you, and burying the things they say in a torrent of payola-funded spam. It’s the vision of someone who thinks of other people as things to use — to pump up your share price or market your goods to — not worthy of consideration.
As Terry Pratchett’s Granny Weatherwax put it: “Sin is when you treat people like things. Including yourself. That’s what sin is.”
Mastodon isn’t perfect, but its flaws are neither fatal nor permanent. The idea that centralized media is “easier” surely reflects the hundreds of billions of dollars that have been pumped into refining social media Roach Motels (“users check in, but they don’t check out”).
Until a comparable sum has been spent refining decentralized, federated services, any claims about the impossibility of making the fediverse work for mass audiences should be treated as unfalsifiable, motivated reasoning.
Meanwhile, Mastodon has gotten two things right that no other social media giant has even seriously attempted:
I. If you follow someone on Mastodon, you’ll see everything they post; and
II. If you leave a Mastodon server, you can take both your followers and the people you follow with you.
The most common criticism of Mastodon is that you must rely on individual moderators who may be underresourced, incompetent on malicious. This is indeed a serious problem, but it isn’t the same serious problem that Twitter has. When Twitter is incompetent, malicious, or underresourced, your departure comes at a dear price.
On Mastodon, your choice is: tolerate bad moderation, or click two links and move somewhere else.
On Twitter, your choice is: tolerate moderation, or lose contact with all the people you care about and all the people who care about you.
The interoperability mandates in the Digital Markets Act (and in the US ACCESS Act, which seems unlikely to get a vote in this session of Congress) only force the largest platforms to open up, but Mastodon shows us the utility of interop for smaller services, too.
There are lots of domains in which “dominance” shouldn’t be the sole criteria for whether you are expected to treat your customers fairly.
A doctor with a small practice who leaks all ten patients’ data harms those patients as surely as a hospital system with a million patients would have. A small-time wedding photographer who refuses to turn over your pictures unless you pay a surprise bill is every bit as harmful to you as a giant chain that has the same practice.
As we move into the realm of smalltime, community-oriented social media servers, we should be looking to avoid the pitfalls of the social media bubble that’s bursting around us. No matter what the size of the service, let’s ensure that it lets us leave, and respects the end-to-end principle, that any two people who want to talk to each other should be allowed to do so, without interference from the people who operate their communications infrastructure.
Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
Heisenberg Media (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Elon_Musk_-_The_Summit_2013.jpg
CC BY 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
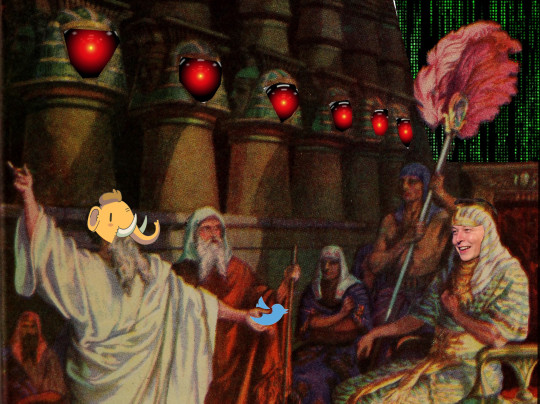
[Image ID: Moses confronting the Pharaoh, demanding that he release the Hebrews. Pharaoh’s face has been replaced with Elon Musk’s. Moses holds a Twitter logo in his outstretched hand. The faces embossed in the columns of Pharaoh’s audience hall have been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from 2001: A Space Odyssey. The wall over Pharaoh’s head has been replaced with a Matrix ‘code waterfall’ effect. Moses’s head has been replaced with that of the Mastodon mascot.]
#pluralistic#e2e#end-to-end#freedom of reach#mastodon#interoperability#social media#twitter#economy#creator economy#artists rights#content moderation#como#right of exodus#let my tweeters go#exodus#right of exit#technological self-determination
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Once more social media companies are starting down the path of "hm, what if we roll in a feature... everyone will hate..."
so I am again reposting my very basic in progress to being polished HOW TO MAKE A ZINE post
I will expand it when the blog launches and I don't know when the blog launches, but this will get you started. Or at least closer.
...and now...

... a ramble...

For Netherworld Post Office:
I'm going to stay where I am on various platforms
Continue building our "Let's Stay in Touch Occasionally" mailing list
I'm fleshing out a blog that is 2/3rds "slice of life stories of monsters living in paradise stories and comics," 2/3rds "Here is how and what to mail, how to make it fun and vibrant, cheaply" and 2/3rds ramble. Also discount math advisories.
The blog will be on a WordPress site. Free, no subscriptions necessary, open to read.
I'm working on a $2/month (USA postage included, global shipping a bit extra but not much) zine. Full color, 8 pages, decorated envelope, discussing Halloween, mail, and Halloween mail.
Spoiler if you're working on a zine and scrambling "how can that zine be $2?!" we lose about $0.05 - $0.10/zine and this is an acceptable loss. Marketing costs money. The strategy is people will subscribe to the zine and then once or twice a year say "oh wait I need a birthday card, I should get it from Netherworld Post" and that 1-2x year order will cover the loss + add profit to our coffers.
This point is made because I'm not seeking to start a pricing war on zines.
I AM seeking to make something fun and enjoyable and as affordable as possible so as many people as possible will say "huh that's neat."
When the blog goes live and the page about how to make a zine goes live, I'll go into the numbers on how I am making it and offer ideas and tips on how You as a Maker of Things For Sale can make one
I'll also offer tips and ideas on how You as a Maker of Things Not Necessarily For Sale can make it too, it's not exclusively for art shops.
There are no zine laws.
The split is purely "do you care about shaving $0.24 per outbound envelope because you're going to send lots or not"

Here is my reality:
As a person, I enjoy Tumblr. As a business, it's been very good to us.
Our Instagram isn't going anywhere. I'm preparing for the eventual bleed of people using it. Maybe it'll affect us, maybe it won't.
This is NOT a doom-and-gloom EVERYTHING IS DYING post. I'm not nearly online enough or smart enough to offer thoughts beyond general vibes and feelings.
I am saying "enough people have commented enough times they enjoy my business ramblings that I want to share what I know/am doing because I strongly feel a diversification of outlets helps more folk make more art and more folks making more art means there is more art and I'm going to enjoy it."

It takes at least a year -- far more likely a few years -- to build up a sizable social media following.
Sizable = "posting on Platform is more valuable to meeting our goals than Doing Something Else"
You can throw money at the problem (ads and/or hiring a consultant and/or an agency). This will scale you up far faster because they'll build the shortcuts do the research and the yadda yadda.
The reason Netherworld Post Office is able to offer very inexpensive, very high quality greeting cards, at a very low shipping price is because we are largely focusing on "What can we do in-house? How can we get smarter, more clever with our very limited resources?"
We just wrapped up Phase 01 and are about to head into Phase 02 on this plan. It's working well.
Slowly
An agreeable pace but well.

The new app-of-the-day, Cara.
Will it be great? No clue!
Will we post there? Probably not!
Why am I offering this part to the news above? I don't want to gate-keep information I have! Recurring theme to my rambles :)
There is a significant chance that someone who says "It makes sense for my personal goals to make Cara" and then that's great.
The key to building a shop or ongoing project is realizing:
There are many paths available
You have to figure out what path is right for you
It will be a unique combination exclusive to you -- elements can be shared but ultimately every path is going to have it's own unique aspects
This path will change over time
You have to tinker constantly
That's part of the fun :)

Final Link List Now That I Am Done Talking Above Image is My Producer's Reaction When I Finish Talking
Netherworld Post Office shop
Netherworld Post Office Let's Occasionally Stay in Touch email signup
Netherworld Post Office first draft writeup on how to make zines, a tumblr post, because I love zines
Netherworld Post Office final disclaimer for reasons: Your art path is your own, it will look unique to you, it will share elements with many other folks but at the very core? It is unique to you :) All above is shared purely in hopes of giving back to the small art shop community that helped get me to where I am
Cheers everyone
I hope we all make it :)
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Jake Johnson
Common Dreams
Sept. 5, 2023
"We are prepared to do whatever it takes, even get arrested in an act of civil disobedience, to stand up for our patients," said one Kaiser Permanente worker.
Dozens of healthcare workers were arrested in Los Angeles on Monday after sitting in the street outside of a Kaiser Permanente facility to demand that providers address dangerously low staffing levels at hospitals in California and across the country.
The civil disobedience came as the workers prepared for what could be the largest healthcare strike in U.S. history. Late last month, 85,000 Kaiser Permanente employees represented by the Coalition of Kaiser Permanente Unions began voting on whether to authorize a strike over the nonprofit hospital system's alleged unfair labor practices during ongoing contract negotiations.
The current contract expires on September 30.
"We are burnt out, stretched thin, and fed up after years of the pandemic and chronic short staffing," Datosha Williams, a service representative at Kaiser Permanente South Bay, said Monday. "Healthcare providers are failing workers and patients, and we are at crisis levels in our hospitals and medical centers."
"Our employers take in billions of dollars in profits, yet they refuse to safely staff their facilities or pay many of their workers a living wage," Williams added. "We are prepared to do whatever it takes, even get arrested in an act of civil disobedience, to stand up for our patients."

Kaiser Permanente reported nearly $3.3 billion in net income during the first half of 2023. In 2021, Kaiser CEO Greg Adams brought in more than $16 million in total compensation.
According to the Coalition of Kaiser Permanente Unions, the hospital system "has investments of $113 billion in the U.S. and abroad, including in fossil fuels, casinos, for-profit prisons, alcohol companies, military weapons, and more."
Healthcare workers, meanwhile, say they're being overworked and underpaid, and many are struggling to make ends meet amid high costs of living.
"We have healthcare employees leaving left and right, and we have corporate greed that is trying to pretend that this staffing shortage is not real," Jessica Cruz, a nurse at Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, toldLAist.
"We are risking arrest, and the reason why we're doing it is that we need everyone to know that this crisis is real," said Cruz, who was among the 25 workers arrested during the Labor Day protest.

A recent survey of tens of thousands of healthcare workers across California found that 83% reported understaffing in their departments, and 65% said they have witnessed or heard of care being delayed or denied due to staff shortages.
Additionally, more than 40% of the workers surveyed said they feel pressured to neglect safety protocols and skip breaks or meals due to short staffing.
"It's heartbreaking to see our patients suffer from long wait times for the care they need, all because Kaiser won't put patient and worker safety first," Paula Coleman, a clinical laboratory assistant at Kaiser Permanente in Englewood, Colorado, said in a statement late last month. "We will have no choice but to vote to strike if Kaiser won't bargain in good faith and let us give patients the quality care they deserve."
A local NBC affiliate reported Monday that 99% of Colorado Kaiser employees represented by SEIU Local 105 have voted to authorize a strike.
Our work is licensed under Creative Commons (CC BY-NC-ND 3.0). Feel free to republish and share widely.
389 notes
·
View notes
Text
Completely stealing this summary from Reddit so here's the link to that (new link since original reddit post with this summary was deleted)
'Dragon Age Dreadwolf' was internally planned for a September 2023 release but got pushed back to 2024. Currently it's planned for Summer 2024 at the earliest but could be pushed back even further (likely by the end of next year, but possibly even as late as March 2025, aka the end of EA’s fiscal).
Incidentally, the next Mass Effect has been pushed further as well, as some people from the Mass Effect team have been pulled to work on Dragon Age instead.
As for EA, they have started to acknowledge internally that Apex Legends, their major money-maker, is on the decline. The live-service hit has historically been able to offset the costs of their other studios, including BioWare
On that note, the publisher has also recently restructured its operations. Unlike before, EA Sports is now evaluated separately from their other gaming efforts, which now fall under EA Entertainment. By decoupling FIFA and Madden from the rest, studios like BioWare will now be under more pressure to justify themselves to the publisher and its shareholders.
Consequently, BioWare now finds itself in a bottom rung position at EA, making them the most obvious candidate for layoffs. Morale is low, these firings won’t help, and Jeff does not feel optimistic about the studio’s longterm future, particularly if Dreadwolf doesn’t land.
I post this to say this confirms my unfortunate belief that Dragon Age Dreadwolf has to be the best game Bioware has ever done (which frankly isn't gonna happen) and unfortunately kinda has to have the combination of a mass appeal, high quality, and mainstream success Bioware hasn't had in YEARS. And if Dreadwolf doesn't do what it needs to do, well the next Mass Effect can't be guaranteed.
I will say it'll definitely suck if Bioware as a whole ends up going under, but it'll suck hard cause EA caused it with their practice of neutering and changing so much of what made Bioware work as a major gaming company for so long. And now it's such a shell of what it was before this attempt to save it puts so much pressure the team doesn't deserve.
398 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Back in the 21st century, however, not everything was rosy. Indeed, the two-part "Star Trek: Deep Space Nine" episode "Past Tense" (January 2 and 9, 1995) threw its main characters back in time — via a transporter accident — to the year 2024 when everything seemed to be at its worst. Earth in 2024 was overrun with poverty, and Captain Sisko (Avery Brooks) had to explain to Dr. Bashir (Alexander Siddig) that housing insecurity had reached epidemic proportions. Indeed, the population of unemployed and unhoused people in major cities had reached such high levels, that the American government had built special "Sanctuary Districts" where the unhoused were rounded up and imprisoned in a ghetto.
The mentally ill weren't treated, and the hungry were fed with a malfunctioning rationing system. It wouldn't be until an activist named Gabriel Bell rose up in protest and led a riot against the police that conditions would change. The Bell Riots were said to be a significant part of Trek's history.
Given the recent news that Governor Gavin Newsom has signed an executive order to sweep the state of unhoused encampments, "Past Tense" — set in 2024 — is beginning to feel weirdly prescient.
Housing insecurity and homelessness, it should be said, is a serious problem in California. Rents are high, and there is little effort made to provide low-cost housing or shelters for the state's many unhoused citizens. At last count, there were over 181,000 unhoused people in the state, 28% of the entire country's unhoused population. Many people live in tents, often set up under freeways or other sheltered areas, and form miniature encampments. There is little sanitation in such encampments, and the quality of life isn't great. Every so often, the police department is called in to sweep these encampments off the streets, forcing the people to move on to another neighborhood. However, they are not taken to shelters but merely told to go elsewhere. They then set up camps under another freeway and the cycle continues.
On July 25, Gavin Newsom signed an order that would only exacerbate the problem, an order stemming from a Supreme Court Decision that allowed states to ban public sleeping at their own discretion. While Newsom has pledged billions of dollars to build shelters, the measure to "sweep the streets" of encampments has been called a wonton and unhelpful measure by critics.
It's a strange coincidence that "Star Trek" should have written a story, back in 1995, about how 2024 will be the year the housing insecurity problem in the United States will boil over. Gavin Newsom has essentially signed a measure that opens the door for the cruel "Sanctuary Districts" seen in "Deep Space Nine." If Newsome is a "DS9" fan, he seems to have taken the wrong lessons from "Past Tense."
(…)
On the DVD commentary track for "Past Tense," the episode's writers — Robert Hewitt Wolfe, Ira Steven Behr, and René Echevarria — said they were inspired by a previous mayor's actions. The Republican Richard Riordan (who was mayor of Los Angeles from 1993 to 2001) suggested in the early 1990s that the city build what he called "havens" for the city's homeless, essentially herding them into tent cities. Riordan said he wanted to keep the streets clear because it was good for local businesses, but he never suggested how these fenced-off "havens" were meant to be run, or how the homeless insides of them were to be helped.
The writers of "Deep Space Nine" were trying to invent a fictional, near-future scenario where the world was too far gone to save. Outside their windows, politicians were merely suggesting it in real life.
While Newsom's new measure doesn't spell out the same kind of "havens" that Riordan suggested, it is uncanny that the new homelessness measures should come tumbling down the pipeline in 2024, when "Past Tense" takes place. We'll have to wait to see if Gabriel Bell is also real. It's starting to feel like it.“
#star trek#deep space nine#deep space 9#star trek ds9#2024#homlessness#homeless#unhoused#california#gavin newsom
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
something about that "most expensive item of clothing" poll (and, in particular, the post responding to the many tags about $100‐$200 clothes) has been bugging me, and I finally figured out what it is:
you are on the Reject Fast Fashion Buy Sustainable Clothing And Support Small Craftspeople To The Best Of Your Ability website. how much do you think clothing costs? do you not understand the value of labor?
Obviously big fashion labels will mark up their goods to turn a huge profit (basically all labels will), but when you're looking at ethical/sustainable new clothing, you'll see the same prices for similar items. what you need to understand is that the company making those products is turning significantly less profit than the ~designer~ brand. you cannot avoid the higher costs!! growing the fiber takes labor and resources! manufacturing the textiles takes labor and materials! designing and patterning the garments takes labor and skill! sewing the garments take labor and skill and materials! the workers at *every single step* need to be paid a living wage, and all of the processes in general - from growing the fiber to dyeing the textile - take longer and cost more than the industry standard demands. It makes the clothes expensive!!
one of the biggest problems with fast fashion imo is that the obscene level of exploitation of people and resources has allowed giant corporations to drive prices so fucking low that no one understands the value of their *own* labor, let alone the labor of a seamstress they can't see in a factory they've never heard of getting paid 5 cents an hour to work her fingers to the bone finishing a $20 t-shirt.
Bernadette Banner explained once the reason she doesn't take commissions or sew clothing for other people: To use the materials she uses (high quality natural fibers) plus the hours and hours and hours of labor at a living wage, and then a small mark-up to turn any kind of profit, each piece would cost literally thousands of dollars. This shit is fucking expensive.
so anyway. yes, $400 is a lot of money for a pair of sweatpants, but for people who are interested in supporting sustainable fashion brands and who have the means to do so, $100-$200 is beyond reasonable for basically any given item, and the people who buy those clothes certainly aren't your enemy for it.
#textiles#fast fashion#anyway. this is one of those 'i dont think you understand the difference between a million and a billion' situations lol#sustainable clothing
76 notes
·
View notes
Note
OH MY GOD MS. LINSKY HAS DONE IT AGAIN!!! Absolutely loving Kiss Your Boyfriend so far. Can I ask how do you maintain such a high level of productivity with your writing? Your output is incredible! If you feel like sharing how much time you spend writing per day / how many words you average per day that would be really interesting, plus how you find the time / inspiration to write so much? Thanks.
This is so kind, thank you!! This answer got super long and somewhat off-topic, so I'm putting it below a cut.
I am incredibly lucky in my writing time, especially for someone with a small baby. A bunch of years ago I talked my office into letting me go half-time so that I'd have more time to write -- at the time I was thinking specifically of novels, which I have written several of (though not with a level of quality that I'm happy with). Since having a baby last year, I've pretty much only been interested in writing fanfiction; hence the output you've seen. You can pretty much track how much novel-writing I've been doing by looking at my ao3 stats page and seeing how high the wordcount is for a given year. if it's low, there's probably a novel draft or two to blame.
This is a digression, but one that I'm going to include because it's inextricably tied up for me with thoughts about my writing time: having a baby has made me feel much more conflicted about my schedule. We have her in full-time daycare -- partly because it's pretty hard to find anything else around here and it's not nearly as much of a discount to go part-time as you feel like it should be, but also because it's always been understood, between my husband and me, that my writing time is something to be protected at most (not all) costs. I cannot overstate how glad I am for this. That writing time has been absolutely sanity-preserving for me in the first year of motherhood. Baby sleep-and-wake times have pretty much eaten my evenings and weekends, but I still have Thursdays and Fridays and the occasional Wednesday where the only work I have to do is write. It's an unbelievable luxury, and one that's let me feel like I'm still a person and not just a mother. And it's one that I still feel guilty about, even while feeling grateful.
Part of the reason I feel guilty and not just grateful is that over the past year I've been wrestling with my relationship with original fiction. When you're working towards becoming a novelist, you can feel like, okay, it's lucky that I can support myself on half a week's salary, and also it's morally okay because I'm working on acquiring this other Real Job! A Novelist! That's a real thing that pays the bills! (Ha. If only it did, cry a million novelists as I type this.) Capitalism is a scam but it's also a real force that operates on our lives and our psyches. That half a week that I'm not working is half a week when my husband is doing something to further our family's survival and I am not. It's half a week when I could be spending full days taking care of my baby, as certain segments of society would tell you is the greatest thing a woman or person can do, regardless of whether or not they enjoy that type of work (I do not). It would feel more justifiable to me if I were using that time to become A Real Artist -- by which I of course mean one who gets paid. But that part of it really is a scam: fanfiction isn't less of an art just because I don't get paid for it. It's just an art that people can't make a living at, and I'm unbelievably lucky that I don't have to.
I don't know if I'll find myself motivated to return to novel-writing anytime soon. There are parts of me that want the challenge of creating something more structurally complex, that love inventing something entirely new, and those parts are worth listening to, unlike the parts of me that feel like an inadequate imposter because I'm not published. So: maybe. But the publishing industry is its own nightmare, and it's hard to want to dive into it when I currently have so much creative freedom and a place to share my work that doesn't rely on the professional gatekeepers. We also don't currently need the income I might make as a novelist -- which is good, because my understanding is that the idea of making even minimum wage as a novelist is laughable, and I'd do much better going full-time at my job and only writing during weekend baby naps.
So those are the current, very fortunate circumstances of my writing life. Hopefully they will make you feel better if you're someone who works full-time or has other full-time responsibilities or just otherwise can't spend the equivalent of two full working days each week writing, and you're looking at how much I've posted so far this year and thinking that you should have been able to write just as much. Maybe you can, if you're able to find that kind of time in your own life and want to spend it writing, but maybe you can't or maybe you just don't want to and I hope it helps to know I haven't been dashing these stories off during my lunch break or something.
As for speed, I am a relatively fast writer, I think, though not exceptionally so. I usually aim for about 1K an hour when working on a rough draft. If I know a lot about where I want a story to go, it can be faster than that, but I can't sustain that for too many hours in a row. There have been days in recent history when I knew what I wanted to happen and I wrote 9-10K in a day, and I always feel like my brain has been scoured out afterwards and then I'm not usually very productive for a couple days afterward. So probably a more sustainable pace for me is 5-6K of new words per writing day, and then sometimes I'll realize I've taken the wrong approach and have to scrap a bunch of words and go back, and other times it'll have been a while since I last looked at a story so I'll have to go to the beginning and catch myself up, which involves a lot of rewriting also. And then there are days that are supposed to be writing days but something won't click, or I'm sick because I have a daughter in daycare and that means all the germs. So my output is super variable.
I will say, though, that one of the most profound impacts fanfiction has had on my life is that I WANT to sit down and write now. When I first decided I was serious about writing I had a few months off between jobs and decided to use them to write a novel that had been living in my head for a few years at that point. Getting myself to sit down and work on it was like herding slugs. It was an agony of procrastination. At one point I think I watched the entirety of The West Wing between one writing session and the next. I wanted to write, or at least I wanted to want to write, and it made me miserable that I wasn't and yet I still didn't. Writing is really, really hard, and almost anything feels easier in the moment!
But fanfiction has never felt like that to me. It's challenging in plenty of ways, and it's still a lot of work to create a story, but for me it's also a joy. It makes me think of how I used to play dolls when I was a kid, coming up with stories for them to act out. And they didn't have to be the world's most complex stories, with multiple interlocking plots and no words wasted, the way I feel like a novel has to be (I'm probably slightly wrong about this, but only slightly). Writing fic has taken away the barrier I used to face when sitting down to write, where it felt like I needed to hurdle a small building to even start putting words on the page. And the amazing thing is that that ease of starting has transferred to original writing as well. My body and mind have a habit of sitting down at the computer and having fun with words, and I can tap into that even when what I'm writing isn't fic.
And I really do love it. There is nothing in the world as satisfying to me as writing. I'm a little bit of a control freak, and writing is something where I can make things happen exactly the way I think they should. Sitting down, playing out the characters' emotions, figuring out how to make it feel real and compelling, guiding them towards the story I want them to have...there is literally nothing I am better suited for or enjoy more.
As for inspiration...well, in addition to the above, I just really, really want these stories to exist. There is something absolutely irresistible to me in getting characters together, especially if being together means having something that they desperately need but can't admit that they want. The most alluring story premises to me are the ones where there's An Obstacle, a thing that seems like it will bar these two (or three, or four) being together in a real way -- a dam behind which tension can build up, more and more over the course of the story, until the obstacle finally gives way and we have all that lovely tension release. And then the poor deprived main character who didn't think he was even allowed to want what he wanted can finally have it. One of the reasons I DON'T enjoy writing original fiction as much is that genre conventions tend to demand that other things happen in addition to that delicious tension buildup and release. Why dilute it when you could just write the pure thing??
So that's the long answer about my writing circumstances and motivations. I hope you found it interesting, anon -- or at least that you continue enjoying the effects! I have such a voracious appetite to write these stories right now; as long as I keep having the time, I don't see that changing anytime soon.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
All Clothes Are Handmade
As a sewist with access to a lot of fancy commercial-grade equipment, I think about this a lot. People have this idea that there's a lot of automation in making clothes, that robots do most of the work. They do not. Very low-wage humans do.
The machines can make fancy stitches, but they can't guide them. Cloth takes fine dexterity and constant adjustments to work with. Any sewist who's tried to sew a straight line but had their thoughts stray know how fast it goes tits up. The 2+ pieces need to be carefully pinned together (expert sewists can use very few pins, but still need some), and then carefully guided and managed so they stay exactly together as the same tension without wrinkles. And if there's any kind of curve, it takes great skill to do all of that while turning at precisely the right angle at the right time while keeping everything together. And then a human has to detect the end and change the stitch appropriately to secure the ends.
And then there's fabric management. A the front the fabric bunches in your lap and tries to fall down at weird angles. At the back in bunches up and tries to pull at weird angles. So you're constantly having to manage where all that fabric is going that you aren't currently sewing. And if you're sewing in the round (like putting on a sleeve), you have to manage bringing the back around to the front. All of this twists the entire garment, which has to be managed even when most of it is sitting next to you. In home sewing this is sometimes a 2-person job.
A machine cannot do any of that that. Automating clothing manufacturing is a holy grail people have been working on for a couple hundred years and are nowhere close to achieving. It takes the kind of very precise and constant adjustment with a sharp mind and keen eye that humans are very good at and machines are very bad at. Machines only sew in straight lines.
But people look at fast fashion prices and assume robots must be making their clothes. But they aren't. Highly skilled human beings in horrific work conditions at breakneck speed and brutal hours are being paid pennies to make even the cheapest and most low-quality garment. The entire commercial and consumer chain has simply dehumanized them into "must be robots."
This red swimsuit is selling for $10.99 from Walmart. It probably cost $2-$3 to produce.

This striped swimsuit is selling for Beefcake Swimwear for $99. This is the fair price for a swimsuit made with ethical labor.

Beefcake is a small Portland, Oregon company that uses local labor, local materials, and doesn't have a high markup. They cost $49 to manufacture (maybe more now with inflation). (With business expenses, trust me that margin is really slim.) Beefcake talks about "The real cost of American-made swimwear." Half the cost to produce is labor costs. I'd wager half the cost of the fabric is also labor costs. This is why clothing isn't typically made in the US, except using prison labor that's pretty literally slavery.
This is the true cost of a product that attempts to not exploit its workers. It's a luxury most people can't afford because the entire labor market exploits workers to the point of being unable to afford anything but exploitative goods and services. Fast fashion has convinced people they greatly benefit from supporting the worst of that exploitation.
These swimsuits were made on similar machines with similar materials by people with similar skill. The same degree of automation went into both of them. But the Walmart manufacturer sewists got paid less than a dollar to make that one and live in abject poverty, and the Beefcake sewists got paid $22, which is livable.
But robots didn't make either of these. human hands did. Human hands made every single piece of clothing in your closet. Think of how to cherish and care for their work.
614 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cheaply Starting Seeds
This is my fourth post in a series I’ll be making on how to increase biodiversity on a budget! I’m not an expert--just an enthusiast--but I hope something you find here helps!
Having a high-quality seed-starting setup can feel like an ultimate but distant dream. An entire shelf--an entire room, even, filled with grow lights and plant trays in the optimal setup to make tons of plants? Tons of garden tools, each with a diverse and dedicated purpose? That’s just not an option for some of us. But that doesn’t mean we can’t get started at a low cost!
Seed Starting Set-Ups
Speaking from a somewhat biased Floridian perspective, I’ve had great success starting seeds outside! My usual set-up is on a rarely-used outdoor patio table that’s moved to a sunny spot in the yard, but I’ve even grown seeds in solo cups on sidewalks, or directly in the ground, with great results!

Some seeds grow best when they go through a cold period before germinating, while other seeds aren’t affected much by it and just wait for warm weather. As such, a viable option is to sow your seeds in late fall, let winter roll by, and wait until the seeds sprout on their own come spring! I would try and mark off where you planted said seeds, so you don’t lose track of them and accidentally dig them up.

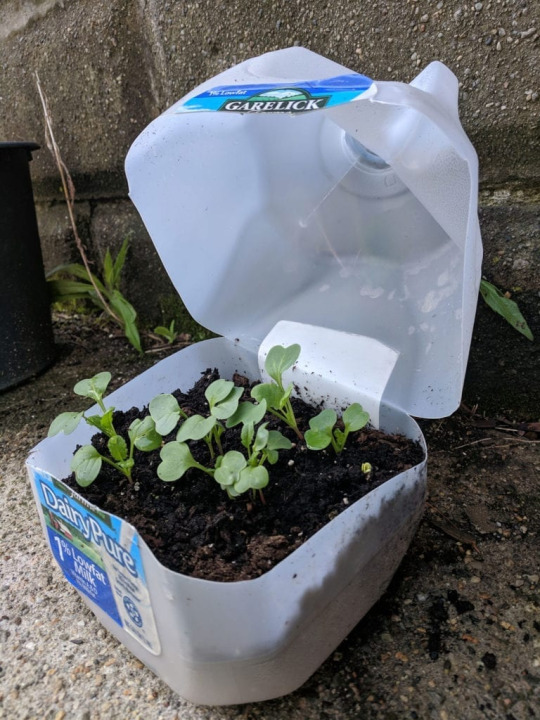
Alternatively, if you want to get started while it's cold outside, a popular option I've seen is to grow in milk jugs! There's a lot of different ways to do it--everyone has their preference--but if you're already drinking things like milk or juice or sweet tea, and you're going to get jugs at some point in time--why not use them for gardening?

An easy way to clear up a section of lawn to create open gardening space is by using a sheet mulching or lasagna gardening method (though I like to call it the Cardboard Snuff-Out). Place cardboard or newspaper down in fall/winter to mark out where you want to garden. Layer compostable materials like grass clippings and wood chips on top of it, or potting soil/bagged compost. It’ll decompose over Winter into an organically rich bed that’ll have killed the grass and weeds underneath it. You don’t have to break out any tools and sweat over it come spring, and the cardboard itself will slowly decompose as well!

Though it's often recommended to plant things directly into the ground to decrease watering needs and increase nutritional independence, there’s plenty of reasons you may not be able to. Whether you’re renting, living in a place without a yard, or even just can’t or don’t want to break ground in a yard, you can still help biodiversity by growing in pots. Some plants have rather extensive root systems and aren’t well suited for pots, but there are still plenty of options available for plants that’ll boost biodiversity, be beautiful to look at, and grow just fine in pots! A recommendation is to get a larger pot, if you’re able, as it’ll hold onto more water and need watering less often. Not only are potted plants great for providing food for insects, but they can be shelter for other creatures too--there’s been a good few times I’ve moved a pot and found a frog or toad living underneath it.

If you don’t have room for pots on the ground, you could consider using hanging pots or window boxes! These can be great and easily-maintained options to provide food and habitat for insects and birds in an urban living situation like apartments or townhouses, but they can also be a fun way to add even more habitat to an already-robust home garden. You can even make an entire mini habitat in a window box or pot! I can personally say I’ve seen tons of pollinators visit my yearly hanging basket garden that consists of about five to seven plants, and I’ve always loved the idea of having a window box for blooms right out my window. Just make sure that it’s safe--make sure they’re securely fixed, and that whatever they’re hanging from can handle their weight when they’re freshly watered and loaded with plants.

If you want to start indoors, you don’t necessarily need grow lights or heat mats (though it will make things a bit easier.) I’ve successfully grown milkweed, peppers, tomatoes, zucchinis, and even sprouted lemon seeds in college dorm rooms, and kept tomato and pepper plants in a dorm room on a sunny windowsill. For the most part, you need a nice and sunny window, some kind of container, and a source of heat (in my case, I used anything from a space heater to the warmth of my laptop running nearby. If you don’t have any sunny windows, or enough windowsill space to start plants on, its possible to obtain cheaper grow lights. One year, my mom bought me some gooseneck grow lights that could clip onto things for cheap off of Amazon. (Fair warning, though, they did light up my entire room in purple. I lived alone that year (covid year, my roomies bailed), so it was fine, but it was kind of trippy,)
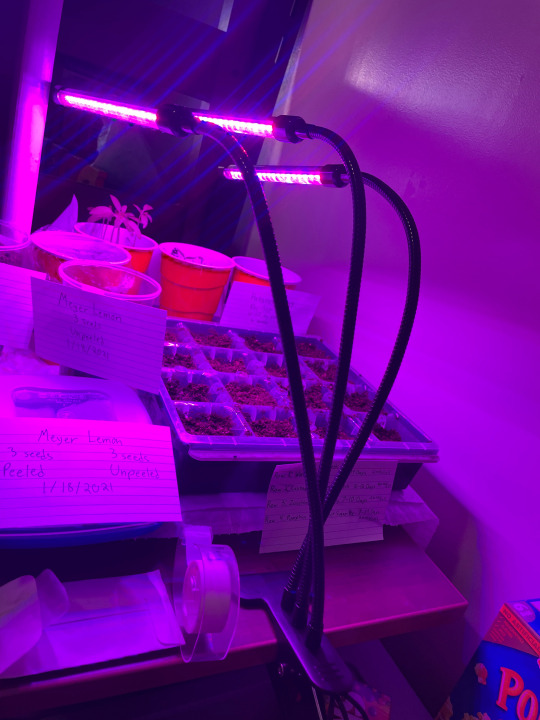

Another year, when I was in an apartment on my own, I bought a grow light modeled like a normal light bulb from the lightbulb aisle in Lowe’s and put it in my desk lamp. Growing seeds indoors can make them grow fast and leggy, so it’ll help if you can keep a desk fan on them so they focus on growing strong instead of tall and fast.
If you’re fortunate enough to have a friend with a nice set up, you could see if they’re willing to let you borrow some of their space to start your own plants as well! My set-up in college was by no means High Class, but I was still more than willing to start seeds for my friends who asked!
Containers for Seed Starting
So now that we’ve talked starting seeds indoors and out, we need to address what to start them in. It’s important that whatever you’re using has drainage holes, and be large enough to support your plant (starting something like milkweed or a squash in a tiny little pot won’t yield great results). Fortunately, there are options here!
If you’re looking to buy pots, Dollar Tree will sell some small plastic pots for cheap in the spring! They’re kind of thin, and won’t last forever, but they’re great for a few uses and don’t cost a lot of money. Something that’s a bit more pricey but are longer-lasting, in my experience, are the Burpee SuperSeed trays. They come in different sizes, but I’m fond of the 16-cell trays--they have silicone bottoms and are made of a nice solid plastic with a tray to hold water, so they hold up for a long time and are easy to clean and reuse!
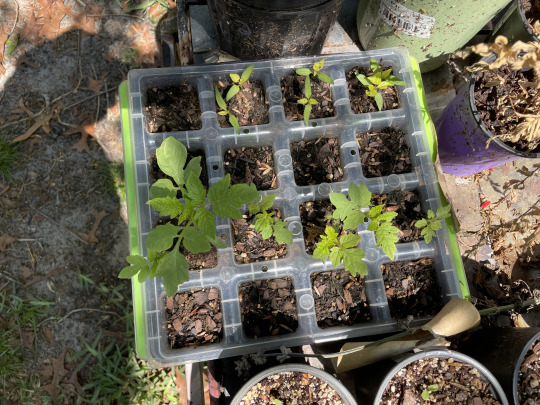

Burpee seed tray, my beloved.
What’s better than a cheap pot? Free ones, and there’s plenty of options there! I’ve seen people use toilet paper or paper towel rolls as pots by folding the bottoms in and have it work well for them! I think this method would work best if you had some kind of tray to keep them moist, because mine dried out fast last time I tried this method. I’ve also seen people make pots out of newspaper with a few different methods, and the people who use this method love it--apparently, the roots pass through the paper easier and it decomposes faster when buried, so you can just transplant the whole pot and avoid any kind of transplanting shock. If you don’t have any newspaper on hand, you can likely ask your friends or neighbors!

I’ve gotten lots of mileage from reusing old containers by poking a few holes in the bottom with knives or scissors--just be careful while you’re doing it! I, personally, am more likely to use an already-used solo cup for it--they’re a nice size, so they hold a good amount of soil and moisture and give the seedling a good amount of root space. I tend to write the plant information on the side of the cup in sharpie marker, or on an index card in pen. I’ve also heard of people making use of egg cartons, fruit containers, yogurt cups, milk cartons, soda bottles--the more you start thinking about what you could easily poke a hole in, the more options start coming around!

This photo may be from 2018, but I'll still regularly reuse cups like this! They're also great for cuttings!
As you start planning to move your seedlings into the ground and preparing planting sites, you’ll likely need a few tools to do it! How do you get these? You may be able to borrow some tools from a neighbor! As long as you make sure to return them in good condition, depending on how friendly your neighbors are, they might be totally fine with you borrowing their tools for awhile. If you don’t want to take that route, there may be a tool library you can borrow from, or a mutual aid group that can loan you tools for awhile. Either way, borrowing tools is cheaper than buying them--though, if you do have to buy tools, cheap hand-tools from Walmart or the dollar store work just fine. They’ll even last a good while if they’re taken care of when not in use! I've even seen places like Ross sell some tools and pots in spring!

Spotted in a Walmart gardening section by the registers, 2023.
Of course, your mileage may vary with these. I genuinely cannot think of the last time my house got a newspaper, and as I've mentioned I don't have to worry about snow. Similarly, maybe you don't use plastic cups when you can help it, or don't have a particular affinity for eggs and yogurt. Maybe there isn't a tool library in your area--I sure don't know if there is in mine--but it could still be worth poking around and asking a neighbor!
That's the end of this post! My next post is gonna be about ways to support your plants for cheap--we're gonna be talking compost, mulch, and trellises. Until then, I hope this advice was helpful! Feel free to reply with any questions, your success stories, or anything you think I may have forgotten to add in!
#biodiversity#solarpunk#gardening#outdoor gardening#growing from seed#budget gardening#cheap gardening#indoor gardening#ani rambles#out of queue#the biodiversity saga#I can make a post later about how I prepare solo cups for being used as pots if yall want#I've found its safest to just use a nice pair of scissors and keep the cup upside-down on the table while I cut into the bottom#and when i say 'take care of the tools when not in use' i mean 'dont be me and leave a cheap shovel from dollar tree out in the rain'#it had a wooden handle and it basically just like. rotted. fell apart in my hand when I picked it up#generally keeping tools in the garage will also help them not rust as fast too#but if you're gonna leave them outside at least put them in shade#the number of times i have lost feeling in my hands because i picked up a hoe that was laying in the sun and fuckin SCALED my palms#its not fun. dont do it. maybe its a Floridian problem but still#if you read all these tags. uh. shovel emoji. idk. sorry dude.
219 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lore: Music
Link: Disclaimer regarding D&D "canon" & Index
[tldr: D&D lore is a giant conflicting mess. Larian's lore is also a conflicting mess. There's a lot of lore; I don't know everything. You learn to take what you want and leave the rest]
Useful for bards and priests, one assumes. I had to look up so many songs I'd never heard of to have a clue what half the comparisons were...
Musical education in the Realms (plus what the core Colleges (Lore and Valor) translate to in the Realms (where they aren't called that))
Musical vocabulary
Instruments
Music itself, including: operatic, 'symphonic'-ish, renaissance-style, hymns, 70s folk bands, and 70s rock music.
[Popular music | Hymns | Opera | Demihuman traditions]
(we got music that sounds like Leonard Cohen, Sinéad O'Connor, 70s folk music, 50s folk music, ELO, Genesis...)
Education
The majority of trained musicians, including bards, start off being apprenticed to accomplished bards willing to tutor, and some seek out Bardic Colleges. The exact focus, quality and curriculum varies by the institution.
To be admitted one must have some experience performing, and be able to pass an audition. They will perform before one of the master bards of the college, as well as one 'invisible' listener they're unaware of. Both masters must agree that the candidate is worth teaching or not for admission, if they don't agree further auditions will follow until they do agree on a verdict.
'Low-order' colleges generally concentrate on mastery of pitch, timbre and nuance. Students are taught to sing scales and perfectly duplicate overheard notes and tunes with their voice, as well as memorizing a set of tunes on a range of instruments to familiarise themselves with different keys and methods. The crafting and repair of one form of instrument is also part of the training.
'High-order' colleges offer a wider range of instruments and repertoire, teaching the history behind the music and lyrics, as well as some language tutoring - not necessarily to speak the language, but to be able to sing such songs perfectly.
New students to any college will be taught the basics in classes at first, but very soon will be passed onto a tutor for one-on-one tutoring.
Pretty much all official colleges in the Realms would make you a College of Lore bard in core DnD terms.
What is called The College of Valor does not actually involve colleges, and is found amongst warrior cultures like Orcs or the Illuskan Northmen, Uthgardt and Reghed: skalds - warrior poets, lorekeepers and clan storytellers.
The most prestigious colleges are the College of Fochlucan in Silverymoon, an ancient bardic tradition which I assume from the name is supposed to be from Ffolk tradition (the Moonshaes). This college has close ties to the Harpers, though most members will stress that their mission and activities are separate to avoid being targeted by the Harpers' enemies.
The College of the Herald is also found in Silverymoon and was founded by a Harper in 922 DR to preserve history. The college maintains a strict neutrality towards the conflicts of the world, and its focus is on preservation of history, folklore and legend over music.
The College of New Olamn, once Ollamh, another ancient bardic tradition, is in Waterdeep, established in 1366 by wealthy patrons of the arts.
On a less formal level, priests of Milil are charged with spreading music and teaching as many as possible to play and sing, and followers of EIlistraee are to 'nurture beauty, music, the craft of making musical instruments, and song wherever they find it.'
Vernacular
'Minstrelsy' is a term for live music, not including hymns and holy music. Recorded music does exist, though mostly in the form of spells that exist to capture and play the song back on command. People like to use them for study, meditation, fun, etc.
If you don't have access to magic, due to cost or general mistrust of the stuff, the Gondians have invented music boxes. You can also get those jewellery boxes with the spinning dancer that play music when they open.
A 'song' is monophonic performance or piece, consisting pof a single vocalist with no instrumental accompaniment.
'Allsong' is the term for polyphonic pieces; covering vocals with instrumental accompaniment, multiple singers such as choirs, and orchestras.
'Newclang' is recent music that starts playing with or breaking conventions. May be viewed as a brilliant invention or modern pop garbage, depending on your tastes.
'song-cycles': 'extended stories told by ballads being sung in a particular sequence. Most of these are 'later inventions,' concocted by a minstrel or bard stringing together their personal favourites (or tunes that they could perform well, and that were popular with paying audiences) into a story of sorts, and then knitting them together with altered lyrics, additional linking songs, and sometimes short spoken-word orations, into the tale of one hero's life, or a romance, or the reign of a villainous king, or the saga of a fearsome dragon or other predatory monster (and its eventual defeat).'
If the performance is 'wordless' then there are no sung lyrics. There might be vocalisations along with the music, but as per the name, no words.
The concept of sorting music into genres apparently hasn't much occurred to anybody yet; music is music in most people's eyes. Historical music trends are named after popular artists of the time. Still you have lammuer (slow waltzes), whirls (reels) and tonsets (courtly formal dances).
There is no standard agreed upon scale that is used by the whole of the Realms.
-
Instruments
The instruments most frequently seen in the hands of common minstrels are lutes and harps. Bells, clapping or stamping one's feet, rhythm sticks and a small wooden pipe akin to a penny whistle serve as accompaniment, and for major percussion instruments you have hand drums and 'great drums' (kettle drums).
Ocarinas, kazoos and mouth harps are pretty common.
Yarting: An acoustic guitar, basically, with origins in Amn and Calimshan, but variations exist everywhere.
Songhorn: Recorders
Straele: A violin-like instrument, shaped a bit like a metronome and played cradled in one arm (preferably while sitting).
Great staele: Cellos and basses
Drone: A large, stationary double-reed instrument with a bladder and several mouthpieces, played by multiple musicians and sounding either like the drones of a bagpipe or an organ or synthesizer.
Jassaran: a crude 'keyboard-and-wires' instrument invented in Sembia that sounds something like a harpsichord.
Artang: A dulcimer, though artangs are only plucked or bowed.)
Shawm: A gnomish instrument that's something like an oboe or bassoon in form. There's also a bellows powered variant.
Zulkoon: A Thayan pump organ.
Pipe organs also exist.
Tantan: tambourines. Popular with halflings.
Longhorns: flutes
'Birdpipes' or Shalm: pan pipes. Most popular with Lliirans and elves, particularly copper and green elves.
Tocken: carved oval bells set to hang so that they can be lightly struck. Instruments such as this are found in subterranean cultures (Dwarves and goblins, mostly). The sound echoes through the structures.
Glaur: Basically a trumpet (more specifically it sounds like a renaissance instrument called a serpent), shaped something between a cornucopia and a saxophone.
Gloon: Much like a glaur, but lacking in valves and it produces a markedly mournful sound.
'Whistlecanes' or thelarr: The bane of parents. Basically just a cut reed you can whistle with. People like to give them to children, who do as children do and proceed to give everybody ear aches from badly played instruments.
-
Music
With a note that a lot of the following kind of applies to the Sword Caoast, Heartlands, Cormyr, Dalelands and etc. Different regions of Faerûn have different music. The kind of Thayan music you'd hear in alehouses in East Faerûn, for example, apparently sounds like this. (Songs with such tunes are called 'thaeraeden,' or 'life laments', and the lyrics are often melancholy questions and challenges. Usually break up songs and unrequited love, the usual.)
So, switching out more modern instruments like drumkits and electric guitars, this is the kind of music you'd apparently expect to hear from minstrels, street and tavern performers and etc. This is basically turning on the radio:
Popular ballads and songs sound something like:
These: X, X, X, X,
Stuff like Leonard Cohen. X
1970s folk music, like Steeleye Span and Maddie Prior. Like the Prickle Eye Bush X, X.
Tongue-in-cheek songs like the Irish Ballad are popular with the working class. I feel like that one specifically would be popular with drow and Bhaalspawn, personally.
'Easy listening' being played in the background while you're passing the evening at a tavern sounds like standard Renaissance fare like Packington's Pound and My Thing is My Own.
Dance music would sound something like this: X
The kind of music you're likely to hear at an upper class party is going to be bringing in musicians and possibly orchestras and dancing. Stuff like this: X, X, X, X,
Orchestral music doesn't utilise strings very much, and prefers to use vocalisation in its place. You generally get more stuff like this.
-
The Opera
Inasfar as I can tell, the opera is exactly what you expect.
The most famous/popular operas include:
'the War of Three Castles:'
Featuring a bunch of kings throwing their sons and daughters off to lead armies against each other. Disaster strikes, two princes and a princess are trapped in a tomb in the Underdark and a love triangle ensues. The princess decides fuck that nonsense, she will have both or neither but she's not having this drama, and they work out a polyamorous relationship, and agree that they will go home and have a 'marriage of three crowns' where they all marry each other, even if their fathers may try to stop them or execute them for it. Then they get back up there, discover that their fathers have been killed turning the entire region into a war torn region. They recover what is left, and they get married and unite their kingdoms in peace and like happily ever after.
'Alvaericknar:'
The lovable rogue archetype who shares his name with the title bites off more than he can chew trying to rob a lich - who kills him. But he's prepared for that, and due to ensuring that the lich killed him in a spot that would set of several enchantments he manages to come back as undead, and proceeds to continue his hijinks. 'As an undead, he goes right on being a swindling, fun-loving rascal, only now he doesn’t need food or drink or shelter.'
'Downdragon Harr':
An evil sorceress turns a princess into a dragon, uses magic to disguise herself as the princess, murders the king and takes over the kingdom. Her first decree is to have every dragon in the kingdom slain (all dragons are played by bassi profundi). A knight with a magic sword wounds the princess in her dragon form, and the enchantment on the blade breaks the spell on her. They fall in love via duet, and then go to the most ancient wyrm in the land (the titular Harr), wake him from his centuries long slumber and use him as their steed to fly off and challenge the sorceress. 'She sees their approach and uses mighty sorcery, that drains the life from most of her courtiers and all of her guards, to slay the dragon as it dives down on the castle—but in death, it slays her, crashing into the castle and crushing her to pulp under its great bulk as it slides to a (dead) stop. (It sings in death, and so does the queen from somewhere under it.) The princess and the knight begin their happy rule, and wedded bliss, atop the carcass of the great dragon.'
One suspects dragons do not care overmuch for this opera.
-
Hymns:
Religious music is typically plainchant, a form of music that usually consists purely of vocals (typically a solitary singer). There is no set rhythm, as the song consists of singing prayers and religious verse. Sometimes there's the occasional accompaniment from a instrument, such as an organ, or a slow heavy drum beat, in the case of Banite hymns.
They can be more complex: polyphonic hymns involve 'two or more singers or instrumentalists playing independent melodic lines at the same time.'
The hymns of most faiths sound most akin to Gregorian chanting. At its softest and most elaborate, you get something that sounds something like a simplified Enya song.
-
Elves
Ah yes, the mysterious and magic melodies of the Tel'Quessir...
Which apparently sound a lot like, say, Don't Bring Me Down, Land of Confusion, Domino Medley, Mr Blue Sky...
They also have your Enya and Loreena McKennit type stuff.
Replace the guitar with a harp, maybe throw in a flute, that's elven music. It's rock. Elven instruments are the only instruments thus far capable of sustain. The effects on the vocals can be replicated by elves, who have a strange quirk with their vocal chords where they can produce two notes/sounds at once, distorting their voice in a way that's similar. Some have a genetic quirk that allows them to sort of say 'two things at once.' Generally elves prefer softer singing voices.
Elven musical performances feature galadrae - three dimensional illusions depicting scenes to go along with the song, not dissimilar to what one might see at a modern concert. Generally the theme is the history/story behind the piece.
Common elven folk songs are apparently these:
Laeryn's Lament
My Love Green And Growing
Blood of My Sisters
The Moondapple Stag
Knights On The Ride
Thorn Of Rose
Winterwillow [an instrumental]
Greenhallow Mantle
Stone Fall, Tree Rise
The Lady Laughing
-
Dwarves
Dwarves like drums and metallic percussion for their music, and vocals tend to be plainsong.
Large clanholds with volcanic vents may build giant complex pipe organs.
'...usually dwarves play piano-like personal instruments (strings hit with hammers; hitting things with hammers is the dwarven way). Most such dwarf instruments look more like an accordion (small portable keyboard) and have metal strings.'
-
Gnomes
Gnomes like drones and oboes (or shawms, I guess). Traditionally, history and lore has been an oral tradition kept by women, so it wouldn't surprise me if some lorekeepers sing it.
-
Halflings
Halflings are apparently known for their comic, and usually bawdy, operas, which are popular with gnomes and dwarves. Titles include 'Ravalar’s Roister In The Cloister; Yeomen, Bowmen, and The Taming Maiden; The Seven Drunken Swordswingers Of Silverymoon; The Haunted Bedpan; The Laughing Statue Of Beltragar; and The Night Six In-Use Beds Fell Into The Castle Moat.'
Outside of that their music overlaps a lot with human music trends.
-
Orcs and goblins
Heavy drumbeats, gongs, warhorns and rhythmic shouting/chanting.
-
Dragonborn
Nothing outside of BG3 that I see, so I'd go with what the game says: throat singing.
#Music on Toril: apparently a grab bag of genres where the 1400s and the 70s collided#'The Prickle Eye Bush' is going to be in my head for a while...#lore stuff#long post
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
over 20,000 people in the United States died of Covid-19 since the beginning of 2024.
Millions who avoided death are nonetheless still living with Long Covid, and this number grows each month. We are still in crisis.
Most importantly, though, implementing accessibility measures during an active pandemic is the right thing to do, as it makes events safer for everyone. Black communities, people of color, the disability community at large, members of the LGBTQIA+ community, and low-income communities continue to be especially hard-hit by the pandemic and the abandonment of Covid-19 precautions. The pandemic reproduces the very forms of ableism, classism, and racism that existed before 2020. There are millions of already systemically marginalized people who are being further pushed out of public life. This is unjust, and we must do better.
[However,] a blueprint for radical inclusion and living a full, safer life within the context of Covid-19 exists.
source

Install HEPA filters in your space. Installing a plug-in air purifier in your space is a great place to begin. Because almost all public spaces currently fall short of the ventilation needed for Covid-19 safety, it’s safe to assume that your space would also benefit from this efficient first step. Make sure it’s appropriately sized for your space and continuously running. If funds allow, upgrade your HVAC system to include HEPA filtration.
Practice mask requirements. Consider requiring and providing high-quality masks for everyone who will be in your space and attending your events. Contrary to popular belief, mask requirements do not deter guests in any meaningful numbers. Clean Air Club has been hosting Covid-safer events in Chicago for over a year, and a majority of the mask-required events sell out every time. If obtaining masks for your event is cost-prohibitive, check in with your local mask bloc for assistance.
Collect and share data on the safety of your space and region. Collect data on the ventilation in your space using a carbon dioxide (CO2) monitor. The higher the number, the more attention you need to pay to improving the ventilation and air purification in the space. Open windows and doors, crank up the HVAC, and plug in another purifier. You’ll know you’ve succeeded when the CO2 levels in your space are close to the levels expected outdoors in fresh air (around 400 ppm). As a bonus, this improved ventilation and purification will remediate poor air quality due to climate-change induced wildfires, improve concentration, and aid in accommodating disabling conditions such as asthma and allergies. Data collection should also include monitoring wastewater data, now our most accurate picture of the true prevalence of Covid-19 and other wastewater-monitored viruses in our population at any given time. We can use this data to increase the number of mitigation strategies adopted when wastewater levels are high. Consider creating an internal chart at your organization that lists protocols associated with different wastewater levels, reducing the burden of communication and oversight during higher periods.
Consider additional mitigation layers. Some of the other layers of protection from the swiss cheese model include: pre-event testing, far-UVC lights, providing options for virtual participation, and asking guests to stay home if they’re showing any symptoms of contagious or novel illness. Consider promoting individualized mitigation approaches within your organizations, such as the usage of nasal spray and CPC mouthwash. The key is to remain creative, flexible, and open to adding layers of protection in response to changing risk levels in the environment.
Open up lines of communication. As you implement mitigation layers, communicate them to your community. Ask them how they’ve been impacted by Covid-19 and give people space to share their access needs and ideas. This will provide a crucial why behind your actions and investments. Using the accessibility principle of designing for the highest possible need, your virus safety plan should accommodate the most vulnerable and impacted community members rather than those who have high risk thresholds or behave as though the pandemic is over. Part of effective pandemic communication includes providing accessibility and virus safety information in an Access Note or in an Accessibility Guide. This information should be repeated often in marketing and outreach materials.
Resources
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
At a societal level, most people grasp the importance of plants to their lives and the ecosystems they inhabit. The success of humans as a species is inextricably interwoven with the success of plant life on Earth. Without the growth of ancient forests, the biosphere in which we live would not have enough oxygen-rich air for humans to have evolved. Without the cultivation of plants for food, humans could not have settled, built shelters and developed rich and diverse cultures. In practical terms, too, building with plants makes a lot of sense. They grow back and are relatively easy to cultivate, harvest and process into useful materials. Their inherent fibrous structures give our buildings integrity. Trees, processed into timber, work extremely well in both compression and tension. Hollow straws and grasses hold air within them, making them great insulators. The lignin in many different plants can act as a natural binder when heated, meaning that you can essentially squash them, heat them and they stick together into useful sheet materials. Mixed with different binders like clay and lime, they can be given resistance to fire, insects and mould. Bio-based materials are also hygroscopic – meaning that they hold and release moisture. The fact that they can absorb humidity from a room helps to regulate damp and prevent mould from growing. That they are moisture permeable means that water vapour trapped in walls, from rain ingress or generated through leaks, always has somewhere to go. Contemporary buildings, on the other hand, are essentially wrapped in plastic sheets, trapping in moisture and resulting in poor indoor air quality.
Some of the best examples of bio-based buildings are hiding in plain sight in villages, towns and cities across the globe, having withstood decades, sometimes centuries of wear and tear. Timber-framed barns, reinforced with hazel wattle and clay daub can be found dotted across the British countryside. The technique of cob building, using loadbearing clay and straw, was very commonly used in the south-west of England in the 19th century, and many of those cob buildings still stand in Devon and Cornwall today. They are finished in a lime render and look from the outside like any other stone or brick building.
That these techniques have not become more widespread is, at first glance, surprising. The local materials and skills used to build with them were relatively low cost, and when well maintained, extremely durable. The critical thing about these materials, however, is how they were intrinsically linked to land, and specific geographies or bioregions. Industrialisation brought with it a change in agricultural practices and land ownership. Bio-based materials were conventionally derived from agricultural waste; long wheat straw was for example used for thatching, until modern chemical fertilisers that help the wheat grow more quickly weakened the structure of the straw, making it too brittle. Water reed, also used in thatching and as a render substrate, was once abundant in wetlands, but these were drained over the course of the 19th century to develop more arable farmland, cutting by approximately 90 per cent the amount of land on which the reed could grow.
Industrialisation also brought about the development of contemporary insulations, designed initially to prevent energy loss from high-energy machinery and factory spaces. Materials such as concrete and steel, which enabled the quick assembly of spaces of production, ultimately sought markets in domestic construction too. These materials were produced at an unprecedented scale and advertised as technologically advanced, in need of little or no maintenance: symbols of a bright future in which being cold, damp and living with fire risk were a thing of the past. And as these materials became more and more popular, regulatory frameworks began to be designed around them, with lawmakers falling victim to aggressive lobbying and marketing campaigns. Today, testing and certification, mortgages and insurances in the UK and beyond are generally designed around contemporary building systems, and materials which have proven their efficacy over decades of service are considered risky, fringe and ultimately more costly.
The petrochemical and mineral materials we have been building with since the Industrial Revolution require an enormous amount of energy to be extracted and processed. The cement industry, for example, is responsible for about eight per cent of planet-warming carbon dioxide emissions – far more than global carbon emissions from aviation. We cannot continue to build using materials that generate enormous outflows of emissions and have to be shipped across great distances. We need to use materials that are lower in embodied carbon: bio-based materials, derived from plants which can regenerate sustainably and sequester carbon into our buildings.
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
Between 2000 and 2020, the total number of Americans owing federal student loans more than doubled from 21 million to 45 million, and the total amount they owed more than quadrupled from $387 billion to $1.8 trillion, growing much faster than any other form of household debt. Figure 1 shows the growth in student loan borrowers and balances

Prior to 2020, when payments were temporarily frozen, a million students defaulted each year, and millions more struggled with their loans and failed to make payments. As recently as 2018, the Congressional Budget Office expected taxpayers to earn a profit on federal student lending programs. It now expects new loans issued over the next decade will instead cost $393 billion—more than will be spent on Pell grants for low-income undergraduates (Congressional Budget Office 2024). Moreover, that prospective cost estimate excludes hundreds of billions of write-downs on existing loans expected because of new policies that will reduce borrowers’ payments and provide debt forgiveness. Compounding these financial costs, many students left college without a degree or with a degree of dubious value, having missed out on the opportunity to rise up the economic ladder. What went wrong?
Since federal student lending programs started in the 1950s, such programs have exhibited boom-and-bust credit cycles. Legislation expanding financial aid to increase educational opportunities led to increased enrollment but also to the proliferation and expansion of institutions providing low-quality education to riskier students. The subsequent deterioration of student outcomes—and reports of scandals—caused Congress to limit lending using so-called “accountability rules,” regulating how postsecondary institutions participate in federal lending programs. When these new rules constrained opportunities for some would-be students, Congress would then whittle away at the rules, allowing student loans to expand again, until a new range of concerns appeared.
After a previous student loan crisis in the 1980s was arrested by new accountability rules passed by Congress, those rules were gradually loosened in the late 1990s. Almost immediately, college enrollment and student borrowing accelerated, particularly among groups that had historically been underrepresented at traditional institutions—students who were lower-income; first-generation students; Black and Hispanic; older; enrolled less than full time; pursuing degrees other than a B.A.; and much more likely to rely on federal aid not just for tuition but also for other costs of attendance, like living expenses. Expanding educational opportunities for these groups is clearly desirable and a key purpose of financial aid programs. But from the perspective of student lending, these new borrowers were much riskier, partly because of their socioeconomic backgrounds and partly because of the institutions they attended.
The institutions that enrolled this new wave of borrowers were disproportionately not traditional four-year institutions with strong educational and economic outcomes. Starting around 2000, for-profit institutions tripled their enrollment and community college students tripled their rate of borrowing. In 2000, only one of the top ten schools in terms of aggregate student loan volume was for-profit. By 2014, for-profits accounted for eight of the ten schools whose students owed the most (Looney and Yannelis 2015). In general, the schools that enrolled the surge of new students were those with high default rates and low student loan repayment rates, where few students complete their intended degrees, or where graduates’ earnings are the lowest. This influx of disadvantaged borrowers to lower-quality schools was catastrophic for those students’ finances, aggregate student loan outcomes, and the federal student loan budget. Between 2000 and 2014, the student loan default rate rose by 75% (Looney and Yannelis 2015).
Today’s student loan crisis—and the fact that it is one of a series—highlights the challenges of using a student loan financial aid system to promote access to educational opportunities that vary enormously (but in opaque ways) in their quality, value, and student outcomes. Today, the student loan program is the most costly federal program for subsidizing higher education. In contrast to other federal aid to students, however, loan eligibility is not means tested, and few guardrails exist to prevent using loans to pursue low-quality or excessively costly programs. As a result, the program’s budget cost and its distributional effects are delegated to the program’s beneficiaries themselves—the institutions, which enroll students and set the cost of attendance, and the students, who decide where to enroll and how much to borrow. Schools’ payments are only very weakly linked to students’ outcomes. As a result of these misaligned incentives, students—particularly disadvantaged students and those historically underrepresented at universities—face high costs, variable quality, and inequity in who goes to college and graduate school.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
As environmental, social and humanitarian crises escalate, the world can no longer afford two things: first, the costs of economic inequality; and second, the rich. Between 2020 and 2022, the world’s most affluent 1% of people captured nearly twice as much of the new global wealth created as did the other 99% of individuals put together, and in 2019 they emitted as much carbon dioxide as the poorest two-thirds of humanity. In the decade to 2022, the world’s billionaires more than doubled their wealth, to almost US$12 trillion.
The evidence gathered by social epidemiologists, including us, shows that large differences in income are a powerful social stressor that is increasingly rendering societies dysfunctional. For example, bigger gaps between rich and poor are accompanied by higher rates of homicide and imprisonment. They also correspond to more infant mortality, obesity, drug abuse and COVID-19 deaths, as well as higher rates of teenage pregnancy and lower levels of child well-being, social mobility and public trust. Bullying among schoolchildren is around six times as common in more-unequal countries. The homicide rate in the United States — the most unequal Western democracy — is more than 11 times that in Norway. Imprisonment rates are ten times as high, and infant mortality and obesity rates twice as high.
These problems don’t just hit the poorest individuals, although the poorest are most badly affected. Even affluent people would enjoy a better quality of life if they lived in a country with a more equal distribution of wealth, similar to a Scandinavian nation. They might see improvements in their mental health and have a reduced chance of becoming victims of violence; their children might do better at school and be less likely to take dangerous drugs.
The costs of inequality are also excruciatingly high for governments. For example, the Equality Trust, a charity based in London, estimated that the United Kingdom alone could save more than £100 billion ($126 billion) per year if it reduced its inequalities to the average of those in the five countries in the OECD that have the smallest income differentials — Denmark, Finland, Belgium, Norway and the Netherlands. And that is considering just four areas: greater number of years lived in full health, better mental health, reduced homicide rates and lower imprisonment rates.
Many commentators have drawn attention to the environmental need to limit economic growth and instead prioritize sustainability and well-being. Here we argue that tackling inequality is the foremost task of that transformation. Greater equality will reduce unhealthy and excess consumption, and will increase the solidarity and cohesion that are needed to make societies more adaptable in the face of climate and other emergencies. (...)
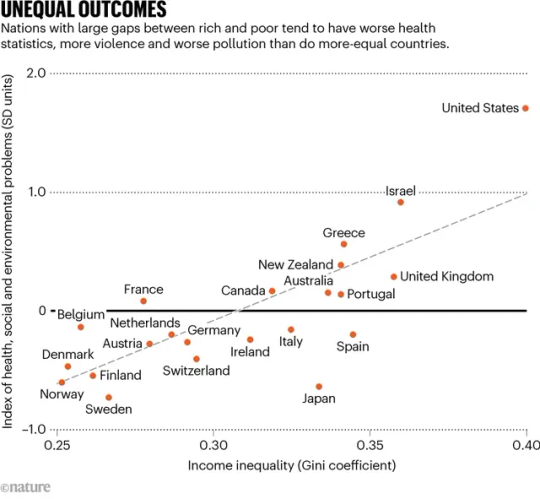
The scientific evidence is stark that reducing inequality is a fundamental precondition for addressing the environmental, health and social crises the world is facing. It’s essential that policymakers act quickly to reverse decades of rising inequality and curb the highest incomes.
First, governments should choose progressive forms of taxation, which shift economic burdens from people with low incomes to those with high earnings, to reduce inequality and to pay for the infrastructure that the world needs to transition to carbon neutrality and sustainability. (...) International agreements to close tax havens and loopholes must be made. Corporate tax avoidance is estimated to cost poor countries $100 billion per year — enough to educate an extra 124 million children and prevent perhaps 8 million maternal and infant deaths annually. (...) Bans on advertising tobacco, alcohol, gambling and prescription drugs are common internationally, but taxes to restrict advertising more generally would help to reduce consumption. Energy costs might also be made progressive by charging more per unit at higher levels of consumption.
Legislation and incentives will also be needed to ensure that large companies — which dominate the global economy — are run more fairly. For example, business practices such as employee ownership, representation on company boards and share ownership, as well as mutuals and cooperatives, tend to reduce the scale of income and wealth inequality. (...)
More in-depth explanation for the reasons behind the fragment I've included in this post can be found in the article linked above, as well as the sources for all the claims.
#sustainability#climate emergency#environmentalism#environment#capitalism#anticapitalism#science#💬#social science#anti capitalism#anti advertising
7 notes
·
View notes