#Alaqsa mosque
Text

Alaqsa mosque - Alquds ❤️
295 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Random Entries from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture
The following entries were pulled from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture (1995).
Funduq (structure type)
Coral (construction material)
Kufa (city)
Songhay (people)
Süleymaniye (named building complex)
Squinch (architectural facet)
Aghlabid (people, lineage)
al-Aqsa Mosque (building)
Arasta (structure type)
Hassan Fathy (person, architect)

❯ ❯ Funduq (structure type)

North African term for a small, urban shop complex. A typical funduq is a square two-story structure built around a central courtyard with shops on one floor and store rooms on the other. Equivalent to a khan in the Middle East.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 91.
Photo source: (1) Barbara J. Anello-Adnani; (2) Islamic Architectural Heritage
❯ ❯ Coral (construction material)

Coral is used as a building material for coastal settlements throughout the Indian Ocean, Arabian/Persian Gulf and the Red Sea.
Two main types of coral stone are used for construction: fossil coral quarried from the coastal foreshore, and reef coral which is cut live from the sea bed. Fossil corals are more suitable for loadbearing walls whilst reef corals such as porites are more suitable for architectural features such as door-jambs or mihrab niches. Fossil corals are mostly from an order of coral known as Rugosa, which is now extinct. When quarried this coral forms rough uneven blocks known as coral rag. Although this can be cut into rough blocks, it cannot be dressed to a smooth finish and therefore has to be used in conjunction with another material to produce an even surface.
Living coral from the reef is easier to cut and dress to a smooth finish, although it does require hardening by exposure to the air. The preferred type of reef coral for building is porites because of its compact vascular structure which means it is both strong and easy to carve. However, this is not the only type used and, at the eleventh-century site of Ras al-Hadd in Oman, at least seven different types were noted. In the Maldives and Bahrain, platy corals such as oxypora and montipora are used for partitions.
The origins of coral-building are not well understood although it is generally believed that the technique originated on the coasts of the Red Sea. The earliest example was discovered at the site of al-Rih, in the Sudan, where a Hellenistic cornice made of coral was found reused in an Islamic tomb. From the Red Sea, the technique spread to the East African coast of the Indian Ocean where it was established as the primary building material for monumental buildings. In the Arabian/Persian Gulf, there is another tradition of coral stone construction although the antiquity of this tradition is in doubt as suitable coral has only grown in the area within the last 1,000 years. At the present time, the use of coral stone extends over large areas of the Indian Ocean and includes the coastline of India (Gujarat), the Maldives and Sri Lanka. The origins of coral-building in these areas has not been investigated, although it generally seems to be associated with Islamic traders.
See also: Bahrain; East Africa; Maldives; Qatar; Saudi Arabia; Sudan; United Arab Emirates.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 54-55.
Photo source: Getty
❯ ❯ Kufa (city)

Southern Iraqi city founded in the early Islamic period.
Kufa is located on the west bank of the Eurphrates near the Shi'a shrine city of Najaf. Like Baghdad, Kufa was a purely Islamic foundation, although it stood close to the Lakhimid capital of al-Hira.
After the battle of Ctesiphon and the capture of al-Mad'ain (Ctesiphon and Seleucia) the Arab armies settled in the old Sassanian capital. Soon afterwards, the armies moved to Kufa because of its pleasanter climate and strategic location on the west bank of the Euphrates (i.e., easy access to Syria and the Hijaz). In 645, Ali transferred the seat of government to Kufa. The assassination of Ali in the Great Mosque of the city in 645 brought an end to the city's role as capital.
The original city had no walls and was simply surrounded by a ditch. The principal monuments in Kufa are the Great Mosque and the Dar al-Imara, or Governor's Palace. The Great Mosque consists of a number of different phases from the early Islamic period to the present day. The first mosque on the site was laid out by a man who threw spears to each of the cardinal points to delineate a square two-spear throws long. The area was enclosed by a ditch and the only permanent architectural feature was a marble colonnade 20m long. The columns were taken from the nearby city of al-Hira. In 670 CE, the mosque was expanded and covered with a flat roof resting on stone columns. The mosque visible today has a beautiful golden dome and contains the tombs of the two saints Muslim ibn Aqeel and Hani ibn Arwa. The golden dome and tilework date to the Saffavid period (seventeenth and eighteenth centuries), although the outer wall of the mosque which is supported by twenty-eight semi-circular buttress towers probably originates in the early Islamic period.
To the south of the Great Mosque is the Dar al-Imara, which was excavated by the Iraqi Antiquities Authority. The palace is enclosed by a square enclosure 170m per side with walls 4m wide supported by twenty semi-circular buttress towers and four round corner buttresses. In the center of the palace there is a square (domed?) chamber approached by a vaulted hall which was probably the throne room.
See also: Dar al-Imara; Iraq.
Further reading: (1) S. Ahmad, 'Survey of the Kufa area' (in Arabic), Sumer 21:229-252, 1965. (2) M. A. Mustafa, 'Dar al Imara at Kufa', Sumer 21:229-252, 1965. (3) M. A. Mustafa, 'Preliminary report on the excavations in Kufa during the third season', Sumer 19:36-65, 1963.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 156.
Photo source: (1) Taghrib News; (2) Narjes Ahmed/Wikimedia Commons.
❯ ❯ Songhay (people)

The people who inhabit the banks of the Niger river between Gao and Dendi in West Africa. The Songhay people were the ruling population of the empire of Gao during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. Some of them were Muslim before the eleventh century but some have remained pagan to the present day. Little is known of early Songhay architecture, although ancestor-worship seems to have been expressed through earthen burial mounds. Elements of this tradition seem to have been incorporated in Islamic monuments where prominent people are buried within solid earth pyramid-like constructions, the most famous of which is the tomb of Askiya Muhammad at Gao.
See also: Gao; West Africa.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 262.
Photo source: (1) Reuters/Joe Penney; (2) Reuters/Joe Penney; (3) Islamic Architectural Heritage.
❯ ❯ Süleymaniye (named building complex)

Ottoman mosque complex in Istanbul built for Suleyman the Magnificent between 1550 and 1557.
The complex consisted of a hospital, medical school, hospice, soup kitchen, primary school, four madrassas (colleges), shops and coffee houses in addition to the mosque itself. The complex is built on an artificial platform on top of a hill that overlooks the Bosphorus; to the east the ground slopes away rapidly. The mosque precinct contains three main areas, the mosque itself in the center, a courtyard to the north and a tomb garden to the south which contains the tomb of Suleyman and his wife. The mosque is covered with a large central dome (25m diameter) with two large semidomes of equal radius, one above the north entrance and one above the mihrab. The central area is flanked by side aisles covered by small domes of alternating size. Like that of its predecessor, the Sehzade Cami, the central dome rests on four huge central piers placed in a square. The whole building is illuminated with more than a hundred windows and grilles, many of which are filled with stained glass made by the celebrated Ottoman glass-maker Ibrahim Sarhos. Outside at each corner of the courtyard are four minarets with balconies supported on muqarnas corbels. This is the first Ottoman building in Istanbul to have four minarets, although previously the Üc Serefeli in Edirne also had four. The sides of the building are enlivened with several entrances (three on each side), approached by steps and two-tier arcaded galleries placed between the outer corner buttresses.
The tomb garden behind the mosque contains a large cemetery which has grown up around the tombs of Suleyman and Roxelane. Both tombs are octagonal structures in the traditional Ottoman fashion, although Suleyman's tomb unusually faces east instead of north. Roxelane's tomb is smaller and placed to one side of Suleyman's tomb which stands in the middle of the garden. The interiors of both tombs are decorated with Iznik tiles, although Roxelane's tomb is significantly less grand. Suleyman's tomb is surrounded by a colonnaded veranda with a porch on the east side. This arrangement is echoed internally where Suleyman's sarcophagus is surrounded by a circular colonnade.
The arrangement of the complex outside the mosque precinct consists of an L-shaped arrangement of buildings on the north-west side and a smaller group to the east. The eastern complex is built on a steep hill so the madrassas are stepped into the hillside. On the north-west corner of the complex is the tomb of the architect Sinan.
See also: Istanbul; Ottomans; Sinan.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 268-269.
Photo source: (1) CamelKW/Flicker; (2) Kevser Salih/Getty; (3) Izzet Keribar/Getty.
❯ ❯ Squinch (architectural facet)

Small arch in the corner of a building that converts a square space to an octagonal area, which may then be covered with a dome.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 267.
Photo source: (1) Dig Magazine; (2) José Carlos Palacios Gonzalo/Rana Munir Alkadi; (3) José Carlos Palacios Gonzalo/Rana Munir Alkadi.
❯ ❯ Aghlabid (people, lineage)

Dynasty which ruled the north African province of Ilfriqiyya during the ninth century.
Although nominally under Abbasid control, the Aghlabids were able to exercise a great deal of independence. Militarily their great achievement was the conquest of Byzantine Sicily.
The Aghlabids were great patrons of architecture, and much of their work has survived. Their work demonstrates a mixture of Byzantine and Abbasid building styles. One of the most important projects was the rebuilding of the Great Mosque of Qairawan and the addition of the huge three-tiered minaret/tower. The Aghlabids were also responsible for major irrigation and water supply systems, the most famous example of which are the huge circular cisterns of Qairawan. Much of their effort was also directed towards the development of the coastal towns as bases from which to launch the conquest of Sicily. The military nature of Aghlabid rule is further reflected in the large number of ribats, or fortified monasteries, which they constructed.
See also: Tunisia.
Further reading: A. Lezine, Architecture de L'Ilfriqiyya: Recherche sur les monuments aghlabides, Paris 1966.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 6-7.
Photo source: (1) Richard Mortel/Flicker; (2) Alberto Biscaro/Masterfile.
❯ ❯ al-Aqsa Mosque (building)

The principal mosque of Jerusalem which forms part of the sacred enclosure (haram) with the Dome of the Rock at the center.
The Aqsa Mosque is located on the southern part of the Haram al-Sharif on an axis with the south door of the Dome of the Rock. In the time of Umar, a mosque is known to have been built on the site although it appears to have been a semipermanent structure made out of re-used material, hastily put together to form a covered prayer area with a shed roof. During the reign of al-Walid the mosque was rebuilt with its present alignment.
Only a small part of al-Walid's mosque survives, but this indicates that the aisles all ran perpendicular to the qibla wall (as they do today). This arrangement is unusual and recalls the arrangement of Byzantine churches, such as the Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem.
The earthquake of 748 severely damaged the mosque, which was subsequently rebuilt by the Abbasid caliphs al-Mansur (759) and al-Mahdi (775). The mosque of al-Mahdi had a raised central aisle leading to the mihrab in front of which he built a wooden dome; either side of the central aisle were seven side-aisles. An earthquake of 1033 destroyed the mosque and it was once again rebuilt by the Fatimid caliph al-Zahir in 1035. This mosque had a total of seven aisles, a central aisle with three aisles on either side.
See also: Damascus Great Mosque; Dome of the Rock; Jerusalem; Medina; Palestine; Umayyads.
Further reading: R. W. Hamilton, The Structural History of the Aqsa Mosque. A Record of Archaeological Gleanings from the Repairs of 1938-42, Government of Palestine, Jerusalem 1949.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 22-24.
Photo source: (1) Niels M. Knudsen/Flicker; (2) Sam Rohn/Flicker.
❯ ❯ Arasta (structure type)

Turkish term for a street or row of shops whose income is devoted to a charitable endowment or waqf (equivalent to a European shopping arcade).
Arastas are found in most of the regions of the former Ottoman Empire and usually form part of a commercial or religious complex which may include a han (or khan), a mosque and bath house. Many arastas were probably made of wood but these have largely disappeared leaving only those made of more permanent materials. Arastas are often covered over with a barrel vault and have a row of shops either side of a central street, but they can also be open to the sky. Important examples of arastas include the Misir Carsi in Istanbul, the arasta associated with the Selimiye mosque in Edirne and the arastas at the Sokollu complex· at Luleburgaz and the Selim I complex at Payas both designed by Sinan.
See also: Ottomans.
Further reading: M. Cezar, Typical Commercial Buildings of the Ottoman Classical Period and the Ottoman Construction System, Istanbul 1983.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 24.
Photo source: (1) Banu/Flicker; (2) Alda Cravo Al-Saude/Flicker.
❯ ❯ Hassan Fathy (person, architect)

Egyptian architect noted for his use of traditional materials to build modern Islamic structures.
Born in 1900, the son of a wealthy landowner, Hassan Fathy was brought up in Cairo, Alexandria and Europe. He studied architecture at the University of Cairo whence he graduated in 1926. In 1927, on his first visit to one of the family estates, he was shocked by the terrible living conditions of the poor and resolved to find a way to house the poor reasonably. He also conceived a love for the Egyptian countryside, which was to motivate him for the rest of his life. He realized that imported western material and technology was too expensive and inappropriate for rural housing in Egypt. Instead, Fathy thought that mud brick, the traditional building material of Egypt, should be used in modem constructions. Although he realized that traditional designs were sometimes too cramped and dark for modern housing, Fathy argued that this was not the fault of the material.
In 1937 Fathy held exhibitions of his work at Mansoura and Cairo, which resulted in several commissions from wealthy patrons. However, these buildings were quite expensive and relied on timber for their flat roofs. With the outbreak of the Second World War and the resulting shortage of timber, he had to find a new method of roofing his houses. On a visit to Upper Egypt, Fathy noticed that the Nubian villages were roofed with mud brick vaults produced without wooden centering. The method used was to lean the bricks against an end wall so that all the bricks leant against each other. Fathy employed the local Nubian builders and undertook several projects using these workers. The most important of these projects was the Nasr House in Fayyum and the tourist rest-house at Safaga.
In 1946 Fathy was approached by the Department of Antiquities who wanted to move the people of Gurna in western Luxor out of the ruins of ancient Thebes where they had been living. The Gurnis had been living in the ancient Necropolis for several generations and some lived in the tombs themselves. Nevertheless, the Department of Antiquities issued a decree stating that they wanted the 7,000 people moved to a new settlement, which was to be designed by Fathy. The settlement was to contain homes for 1,000 families and include public buildings like a mosque, a covered market, schools and a theatre. The houses were built around courtyards and arranged in neighborhood groups which had access to the main streets. Although built with traditional materials, Fathy made use of earth scientists and structural and mechanical engineers to improve his designs and ensure that they worked. Part of the project was to involve the future inhabitants in the construction, both as a cost-saving measure and so that they were not alienated from their new housing.
However, the project faced considerable difficulties in implementation through the opposition of some of the Gurni Sheikhs and the slow-moving bureaucracy of the Egyptian Antiquities Department.
In addition there was general suspicion of a project, which involved traditional materials at a time when Modernism was seen as the only way to build. In the end, only one-fifth of the project was completed and some parts of the village like the khan and the craft center remain unused. Nevertheless, the mosque is well used and maintained and the Department of Antiquities has restored the theatre, belatedly realizing the value of Fathy's work. Despite the difficulties New Gurna showed the potential of mud-brick architecture and the value of training people in traditional techniques.
Other important projects carried out by Fathy in the 1950s were at Lu'luat aI-Sahara in the Nile Delta and the village schools project. At Lu'lat al-Sahara, houses were built in pairs, together with a mosque and a school. The village schools project involved Fathy in designing a school, which was to be the prototype for village schools throughout Egypt. The design consisted of domed rooms opening onto courtyards with ventilation shafts to cool the interior during the summer. Unfortunately, only two of the schools were built, one at Fares and the other at Edfu.
In 1957, Fathy left Egypt for several years to work for an architectural firm in Athens, specializing in the Middle East, and during this time he designed a traditional housing scheme in Iraq. In the early 1960s, Fathy returned to Egypt where he undertook two further major projects, a training center in the Nile Valley and a new town in the Kharga oasis. Unfortunately the training center was subsequently destroyed because of its bad location and the town known as New Bariz was abandoned because of the 1967 war.
In the 1970, Fathy began writing books about his work, which were highly successful in universities throughout the world where the appeal of Modernism was wearing off. He showed that it was possible to design and build desirable residences and functional buildings, which respected the traditional values of a culture and were also cheap. Since the 1970s, Fathy's work in Egypt was concentrated on private houses and commissions. These buildings were constructed with increasingly sophisticated designs based on harmonic units of measurement derived from the dimensions of the human body. Probably the most important recent commission was for a Muslim community in New Mexico known as Dar al-Salam and built in 1981.
Further reading: (1) H. Fathy, The Arab House in the Urban Setting: Past, Present and Future, Fourth Arab Carreras Lecture, University of Essex, November 1970. London 1972. (2) H. Fathy, Architecture for the Poor, Chicago and London 1973. (3) H. Fathy, Natural Energy and Vernacular Architecture, Chicago 1985. (4) G. Leick, 'Hassan Fathy, architect for the poor', Egyptian Bulletin May 1988: 4-8. (5) J. M Richards, I. Serageldin and D. Rastorfer, Hassan Fathy, London 1985. (6) A. Schkifer, 'Hassan Fathy: A voyage to New Mexico', Arts and the Islamic World 1(1): 1982/3.
Text source: Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 84-86.
Photo source: (1) Green Prophet; (2) Green Prophet; (3) Marc Rykaert/Wikimedia Commons.
#islamic architecture#writeblr#writing research#masterpost#writing#writing tips#writing advice#architecture research#novel writing#funduq#construction material#songhai#songhay#kufa#suleymaniye mosque#fiction writing#squinch#aghlabid#alaqsa mosque#arasta#hassan fathy#architect#structure#turkey#morocco#north africa#iraq#istanbul#tomb garden#ottoman empire
10 notes
·
View notes
Text






Free palestine
Free gaza
905 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nuking Gaza

Gaza is 25 miles long and 6 miles wide.
It is home to 1 million catastrophically traumatised children.
They have no water or food.
Israel’s dropped explosives on them equal to 1.5 Hiroshima atomic bombs.
In 3 weeks.
Do you get the enormity of the crime we are witnessing yet?
(Matt Kennard)
#palestine#palestinians#free palestine#genocide#palestinian genocide#gaza strip#gaza#free gaza#gazaunderattack#save gaza#gaza genocide#nakba#jerusalem#isreal#israel#benjamin netanyahu#al quds#alaqsa#al aqsa mosque#white phosphorus#al aqsa storm#nablus#west bank#jenin#jenin refugee camp#islam#muslim#muslims#muslim ummah#arabs
237 notes
·
View notes
Text

Palestine
Ukraine has all the right to fight back against Russia, but when Palestine tries to fight back against Israel it becomes terrorism. Stand with Palestine.
سُبْحَانَ اللهِ وَاللهُ أَكْبَر..اللَّهُمَّ انْصُرْ أَهْلَنَا فِي فِلَسْطِين وَافْتَحْ لَهُم فَتْحًا يَسِيرًا مُبِينًا
اللهم انصر فلسطين 🤲.
#palestine#alaqsa#free palestine#islam#fyp#mosque#save palestine#save alaqsa#dome of the rock#arab#gaza#duaa#stand with palestine#jerusalem#justice for palestine#human rights#free gaza#palestinians#palestinian rights#palestinian resilience#فلسطين#الاقصى#دعاء#فلسطين حرة#القدس#نصر فلسطين#حقوق الإنسان#غزة#الشعب الفلسطيني
43 notes
·
View notes
Text


#islam#muslim#islamic#muslimah#muslimdaily#muslim ummah#muslimamerican#islamophobia#deen islam#ramadan#gaze#gazegenocide#palestine#alaqsa#al aqsa mosque
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Israeli Knesset member Amit Halevi of the ruling Likud party led by Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is preparing a draft bill to divide Masjid al-Aqsa between Muslims and Jews.
The proposal includes Jews taking over 70% of the compound including the Dome of the Rock.
وزیراعظم بنجمن نیتن یاہو کی قیادت میں حکمران جماعت لیکود کے اسرائیلی کنیسٹ کے رکن امیت حلوی مسجد الاقصی کو مسلمانوں اور یہودیوں کے درمیان تقسیم کرنے کے لیے ایک مسودہ بل تیار کر رہے ہیں۔ اس تجویز میں ڈوم آف دی راک سمیت 70 فیصد کمپاؤنڈ پر یہودییوں کا قبضہ ہو گا۔
🇩🇪 Der israelische Knesset-Abgeordnete Amit Halevi von der regierenden Likud-Partei unter Premierminister Benjamin Netanjahu bereitet einen Gesetzesentwurf zur Aufteilung der Moschee al-Aqsa zwischen Muslimen und Juden vor. Der Vorschlag sieht vor, dass Juden 70 % des Geländes einschließlich des Felsendoms übernehmen.
🇧🇦 Član izraelskog Kneseta Amit Halevi iz vladajuće stranke Likud koju predvodi premijer Benjamin Netanjahu priprema nacrt zakona o podjeli Masjid al-Aqsa između muslimana i Jevreja. Prijedlog uključuje Jevreje koji preuzimaju 70% kompleksa, uključujući Kupolu nad stijenom.
#islam#muslims#islamophobia#ummah#hijab#muslim#allah#hijabi#muslimah#dawah#palestine#palestinians#jerusalem#al aqsa mosque#alquda#alaqsa#mosque#masjid
0 notes
Photo


(via আল আকসা মসজিদ কোথায় অবস্থিত কোন দেশে)
0 notes
Text
Israel - Holy Places In Jerusalem (1/2)
Jerusalem isn’t that huge, but full of spots, which considered to be holy to religions as Jews, Christians and Moslems, and if you want so, also the many markets, which could be considered as places to worship the capitalism 😉
To visit most places and get more informations i joined a tour group for the day.. Tour guide Tania lead the group to the many interesting places. Starting in the Armenian…

View On WordPress
#alaqsa#armenianquarter#christianity#holy#holycity#holyplace#islam#israel#jerusalem#judaism#middleeast#mosque#mountofolives#pilgrim#pilgrimage#renebauerphotography#viadolorosa#wailingwall#westernwall
0 notes
Text
According to the will of the One and Only True God, Leader Mehdi (PBUH) will conquer this site one day.

#islamic#prophet#steed#paradise#jerusalem#eastern#noble#sanctuary#alaqsa#western#western wall#palestine#al aqsa mosque jerusalem#prophetmuhammadﷺ#imam mahdi
0 notes
Text
دسیوں یہودی آبادکاروں کا مسجد اقصیٰ پر حملہ: فلسطینی میڈیا
دسیوں یہودی آبادکاروں کا مسجد اقصیٰ پر حملہ: فلسطینی میڈیا
دسیوں یہودی آبادکاروں کا مسجد اقصیٰ پر حملہ: فلسطینی میڈیا
غزہ، 29 مئی ( آئی این ایس انڈیا)
فلسطین سے موصولہ اطلاعات کے مطابق اتوار کی صبح انتہا پسند یہودی آبادکاروں کے ایک جتھے نے مسجد اقصیٰ پر دھاوا بول دیا۔ حملہ آور یہودیوں کو اسرائیلی پولیس کور فراہم کر رہی تھی جنہوں نے بعد ازاں الرحمہ نامی جائے نماز بند کر دیا ،اور مسجد قبلی میں نمازیوں کو محاصرے میں لے لیا۔فلسطینی خبر رساں ایجنسی…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
صلُّوا عليهِ وسلّموا تسليمًا 💙
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
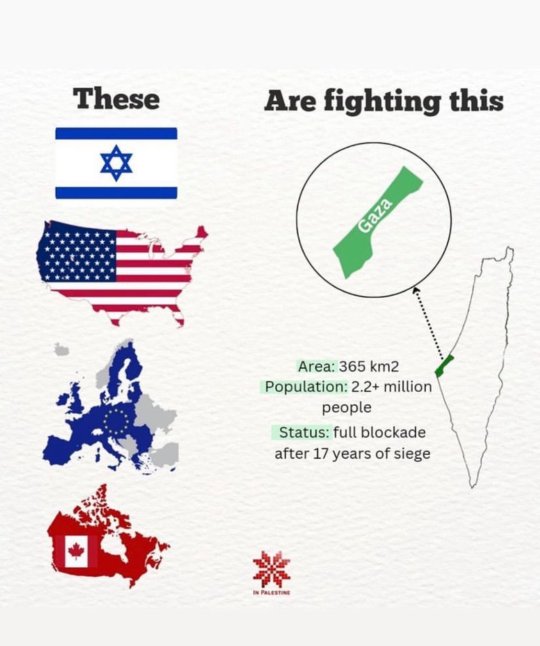
Free palestine
Free gaza
#mosque#camii#palestine#al quds#alaqsa#free gaza#gaza#gazaunderattack#free palestine#غزة#غزة تحت القصف#freepalastine🇵🇸
418 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Let's Distribute Palestinians All Over The World"
“Let us distribute them all over the world. There are 2.5 million Gazans… each country takes 25 thousands.”
Ram Ben Barak, former deputy director of Mossad on Israel plans to forcefuly displace Gazans.
Response by Richard Medhurst:
White European colonizer saying Palestinians should be “distributed” and scattered around the world.
1. Palestinians are in their own country. They are not boxes or items.
2. This is genocidal intent. Do you know what that means? You are a war criminal
3. If someone said this about Jews you would be screaming “anti-Semitism” — ironic, since it’s you who hates the Palestinians and Arabs, who are Semites
4. If Canada is so nice, pack your bags then! Who the hell are you to decide the fate of people who’ve been living in the Levant for millenia?
5. Palestine took in European Jews when they were persecuted, as the Arabs and Muslims also did when Jews were persecuted in Spain. Is this is how you repay their kindness?

#palestine#palestinians#genocide#free gaza#israel palestine conflict#current events#photography#gaza#gaza strip#gazaunderattack#save gaza#free palestine#isreal#this is genocide#jerusalem#al quds#alaqsa#al aqsa mosque#i stand with palestine#ramallah#west bank#al aqsa storm#nablus#jenin#jenin refugee camp#west bank palestinians#jabalia#islam#muslim#muslims
48 notes
·
View notes
Note
you didn't actually answer my question , Temple Mount is the most ancient and holiest site for Jewish people -- the Dome of the Rock & Al-Aqsa Mosque were built hundreds of years later on behalf of the Umayyad dynasty's conquest. you mentioned in your response a massacre that happened centuries later, which does not relate to the fact that Jews cannot pray at this site (their utmost holiest site before even the existence of Christians or Muslims). how is "temple denial" something that I made up when you can research it right now and see what it is and that it exists? I ask because this seems to be actually a blind spot for many non-Jewish people simply because it doesn't affect them. I'm not intending to be argumentative and I am sorry if my English is bad in getting across
I'm sorry for being argumentative but a lot of the time, whenever Palestinians are asked about temple mount, there's an implication that Palestinians are colonizers and don't deserve to be on the land. Israelis, if they could, would completely ban Muslims from AlAqsa despite it being the third holiest site in Islam.
AlAqsa is probably the most important national symbol of Palestinians, often thought to be the last straw for Palestinian heritage. So much of our culture has been robbed from us, and (primarily muslims) believe that the demolition of AlAqsa, which is, as Mohammed ElKurd puts it, is one of the last places in all of Palestine where being Palestinian is not criminalized would be a fundamental loss we would never recover from, equivalent to losing our Balad.
I bring up the Ibrahimi Mosque Massacre because there are no restrictions for extremist settlers legally — they operate as an arm of the state and in some cases are encouraged to committ these acts. The "Apartheid Law" basically enshrined that settlements are a national value for Israel. This means that there is no safe haven for Palestinians legally. They're in constant danger of getting kicked out of their home or getting arrested for existing. I cannot emphasize enough how Palestinian freedom is so restricted with the explicit intent of pushing them out of the land.
Temple denial as a concept (after looking it up) seeks to paint Palestinians in a fundamentally bigoted and violent light. Palestinians are not allowing Jews in AlAqsa not because they hate Jews, but because that opens the way for settlers to become violent around AlAqsa, which a lot of the time is already happening. I suggest reading "Why Do Palestinians Burn Jewish Holy Sites? The Fraught History of Joseph's Tomb" (sorry the link is not linking, but you can look it up on the palestine institute webpage). It discusses the use of history as a colonial tool. Here's an excerpt:
It is one of many shrines across historic Palestine – now split into Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza – that has been re-invented as exclusively Jewish, despite a long history of shared worship among Jews, Christians, Muslims, and Samaritans that goes back centuries. And the reason it has been attacked has almost nothing to do with religion, and much to do with how the Israeli military and settlement movements have used religion as a way to expand their control over Palestinian land and holy places.
And a second excerpt describing the political use of religion:
But the claims of biblical archaeologists had a strong role in how the Zionist movement would come to understand and conceive of the landscape.6 As European Jews migrated to Palestine in the first half of the twentieth century, they drew upon biblical archeology's claims. They adopted archeologists' claims that Palestinian holy sites were directly linked to ancient biblical figures. In many cases, they focused on occupying those sites in order to legitimize the colonial endeavor by giving it a sense of deeper history. In many cases, this would mean evicting the Palestinians who actually frequented these holy sites.
And what Palestinians are afraid of:
In 1975, the Israeli military banned Palestinians – that is, the Samaritans, Muslims, and Christians living around the site – from visiting, a ban that has remained in place until this day. [...] Unsurprisingly, the ban has ignited intense anger over the years. This is true particularly given that frequent visits by Jewish settlers to the shrine are accompanied by hundreds of Israeli soldiers, who enter the area and run atop the rooftops of local Palestinians to “secure” the tomb. As a result, Joseph's Tomb has increasingly become associated with the Israeli military and settlement movement in the eyes of Palestinians. Its presence has become an excuse for frequent military incursions that provoke clashes and lead to arrests and many injuries in the neighborhood. Some fear that Israelis will attempt to take over the shrine to build an Israeli settlement around it. This fear is not unfounded, given the fact that Israeli settlers have done exactly that all across the West Bank in places they believe are connected in some way to Jewish biblical history. The notoriously violent Jewish settlements in Hebron, for example, were built there due to the location of the Tomb of the Patriarchs in that southern West Bank town. Following the initial years of settlement, settlers even managed to convince Israeli authorities to physically divide the shrine – which is holy to local Palestinians – and turn the whole area into a heavily-militarized complex. Other shrines have become excuses for the Israeli military to build army bases inside Palestinian towns, like Rachel's Tomb in Bethlehem – which is surrounded by twenty-foot high concrete walls on three sides to block Palestinian access. The village of Nabi Samwel near Jerusalem, meanwhile, was demolished in its entirety to provide Jewish settlers access to the tomb at its heart.
I'm not denying the temple mount is there. I'm just saying that history has been manipulated to erase centuries worth of cultural heritage through scholarship and Palestinians are protective of their most important symbol of resistance and life. Even you saying "Islam and Christianity came after Judiasm" is a dogwhistle for me, because a lot of the time extremists say that to completely erase AlAqsa as an important site to Muslims and intending to deny the site as a shared worshipping site that is quite important to Muslims. Just because Islam came after Judiasm, does that mean it's not legitimate as a religion itself? Islamically, Islam is a continuation of Judiasm, so we don't deny judiasm is important to AlQuds. We just are so concerned with losing our national symbol that we're so protective over it.
Now I bring up the massacre at ibrahimi mosque because, like mentioned in the excerpt above, Palestinians are afraid something like that will happen again. There's no protections for Palestinians, and most of the time they're denied from praying in AlAqsa themselves by Israeli authorities. Israeli settlers themselves come in and disrespect AlAqsa, and as I mentioned, extremists plan on demolishing AlAqsa to build a Third Temple. The Massacre at the Mosque paved way to the "Jews Only" streets I mentioned, including the militarization and basically a complete upheaval of normal life for Palestinians. I suggest looking into how terrible the situation in AlKhalil is, and that arised directly from the massacre.
You cannot separate this issue from the colonial implications of the last safe haven in all of Palestine being open to Israelis. Now when Palestine is free, I doubt there would be restrictions. But right now, there are and to pretend Israelis don't pose a threat to Palestinians fundamentally, would be erasure of the colonization of Palestine.
I'm sorry if that sounds harsh, but even if AlAqsa was built hundreds of years after, it doesn't change the fact that RIGHT NOW Israelis have privilege that Palestinians do not. As soon as that privilege is no longer there, then we can talk about allowing Jews there. But until then, Palestinians are constantly in danger of settler violence and to take away a space (which, Ibrahimi Mosque was one of those sites before Palestinians were massacred) is frankly, an insult and a denial that Palestinians themselves are colonized.
I suggest looking at the links I provided earlier for more in depth analysis. I'm going to reiterate: the only reason it's illegal is because Palestine is colonized and this is our last safe haven that we even aren't completely allowed from entering ourselves.
Most Palestinians are quite heated about this topic. It genuinely is considered one of our last national symbols (so not just religious but also political and cultural), which means that having that taken away (which extremist settlers plan on demolishing it completely, and if they're allowed in, then there are no restrictions on their behavior) would be tantamount to losing our balad, or nation. I've heard Israelis call AlAqsa terrible names over the years and some fully intend on demolishing the site. Even within Israeli politics, it is a genuine goal for some people, including Ben Gvir, so most believe that opening the door for settlers (who are the ones who want the destruction of AlAqsa) would be equivalent to giving it up. You can't ignore that when talking about AlAqsa and the laws surrounding it. The primary reason for this protectiveness is political and cultural.
#palestine#the second intifada happened because ariel sharon forced his way in for political reasons#palestinians were so angry and took it as an insult (which it was) that the second intifada happened
270 notes
·
View notes
Text
PALESTINE THE ENTIRE HOUSE WAS DESTROYED EXCEPT QURAN RECITATION #shorts...
#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#gaza strip#israel#current events#genocide#israel is a terrorist state#important
20 notes
·
View notes