#ecological feminism
Text
As Chrystos writes in her poem "Shame On" about Indian spiritual exploitation, America is starving to death for spiritual meaning.
It's the price you pay for taking everything.
It's the price you pay for buying everything.
It's the price you pay for loving your stuff more than life.
Everything goes on without you.
You can't hear the grass breathe because you're too busy talking about being an
Indian holy woman 200 years ago.
The wind won't talk to you because you're always right, even when you don't
know what you're talking about.
We've been polite for 500 years and you still don't get it.
Take nothing you cannot return.
Give to others; give more.
Walk quietly, do what needs to be done.
Give thanks for your life; respect all beings.
Simple, and it doesn't cost a penny.
– Ecofeminism, Karren J. Warren
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
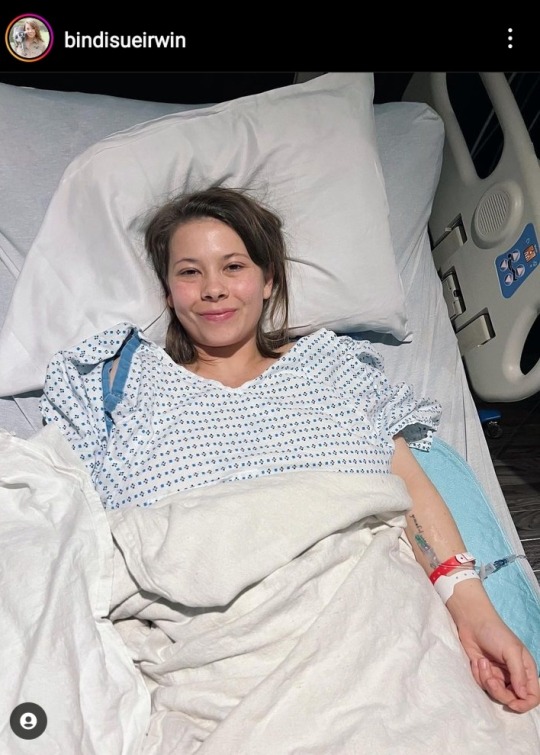
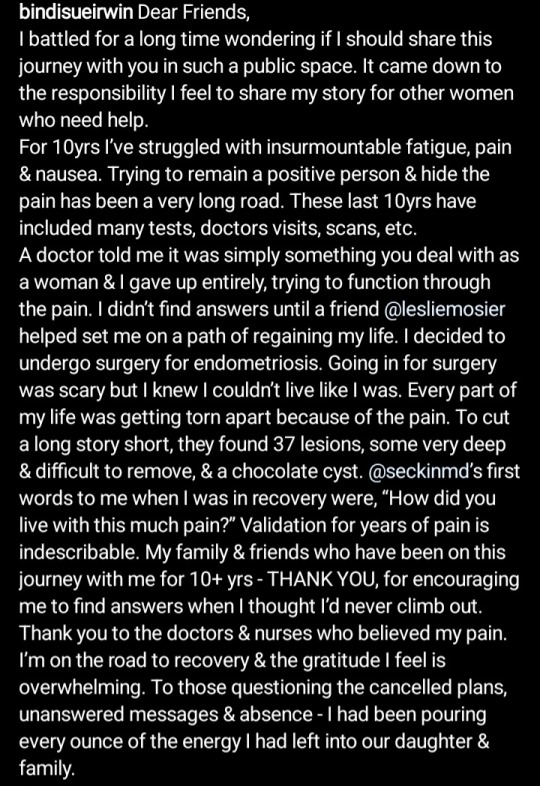

#bindi irwin#feminism#feminist#ecology#endometriosis#endo safe#women's health#chronic fatigue#disability#disabilities#chronic conditions#health#medicine#women's rights#women in science#women in stem#reproductive rights
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
A list of (realistic) things you can do to be more environmentally friendly
(from an earth-loving horticulture student.)
— COSMETICS
Use bar soap instead of soap bottles
Use old toothbrushes for cleaning surfaces
Try exploring and researching some homemade face/body/lip products
Use ice sleeves, sunglasses, and caps instead of sunscreen (Edit: I’ve seen people say that it is safer and even necessary to wear sunscreen at all times so try to use eco friendly sunscreen instead! In my country it’s pretty uncommon to wear sunscreen often as we usually wear ice sleeves which is why I did not know this oof)
Use coffee grinds or homemade tumeric masks instead of cosmetic products with exfoliator beads
Invest in a metal ear cleanser instead of cotton buds
Try placing more importance on skincare instead of contributing to exploitative beauty companies by buying makeup
Use cosmetic products that do not contain palm oil
— CLOTHING
Try as much as possible to rewear your outfits at least twice before washing them
Actually WEAR your clothes! I know some of y’all just wear them once for your Instagram post and let it rot in your closet forever. Stop doing that!
Thrift, stitch up holes in your clothes, and use second hand clothing instead of supporting fast fashion companies like SHEIN, H&M, Zara, etc.
Cut up your old clothing into yarn and do macramè with it
Cut patches of old clothing to turn into reusable cotton pads
Learn how to knit, crochet or stitch your clothes!
If you use tampons, try menstrual cups or discs instead. If you use pads, try reusable pads or period underwear. (Trust me, it works). Also, use reusable panty liners instead of disposable ones. They may seem expensive but you will end up saving a lot more in the long run
— GARDENING
Plant seeds/cuttings in your old bottles, jars, and containers
Propagate your plants and exchange cuttings with your friends instead of buying new plants
Make your own soil mixes instead of buying soil mixes
Better yet, don’t use soil for your indoor plants and try getting into hydroponics or semihydroponics instead. This saves so much water and doesn’t contribute to mining of soil
Fertilise plants with fruit peels, coffee grinds, and tea leaves. (DO NOT use chemical fertiliser on soil)
Plant more legume plants in your garden instead of using nitrogen fertilisers. (Look up the nitrogen cycle if you need an explanation on this)
Avoid pesticides unless really needed. Try sprinkling cinnamon powder on soil or spraying neem oil on plants and soil to keep away pests.
If you have a lawn, try looking into rain gardens and consider making one
Let the (non invasive) weeds in your lawn/garden grow! They are there for a reason!
Stop killing earthworms and millipedes in your garden. This also applies to snails native to your region. They are there for a reason.
Water used to wash fruits and rice can be used to water plants
— REDUCE, REUSE
Use the caps of jars as soap holders
Use recycled paper/notebooks
Wash and dry your glass/plastic items before throwing them in the recycling bin
Keep any plastic bags for future use
Use eco friendly or reusable dish sponges
Use reusable straws and cups
Invest in a fabric cup holder
Bring a water bottle with you wherever you go
Drink more water and less sugary drinks
Bring reusable bags for buying groceries instead of using plastic ones
Always keep a folded up tote/shopping bag with you in case you spontaneously decide to buy something
— ELECTRICITY
Set a timer on your air conditioning instead of letting it run throughout the night
Better yet, use a fan instead of an air conditioner
Open your windows! Aerate your home!
Allow natural light to enter your home during the daytime, so as to avoid turning on your lights
Switch to LED lightbulbs instead of regular lightbulbs
Turn off any switches in your house when they are not in use
Collect the water from your air conditioner/dehumidifier condenser and use that to water plants, clean surfaces, steam ironing, and flushing toilets. Do not drink it though!
— INTERNET
Delete your all of your unwanted emails
Delete your inactive social media accounts
Try not to post excessively on social media and stop scrolling excessively too. This not only reduces energy usage but also improves your mental health and productivity
Try to keep to one social media app instead of having so many
Reduce your internet usage
Save your eBooks on a thumbdrive instead of on cloud
Use Ecosia instead of Google
Stop being influenced by social media trends that only just contribute to consumerism
Download music instead of streaming
Reduce online shopping
— FOOD
Reduce intake of processed foods
Reduce intake of fish, beef, and dairy
Try eating vegan or vegetarian foods at least once or twice a week
Cook your own meals instead of eating out
Bring your own food containers when taking away food from stores
Beeswax wrap instead of cling wrap!
Buy loose-leaf tea or plastic free tea bags instead of regular tea bags
Eat more mushrooms, vegetables, and fruits and drink more water
Support local farmers
And finally, educate yourself more about ecology and the environment!
#environment#ecology#sustainability#ecofriendly#anti lawn#anti beauty culture#hell on earth#save the earth#recycling#fast fashion#plants#feminism#environmental activism#plantcore#ecopunk#solarpunk#horticulture#sustainable#slow fashion#zero waste#plastic free#conservation#climate change#global warming#soil science
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
“We need to understand ourselves as part of nature, but with the acknowledgement of course that the capitalist system has made us alienated from nature. In the case of the Kurds, for example, the mountains have historically always been a very strong protector of people who have been persecuted. In 2014, when ISIS attacked the Yazidis, the first thing that they did was to flee to the mountains. Landscapes, natural geographies, and water have always been sites of protection for people. This is not because nature is there to serve humans, but rather because humans are part of nature. Until the creation of states, big cities, and especially capitalism and industrialism, people understood how to live together with nature. I know this from my own grandparents’ village. They have a very different relationship to the animals they raise. They sing songs to the mountains, not about the mountains. I think many different cultures, especially indigenous people, have this kind of relationship with nature, which is very much a comradeship. For the Kurds and other groups who have always understood themselves in relation to a specific geography, who have never been part of a dominant state, and who have in many ways very local ways of organizing their lives, relying on geography to survive, the relationship to nature is like a friendship rather than an alliance.
Destroying nature is part of a policy of assimilation on the part of the dominant nation-states. The less people are aware of their link with nature, the more likely they are to become liberal individuals, with loyalty only to the state. So the more we are connected to nature through geography, the more likely we are to be conscious of ourselves, be conscious of our place in the universe, our place in ecology in general. The state is actively trying to destroy that because the state is very well aware of the connection between humans and nature. The state knows that in order for it to be legitimized and justified, it needs to break this link between humans and nature.”
Ecofeminist Practices Between Internationalism and Globalism
#kurdish#ezidi#ecology#war and ecology#feminism#colonization#nature#ecofeminism#capitalism#industrialism#txt
105 notes
·
View notes
Text

A.3.5 What is Anarcha-Feminism?
Although opposition to the state and all forms of authority had a strong voice among the early feminists of the 19th century, the more recent feminist movement which began in the 1960’s was founded upon anarchist practice. This is where the term anarcha-feminism came from, referring to women anarchists who act within the larger feminist and anarchist movements to remind them of their principles.
The modern anarcha-feminists built upon the feminist ideas of previous anarchists, both male and female. Indeed, anarchism and feminism have always been closely linked. Many outstanding feminists have also been anarchists, including the pioneering Mary Wollstonecraft (author of A Vindication of the Rights of Woman), the Communard Louise Michel, and the American anarchists (and tireless champions of women’s freedom) Voltairine de Cleyre and Emma Goldman (for the former, see her essays “Sex Slavery”, “Gates of Freedom”, “The Case of Woman vs. Orthodoxy”, “Those Who Marry Do Ill”; for the latter see “The Traffic in Women”, “Woman Suffrage”, “The Tragedy of Woman’s Emancipation”, “Marriage and Love” and “Victims of Morality”, for example). Freedom, the world’s oldest anarchist newspaper, was founded by Charlotte Wilson in 1886. Anarchist women like Virgilia D’Andrea and Rose Pesota played important roles in both the libertarian and labour movements. The “Mujeres Libres” (“Free Women”) movement in Spain during the Spanish revolution is a classic example of women anarchists organising themselves to defend their basic freedoms and create a society based on women’s freedom and equality (see Free Women of Spain by Martha Ackelsberg for more details on this important organisation). In addition, all the male major anarchist thinkers (bar Proudhon) were firm supporters of women’s equality. For example, Bakunin opposed patriarchy and how the law “subjects [women] to the absolute domination of the man.” He argued that ”[e]qual rights must belong to men and women” so that women can “become independent and be free to forge their own way of life.” He looked forward to the end of “the authoritarian juridical family” and “the full sexual freedom of women.” [Bakunin on Anarchism, p. 396 and p. 397]
Thus anarchism has since the 1860s combined a radical critique of capitalism and the state with an equally powerful critique of patriarchy (rule by men). Anarchists, particularly female ones, recognised that modern society was dominated by men. As Ana Maria Mozzoni (an Italian anarchist immigrant in Buenos Aires) put it, women “will find that the priest who damns you is a man; that the legislator who oppresses you is a man, that the husband who reduces you to an object is a man; that the libertine who harasses you is a man; that the capitalist who enriches himself with your ill-paid work and the speculator who calmly pockets the price of your body, are men.” Little has changed since then. Patriarchy still exists and, to quote the anarchist paper La Questione Sociale, it is still usually the case that women “are slaves both in social and private life. If you are a proletarian, you have two tyrants: the man and the boss. If bourgeois, the only sovereignty left to you is that of frivolity and coquetry.” [quoted by Jose Moya, Italians in Buenos Aires’s Anarchist Movement, pp. 197–8 and p. 200]
Anarchism, therefore, is based on an awareness that fighting patriarchy is as important as fighting against the state or capitalism. For ”[y]ou can have no free, or just, or equal society, nor anything approaching it, so long as womanhood is bought, sold, housed, clothed, fed, and protected, as a chattel.” [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Gates of Freedom”, pp. 235–250, Eugenia C. Delamotte, Gates of Freedom, p. 242] To quote Louise Michel:
“The first thing that must change is the relationship between the sexes. Humanity has two parts, men and women, and we ought to be walking hand in hand; instead there is antagonism, and it will last as long as the ‘stronger’ half controls, or think its controls, the ‘weaker’ half.” [The Red Virgin: Memoirs of Louise Michel, p. 139]
Thus anarchism, like feminism, fights patriarchy and for women’s equality. Both share much common history and a concern about individual freedom, equality and dignity for members of the female sex (although, as we will explain in more depth below, anarchists have always been very critical of mainstream/liberal feminism as not going far enough). Therefore, it is unsurprising that the new wave of feminism of the sixties expressed itself in an anarchistic manner and drew much inspiration from anarchist figures such as Emma Goldman. Cathy Levine points out that, during this time, “independent groups of women began functioning without the structure, leaders, and other factotums of the male left, creating, independently and simultaneously, organisations similar to those of anarchists of many decades and regions. No accident, either.” [“The Tyranny of Tyranny,” Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 66] It is no accident because, as feminist scholars have noted, women were among the first victims of hierarchical society, which is thought to have begun with the rise of patriarchy and ideologies of domination during the late Neolithic era. Marilyn French argues (in Beyond Power) that the first major social stratification of the human race occurred when men began dominating women, with women becoming in effect a “lower” and “inferior” social class.
The links between anarchism and modern feminism exist in both ideas and action. Leading feminist thinker Carole Pateman notes that her “discussion [on contract theory and its authoritarian and patriarchal basis] owes something to” libertarian ideas, that is the “anarchist wing of the socialist movement.” [The Sexual Contract, p. 14] Moreover, she noted in the 1980s how the “major locus of criticism of authoritarian, hierarchical, undemocratic forms of organisation for the last twenty years has been the women’s movement … After Marx defeated Bakunin in the First International, the prevailing form of organisation in the labour movement, the nationalised industries and in the left sects has mimicked the hierarchy of the state … The women’s movement has rescued and put into practice the long-submerged idea [of anarchists like Bakunin] that movements for, and experiments in, social change must ‘prefigure’ the future form of social organisation.” [The Disorder of Women, p. 201]
Peggy Kornegger has drawn attention to these strong connections between feminism and anarchism, both in theory and practice. “The radical feminist perspective is almost pure anarchism,” she writes. “The basic theory postulates the nuclear family as the basis of all authoritarian systems. The lesson the child learns, from father to teacher to boss to god, is to obey the great anonymous voice of Authority. To graduate from childhood to adulthood is to become a full-fledged automaton, incapable of questioning or even of thinking clearly.” [“Anarchism: The Feminist Connection,” Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 26] Similarly, the Zero Collective argues that Anarcha-feminism “consists in recognising the anarchism of feminism and consciously developing it.” [“Anarchism/Feminism,” pp. 3–7, The Raven, no. 21, p. 6]
Anarcha-feminists point out that authoritarian traits and values, for example, domination, exploitation, aggressiveness, competitiveness, desensitisation etc., are highly valued in hierarchical civilisations and are traditionally referred to as “masculine.” In contrast, non-authoritarian traits and values such as co-operation, sharing, compassion, sensitivity, warmth, etc., are traditionally regarded as “feminine” and are devalued. Feminist scholars have traced this phenomenon back to the growth of patriarchal societies during the early Bronze Age and their conquest of co-operatively based “organic” societies in which “feminine” traits and values were prevalent and respected. Following these conquests, however, such values came to be regarded as “inferior,” especially for a man, since men were in charge of domination and exploitation under patriarchy. (See e.g. Riane Eisler, The Chalice and the Blade; Elise Boulding, The Underside of History). Hence anarcha-feminists have referred to the creation of a non-authoritarian, anarchist society based on co-operation, sharing, mutual aid, etc. as the “feminisation of society.”
Anarcha-feminists have noted that “feminising” society cannot be achieved without both self-management and decentralisation. This is because the patriarchal-authoritarian values and traditions they wish to overthrow are embodied and reproduced in hierarchies. Thus feminism implies decentralisation, which in turn implies self-management. Many feminists have recognised this, as reflected in their experiments with collective forms of feminist organisations that eliminate hierarchical structure and competitive forms of decision making. Some feminists have even argued that directly democratic organisations are specifically female political forms. [see e.g. Nancy Hartsock “Feminist Theory and the Development of Revolutionary Strategy,” in Zeila Eisenstein, ed., Capitalist Patriarchy and the Case for Socialist Feminism, pp. 56–77] Like all anarchists, anarcha-feminists recognise that self-liberation is the key to women’s equality and thus, freedom. Thus Emma Goldman:
“Her development, her freedom, her independence, must come from and through herself. First, by asserting herself as a personality, and not as a sex commodity. Second, by refusing the right of anyone over her body; by refusing to bear children, unless she wants them, by refusing to be a servant to God, the State, society, the husband, the family, etc., by making her life simpler, but deeper and richer. That is, by trying to learn the meaning and substance of life in all its complexities; by freeing herself from the fear of public opinion and public condemnation.” [Anarchism and Other Essays, p. 211]
Anarcha-feminism tries to keep feminism from becoming influenced and dominated by authoritarian ideologies of either the right or left. It proposes direct action and self-help instead of the mass reformist campaigns favoured by the “official” feminist movement, with its creation of hierarchical and centralist organisations and its illusion that having more women bosses, politicians, and soldiers is a move towards “equality.” Anarcha-feminists would point out that the so-called “management science” which women have to learn in order to become mangers in capitalist companies is essentially a set of techniques for controlling and exploiting wage workers in corporate hierarchies, whereas “feminising” society requires the elimination of capitalist wage-slavery and managerial domination altogether. Anarcha-feminists realise that learning how to become an effective exploiter or oppressor is not the path to equality (as one member of the Mujeres Libres put it, ”[w]e did not want to substitute a feminist hierarchy for a masculine one” [quoted by Martha A. Ackelsberg, Free Women of Spain, pp. 22–3] — also see section B.1.4 for a further discussion on patriarchy and hierarchy).
Hence anarchism’s traditional hostility to liberal (or mainstream) feminism, while supporting women’s liberation and equality. Federica Montseny (a leading figure in the Spanish Anarchist movement) argued that such feminism advocated equality for women, but did not challenge existing institutions. She argued that (mainstream) feminism’s only ambition is to give to women of a particular class the opportunity to participate more fully in the existing system of privilege and if these institutions “are unjust when men take advantage of them, they will still be unjust if women take advantage of them.” [quoted by Martha A. Ackelsberg, Op. Cit., p. 119] Thus, for anarchists, women’s freedom did not mean an equal chance to become a boss or a wage slave, a voter or a politician, but rather to be a free and equal individual co-operating as equals in free associations. “Feminism,” stressed Peggy Kornegger, “doesn’t mean female corporate power or a woman President; it means no corporate power and no Presidents. The Equal Rights Amendment will not transform society; it only gives women the ‘right’ to plug into a hierarchical economy. Challenging sexism means challenging all hierarchy — economic, political, and personal. And that means an anarcha-feminist revolution.” [Op. Cit., p. 27]
Anarchism, as can be seen, included a class and economic analysis which is missing from mainstream feminism while, at the same time, showing an awareness to domestic and sex-based power relations which eluded the mainstream socialist movement. This flows from our hatred of hierarchy. As Mozzoni put it, “Anarchy defends the cause of all the oppressed, and because of this, and in a special way, it defends your [women’s] cause, oh! women, doubly oppressed by present society in both the social and private spheres.” [quoted by Moya, Op. Cit., p. 203] This means that, to quote a Chinese anarchist, what anarchists “mean by equality between the sexes is not just that the men will no longer oppress women. We also want men to no longer to be oppressed by other men, and women no longer to be oppressed by other women.” Thus women should “completely overthrow rulership, force men to abandon all their special privileges and become equal to women, and make a world with neither the oppression of women nor the oppression of men.” [He Zhen, quoted by Peter Zarrow, Anarchism and Chinese Political Culture, p. 147]
So, in the historic anarchist movement, as Martha Ackelsberg notes, liberal/mainstream feminism was considered as being “too narrowly focused as a strategy for women’s emancipation; sexual struggle could not be separated from class struggle or from the anarchist project as a whole.” [Op. Cit., p. 119] Anarcha-feminism continues this tradition by arguing that all forms of hierarchy are wrong, not just patriarchy, and that feminism is in conflict with its own ideals if it desires simply to allow women to have the same chance of being a boss as a man does. They simply state the obvious, namely that they “do not believe that power in the hands of women could possibly lead to a non-coercive society” nor do they “believe that anything good can come out of a mass movement with a leadership elite.” The “central issues are always power and social hierarchy” and so people “are free only when they have power over their own lives.” [Carole Ehrlich, “Socialism, Anarchism and Feminism”, Quiet Rumours: An Anarcha-Feminist Reader, p. 44] For if, as Louise Michel put it, “a proletarian is a slave; the wife of a proletarian is even more a slave” ensuring that the wife experiences an equal level of oppression as the husband misses the point. [Op. Cit., p. 141]
Anarcha-feminists, therefore, like all anarchists oppose capitalism as a denial of liberty. Their critique of hierarchy in the society does not start and end with patriarchy. It is a case of wanting freedom everywhere, of wanting to ”[b]reak up … every home that rests in slavery! Every marriage that represents the sale and transfer of the individuality of one of its parties to the other! Every institution, social or civil, that stands between man and his right; every tie that renders one a master, another a serf.” [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Economic Tendency of Freethought”, The Voltairine de Cleyre Reader, p. 72] The ideal that an “equal opportunity” capitalism would free women ignores the fact that any such system would still see working class women oppressed by bosses (be they male or female). For anarcha-feminists, the struggle for women’s liberation cannot be separated from the struggle against hierarchy as such. As L. Susan Brown puts it:
“Anarchist-feminism, as an expression of the anarchist sensibility applied to feminist concerns, takes the individual as its starting point and, in opposition to relations of domination and subordination, argues for non-instrumental economic forms that preserve individual existential freedom, for both men and women.” [The Politics of Individualism, p. 144]
Anarcha-feminists have much to contribute to our understanding of the origins of the ecological crisis in the authoritarian values of hierarchical civilisation. For example, a number of feminist scholars have argued that the domination of nature has paralleled the domination of women, who have been identified with nature throughout history (See, for example, Caroline Merchant, The Death of Nature, 1980). Both women and nature are victims of the obsession with control that characterises the authoritarian personality. For this reason, a growing number of both radical ecologists and feminists are recognising that hierarchies must be dismantled in order to achieve their respective goals.
In addition, anarcha-feminism reminds us of the importance of treating women equally with men while, at the same time, respecting women’s differences from men. In other words, that recognising and respecting diversity includes women as well as men. Too often many male anarchists assume that, because they are (in theory) opposed to sexism, they are not sexist in practice. Such an assumption is false. Anarcha-feminism brings the question of consistency between theory and practice to the front of social activism and reminds us all that we must fight not only external constraints but also internal ones.
This means that anarcha-feminism urges us to practice what we preach. As Voltairine de Cleyre argued, “I never expect men to give us liberty. No, Women, we are not worth it, until we take it.” This involves “insisting on a new code of ethics founded on the law of equal freedom: a code recognising the complete individuality of woman. By making rebels wherever we can. By ourselves living our beliefs . … We are revolutionists. And we shall use propaganda by speech, deed, and most of all life — being what we teach.” Thus anarcha-feminists, like all anarchists, see the struggle against patriarchy as being a struggle of the oppressed for their own self-liberation, for ”as a class I have nothing to hope from men . .. No tyrant ever renounced his tyranny until he had to. If history ever teaches us anything it teaches this. Therefore my hope lies in creating rebellion in the breasts of women.” [“The Gates of Freedom”, pp. 235–250, Eugenia C. Delamotte, Gates of Freedom, p. 249 and p. 239] This was sadly as applicable within the anarchist movement as it was outside it in patriarchal society.
Faced with the sexism of male anarchists who spoke of sexual equality, women anarchists in Spain organised themselves into the Mujeres Libres organisation to combat it. They did not believe in leaving their liberation to some day after the revolution. Their liberation was a integral part of that revolution and had to be started today. In this they repeated the conclusions of anarchist women in Illinois Coal towns who grew tried of hearing their male comrades “shout in favour” of sexual equality “in the future society” while doing nothing about it in the here and now. They used a particularly insulting analogy, comparing their male comrades to priests who “make false promises to the starving masses … [that] there will be rewards in paradise.” The argued that mothers should make their daughters “understand that the difference in sex does not imply inequality in rights” and that as well as being “rebels against the social system of today,” they “should fight especially against the oppression of men who would like to retain women as their moral and material inferior.” [Ersilia Grandi, quoted by Caroline Waldron Merithew, Anarchist Motherhood, p. 227] They formed the “Luisa Michel” group to fight against capitalism and patriarchy in the upper Illinois valley coal towns over three decades before their Spanish comrades organised themselves.
For anarcha-feminists, combating sexism is a key aspect of the struggle for freedom. It is not, as many Marxist socialists argued before the rise of feminism, a diversion from the “real” struggle against capitalism which would somehow be automatically solved after the revolution. It is an essential part of the struggle:
“We do not need any of your titles … We want none of them. What we do want is knowledge and education and liberty. We know what our rights are and we demand them. Are we not standing next to you fighting the supreme fight? Are you not strong enough, men, to make part of that supreme fight a struggle for the rights of women? And then men and women together will gain the rights of all humanity.” [Louise Michel, Op. Cit., p. 142]
A key part of this revolutionising modern society is the transformation of the current relationship between the sexes. Marriage is a particular evil for “the old form of marriage, based on the Bible, ‘till death doth part,’ … [is] an institution that stands for the sovereignty of the man over the women, of her complete submission to his whims and commands.” Women are reduced “to the function of man’s servant and bearer of his children.” [Goldman, Op. Cit., pp. 220–1] Instead of this, anarchists proposed “free love,” that is couples and families based on free agreement between equals than one partner being in authority and the other simply obeying. Such unions would be without sanction of church or state for “two beings who love each other do not need permission from a third to go to bed.” [Mozzoni, quoted by Moya, Op. Cit., p. 200]
Equality and freedom apply to more than just relationships. For “if social progress consists in a constant tendency towards the equalisation of the liberties of social units, then the demands of progress are not satisfied so long as half society, Women, is in subjection… . Woman … is beginning to feel her servitude; that there is a requisite acknowledgement to be won from her master before he is put down and she exalted to — Equality. This acknowledgement is, the freedom to control her own person. “ [Voltairine de Cleyre, “The Gates of Freedom”, Op. Cit., p. 242] Neither men nor state nor church should say what a woman does with her body. A logical extension of this is that women must have control over their own reproductive organs. Thus anarcha-feminists, like anarchists in general, are pro-choice and pro-reproductive rights (i.e. the right of a woman to control her own reproductive decisions). This is a long standing position. Emma Goldman was persecuted and incarcerated because of her public advocacy of birth control methods and the extremist notion that women should decide when they become pregnant (as feminist writer Margaret Anderson put it, “In 1916, Emma Goldman was sent to prison for advocating that ‘women need not always keep their mouth shut and their wombs open.’”).
Anarcha-feminism does not stop there. Like anarchism in general, it aims at changing all aspects of society not just what happens in the home. For, as Goldman asked, “how much independence is gained if the narrowness and lack of freedom of the home is exchanged for the narrowness and lack of freedom of the factory, sweat-shop, department store, or office?” Thus women’s equality and freedom had to be fought everywhere and defended against all forms of hierarchy. Nor can they be achieved by voting. Real liberation, argue anarcha-feminists, is only possible by direct action and anarcha-feminism is based on women’s self-activity and self-liberation for while the “right to vote, or equal civil rights, may be good demands … true emancipation begins neither at the polls nor in the courts. It begins in woman’s soul … her freedom will reach as far as her power to achieve freedom reaches.” [Goldman, Op. Cit., p. 216 and p. 224]
The history of the women’s movement proves this. Every gain has come from below, by the action of women themselves. As Louise Michel put it, ”[w]e women are not bad revolutionaries. Without begging anyone, we are taking our place in the struggles; otherwise, we could go ahead and pass motions until the world ends and gain nothing.” [Op. Cit., p. 139] If women waited for others to act for them their social position would never have changed. This includes getting the vote in the first place. Faced with the militant suffrage movement for women’s votes, British anarchist Rose Witcop recognised that it was “true that this movement shows us that women who so far have been so submissive to their masters, the men, are beginning to wake up at last to the fact they are not inferior to those masters.” Yet she argued that women would not be freed by votes but “by their own strength.” [quoted by Sheila Rowbotham, Hidden from History, pp. 100–1 and p. 101] The women’s movement of the 1960s and 1970s showed the truth of that analysis. In spite of equal voting rights, women’s social place had remained unchanged since the 1920s.
Ultimately, as Anarchist Lily Gair Wilkinson stressed, the “call for ‘votes’ can never be a call to freedom. For what is it to vote? To vote is to register assent to being ruled by one legislator or another?” [quoted by Sheila Rowbotham, Op. Cit., p. 102] It does not get to the heart of the problem, namely hierarchy and the authoritarian social relationships it creates of which patriarchy is only a subset of. Only by getting rid of all bosses, political, economic, social and sexual can genuine freedom for women be achieved and “make it possible for women to be human in the truest sense. Everything within her that craves assertion and activity should reach its fullest expression; all artificial barriers should be broken, and the road towards greater freedom cleared of every trace of centuries of submission and slavery.” [Emma Goldman, Op. Cit., p. 214]
#feminism#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#cops#police
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The late Ana Mendieta was born in Cuba, and at the age of 13 was sent with her sister, Raquel, to live in Iowa. Her parents wanted them to grow up outside of Castro's Cuba. This painful separation from her primal roots, cultural and familial, ultimately lead Mendieta to feel an intense separation from the earth itself. This fact of both physical and spiritual exile would later prove to be an enormous catalyst in her life as an artist, and as a meta-physical practitioner of earth healing and cleansing rituals."
From Revered Earth exhibition catalog from the Center for Contemporary Arts of Santa Fe, 1990.
Ana Mendieta, O'Nile, 1984. Earth from Egypt, binder, mounted on wood.
#ana mendieta#art#contemporary art#body art#feminist art#feminism#earth art#ecology#ecological art#my scan
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Money>Human life in neo-liberal western news reporting
#money>human#life#neoliberalism#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#western#news#dubailife#business setup in dubai#dubairealestate#dubai visa#dubai#neoliberal thought#neoliberal feminism#neoliberals#neoliberal#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#anthony albanese#albanese government#extreme weather#weather#ecology#earth#capitalism#fascism
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of my favorite ecofeminism/black feminism reads is definitely The Green Belt Movement by Wangari Maathai, it's an inspiring story of encouraging people to help their country improve the environment with new ideas for the rest of the world to have hope in

there's only one book left on Amazon but you can buy used ones there!
#ecofeminism#eco conscious#intersectional feminism#black feminism#womanism#feminism#ecology#ecosystem
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
I would argue that colonization and not overpopulation is the cause of poverty in the Third World. Land which formerly supported local subsistence has been appropriated by imperialist countries to produce export crops for the First World. Since much of the land is going to produce export crops rather than crops to meet local needs, people in the Third World find themselves increasingly relying upon imports. The money they spend on imports is more than they make from selling export crops. Consequently, they find themselves in spiraling debt. To maintain these systems of economic inequality, the United States and other colonial powers provide covert and overt support to military regimes to crush popular uprisings. I would argue that is the cause of war.
– Ecofeminism, Karren J. Warren
1 note
·
View note
Text
People calling our planet "Mother Earth", because she allows us to live and then exploiting her and treating her like shit and hoping she cleans all their giant mess herself is the final boss of misogyny, I think
#idk though#or maybe the real final boss is when our inner lives are dismissed#so that men can focus on their most shallow desires and feel justified#but idk#I'm no expert#ecology#earth#feminism#misogny#random thoughts
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
“If human beings are no longer considered above nature, one's relationship with the earth, other life forms, ecological process, and especially with one's own body and mind radically changes. […] By this shift in perception one is no longer placed in an alien environment. Instead, in and through existence one enters community.”
Susan Griffin. The Eros of Everyday Life.
#susan griffin#ecology#qoute#the eros of everyday life#feminism#feminist#community#saw sum shit on twitter that made me think of this book/ qoute
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2023 READING LOG
JANUARY
-> Books:
HURSTON, Zora Neale; Their Eyes Were Watching God
WILLIAMS, Tennessee; A Streetcar Named Desire
-> Essays & articles:
CHRISTENSEN, Joel; How do chatbots dream of electric Greek heroes?
DYHOUSE, Carol; Why Are We So Afraid of Female Desire?
EDWARDS, Stassa; A Little Madly: Hysteria at the Moulin Rouge
HOOKS, bell; Romance: Sweet Love
LAING, Olivia; NYC blue: what the pain of loneliness tells us
LIEBERMAN, Jeffrey A.; “The Miracle Cure”: A Brief History of Lobotomies
LORDE, Audre; The Uses of the Erotic: The Erotic as Power
SHUSHAN, Gregory; Near-death experiences have long inspired after life beliefs
STADONILK, Joe; We’ve always been distracted
TÁÌWÒ, Olúfémi; The idea of ‘precolonial Africa’ is vacuous and wrong
WYPIJEWSKI, JoAnn; How Capitalism Created Sexual Dysfunction
FEBRUARY
-> Books:
DOUGLASS, Frederick; Narrative of the life of Frederick Douglass
WINTERSON, Jeanette; 12 Bytes: How We Got Here, Where We Might Go Next
-> Essays & articles:
BLACK, Bob; The Abolition of Work
BURDEN-STELLY, Charisse; How Black Communist Women Remade Class Struggle
COBB, Michael; Bigmouth Strikes Again
GOODLAD, Lauren M.E.; Now The Humanities Can Disrupt “AI”
HALBERSTAM, Jack; Towards a Trans* Feminism
HARVEY, Katherine; Medieval babycare
ROTHFIELD, Becca; A Body of One’s Own
RUKES, Frederic; The Disruption of Normativity: Queer Desire and Negativity in Morrisey and The Smiths
STRINGER, Julian; The Smiths: Repressed (But Remarkably Dressed)
VENKATARAMAN, Vivek V.; Lessons from the foragers
MARCH
-> Books:
AMADO, Jorge; Gabriela, Clove & Cinnamon
-> Essays & articles:
ALEXANDER, Amanda; Making Communities Safe, Without the Police
BOURDÉ, Guy; The philosophies of history
ELLIOTT, John H.; An Europe of composite monarchies
ERNAUX, Annie; A Community of Desires
HARCOUT, Bernard E.; Policing Disorder
JABBARI, Alexander; After the mother tongues: what we lost with Persianate modernity
MANTEL, Hilary; Anne Boleyn: witch, bitch, temptress, feminist
MANTEL, Hilary; Holy disorders
MANTEL, Hilary; Night visions
MANTEL, Hilary; No passport required
MANTEL, Hilary; The shape we’re in
MINER, Horace; Body Ritual among the Nacirema
RUSSEL, Francey; What It Means to Watch
WEBB, Claire Isabel; Cosmic vision
APRIL
-> Books:
MISHIMA, Yukio; Sun and Steel
OLADE, Yves; Bloodsport
-> Essays & articles:
BATESON, Gregory; A Theory of Play and Fantasy
CÉSAIRE, Suzanne; The Great Camouflage
CHARALAMBOUS, Demetrio; The Enigma of the Isle of Gold
DAVID, Kathryn; How Stalin enlisted the Orthodox Church to help control Ukraine
SINGLER, Beth; Existential Hope and Existential Despair in AI Apocalypticism and Transhumanism
WYATT, Justin; The Smiths, Pop Culture Referencing and Marginalized Stardom
-> Short stories:
ELLISON, Harlan; The Man Who Rowed Christopher Colombus Ashore
SAYLOR, Steven; The Eagle and the Rabbit
MAY
-> Books:
PLUTARCH; Life of Sulla
-> Essays & articles:
BRAUDEL, Fernand; Clothes and fashion
CHAMPLIN, Edward; Nero Reconsidered
GARTON, Charles; Sulla and the Theatre
HAY, Mark; The Colonization of the Ayahuasca Experience
HSU, Hua; Varieties of Ether: Toward a history of creativity and beef
PROBYN, Elspeth; Cannibal Hunger, Restraint in Excess
STAR, Christopher; How the ancient philosophers imagined the end of the world
TELUSHKIN, Shira; Meet Eva Frank: The First Jewish Female Messiah
#reading log#articles#essays#reading recommendations#reading recs#feminism#psychiatry#leftism#communism#anarchism#race#nationalism#imperialism#anthropology#anti-work#the smiths#tech#ai#ecology#religion#occult#bob black#thomas sankara#hilary mantel#audre lorde#bell hooks#annie ernaux
43 notes
·
View notes
Text

Feminism, Sculpture, Photography, Nature & Ecology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Toward a Queer EcoFeminism
“Today all those associated with nature and the erotic continue to experience the impact of centuries of Western culture’s colonization, in our very bodies and in our daily lives. Rejecting that colonization requires embracing the erotic in all its diversity and building coalitions for creating a democratic, ecological culture based on our shared liberation” (132).
We must combine insights from queer and ecofeminism theories—there must be a genuine transformation of Western conceptions of the erotic as fundamentally opposed to reason, culture, humanity, and masculinity” and we must be concerned with the collective freedom of women, queers and nature if we want to achieve full liberation.
#toward a queer ecofeminism#decolonialism#queer ecofeminism#critical ecology#ecofeminism#queer ecology#colonialism#colonization#environmental politics#environmental justice#queer theory#feminism
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Comic by the Institute for Social Ecology



#socialist#socialism#communist#communism#social ecology#communalism#murray bookchin#abdullah ocalan#envrionment#environmentalism#ecology#comics#politics#us politics#hierarchy#feminism#democracy#racial equality#equal rights
35 notes
·
View notes




