#IT Security South Africa
Text

#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#apartheid#imperialism#settler colonialism#palestinian state#security council#united nations#south africa
608 notes
·
View notes
Text
ICJ, Security Council and What the ICJ Ruling Means
I want to start by saying that the recent ICJ ruling isn’t enforceable, but we can make it useful if we choose to. It’s a landmark decision in international law that we can mobilise for our activism. We’ve now seen Britain resume funding of UNRWA. And this ruling is something that is much more tangible for trying to convince governments to place diplomatic and economic sanctions on Israel, demanding ceasefires, recognising Palestine etc.
More on that below but I’m now going to explain a bit more about that and some of the UN bodies/structure stuff as I saw a couple of reblogs on this post have questions about what this means and what the ICJ’s powers really are. (This post responding to a question about the original post has some information as a much shorter read)
There’s a lot of flaws with the United Nations System (the General Assembly, Security Council, UN Secretariat, International Court of Justice, Trusteeship Council, and the Economic and Social Council), it acts as a tool of neocolonialism for the interests of the global powers, especially the Western powers, its binding/enforcement status makes it superficial, is often arguably undemocratic, and has a poor separation of powers. In this long read (I’m sorry) I’m mainly going to be talking about the Security Council and International Court of Justice (ICJ).
The Security Council technically has greater enforcement powers than the ICJ and can technically apply them to ICJ rulings if they’re taken to the Security Council. But the five permanent members of the UN Security Council USA, UK, China, France, and Russia have veto powers.
This has been justified for reasons like maintaining international political stability and to ironically prevent US domination but it has been understandably criticised for being undemocratic and also for preventing action to stop crimes against humanity and war crimes as this veto means that the UN can’t take action against these permanent members and their allies.
Nicaragua v. United States of America [1986] was one of the biggest ICJ cases. It ruled that the US has violated international law by supporting the Contras (right-wing rebellion group) in their rebellion against the Nicaraguan government and mining of the Nicaraguan harbours. The ICJ ordered the US to pay reparations to Nicaragua, which the US refused to do. Nicaragua then took their case to the Security Council to try and make them enforce the ICJ’s ruling. To no one’s surprise, the US used their veto powers and vetoed this at the Security Council. It then went to the UN General Assembly and passed as a non-binding resolution urging US to follow the rulings.
Recently, we saw the US use their veto power earlier in the year to block immediate ceasefire resolutions from other countries.
The ongoing case South Africa v. Israel with South Africa accusing Israel of being in violation with the Genocide Convention. The Genocide Convention is an international treaty that basically says as a state, you have obligations to prevent, stop, and not commit genocides and if you do, there are consequences. The Genocide Convention was born from the atrocities that happened during World War II with the Holocaust, Armenian Genocide etc. Genocide became a crime against international law in 1946 and the Genocide Convention was signed in 1948 but became effective in 1951.
The scope of the Genocide Convention has been raised as an issue in a few cases. And cases of genocide taken to the ICJ are pretty complicated with the findings. It’s something they find very hard to find a state guilty of and are hesitant to do. There’s a few different reasons for that but this post is already super long and I’m trying to keep it short. One of the first cases that was submitted to the UN as an alleged violation of the Genocide Convention was the ‘We Charge Genocide’ paper written by the Civil Rights Congress (CRC), which accused the United States of America of genocide against black Americans under the genocide convention, the CRC paper cited lynching, police brutality, inequalities in health, disenfranchisement of black people in the south (it was over a decade after this paper did black women get the right to vote in 1965), and legal discrimination. It was rejected by the UN for being a misuse and was laughed at by the US government and Press, accusing it of being exaggerated and even as an attempt to advance communism. It’s a paper that’s worth a read and also has an interesting history and legacy worth looking into. The US was never a really big fan of the Genocide Convention, they signed 30+ years later and have since withdrawn.
In Bosnia and Herzegovnia v Serbia and the Montenegro [2007], the ICJ found that the Srebrenica massacre was a genocide but the ICJ did not find that the Serbian government was responsible or complicit in the genocide. They were still found in breach of the convention though for not cooperating with UN bodies and for failing to prevent the genocide and acquitted Serbia. The ICJ rejected Bosnia’s request for reparation repayments.
These two papers/cases are some of the bigger ones that I think show how the ICJ is hesitant to and struggles to define and hold states accountable with violations of the Genocide Convention.
The findings of the recent ICJ ruling and their ordering of Israel to return land, leave settlements and remove settlers, are not binding. Israel does not need to comply! And with a refusal of this, the ICJ ruling could potentially be taken to the Security Council to try and make it more enforceable, but it is likely that if that situation happened, the US would veto that resolution.
This current ICJ ruling is still a landmark for International Law and carries political weight. Since this ruling we’ve seen the British government say they will resume funding to UNRWA (they stopped this after Oct 7th).
I said it before but the ruling isn’t enforceable but we can still make it useful. It carries the political weight of
We need to continue advocating so that there is a free Palestine in the lifetime of every single living Palestinian, they deserve it and we owe it to them.
Israel and its supporters now have international law saying that what they’re doing is wrong, they can no longer hide behind grey legal matter. This is political and justice ammunition that we can mobilise for activism to put pressure on our governments, especially those of us with western governments, governments who have been complicit, tried to play both sides etc. We need to use this to pressure out governments, contact our head of governments, different representatives and ministers to place economic and diplomatic/political sanctions on Israel, recognise the state of Palestine, withdraw recognition of the state of Israel, demand an immediate and permanent ceasefire, create and approve Palestinian visas, increase Palestinian aid funding etc.
The west no longer has grey legal matter to continue what they’re doing, especially with plausible deniability and the narrative they’ve been subscribing to. They can’t hide behind this grey area as what they’re doing directly contradicts and violates international law.
Thanks for reading this far if you made it, I will answer genuine questions but I will delete, report and block any comments and asks that are anti-Arab, zionist, Islamophobic, racist, and/or antisemitic.
#free palestine#palestine#icj#icj genocide case#south africa#icj ruling#icj case#genocide#genocide convention#security council#united nations#international court of justice#colonisation#neocolonialism#social justice#social issues#important#gaza#west bank#usa#uk#politics#middle east#current news#unrwa#human rights#global news#solidarity#israel#activism
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
Live coverage of the 11th of January 2024 has now begun.
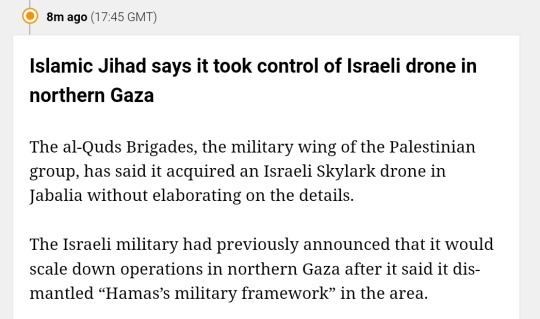
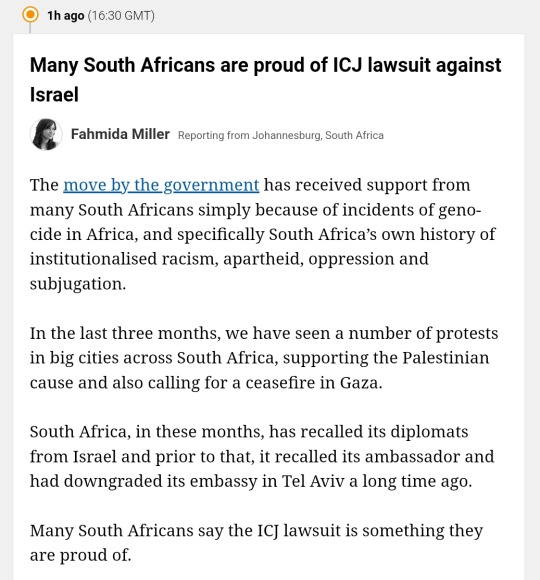



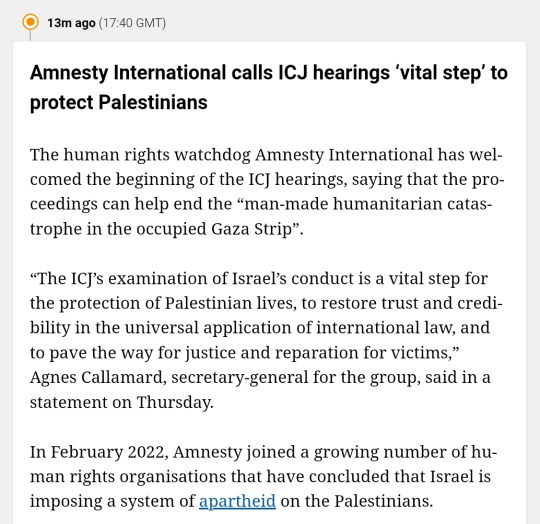


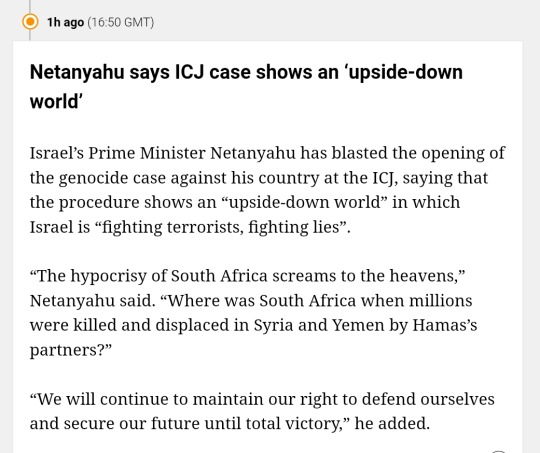
Here is an amalgamation of news from the last near 2 hours.
Below is the opening of the ICJ case of South Africa VS Israel, given my intense disgust at my government for not backing this I'm pleased that one of the lawyers is an Irish woman. I watched it all earlier, it was utterly phenomenal. Don't wanna sit for 3 hours? Put it on 1.5x speed and cut it in half.
#free gaza#free palestine#gaza strip#irish solidarity with palestine#palestine#gaza#news on gaza#al jazeera#boycott israel#israel#International Court of Justice#ICJ#South Africa VS Israel#Fahmida Miller#Rashida Tlaib#benjamin netanyahu#Khan Younis#Nasser Hospital#UNSC#United Nations Security Council#Hoda Abdelhamid#Al-Quds Brigades#YouTube#Video#Important#Signal boost#Amalgamation#Summary
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

JOHENNESBERG, SOUTH AFRICA.
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Firewatch (March 2024 edition, Part 2)

(This is Part 2 of my innagural edition of "Firewatch" becuase I was dumb and didn't realize what the character limit is. Read Part 1 here).
Full piece beneath the cut.
Smoldering Embers
These are the conflicts that, while not yet to the point where the flames are rising and heating up, smoke is starting to billow (or has been billowing) and there's potential for a real blaze to suddenly flare up at a moment's notice. You may have heard about them in the news here and there, but they're likely only popping up for your attention once in a blue moon because they haven't gotten bad or dramatic enough yet to fully grab the world's attention amid everything else going on.
West Africa/Sahel
The Sahel regions of West Africa are no stranger to crisis and conflict. Multiple countries in the region have already been dealing with internal political discord and armed conflict for years, but now multiple factors and various players seem to be converging in this part of Africa, positioning it to take a number of different paths forward in the coming months and years – few of which look very good.
West Africa and the Sahel are feeling a series of different pressures converging all at once. Since 2020, the region has seen a historic number of coup d'etats – both failed attempts and successful ones – which often come with a large amount of public support amid frustration with institutions and leaders that appear to be failing them. One reason for this frustration (among others that should be unsurprising, like economic troubles) is increasing amounts of instability throughout the region. Affiliates of both Al-Qaeda and the Islamic State both have footholds in the region, and are engaged in insurgencies against the governments of Mali (its most recent coup being in 2021, and also fighting a simultaneous insurgency by Tuareg separatists), Burkina Faso (most recent coup in 2022), and Niger (most recent coup in 2023), with Nigeria also dealing with a well over-decade old insurgency against Bokho Haram.
Niger's coup last year, in particular, seems to have been a watershed moment for the region and beyond. The country was strategically important both for its mineral resources (which unsurprisingly have not translated into economic and social development for the people of Niger themselves) and as a geographically well positioned outpost both for France (who's colonial legacy hangs heavily over the region) and the Untied States and other foreign powers, who all had troops stationed in the country to conduct counter-terrorism operations. The coup was seen as serious enough that the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) issued an ultimatum to the Nigerien junta this past summer, threatening that if it did not cede power back to the elected President that ECOWAS would intervene to restore the legitimately elected government (as it has in the past).
Ultimately, the ECOWAS threats have not come to fruition and don't seem likely to – despite some apparent moves to do so in the aftermath of the coup. But out of those threats, Niger has joined into a new political and military alliance called the Alliance of Sahel States with both Burkina Faso and Mali (all of which had been suspended from ECOWAS due to their respective coups) to provide for collective self-defense against foreign intervention. Since 2023, French troops have been forced out of both Burkina Faso and Niger – with Niger now seemingly on the verge of doing the same to the remaining US troops in the country, while Vladimir Putin's Russia has seemingly been on a charm offensive to befriend the members of new alliance signing economic and military agreements and even reportedly dispatching troops – with mercenaries such as those from Wagner already having been active in the area (now operating under the new name of the "Africa Corps").
All these factors and more combined suggest that things in the Sahel are liable to get very interesting in the near future. As stated before, a number of different paths seem to unfold ahead for the region: if the ongoing radical insurgencies continue and are victorious, we could see a new territorial caliphate in West Africa and the Sahel mirroring that of IS in Iraq and Syria in the 2010s (and all the horrors that came with it). Barring that, as Russia deepens its ties to the AES, it could further turn the region into even more of a battleground in the multilateral Cold War we find ourselves in (as Russia is not the only authoritarian power seeking to deepen its influence in West Africa, as Turkey under Recep Tayyip Erdogan is also attempting to get involved there). Those are only two potential options out of many, and the myriad of other options in a region that is heavily populated and on the radar of multiple great powers means that it bears continued monitoring going forward.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo/Rwanda
Now this is one that I imagine is probably flying under the radars of most people who aren't deeper into my field, but is probably one of the most immediately pressing in Africa. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has been fighting against a rebellion by the armed group known as "M23" in its East for a decade now – that much isn't new. But now the conflict is threatening to turn onto a state-on-state war in Africa's Great Lakes region, as M23's primary back of neighboring Rwanda seemingly steps up its direct involvement into the conflict.
Rwanda has been backing M23 for some time now, with both Rwanda's government (under long-time President Paul Kagame) and M23 itself being primarily led by members of the Tutsi ethnic group. Rwanda also has a history of armed interventions in the DRC as well, so that in itself is not new. But in recent months the long-running tensions and low-level conflict between the DRC and Rwanda has threatened to boil over into outright, full-scale war, amid a series of fresh escalations – one prominent example being Rwanda firing on a DRC fighter-jet that it claimed violated its airspace. The high level of tensions has been further evidenced by more direct US involvement recently than is typically seen in this part of the world, with the United States and other governments attempting to broker some kind of peaceful resolution between the DRC and Rwanda. These efforts do not seem to have made much headway, with this past month the United States resorting to publicly urging both the DRC and Rwanda to "walk back from the brink of war." US mediation efforts may well be undermined, however, by it's (and many other Western countries') cozy relationship with Rwanda – despite its autocratic leader.
The trajectory for the current crisis remains unclear. A sideline meeting during the African Union summit in the Ethiopian capital of Addis Ababa appeared to make some progress in at least getting both the DRC and Rwanda to sit at one table and discuss a return to a peaceful dialogue to resolve their differences. However, that same day, the DRC accused Rwanda of having launched a drone attack in the city of Goma – a key objective of M23's advances, seemingly pouring cold war on the idea of constructive and peaceful reconciliation for the time being. Most recently, the DRC appears to be acquiring drones of its own, with China reportedly set to supply the DRC with nine CH-4 armed drones (apropos of nothing, China has also supplied a fair amount of military hardware to Rwanda in recent years, as well as military training).
With little other news available on the crisis since February (with other global events taking precedence), it remains unclear where things with the DRC and Rwanda go from here. There have been reports that the DRC and Rwandan leaders may be preparing to meet face-to-face once more, through mediation by Angola. At the same time, little seems to have changed with the personalities at play. DRC President Felix Tshisekedi was recently re-elected (under conditions labeled a "farce" by the DRC opposition), and has previously taken a hard line on the crisis, threatening to "march on Kigali" if re-elected and the issues with Rwanda persist. The DRC's acquisition of drones from China seems to reinforce that it has no plans of backing down in its confrontation with M23 and Rwanda, even if Tshisekedi doesn't follow through on his more bellicose threats. Meanwhile in Rwanda, Kagame announced his intent to seek a fourth term as President – amid criticism for lifting term limits in order to stay in office longer (criticisms that he has made clear he cares very little for if at all), and so has an impetus to maintain his own hard-line on issues with the DRC.
A further ticking clock has been added to the DRC-Rwanda situation by the fact that the United Nations mission in the Congo – which has been assisting the DRC fight against rebels (including M23) for almost two decades – will now be leaving the DRC by the end of 2024 at the request of the DRC government, stating that the force had not been able to resolve the war with M23. This comes after the DRC government also ordered troops from the East African Community (EAC) that had been present in the country as well to leave in late 2023 – for the same reasons it ordered the UN force to leave. While the DRC may well be right that neither force has helped it to beat M23, the withdrawal of these troops may very well shift the entire balance of the conflict and not necessarily in a way that the DRC wants. The South African Development Community (SADC), led by South Africa itself, is seeking to fill the gap left by the UN and EAC, but it remains to be seen how quickly they can do so and if they can change facts on the ground any more than the UN or EAC could. Once again, we see a number of potential factors on a collision course, and while cooler heads may still prevail, we see the prospect of yet another major war in the heart of Africa's Great Lakes regions that could have significant impacts for the people of the region, the continent, and the world. It is definitely worth keeping an eye on this developing situation (to the extent you can even find news on it).
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, like Myanmar, is a country that has shown up in the past when I've done a round-up on pertinent conflicts in the world. However, unlike with Myanmar, I'm afraid I can't report that things are getting better in Ethiopia's case or that there's much cause for hope at this point. In fact, things seem to be getting actively worse.
The last time I substantively talked about Ethiopia, the government of Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed was engaged in a war in the Tigray region against the Tigray People's Liberation Force – even allying with his former long-time adversary of Eritrea to do so in a war that threatened to rip the country apart while engaging in brutal authoritarian actions that I'm sure are making the Nobel Committee really regret giving him that prize in retrospect. After a seesawing of the fortunes of war back and forth for both sides, the conflict was seemingly brought to a close by the signing of a peace agreement between the TPLF and the Ethiopian federal government. All's well that ends well, done and dusted, right?
Well, actually: no.
Just less than a year after the Tigray War ended, Abiy apparently tripped over his dick into a new internal conflict in mid 2023, this time with Amhara people and forces in the eponymous Amhara region (Ethiopia's second most populous) rather than Tigray. The spark for this conflict was apparently born out of the haphazard way in which Abiy ended the previous one. One of Abiy's key allies in the Tigray War were militias and security forces from the region of Amhara, including an influential armed group known as the "Fano." However, the peace deal that Abiy struck with Tigray did not sit well with many Amahara people, who felt betrayed by the deal due to Tigray claims on their territory (as well as the fact that the Ethiopian federal military and security forces had been unable to prevent the TPLF from occupying Amahara territory during the war). This rift was only made worse by crackdowns by Abiy's government against the Fano, coupled with a plan to absorb Ethiopia's regional security forces into Ethiopia's federal military and security forces, which was not received well among the Amhara. These tensions and more came to a head from April through August 2023, with the result being Abiy's government facing down a fresh and ongoing revolt that doesn't appear to be ending soon.
The result of this bridge burning by Abiy has been a growing war in Amhara occurring under the umbrella of an ever prolonged state of emergency in Amhara that gives Ethiopian authorities broad powers to carry out arrests, impose curfews, and ban public gatherings. This is a continuation of the Abiy's playbook of gross human rights violations from the previous war in Tigray, with accusations being leveled against his government of arbitrary arrests, extrajudicial executions, and indiscriminate killings – including indiscriminate drone strikes against targets such as schools and public transit stations (apropos of nothing, once more, Abiy has acquired his fleet of armed drones from Iran, Turkey, and China – as well as purchasing new fighter jets from Russia). If you're wondering why you haven't heard more about all this, its because Abiy has made heavy handed use of another favorite tactic of his from the previous war (and that it has even used against Amhara in the past), which is information and specifically internet blackouts, which make it very difficult to get information out of Amahara as the conflict drags on (as it did in Tigray during that war).
Abiy's uncanny knack for burning bridges and making enemies isn't limited to within his own country, but has made tensions rise throughout East Africa. At the start of 2024, Abiy signed an agreement with the breakaway region of Somaliland in Somalia, which reportedly gives Ethiopia a naval port on Somaliland's coastline in exchange for recognizing the region's independence from Somalia (something that no other UN member state does). All of this appears to be part of Abiy's quest to regain Ethiopian access to the sea (lost after Eritrea became independent), which has included efforts to re-establish the Ethiopian Navy. The reaction to this deal has been, unsurprisingly, poorly received in Somalia, with Somali President Hassan Sheikh Mohamud even threatening the possibility of war if Ethiopia follows through with it and accusing Ethiopia of outright trying to annex part of Somalia. Somalis are not the only ones unease about Ethiopia's quest for access to the Red Sea, with other East African states such as Djibouti, Eritrea, and Kenya all having previously voiced concern about Ethiopian actions.
There's also the matter of Ethiopia's previously mentioned issues with Egypt over the Nile River, in particular Ethiopia's construction of a massive hydroelectric dam known as the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (or "GERD") on the river that Egypt worries could have a devastating effect on its water supply downstream if Ethiopia acts without considering Egyptian concerns. Despite numerous efforts to come to an agreement over the dam and the river, every attempt thus far has ended in failure, with Egypt continuing to refer to GERD an "existential threat." Egypt has also made it clear that it stands squarely with Somalia regarding the sea access debacle, with Egypt's autocratic President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi asserting that "Egypt will not allow anyone to threaten Somalia or affect its security," creating a fresh avenue for tension between Egypt and Ethiopia in addition to the GERD issue. This is all in addition to concerns that both Egypt and Ethiopia could be drawn into the aforementioned civil war in Sudan, with numerous potential negative consequences for all involved.
The long and short of things when it comes to Ethiopia, is you have no shortage of opportunities for more intense conflict in the near future, both within and around the country. Abiy's continued heavy handed approach to both domestic and foreign politics creates an ever increasing possibility that one day he will bite off more than he can chew, and potentially spark a conflict of such scale and scope that it could engulf all of East Africa in a major war and potentially even destroy Ethiopia – the second most populous country in Africa – as a polity. Given the potential consequences, this is a part of the world meriting very close observation going forward.
"Do You Smell Something Burning?"
In this final section, I want to touch briefly (as I've already gone on for a few thousand words) on some hot spots in the world that are cause for concern and have been for a while, but have nothing major going on at this moment in time. While they may be quiet (at least relatively speaking, compared to everything else we've just talked about), they have the potential to spark up in the mid to long term and become a problem once again.
The Korean Peninsula
By this point, we're probably all used to North Korea (under its dictator, Kim Jong-Un) shooting off missiles and making bellicose statements. That's par for the course for them. But in recent months, Kim and his government's rhetoric have taken a new and more hostile turn. North Korea has stated it has abandoned the idea of peaceful unification with the South, instead naming it North Korea's "principal enemy" which it will "annihilate" if it is provoked. This comes as North Korea continues weapons tests and conducts multiple military drills – with Kim often in attendance.
While I wouldn't worry about a continuation of the (yet unresolved) Korean War just yet, this may well be cause for concern. While tensions are typical on the Peninsula, we haven't seen rhetoric like this from the North in quite some time. And while full-scale war may be unlikely at this moment (though not impossible), 010 showed us that under the right conditions, the Peninsula is never far from violent skirmishes and incidents between the two Koreas, such as the shelling of Yeonpyeong Island and sinking of the South Korean Navy corvette Cheonan. While wider conflict was avoiding in those cases, now that South Korea has a more reactionary President wanting to present a hard line towards the North, it raises questions about it may react to provocation. Again, while I wouldn't be panicking just yet, it may be worth keeping your ear to the ground on this one to keep from being caught unawares if tensions suddenly spike further.
Armenia and Azerbaijan
Well, they finally did it. I've also written about this conflict several times now, and it looks like by all accounts, Azerbaijan has gotten exactly what it said it wanted. After the world stood by and did largely nothing in its 2020 war against the ethnic-Armenian enclave of Artsakh (AKA: Nagorno-Karabakh), Azerbaijan decided to finish the job once and for all with a fresh offensive on the heels of a nine-month blockade this past year. With next to no prospect of outside assistance, and weakened by the blockade, the Artsakh forces quickly folded, and almost the entirety of the ethnic Armenia population promptly fled in the ensuing days and weeks to avoid violence at the hand of Azeri forces, leaving Azerbaijan free to complete its cultural genocide of the region. But now that its over, surely Armenia and Azerbaijan can find a way to live in peace with this new reality? Right?
Ha ha, no.
In what should be surprising to absolutely no one, Azerbaijan has celebrated getting what it wanted in Artsakh by shifting the goal post once more. Now its new demand is a land corridor connecting it to its ethnic exclave of Naxcivan on the opposite side of Armenia – referred to as the "Zangezur Corridor" (after the Azeri name for the Armenian Syunik province that it would pass through). Armenia seems highly unlikely to agree to such a demand, which it views as an unacceptable infringement on its sovereignty, which likely means – as has been the case after every war fought between these two countries in the past – a new war is almost certainly on the horizon as Azerbaijan will not stop until an outside force compels it to stop and will use the Armenian rejection as an excuse for fresh conflict. 2024 has already seen fresh skirmishes on the border between the two countries, showing that the tensions remain very much present.
It's not clear when this new war will occur, but we can only hope that in the interim more nations step up to actually assist Armenia. We have seen hopeful signs of greater support from other countries, with France and India selling arms to the country to help it defend itself. However, I can't take any of that for granted, with how the world has left Armenia out to dry time and time again. If Azerbaijan does decide to go to war for a land corridor, it also risks potentially sparking a wider regional war, as Iran has called such an action to cut off its land border with Armenia a "red line" (though whether or not it would really take military action in response remains unclear). Anyway, keep your ears to the ground on this one, because like with the other wars Azerbaijan has launched it'll likely come out of the blue.
I'm Very Tired.
I've just thrown a lot of information at you, so I'm going to try and keep this conclusion short and sweet (for me). First, I'll lay out a few takeaways about the wider world situation, and then some general closing thoughts.
Looking at the general state of things with the conflicts I've laid out, I'm going to infer a few things about the general state of global security. For one, Africa is in a dire state in multiple regards and seems to be the biggest place to watch for trouble on the horizon at the moment, as it has several crises that seem ready to boil over into major wars in the near future – if they haven't already in some cases. These crises and conflicts have the potential to pit some of the most populous countries on the continent against one another, and also to rip some of those same countries apart internally. Short of that, Africa is also seemingly getting teed up to be the sight of a new round of intense great power competition for influence and resources the likes of which we haven't seen since the Cold War, with said competition not just involving big players like the United States, Russia, or China, but attracting newcomers to the influence game too – as the UAE's involvement in Sudan's civil war has shown. Finally, it's also worth noting that now that we're in a post-Russian invasion of Ukraine world where large scale state-on-state conflict is back on the menu after many "experts" thinking it was dead and gone, it makes some of the fault lines we're watching here even more important to keep a close eye on.
There's almost certainly more that I say here, but these are just some big overarching themes to take away from this round of observation. Now, for the closing thoughts:
I know you're tired. We all are. I am.
That being said, we can't give up in our fight for a better world for everyone living in it. That requires remaining well informed (to the extent that you're able) about what's going on in that world. This is especially true if your government is playing a role in it (for good or for bad), or it isn't and it should be. Information is, in its own right, power.
I know that your emotional energy is precious, and likely being eaten up but a number of different things at any given moment. I'm not ask you to drop everything and devote all your time and energy to these causes or others, nor am I trying to shame you for not paying as close attention to them as I or others have. Simply, to add them to the Rolodex of your brain as something that matters and that you should check in on once in a while so you're not caught unawares when new developments occur that may affect you and others.
There's only so much that all of us can do about any one issue, either at home or abroad. But we do what we can, and in order to do that, we need to have an idea of what's going on. So take that as you will after reading all this (or anything else that I write or post, for that matter).
On that note, I'll let you get back to whatever else you need to do. But thank you for taking the time to read this and potentially learn more about events you may not have known much about and their potential impacts. I'll hopefully see you again for my next essay, but in the meantime: stay safe out there and don't give up.
Photo credit: africanews/AFP.
#War Takes#War Takes essay#War Takes Firewatch#West Africa#Sahel#Niger#Burkina Faso#Mali#Democratic Republic of the Congo#Rwanda#Ethiopia#Armenia#Azerbaijan#South Korea#North Korea#war#international relations#foreign policy#defense#security
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
International researchers from Finland, Germany, South Africa, and Ethiopia report that deforestation during the last two decades induced a higher warming and cloud level rise than that caused by climate change, which threatens biodiversity and water supply in African montane forests.
Montane forests are often cloudy, wet, cold, and occur on isolated mountains in Africa. They are rich in biodiversity and act as water towers by trapping water from fog and clouds, providing high quality fresh water for millions of people in the lowlands of Africa.
In the last two decades, as much as 18% of Africa's montane forests have been lost due to deforestation, which resulted in a warming and cloud level rise two times higher than that caused by climate change. Research shows that air temperature has increased by 1.4 °C, while cloud level has risen by 230 meters during the last 20 years.
"It has strong consequences for the water resources and biodiversity," comments Prof. Dirk Zeuss from the University of Marburg. -The study is published in Nature Communications.
continue reading
#south and eastern africa#montane forests#deforestation#cloud level rise#less rainfall#water security
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
(liars )
A cry of truth against👇🏼
The representative lawyer of zionists at the court of justice .
#gaza#war criminals#palestine#free gaza#united nations#war crimes#amnesty international#unicef#free palestine#stop the massacre#stop genocide#no pride in genocide#united nations security council#star wars#save children#human rights#human rights watch#save the children#international criminal court#stop the genocide#south africa#space#astronomy#nasa#liars#save rafah#save gaza#ceasefire now#cease fire in gaza#ceasefire
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Canadian spies, white supremacists and South African secret agents affair...
This all started three days ago with a blog about a Canadian striptease club called Le Strip.
Life seemed so simple then.
Yesterday’s follow-up blog was titled: THE NOT-SO SIMPLE TALE OF A CANADIAN STRIP CLUB AND TERRORISM IN THE 1980s.
It was about David Hughes, who worked as a doorman/cashier/DJ at Le Strip 1982-1994… and as a trainman on the Canadian Pacific Railway system 1986-2019… and as a…

View On WordPress
#ANC#apartheid#Army#BOSS#Canada#CSIS#David Hughes#Grant Bristow#Heritage Front#Le Strip#Max French#new Nazi#politics#Rhodesia#secret agent#Security Intelligence Review Committee#South Africa#spy#strip club#Toronto#undercover#Val Meredith#white supremacy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chinese Senior Diplomat Calls To Resist Cold War Mentality At BRICS Security Meetings
— Global Times Staff Reporters | July 25, 2023

Photo: BRICS. VCG
Cyber security as well as other threats in traditional and non-traditional security fields have taken the spotlight at the ongoing meetings of BRICS countries in Johannesburg, South Africa, as analysts said that amid growing global uncertainties, more developing countries are seeking to improve solidarity to jointly tackle challenges to their development under the auspices of the BRICS mechanism.
While attending the 13th Meeting of BRICS National Security Advisers and High Representatives on National Security in Johannesburg, South Africa on Tuesday, senior Chinese diplomat Wang Yi said that after more than 10 years of development, the BRICS has become an important platform for emerging market countries and developing countries to unite and self-development.
Under the new situation, we must grasp the future development direction of the BRICS countries, further strengthen political mutual trust and strategic coordination, continue to provide international public goods that meet the requirements of the times, and strive to translate the BRICS spirit of openness, inclusiveness, and win-win cooperation into practical actions, and polish the "golden brand" of BRICS cooperation, Wang said.
To deal with the current global security challenges and solve the security dilemma, Wang also called for countries to resist unilateralism, hegemony and oppose "decoupling" and "double standards" and oppose Cold War mentality and zero-sum game.
Analysts said that the ongoing meetings for security advisors and senior diplomats from BRICS countries and "Friends of BRICS" underscored the security concerns of developing countries and new emerging economies over the destructive activities, "color revolutions" and cyber attacks plotted by some countries who have posed great threats to the stable development of developing countries and global peace.
Aside from expressing their concerns over traditional and non-traditional security fields, BRICS countries and developing countries are seeking to improve solidarity to jointly tackle development challenges under the BRICS mechanism, which will also be part of the build-up to the 15th BRICS Summit in South Africa to be held from August 22 to 24, they noted.

On Monday, a meeting, which was held under the theme of "Cyber security is increasingly becoming a challenge for developing countries," is also being attended by Minister in the Presidency of South Africa Khumbudzo Ntshavheni, Chief Adviser of the Presidency of Brazil Celso Luiz Nunes Amorim, Secretary of the Security Council of the Russian Federation Nikolai Patrushev, National Security Adviser Ajit Doval of India and representatives of Belarus, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Burundi, the United Arab Emirates, Kazakhstan, Cuba and other countries.
Security Concerns Under Spotlight
During the Tuesday meeting, Wang, member of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee and also director of the Office of the CPC Central Commission for Foreign Affairs, said that the "Global South" is a collection of emerging market countries and developing countries, reflecting our collective rise on the international stage. Countries in the "Global South" face the important mission of resisting the external intervention and maintaining political security and regime security.
Wang Yi said that unity is strength, action is direction, and openness is motivation. China is willing to work with BRICS partners to support each other's efforts to maintain national security and stability, and to carry out more practical cooperation in dealing with international security challenges, so that the world can hear more BRICS voices and witness a greater role of the BRICS.
Senior officials on security from BRICS countries also exchanged in-depth views on issues such as current security challenges, anti-terrorism and cyber security, food and water security, and energy security, and reached broad consensus, according to a release from Chinese Foreign Ministry.
The issue of cyber security has been discussed at length at the ongoing BRICS meeting as some Western countries have intensified using the internet to conduct destructive activities in other countries, including inciting domestic riots, fooling the public or organizing cyber attacks on governmental departments, which have posed threats to developing countries' stability and development, Song Zhongping, a Chinese military expert and TV commentator, told the Global Times on Tuesday.
The meeting on security, together with other meetings in various fields, will lay the groundwork for the leaders' summit in August, as the BRICS mechanism is a cooperative mechanism beyond economic and security fields, and whether it is regarding traditional or non-traditional fields, it would safeguard development and cooperation in other areas, Song said.
This year's BRICS summit will focus on improving cooperation between BRICS members and African countries in technology, economy and other fields, and security would also be the basis for cooperation, said Song.
South Africa has invited the heads of state of all African countries to the summit, which is themed as "BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development, and Inclusive Multilateralism." The summit is anticipated to discuss how BRICS countries can better work with African countries, media reported.
Security is the core concern for the financial cooperation of BRICS countries and other developing countries. This is also why BRICS countries are studying the potential use of alternative currencies to the US dollar, analysts said.

For the past months, many media, especially those from the West and the US, have reported that BRICS countries are seeking to shift from the dollar in mutual trade to avoid becoming "victim" to sanctions. For example, in April, Bloomberg reported that Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva called on BRICS countries to come up with an alternative to the dollar in foreign trade.
South Africa, the BRICS chair, has put the stability of the global financial system as a priority for the BRICS meetings, as BRICS countries and developing countries have been put in an unfavorable position that would be affected by global financial hegemony, Wang Lei, director of the Center for BRICS Cooperation Studies at Beijing Normal University, told the Global Times.
However, de-dollarization is not the core mission of BRICS countries and what they want is to make the global financial system fairer and more inclusive, and to better reflect the major changes that have happened in the global governing system, Wang Lei said.
Against the backdrop of the continuous Russia-Ukraine conflict and drastic global changes unseen in a century, developing countries are seeking to inject more stable and secure impetus to the world and to promote the international governing system to be more inclusive and better reflect their interests. However, the US and some Western media have smeared their efforts, analysts said.
What BRICS countries are working toward is not to compete with the US for its hegemony, but to build a multipolar world in which each country's concerns on security, economy and developments can be respected by others - this may also be the reason for the US and West's increasing worries of the growing influence and attractiveness of BRICS, Song said.
#BRICS#South Africa 🇿🇦#Cold War Mentality#Decoupling#Double Standards#Cyber Security#Global South#China 🇨🇳#Mutually Accelerated Growth#Sustainable Development#Multilateralism#Bloomberg#Brazil 🇧🇷#President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva#Global Times#Alternative Currencies#US Dollar 🇺🇸
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
We offer a variety of security solutions to ensure your home, apartment or business is protected 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Our guards are trained professionals who respond quickly if they notice anything suspicious.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Week on the Brink: Escalating Ethiopia-Somalia Tensions
Escalating tensions b/t #Ethiopia & #Somalia mark a volatile shift. Reports of #Ethiopian forces seizing Luuq airport raise concerns of further confrontation. Local sentiments favor ET forces, but SFG sees this as a threat to national sovereignty.
Continue reading A Week on the Brink: Escalating Ethiopia-Somalia Tensions
#2024 Ethiopia-Somaliland Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)#Egypt#Ethiopia#Gedo Region#Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)#Horn of Africa#Jubaland#Sahan Research#Security and Conflict#Somali Wire#Somalia#Somaliland#South West state#Sovereignty
0 notes
Text
WI vs SA, 2nd T20I: West Indies wins to secure series victory after South Africa stumbles in run chase
West Indies smashed 13 sixes in its innings to beat South Africa by 30 runs on Sunday at the Brian Lara Cricket Academy and secured the Twenty20 international series with a game to spare.
West Indies scored 179-6 after being asked to bat first in the second T20, accelerating from 111-4 after 14 overs. Shai Hope hit a 22-ball 41 with two fours and four sixes. Captain Rovman Powell contributed 35…
0 notes
Text
youtube
Community Heroes & South African Slang With Real Life 'Batman' K9_Reaper - HWSR Ep 57
Welcome to the He's Wrong She's Right Podcast! In this episode titled 'Community Heroes & South African Slang With Real Life 'Batman' K9_Reaper', we introduce a special guest, Dave, also known as the 'K9_Reaper' from Twitter. Hailing from South Africa, Dave gives Andrew and Nóna a glimpse into the challenges and realities of community safety efforts in his home country. From daring patrols to the innovative ways communities come together, Dave's stories are packed with action and resilience. We also dive into some South African slang, giving listeners a fun linguistic twist. Don't miss this captivating mix of heroism, everyday struggle, and a dash of humor!
Follow K9_Reaper on Twitter (X) https://x.com/k9_reaper
Visit our website https://heswrongshesright.com
All HWSR Links https://heswrongshesright.com/links
Sponsor inquiries https://heswrongshesright.com/sponsors/
Get a Shoutout in a future episode or check out the merch https://heswrongshesright.com/shop/
Donate to @veteranwiki by visiting https://veteranwiki.org
@LemacksMedia https://lemacksmedia.com
Nóna Phelps - Independent Insurance https://nonaphelps.com
Social Media
YouTube https://lemacks.app/hwsryt
Twitter (X) https://lemacks.app/hwsrtwitter
Facebook https://lemacks.app/hwsrfb
Instagram https://lemacks.app/hwsrig
Reddit https://lemacks.app/hwsrreddit
Tumblr https://lemacks.app/hwsrtumblr
Pinterest https://lemacks.app/hwsrpinterest
LinkedIn https://lemacks.app/hwsrlinkedin
Podcasts
YouTube https://heswrongshesright.com
Patreon https://lemacks.app/hwsrpatron
Spotify https://lemacks.app/hwsrspotify
Apple https://lemacks.app/hwsrapple
Amazon https://lemacks.app/hwsramazon
iHeart https://lemacks.app/iheartradio
PocketCast https://lemacks.app/pocketcast
Rumble https://lemacks.app/hwsrrumble
Deezer https://lemacks.app/hwsrdeezer
RSS Feeds
FeedBurner https://lemacks.app/feedburner
Spotify https://lemacks.app/spotifyrss
#youtube#podcast#apple podcasts#podcasting#adhd#hwsr#marriage#fyp#alpha#bewbs#Podcast#South Africa#Crime Prevention#Community Safety#Volunteer Work#Human Rights#Security#Urban Safety#Citizen Patrol#Social Issues#Community Support#True Crime#Neighborhood Watch#Safety First#Podcast Life#Interactive Podcast#Global Issues#Crime Stories#Real Life Heroes#Society And Culture
1 note
·
View note
Text
Collins Career Solution
Phone: 068 576 1532
Address: Pretoria West, Pretoria 0183, South Africa
Website: https://collinscareersolution.co.za/
Welcome to Collins Career Solution, your go-to platform for job seekers and employers in South Africa. At www.collinscareersolution.co.za, we connect top talent with leading companies across various industries. Our user-friendly website offers comprehensive job listings and efficient hiring solutions. Join us today to advance your career or find the perfect candidate!
#Security job Vacancies#Internships#Learnership#apprenticeship#general jobs#Artisan jobs#Hospitality#Goverment jobs#Cleaner jobs#Engineering jobs#Sassa Grant 370 status check#Upload Cv to hiring companies. Matric jobs in South Africa#Jobs Without Matric#Youth Opportunities#Online Courses#admin Clerk#warehouse#forklift
1 note
·
View note
Text
Solar Panel Alarm Products South Africa
Secure your solar investment with Solar-Cop's advanced alarm solutions. Explore our cutting-edge solar panel alarm products in South Africa to protect your solar energy investment with relief. Our advanced solutions are designed and engineered to protect your solar panels from theft or tampering and ensure the security of your solar panels. With advanced features such as fire alert, tamper detection, and seamless integration options, our alarm products provide reliable protection and peace of mind. Invest in the best defense for your solar panels with Solar-Cop's trusted alarm products. Visit solar-cop.com now to learn more and secure your solar energy assets today!
#Solar Panel Alarm Products South Africa#Solar Panel Security System South Africa#Solar Panel Security Alarm System South Africa#Solar Panel Alarm Connector South Africa
1 note
·
View note
Text
many people have said it but bears repeating again:
Palestinian liberation calls for a 1 state solution under which all people are equal under both under the law and in practice.
In order to have peace the genocide, apartheid, and occupation must end. Settler colonialism must end. Second class citizenry must end. All Palestinians imprisoned must be released. Reparations must be made to Palestinians who have been affected by both current events and historical, from the Nakba in 1948 to today. Everyone who participated in the facilitation of the apartheid, and the violence of the apartheid and occupation required to maintain the oppressive regime, must be held accountable. Palestinians must be granted the right to return to their homes.
The idea that Palestinian liberation = carrying out a genocide on Israelis is nothing more than baseless, racist, orientalist fearmongering (and, to an extent, pure projection) that serves to justify the current genocidal regime and the apartheid having been maintained for decades. One people's freedom does not threaten another people. People are fearmongering over a hypothetical scenario (the same fearmongering used in South Africa; both during the reconstruction era following the abolition of slavery & also against abolitionists while slavery was still legal in the United States; in regards to the North American indigenous population; and so on) while an actual genocide is going on.
the only way to real actual peace, safety, and security is through the complete liberation of the Palestinian people, not the continued maintenance of the current regime or the apartheid that led to this current moment in time. apartheid is inherently violent; oppression is inherently violent. colonialism is inherently violent. if YOUR 'safety' is dependent on the oppression, displacement, and murder of OTHER PEOPLE then your conditions are not and will never be safe.
#palestine#geopol#seeing people on twitter being like 'this is so complex' and 'but what will happen' like PEOPLE HAVE SAID WHAT!#📁.zip
30K notes
·
View notes