#operations management in agriculture
Text
Encouraging Operational Management Superiority in the Nashik Center
Exemplary business education can be found at the Symbiosis Institute of Operations Management (SIOM). This article examines the unique characteristics that set SIOM apart from other MBA programs offered in Nashik. It makes an effort to draw attention to the school's commitment to operations management and its unique position among agri-MBA programs in India.

What does OM really mean?
Let’s begin by asking: what is operations management in MBA? Managing business processes to achieve optimal efficiency within an organization is known as operations management (OM). The aim is to optimize an organization's profit by transforming resources like labor and materials into goods and services as effectively as possible.
Aims and Goals
The well-designed MBA in Operations Management program in India aims to provide students with the tools. These tools are essential to improve supply chain efficiency and optimize workflows. It also effectively oversees all facets of business operations.
Diverse Coursework
By fostering an international viewpoint, SIOM prepares its graduates for careers in the Indian business sector as well as abroad. The curriculum is designed to give graduates of SIOM the right mindset for work in elite organizations, ensuring they are ready for the demands of conducting business internationally. Out of the top colleges for MBA in operations management, this is why SIOM stands out.
SIOM's curriculum demonstrates a thorough comprehension of business complexity. Practical applications and interdisciplinary knowledge are highly valued. The most recent industry knowledge will be incorporated into the MBA in Operations Management program.
All-encompassing development
A framework for holistic development is used by SIOM. This goes beyond traditional teaching methods. It guarantees students' academic success. Additionally, it is meant to be a life-changing experience that will mold them into well-rounded professionals. Graduates in business leadership who focus on technology are better suited for challenges in their career.
Exposure Related to Industry
The institute provides a range of opportunities for exposure to pertinent industries, such as case studies, industry visits, and internships. These experiences give students insightful knowledge that helps them bridge the gap between abstract ideas and real-world application.
The Strategy of Location
Because SIOM is located in Nashik, it has a prime location. This city is renowned for both its thriving business sector and extensive cultural heritage. Because of its proximity to important agricultural and industrial hubs, Nashik offers students a unique learning environment. It combines the vitality of the city with the intricacy of multiple industries. This distinct feature distinguishes SIOM from other MBA programs in Nashik.
Focus on Agri MBA
SIOM states that studying operations management ought to be given top priority. This is particularly true in light of the agriculture sector's importance to the Indian economy. SIOM acknowledges this need and its significance, keeping in mind that we need experts in both management and agriculture. Operations management in agriculture is given due importance here and studied in great detail.
Strong Faculty Group
SIOM is pleased with the caliber of its faculty, which consists of both accomplished academics and business experts. This wide range of expertise ensures that students receive guidance based on both solid theory and practical industry experience.
SIOM's strategic location, commitment to holistic development, and agri-MBA specialization set it apart in the highly competitive Indian business education market. As SIOM continues to shape the upcoming generation of techno-business leaders, its influence is felt not only in Nashik but also in the national and international business spheres.
#What is operations management in MBA#Top colleges for MBA in operations management#Operations management in agriculture#siom nashik
0 notes
Text
How Big Should Your Farm Be to Make a Profit?
Many new agripreneurs believe that the size of their farm will determine how profitable they’ll be. However, you can be profitable whether you’re farming 1 hectare or 100 hectares; it all depends on how you farm. When it comes to land, the most important thing to consider is not the number of hectares at your disposal, but rather the commodity that you farm and how you manage and control costs.…

View On WordPress
#Agricultural business success#Crop diversification benefits#diversified farming#Effective irrigation systems#Efficient farming methods#Farm cost management#Farm operational costs#Farm planning strategies#Farm productivity tips#farm profitability#Farm risk management#Farming market trends#Farming technology#high-value crops#High-yield crop varieties#Large-scale farming#Livestock integration#Low-cost farming solutions#Micro-farming#Modern farming tools#Niche crop farming#Organic farming practices#precision farming#Profitability in agriculture#Small farm equipment#Small-Scale Farming#Smart farming techniques#Starting a farm business#Successful farming examples.#sustainable farming
0 notes
Photo

Mozambique: EU allocates €50 million in humanitarian aid for Southern Africa and Indian Ocean region
Countries: Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe Source: European Commission's Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations These funds will help combat food insecurity and malnutrition, improve access to basic services, enhance disaster preparedness and promote education in emergencies throughout the region.
https://reliefweb.int/report/mozambique/southern-africa-and-indian-ocean-region-eu-allocates-eu50-million-humanitarian-aid-commissioner-lenarcic-visits-madagascar
#Lesotho#Madagascar#Malawi#Mozambique#Zimbabwe#European Commission's Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations#Agriculture#Contributions#Disaster Management#Education#Logistics and Telecommunications#News and Press Release#Drought#Flood#Tropical Cyclone#ReliefWeb - Updates (Headlines)
0 notes
Text
"Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo has a lot to celebrate.
The park, which celebrated its 30th anniversary on December 31 of 2023, also shared an exciting conservation milestone: 2023 was the first year without any elephant poaching detected.
“We didn’t detect any elephants killed in the Park this year, a first for the Park since [we] began collecting data. This success comes after nearly a decade of concerted efforts to protect forest elephants from armed poaching in the Park,” Ben Evans, the Park’s management unit director, said in a press release.
Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park was developed by the government of Congo in 1993 to maintain biodiversity conservation in the region, and since 2014, has been cared for through a public-private partnership between Congo’s Ministry of Forest Economy and the Wildlife Conservation Society.

Pictured: Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park. Photo courtesy of Scott Ramsay/Wildlife Conservation Society
Evans credits the ongoing collaboration with this milestone, as the MEF and WCS have helped address escalating threats to wildlife in the region.
This specifically includes investments in the ranger force, which has increased training and self-defense capabilities, making the force more effective in upholding the law — and the rights of humans and animals.
“Thanks to the strengthening of our anti-poaching teams and new communication technologies, we have been able to reduce poaching considerably,” Max Mviri, a park warden for the Congolese government, said in a video for the Park’s anniversary.
“Today, we have more than 90 eco-guards, all of whom have received extensive training and undergo refresher courses,” Mviri continued. “What makes a difference is that 90% of our eco-guards come from villages close to the Park. This gives them extra motivation, as they are protecting their forest.”
As other threats such as logging and road infrastructure development impact the area’s wildlife, the Park’s partnerships with local communities and Indigenous populations in the neighboring villages of Bomassa and Makao are increasingly vital.
“We’ve seen great changes, great progress. We’ve seen the abundance of elephants, large mammals in the village,” Gabriel Mobolambi, chief of Bomassa village, said in the same video. “And also on our side, we benefit from conservation.”
Coinciding with the Park’s anniversary is the roll-out of a tourism-focused website, aiming to generate 15% of its revenue from visitors, which contributes significantly to the local economy...
Nouabalé-Ndoki also recently became the world’s first certified Gorilla Friendly National Park, ensuring best practices are in place for all gorilla-related operations, from tourism to research.
But gorillas and elephants — of which there are over 2,000 and 3,000, respectively — aren’t the only species visitors can admire in the 4,334-square-kilometer protected area.
The Park is also home to large populations of mammals such as chimpanzees and bongos, as well as a diverse range of reptiles, birds, and insects. For the flora fans, Nouabalé-Ndoki also boasts a century-old mahogany tree, and a massive forest of large-diameter trees.
Beyond the beauty of the Park, these tourism opportunities pave the way for major developments for local communities.
“The Park has created long-term jobs, which are rare in the region, and has brought substantial benefits to neighboring communities. Tourism is also emerging as a promising avenue for economic growth,” Mobolambi, the chief of Bomassa village, said in a press release.
The Park and its partners also work to provide education, health centers, agricultural opportunities, and access to clean water, as well, helping to create a safe environment for the people who share the land with these protected animals.
In fact, the Makao and Bomassa health centers receive up to 250 patients a month, and Nouabalé-Ndoki provides continuous access to primary education for nearly 300 students in neighboring villages.
It is this intersectional approach that maintains a mutual respect between humans and wildlife and encourages the investment in conservation programs, which lead to successes like 2023’s poaching-free milestone...
Evans, of the Park’s management, added in the anniversary video: “Thanks to the trust that has been built up between all those involved in conservation, we know that Nouabalé-Ndoki will remain a crucial refuge for wildlife for the generations to come.”"
-via Good Good Good, February 15, 2024
#conservation#congo#republic of congo#elephant#gorilla#endangered species#biodiversity#conservation news#conservation efforts#indigenous communities#national park#protected areas#poaching#elephant poaching#ecology#biology#environment#environmental news#forests
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
CSIAP Vacancies 2022 - Data Entry Operator
CSIAP Vacancies 2022 – Data Entry Operator
CSIAP Vacancies 2022 – Data Entry Operator, Climate Smart Irrigated Agriculture Project Vacancies 2022 – Data Entry Operator, Climate Smart Agriculture Specialist, Deputy Project Director, Financial Management Specialist, Monitoring and Evaluation Officer, Procurement Officer
English AdvertisementDownloadModel ApplicationDownload

View On WordPress
#Climate Smart Agriculture Specialist#Data Entry Operator#Deputy Project Director#Financial Management Specialist#Government Job Vacancies 2022#Monitoring and Evaluation Officer#Procurement Officer
0 notes
Link
Deputy Project Director, Procurement Officer, Monitoring and Evaluation Officer, Agriculture Specialist, Data Entry Operator, Financial Management Specialist job vacancies in the Ministry of Agriculture.
#Deputy Project Director#Procurement Officer#Monitoring and Evaluation Officer#Agriculture Specialist#Data Entry Operator#Financial Management Specialist
0 notes
Note
Hi! Big fan :) You're an environmental lecturer, right? I recently got into a debate with someone about rewilding in the UK, and the clash with farmers and agriculture. To me, this is a no-brainer - I absolutely do feel for farmers losing their livelihoods, and I think there needs to be a system to help them transition to something else, but also, the planet is dying. But you explain things well, so I wondered if you have thoughts? Particularly on the Welsh side of things. Thank you in advance!
Hah. I literally have a lecture on this. Or, well, a chunk of a lecture, anyway; so yes! I have thoughts. I'll use those notes, and stick a big reference at the end in case you want to read more
I'll talk about this specifically from the Welsh perspective, okay so:
The rewilding project in Wales is the Cambrian Wildwood, launched in 2004ish by a guy who bought an abandoned farm in the northern end of Mid Wales with the express intention of rewilding it. The aim is to convert some 7000 acres, and the initial mission statement said they'd reintroduce wolves and lynx. That's the project I'm going to talk about, because it's a great case study for how to spectacularly fuck something up (and eventually realise you've spectacularly fucked up, and do something about it.)
These are the Cambrian Mountains:

When looking at that, there are two competing viewpoints that are relevant here:
The Cambrians are ecologically depleted. Their biodiversity has crashed since the Second World War, when modern farming methods were introduced. Environmentally, there is a perception of emptiness and degradation.
The landscape is a glorious one that has been shaped by the human actions taken on it for generations, as we are a shepherding culture – culture and land are inextricably intertwined.
That's a big fundamental difference! Two people can look at that same photo, and see something diametrically opposed. But there's more lying on it, so you also need to understand the socio-political background.
Socio-Political Background
(I know! Headings! So professional)
A lot of rewilding – Cambrian Wildwood included – is taking place in areas where farming is declining for various political/socio-economic reasons, so this can be ENTIRELY FAIRLY seen as yet another threat. This goes hand in hand with rural migration and community decline, too.
In Wales, we’re mostly rural, and characterised by extensive upland livestock farming (sheep in particular). Most farms are small to medium family-run setups. ON TOP OF THAT, the vast majority of Welsh farmers are Welsh-speaking, and the right to operate a farm the ‘traditional’ way without UK government oversight is seen by Welsh Nationalists as an important post-colonial act.
Many of them didn’t even like the National Parks being set up, as they were seen as an English outsider imposition that ignored the working nature and cultural history of the land. Remember: the farmed uplands are often seen as a heartland of Welsh identity, and those have historically been intentionally destroyed by UK central government land management decisions (e.g. Tryweryn, Elan, Claerwen, etc)
“Over the past half century we have witnessed the arrival of countless environmental fundamentalists… seemingly oblivious to the fact that their new-found paradise is already occupied by people whose connection with the land is deep rooted, dates back thousands of years, and is embedded in their language and culture.” (Nick Fenwick [Farmers’ Union of Wales] 2013)
SO IT’S CULTURALLY DICEY
(And in my opinion an incredibly stupid idea to go and give it a primarily English name with a Welsh translation as an afterthought but that is Elanor’s Opinion and not Scientific Fact)
(But fr fr if you ever have to get involved in these sorts of projects you will go a long way if you have the basic respect of learning the Welsh names and pronouncing them right rather than lazily expecting everything to be in English sorry sorry I digress)
From the Cambrian Wildwood’s Mission Statement on their website, their objective is:
“To rewild or restore land to a wilder state to create a functioning ecosystem where natural processes dominate by carrying out habitat restoration, removing domestic livestock, and introducing missing native species as far as feasible.”
Can you see the controversial bit of the statement
Can you see the bit where they directly say they want to remove domestic livestock
Jesus Christ
Cultural Differences
AND THEN HERE'S THE BIGGER PROBLEM
‘Culture’ in Welsh is diwylliant – literally, a ‘lack of wildness’. There is no direct translation into Welsh for the term ‘rewilding’ – the closest you can get is anialwch or diffeithwch, which mean ‘wilderness’ in the sense of ‘desert’ or ‘wasteland’. So right off the bat, if you tell a Welsh-speaking farmer that you want to rewild the place, what they hear is "We want to make it dangerous and empty and degraded."
A related concept is cynefin - knowing one’s ‘patch’ and the feeling of belonging associated. The term has its roots as a description of the way grazing animals know their area of mountain land, but it is also used to describe how people come to form an intimate experiential knowledge of place - and specifically, a Welsh farmer's cultural attitude.
Basically, Welsh literature and oral traditions speak of a relationship with the land, not a separation and longing for an untouched wilderness. Farmers feel this especially keenly. Culturally, this is a big part of why they do it – they’re rooted to the land, and therefore to their identities.
“Interviewees conveyed this by referring to areas proposed for rewilding as being comprised of “a quilt of cynefinoedd: interwoven stories, the layered and collective place-making of families and individuals over-generations, co-constituted with the physical landscape” (Wynne-Jones, Holmes and Strouts, 2018)
So, to them, rewilding is erasing and disregarding these stories. To them, this is not just a land-use change, but the latest colonial attack. They've known the family who lived on that farm for generations - every birth, marriage, death, joy, triumph, loss, everything. You are saying that you are going to strip that family, all those stories, all those people out of that land, to be forgotten.
…
However. There is a counterpoint to this.
Many farmers taking this view have therefore identified themselves as the only “truly Welsh” people in the debate, accusing environmentalists as being outsiders. The problem with this being, most of the environmentalists involved with the project are also Welsh; so who the fuck are they to say who is or is not Truly Welsh? It's what we on the internet would recognise as gatekeeping, with a big side order of No True Scotsman fallacy.
Also this quote sums it up well:
“Sheep farming in this country goes back a few hundred years. I think if you go deep enough into our culture and ancestry, we have a really deep native relationship with wild forest areas and with the wild animals that are native to this country…I just don’t agree that sheep farming is really part of our traditional culture.” (WWLF Interview [15] 2016) (Wynne-Jones, Holmes and Strouts, 2018)
This is also a fair point. It is true that upland sheep farming, the way we now practice it, is only a few hundred years old, and at the current intensity only a few decades (since WW2).
On top of which, there has been plenty of exploration over the years of farmers as being a government-subsidised landed gentry, which I won't go into here, but it also contains some fair points.
In truth, all of it and none of it is true. It’s far more complex and nuanced than either side might want to believe.
Solutions So Far
This is an ongoing project and they're still learning and changing new things and stuff, but a big thing they did was get someone in to basically be a mediator and listen to both sides, because Jesus, those sides were not listening to each other.
But to date:
They actually worked with a first-language Welsh speaker (WHY DID THEY NOT DO THIS FIRST I'm sorry I'm fine). Originally the Welsh translation of the project was Tir Gwyllt – wild land. But given that Welsh connotations with gwyllt are something out of control or dangerous, Coetir Anian has been chosen – anian refers to a sense of natural order and creation, a sense of health and vitality.
Similarly, ‘rewilding’ is being translated as ‘di-ddofi’ – ‘de-taming’. This acknowledges the labour and culture taken to tame it, and just suggests an avenue for discussing some relaxation of farming practice in appropriate locations rather than, you know, releasing packs of wolves directly into sheep pens
In online materials and in community engagement events where traditional storytellers and musicians have performed to celebrate the Wildwood, the trustees have drawn heavily from Welsh myth in the form of the Mabinogion. Enormous amounts of the Mab lovingly and respectfully feature wild woods and wild animals. The emphasis is therefore on how wilderness is also part of Welsh identity – and arguably a much older part, going back to the Celts. (This is clever, in my view, but something to approach with care - it's rarely a good idea to play the game of "What's the most Welsh". But so far it's been done sensitively)
Land purchased for the project has so far been wholly limited to that available in the public domain. The main site, Bwlch Corog, was empty and unfarmed for six years before purchase, which has been stressed in all media interviews and releases; this is important, because farmers do have a sense of "Productive land is being stolen by environmentalists".
Large predator reintroductions have largely been abandoned. Lynx and wolves are no longer on the agenda. It’s possible they’ll be included in the future, but it is acknowledged as currently impractical (both from clashes with farmers and lack of habitat).
Instead, they’ve supported smaller species reintroductions, such as the Vincent Wildlife Trust’s pine marten translocations, and some proposed red squirrel ones.
Bwlch Corog is to be managed as an experimental plot that farmers are encouraged to engage with.
Assessing the potential for new income streams (from improved tourism and educational activities) rather than just the ecological benefits – this has become central to the project, and the emphasis is on how this might benefit farming communities and keep them together. This has been huge, and has also been successful in rewilding schemes in Europe.
Tensions are a lot lower now than they were ten years ago, but ultimately the problem was a bunch of outsiders came in and decided they knew best without listening to anyone else's point of view, and that meant both sides really dug their heels in. Much better now.
Ultimately... yes, I am in favour of rewilding, in a general sense. But I think it needs to go hand in hand with supplying farmers with the necessary subsidies to transition back to more traditional and sustainable farming methods, and the two elements run side by side. You can't do one without the other, not if you want them to succeed. The Pontbren Project is a great case study for how a farmer-led scheme can successfully aid them economically while also improving environmental outcomes, and we need to learn and incorporate more lessons from it when discussing this kind of landscape-level management.
Also, with land management in general, I think you're a fucking idiot and dangerously arrogant if you think you can get anything done without all stakeholders being on board. And potentially wandering down the ecofascism path, circumstances dependent.
Anyway, those are my thoughts. Source:
Wynne-Jones, S, Holmes, G & Strouts, G (2018), 'Abandoning or Reimagining a Cultural Heartland? Understanding and Responding to Rewilding Conflicts in Wales - the case of the Cambrian Wildwood.' Environmental Values, vol. 27, no. 4.
825 notes
·
View notes
Text
As urban populations boom, urban agriculture is increasingly looked to as a local food source and a way to help combat inequitable food access. But little is known about how productive urban agriculture is compared to conventional, rural farming. A new study digs in, finding urban gardeners and hydroponics can meet and sometimes exceed the yields of rural farms.
“Despite its growing popularity, there’s still quite a lot we don’t know about urban agriculture, like whether the yields are similar to conventional agriculture, or even what crops are commonly grown,” says Florian Payen, an environmental scientist at Lancaster University and lead author of the study, published today in AGU’s journal Earth’s Future.
The new study compiles studies on urban agriculture from 53 countries to find out which crops grow well in cities, what growing methods are most effective, and what spaces can be utilized for growing. The researchers find that urban yields for some crops, like cucumbers, tubers and lettuces, are two to four times higher than conventional farming. Many other urban crops studied are produced at similar or higher rates than in rural settings. Cost efficiency remains an open but important question.
Most studies on urban agriculture have focused on green spaces, such as private and community gardens, parks and field growing operations. Payen’s work includes “gray” spaces — places in cities that are already built but could be used for growing, such as rooftops and building facades. In both green and gray spaces, the study examines a suite of crops grown in soils versus hydroponics, horizontal versus vertical farming, and natural versus controlled conditions.
“Surprisingly, there were few differences between overall yields in indoor spaces and outdoor green spaces, but there were clear differences in the suitability of crop types to different gray spaces,” Payen says. Certain crops like lettuces, kale and broccoli are more naturally suited to be grown vertically in indoor spaces than others. “You can’t exactly stack up apple trees in a five- or ten-layer high growth chamber,” he says, “though we did find one study that managed to grow wheat stacked up like that.”
Other crops, like watery vegetables (e.g., tomatoes) and leafy greens, performed well in hydroponic environments. And crops grown in fully controlled environments can be grown throughout the year, allowing harvests to happen more times per year than in open-air environments, which leads to higher annual yields. But scientists will need to keep studying these systems to plan cost-effective agriculture solutions.
The finding that urban agriculture can have similar or greater yields to conventional agriculture “is exactly what we have been waiting for in the urban agriculture research community,” says Erica Dorr, an environmental scientist at AgroParisTech who was not involved in the study.
837 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introduction To Supporting Sustainable Agriculture For Witches and Pagans

[ID: An image of yellow grain stocks, soon to be harvested. The several stocks reach towards a blurred open sky, focusing the camera on he grains themselves. The leaves of the grains are green and the cereals are exposed].
PAGANISM AND WITCHCRAFT ARE MOVEMENTS WITHIN A SELF-DESTRUCTIVE CAPITALIST SOCIETY. As the world becomes more aware of the importance of sustainability, so does the duty of humanity to uphold the idea of the steward, stemming from various indigenous worldviews, in the modern era. I make this small introduction as a viticulturist working towards organic and environmentally friendly grape production. I also do work on a food farm, as a second job—a regenerative farm, so I suppose that is my qualifications. Sustainable—or rather regenerative agriculture—grows in recognition. And as paganism and witchcraft continue to blossom, learning and supporting sustainability is naturally a path for us to take. I will say that this is influenced by I living in the USA, however, there are thousands of groups across the world for sustainable agriculture, of which tend to be easy to research.
So let us unite in caring for the world together, and here is an introduction to supporting sustainable/regenerative agriculture.
A QUICK BRIEF ON SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
Sustainable agriculture, in truth, is a movement to practise agriculture as it has been done for thousands of years—this time, with more innovation from science and microbiology especially. The legal definition in the USA of sustainable agriculture is:
The term ”sustainable agriculture” (U.S. Code Title 7, Section 3103) means an integrated system of plant and animal production practices having a site-specific application that will over the long-term:
A more common man’s definition would be farming in a way that provides society’s food and textile needs without overuse of natural resources, artificial supplements and pest controls, without compromising the future generation’s needs and ability to produce resources. The agriculture industry has one of the largest and most detrimental impacts on the environment, and sustainable agriculture is the alternative movement to it.
Sustainable agriculture also has the perk of being physically better for you—the nutrient quality of crops in the USA has dropped by 47%, and the majority of our food goes to waste. Imagine if it was composted and reused? Or even better—we buy only what we need. We as pagans and witches can help change this.
BUYING ORGANIC (IT REALLY WORKS)
The first step is buying organic. While cliche, it does work: organic operations have certain rules to abide by, which excludes environmentally dangerous chemicals—many of which, such as DDT, which causes ecological genocide and death to people. Organic operations have to use natural ways of fertilising, such as compost, which to many of us—such as myself—revere the cycle of life, rot, and death. Organic standards do vary depending on the country, but the key idea is farming without artificial fertilisers, using organic seeds, supplementing with animal manure, fertility managed through management practices, etc.
However, organic does have its flaws. Certified organic costs many, of which many small farmers cannot afford. The nutrient quality of organic food, while tending to be better, is still poor compared to regeneratively grown crops. Furthermore, the process to become certified organic is often gruelling—you can practise completely organically, but if you are not certified, it is not organic. Which, while a quality control insurance, is both a bonus and a hurdle.
JOINING A CSA
Moving from organic is joining a CSA (“Community supported agriculture”). The USDA defines far better than I could:
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA), one type of direct marketing, consists of a community of individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that the farmland becomes, either legally or spiritually, the community’s farm, with the growers and consumers providing mutual support and sharing the risks and benefits of food production.
By purchasing a farm share, you receive food from the farm for the agreed upon production year. I personally enjoy CSAs for the relational aspect—choosing a CSA is about having a relationship, not only with the farmer(s), but also the land you receive food from. I volunteer for my CSA and sometimes I get extra cash from it—partaking in the act of caring for the land. Joining a CSA also means taking your precious capital away from the larger food industry and directly supporting growers—and CSAs typically practise sustainable and/or regenerative agriculture.
CSAs are also found all over the world and many can deliver their products to food deserts and other areas with limited agricultural access. I volunteer from time to time for a food bank that does exactly that with the produce I helped grow on the vegetable farm I work for.
FARM MARKETS AND STALLS
Another way of personally connecting to sustainable agriculture is entering the realm of the farm stall. The farmer’s market is one of my personal favourite experiences—people buzzing about searching for ingredients, smiles as farmers sell crops and products such as honey or baked goods, etc. The personal connection stretches into the earth, and into the past it buries—as I purchase my apples from the stall, I cannot help but see a thousand lives unfold. People have been doing this for thousands of years and here I stand, doing it all over again.
Advertisement
Farmers’ markets are dependent on your local area, yet in most you can still develop personal community connections. Paganism often stresses community as an ideal and a state of life. And witchcraft often stresses a connection to the soil. What better place, then, is purchasing the products from the locals who commune with the land?
VOLUNTEERING
If you are able to, I absolutely recommend volunteering. I have worked with aquaponic systems, food banks, farms, cider-making companies, soil conservation groups, etc. There is so much opportunity—and perhaps employment—in these fields. The knowledge I have gained has been wonderful. As one example, I learned that fertilisers reduce carbon sequestration as plants absorb carbon to help with nutrient intake. If they have all their nutrients ready, they do not need to work to obtain carbon to help absorb it. This does not even get into the symbiotic relationship fungi have with roots, or the world of hyphae. Volunteering provides community and connection. Actions and words change the world, and the world grows ever better with help—including how much or how little you may provide. It also makes a wonderful devotional activity.
RESOURCING FOOD AND COOKING
Buying from farmers is not always easy, however. Produce often has to be processed, requiring labour and work with some crops such as carrots. Other times, it is a hard effort to cook and many of us—such as myself—often have very limited energy. There are solutions to this, thankfully:
Many farmers can and will process foods. Some even do canning, which can be good to stock up on food and lessen the energy inputs.
Value-added products: farms also try to avoid waste, and these products often become dried snacks if fruit, frozen, etc.
Asking farmers if they would be open to accommodating this. Chances are, they would! The farmer I purchase my CSA share from certainly does.
Going to farmers markets instead of buying a CSA, aligning with your energy levels.
And if any of your purchased goods are going unused, you can always freeze them.
DEMETER, CERES, VEIA, ETC: THE FORGOTTEN AGRICULTURE GODS
Agricultural gods are often neglected. Even gods presiding over agriculture often do not have those aspects venerated—Dionysos is a god of viticulture and Apollon a god of cattle. While I myself love Dionysos as a party and wine god, the core of him remains firmly in the vineyards and fields, branching into the expanses of the wild. I find him far more in the curling vines as I prune them than in the simple delights of the wine I ferment. Even more obscure gods, such as Veia, the Etruscan goddess of agriculture, are seldom known.
Persephone receives the worst of this: I enjoy her too as a dread queen, and people do acknowledge her as Kore, but she is far more popular as the queen of the underworld instead of the dear daughter of Demeter. I do understand this, though—I did not feel the might of Demeter and Persephone until I began to move soil with my own hands. A complete difference to the ancient world, where the Eleusinian mysteries appealed to thousands. Times change, and while some things should be left to the past, our link to these gods have been severed. After all, how many of us reading know where our food comes from? I did not until I began to purchase from the land I grew to know personally. The grocery store has become a land of tearing us from the land, instead of the food hub it should be.
Yet, while paganism forgets agriculture gods, they have not forgotten us. The new world of farming is more conductive and welcoming than ever. I find that while older, bigoted people exist, the majority of new farmers tend to be LGBT+. My own boss is trans and aro, and I myself am transgender and gay. The other young farmers I know are some flavour of LGBT+, or mixed/poc. There’s a growing movement for Black farmers, elaborated in a lovely text called We Are Each Other’s Harvest.
Indigenous farming is also growing and I absolutely recommend buying from indigenous farmers. At this point, I consider Demeter to be a patron of LGBT+ people in this regard—she gives an escape to farmers such as myself. Bigotry is far from my mind under her tender care, as divine Helios shines above and Okeanos’ daughters bring fresh water to the crops. Paganism is also more commonly accepted—I find that farmers find out that I am pagan and tell me to do rituals for their crops instead of reacting poorly. Or they’re pagan themselves; a farmer I know turned out to be Wiccan and uses the wheel of the year to keep track of production.
Incorporating these divinities—or concepts surrounding them—into our crafts and altars is the spiritual step towards better agriculture. Holy Demeter continues to guide me, even before I knew it.
WANT CHANGE? DO IT YOURSELF!
If you want change in the world, you have to act. And if you wish for better agriculture, there is always the chance to do it yourself. Sustainable agriculture is often far more accessible than people think: like witchcraft and divination, it is a practice. Homesteading is often appealing to many of us, including myself, and there are plenty of resources to begin. There are even grants to help one improve their home to be more sustainable, i.e. solar panels. Gardening is another, smaller option. Many of us find that plants we grow and nourish are far more potentant in craft, and more receptive to magical workings.
Caring for plants is fundamental to our natures and there are a thousand ways to delve into it. I personally have joined conservation groups, my local soil conservation group, work with the NRCs in the USA, and more. The path to fully reconnecting to nature and agriculture is personal—united in a common cause to fight for this beautiful world. To immerse yourself in sustainable agriculture, I honestly recommend researching and finding your own path. Mine lies in soil and rot, grapevines and fruit trees. Others do vegetables and cereal grains, or perhaps join unions and legislators. Everyone has a share in the beauty of life, our lives stemming from the land’s gentle sprouts.
Questions and or help may be given through my ask box on tumblr—if there is a way I can help, let me know. My knowledge is invaluable I believe, as I continue to learn and grow in the grey-clothed arms of Demeter, Dionysos, and Kore.
FURTHER READING:
Baszile, N. (2021). We are each other’s harvest. HarperCollins.
Hatley, J. (2016). Robin Wall Kimmerer. Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous wisdom, scientific knowledge and the teachings of plants. Environmental Philosophy, 13(1), 143–145. https://doi.org/10.5840/envirophil201613137
Regenerative Agriculture 101. (2021, November 29). https://www.nrdc.org/stories/regenerative-agriculture-101#what-is
And in truth, far more than I could count.
References
Community Supported Agriculture | National Agricultural Library. (n.d.). https://www.nal.usda.gov/farms-and-agricultural-production-systems/community-supported-agriculture
Navazio, J. (2012). The Organic seed Grower: A Farmer’s Guide to Vegetable Seed Production. Chelsea Green Publishing.
Plaster, E. (2008). Soil Science and Management. Cengage Learning.
Sheaffer, C. C., & Moncada, K. M. (2012). Introduction to agronomy: food, crops, and environment. Cengage Learning.
Sheldrake, M. (2020). Entangled life: How Fungi Make Our Worlds, Change Our Minds & Shape Our Futures. Random House.
Sustainable Agriculture | National Agricultural Library. (n.d.). https://www.nal.usda.gov/farms-and-agricultural-production-systems/sustainable-agriculture
#dragonis.txt#witchcraft#paganism#hellenic polytheism#witchblr#pagan#helpol#hellenic pagan#hellenic worship#hellenic paganism#hellenic polytheist#demeter deity#demeter worship#persephone deity#kore deity#raspol#etrupol#etruscan polytheist#etruscan polytheism#rasenna polytheism#rasenna polytheist#rasenna paganism
257 notes
·
View notes
Note
Honest question from someone who also dislikes "invasive species control that amounts to kill on sight": what do you suggest as an alternative control effort should I encounter say a spotted lanternfly or a spongy moth? I really hate just killing bugs for being in the wrong place. Thanks!
i honestly don't think there is much that any individual person can do. like in general once an exotic species has established in an area there's almost nothing short of a fast and concerted multimillion dollar years-long eradication program that even stands a chance of actually removing them entirely. and this is a rant for another day but generally nobody wants to pay for the kind of program that stands an actual chance of being successful. it doesn't matter how many concerned citizens you convince to go around smashing animals, if even a handful get missed, and many many more than a handful will get missed, the survivors can lay enough eggs and rapidly enough that the population will have no trouble rebounding. the way to eradicate an invasive species, when it's even possible, is through very strategic and large-scale application of pesticides, environmental control, parasitoids, and other integrated pest management strategies.
and that's not even mentioning that the whole smash-on-sight thing requires people to recognize the target and not just smash every bug they see which is also another rant for another day because you would not fucking believe how bad people are at identifying insects like i've had fucking crane flies reported as "murder hornets" (another rant). i genuinely believe that entomology should be a core primary and secondary education subject alongside history and math. the world is mostly bugs and it's important to know at least a little about them. without mass knowledge, the whole campaign just engenders a further generalized fear and disgust and violence towards all insects which is fucking nasty to me.
anyway i'm getting distracted. back to your question, what should you do if you encounter a spotted lanternfly or spongy moth or japanese beetle or whatever? report it to your state's department of agriculture if you live in the united states, or to whatever the equivalent is if you live elsewhere. chances are they're already aware of the infestation in your area but there's always the chance that they're not. with any luck they're one of the few ones that actually has the funding to operate a large-scale control program and are working on it already. again i'm very fatalistic about these things and don't think that eradication is possible in most cases by the time the exotic insect is discovered but at the very least it is often possible to keep the populations in check to the point that they're not an ecological/economic catastrophe using the IPM methods mentioned above--with enough funding. you can kill the bug if you want but smashing one bug or a dozen or a hundred or a thousand isn't going to do shit in the long run or the large scale and it's not the bug's fault that it is where it is.
761 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Agriculture: The Role of an MBA in Agriculture

The Growing Importance of an MBA in Agriculture
In a world where the agricultural sector is evolving rapidly, professionals with an MBA in agriculture are becoming increasingly vital. This unique blend of business acumen and agrarian expertise is not just a fancy title; it's about understanding the complex dynamics of the agricultural industry and leading it towards sustainable and profitable growth. But why exactly is an MBA in agriculture gaining traction?
The Intersection of Business and Farming
Consider this: agriculture is not just about planting and harvesting. It's a multi-faceted industry involving supply chain management, marketing, financial planning, and technological innovation. An MBA in agriculture dives deep into these aspects, equipping graduates with the skills to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the agricultural sector.
Imagine analyzing market trends, implementing cutting-edge technologies in farming, and developing strategies that boost productivity while ensuring environmental sustainability. That's the kind of expertise we're talking about!
Operations Management: A Critical Aspect
One of the critical components of an MBA operations management in agriculture operations management. But what does this mean in the context of farming? It's about making the entire agricultural process more efficient and productive. From optimizing resource use to enhancing supply chain processes, operations management is the backbone that supports the farm sector's growth.
Think of it as the art of balancing cost-effectiveness with quality and sustainability. In the ever-changing landscape of agriculture, operations management is not just a skill; it's a necessity.
Top MBA Institutes in India: Paving the Way
With its vast agricultural landscape, India is at the forefront of this educational revolution. Among the top MBA institutes in India, a few stand out for their specialized programs in agriculture. These institutions are not just academic hubs but incubators for future leaders in the agricultural sector.
These institutes offer a curriculum that's a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical, real-world applications. Students learn from industry experts, participate in internships, and work on projects that give them a taste of the challenges and rewards of working in agriculture.
The Future is Bright and Green
As the world grapples with challenges like food security, climate change, and sustainable development, the role of educated, skilled professionals in agriculture becomes ever more critical. An MBA in agriculture is not just a degree; it's a ticket to becoming part of the solution to some of the most pressing issues of our time.
And let's not forget the career opportunities. The demand for professionals blending business insight with agricultural expertise is soaring from agribusiness firms to international NGOs.
SIOM: A Leader in Agricultural Business Education
Speaking of top MBA institutes, SIOM (Symbiosis Institute of Operations Management) deserves special mention. Known for its cutting-edge curriculum and focus on creating industry-ready professionals, SIOM offers a unique blend of academic excellence and practical exposure. Their program in operations management, with an emphasis on the agricultural sector, is tailored to meet the industry's evolving needs.
At SIOM, students are not just learning about agriculture but being prepared to lead it into a new era. With a focus on innovation, sustainability, and efficiency, SIOM stands out as a beacon of excellence in agricultural business education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an MBA in agriculture is more than just a degree; it's a journey into the heart of one of the world's most vital industries. For those looking to make a significant impact, institutions like SIOM are the gateways to a fulfilling and impactful career in agricultural business management. The future of agriculture is bright, and with the proper education and guidance, it's yours to shape.
0 notes
Text
Satellite photos show Egypt building Gaza buffer zone as Rafah push looms
Despite its opposition to displacement of Palestinians, Cairo appears to be preparing for a scenario forced by Israel.

A satellite image shows the construction of a wall along the Egypt-Gaza border near Rafah on February 15, 2024 [Maxar Technologies/Handout via Reuters]
Egypt is building a fortified buffer zone near its border with the Gaza Strip as fears mount of an imminent Israeli ground invasion of the southern city of Rafah, which could displace hundreds of thousands of Palestinians across the frontier, according to satellite images and media reports.
Footage from the site in the Sinai desert and satellite photos show that an area that could offer basic shelter to tens of thousands of Palestinians is being constructed with concrete walls being set up on the Egyptian side of the Rafah crossing, the only non-Israeli-controlled crossing to and from Gaza.
The new compound is part of contingency plans if large numbers of Palestinians manage to cross into Egypt and could accommodate more than 100,000 people, The Wall Street Journal reported on Thursday, citing Egyptian officials.
It is surrounded by concrete walls and far from any Egyptian settlements. Large numbers of tents have been delivered to the site, the report said.
Videos taken by the United Kingdom-based Sinai Foundation for Human Rights show trucks and bulldozers clearing debris from a plot of land of about 8sq miles (21sq km), according to The Washington Post, which obtained satellite images that show 2sq miles (5sq km) was cleared between February 6 and Wednesday.
Mohamed Abdelfadil Shousha, the governor of North Sinai, the Egyptian governorate that borders Gaza and Israel, has reportedly denied that Egypt is building a refugee camp along the border in case of an exodus by Palestinians forced by the Israeli military.
The Sinai Foundation, an activist organisation that has a monitoring team in northern Sinai, said in a report this week that the gated area will be surrounded by 7-metre-high (23ft-high) cement walls.
Israel has said it wants to take over the Philadelphi Corridor, the fortified border area between Gaza and Egypt, to secure it. Egypt has threatened that this would jeopardise the peace treaty the two countries signed four decades ago.
Cairo has emphasised that it does not want Palestinians to be displaced from their land by Israel, comparing such a scenario to the 1948 Nakba, the forced displacement of about 750,000 Palestinians from their homes in the war that led to Israel’s creation.
Tel Aviv’s insistence on going ahead with its planned attack on Rafah despite international pressure has been unshaken even though the area is where 1.4 million Palestinians are living, the vast majority of whom have been forcibly displaced – some multiple times – by Israeli bombardments and ground operations.
Palestinians displaced to Rafah are suffering from a lack of sufficient shelter, food, water and medicine, and the United Nations and human rights groups have warned that the humanitarian disaster in the besieged enclave is rapidly worsening.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has ordered the army to work on a plan of evacuation for more than half of the 2.3 million people of the Gaza Strip who are now crammed into Rafah, but has provided no detailed steps.
He has suggested Palestinians could be sent to areas north of Rafah that the Israeli military has already cleared through a ground invasion backed by bombings.
Avi Dichter, Israel’s minister of agriculture and rural development, has suggested areas west of Rafah and the bombed al-Mawasi refugee camp near the Mediterranean coast, where many are already sheltering.
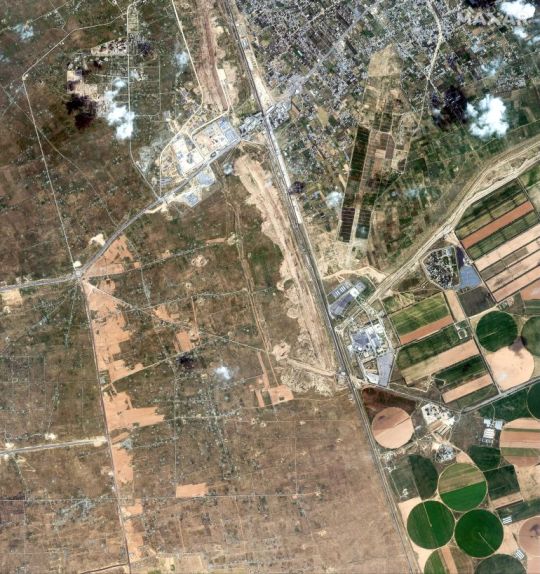

A satellite image shows new construction and earth grading along the Egypt-Gaza border near Rafah on February 10, 2024 [Maxar Technologies/Handout via Reuters]
The United States and a number of other key allies of Israel have said they oppose a ground assault on Rafah, some warning it would be “catastrophic”.
US President Joe Biden “has been clear that we do not support the forced displacement of Palestinians from Gaza”, the Reuters news agency quoted a US Department of State spokesperson as saying on Friday. “The US is not funding camps in Egypt for displaced Palestinians.”
Israel on Wednesday pulled out of US- and Arab-mediated talks with Hamas because it said the Palestinian armed group has had “ludicrous demands” that have included Israel’s withdrawal from Gaza.
Netanyahu and the Israeli war cabinet have continued to push for “total victory” with the prime minister calling Rafah the “last bastion” of Hamas.
For weeks, the fiercest fighting in the Gaza Strip has been taking place in Khan Younis, also located in southern Gaza, with the Israeli military claiming its attacks are aimed at destroying Hamas battalions in the area.
Using shelling, sniper fire and drones, the Israeli army has also for weeks been laying siege to Nasser Hospital, the largest medical facility in the area, which has hundreds of patients and staff and has been a shelter for thousands of displaced Palestinians.
Dr Nahed Abu Taima, the hospital’s director, told Al Jazeera on Friday that Israeli forces were rounding up patients and civilians and had cut off electricity to the medical complex.
“We stand helpless, unable to provide any form of medical assistance to the patients inside the hospital or the victims flooding into the hospital every single minute,” he said.
Israel’s attacks on Gaza have killed at least 28,775 Palestinians and wounded 68,552 since October 7, according to the Ministry of Health in Gaza. Several thousand more are missing, presumably buried under rubble.
#palestine#free palestine#save palestine#gaza#save gaza#free gaza#world news#current events#egypt#israel#israel palestine conflict#israeli apartheid#war on gaza#gaza strip#gaza genocide#gazaunderattack#palestine genocide#palestinian genocide#stop the genocide#genocide#humanitarian crisis#humanitarian aid#human rights
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
shido's conspiracy is big: koenkai (supporters associations) in japanese politics
How do you take over Japan, if you're a corrupt piece of shit?
On 11/25, when the Shido's Palace mission starts and you're finally released from captivity in Leblanc, the Modest Housewife in the Shibuya underground mall suddenly becomes the Not-So-Modest Housewife. And what does she tell us?


shido has a what now
What's the "supporters association"? In Japanese, it's a 後援会 kouenkai. From Wikipedia:
Koenkai (後援会, lit. "local support groups") are an invaluable tool of Japanese Diet members, especially of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP). (note: in P5, this is the "Liberal Co-Prosperity Party" or LCP, Shido's original party and the original ruling party.) These groups serve as pipelines through which funds and other support are conveyed to legislators and through which the legislators can distribute favors to constituents in return.
The article is fascinating; do give it a read, as I can't possibly do it justice here. These are massive organisations, and relay vast amounts of cash to their members. They organise endless activities for their members—that meeting at the Wilton Hotel on 5/5 is one. They often require a personal connection to be invited, which is why the Housewife says this to her friend:

... she knows she wasn't invited.
Though koenkai are weaker in modern times, there are many examples of them being involved with corruption; here are a couple.
"The Asahi reported in the mid-1970s that the [koenkai of former Prime Minister Tanaka Kakuei] "virtually controls… agricultural committees, popular welfare committees, election management committees". This thorough penetration of Tanaka's koenkai into all important facets of Niigata's people's lives propelled him into becoming the father figure of the district. After his arrest in 1976 on corruption charges, many of Niigata's residents still expressed deep respect towards him."
"Due to the huge support [former Prime Minister] Takeshita Noboru enjoyed as a result of his koenkai, his electoral district in Shimane came to be known as ‘Takeshita Kingdom'. Despite being embroiled in many political scandals, related to insider trading and corruption (for which he was never charged), Takeshita's immense local support never waned."
so what does this tell us
In short, Shido's conspiracy is not a few corrupt high-level officials. It's not just Shido, Akechi, the SIU Director and those people on the ship. It is a vast organisation.
It recruits people by reputation (remember those five recommendations in the Palace?) from all levels of society—and those recruits then operate as a bloc, networking, doing favours for each other, advancing their mutual interests, connected via a hierarchy to Shido at the top. This is why Shido can control everything.
It also explains why everyone seems to be linked to the conspiracy—including the hapless Principal Kobayakawa. Did you think it was unrealistic for him to be involved? It seems likely that he was just a low-level member of Shido's koenkai.
When Shido needed someone at Shujin to investigate the Phantom Thieves, Kobayakawa was there—because they have people everywhere. A quick phone call from a higher-up in the organisation—the SIU Director, most likely, who we know Kobayakawa speaks to—and he's eating out of Shido's hand. And will do anything he wants....
So Kobayakawa wasn't anybody at all. He wasn't important. He wasn't somehow part of the deep state. He was just one of likely hundreds of thousands of paid-up Shido supporters looking to advance themselves, getting the vote out, and funding the cause.
He was in the right place at the right time. After all, the koenkai got Kobayakawa his job at Shujin. All his hopes for advancement are centred on it:

Because just like the two housewives in the underground mall, and probably like everyone else in the koenkai, Kobayakawa is a desperate social climber, impressed by wealth and fame and power and flashy titles.
I hope he thought it was worth it.
revision history
Click here for the latest version.
v1.0 (2023/10/31)—first posted.
229 notes
·
View notes
Text
I wanted to make so many metaphors from livestock welfare for that post, but didn't feel like catching the associated snarl of feelings and ideas that people have about animal management and food in response, because that's its own kettle of fish. But while I was looking for an easily accessible concept to tap into, I found something really cool.
Let me talk about farrowing rails for a second. When sows give birth to piglets, it's unfortunately rather common for little piglets to get crushed beneath their mother's weight. No one, least of all sows, wants this to happen, but the sow is huge and has to lie down a lot so the piglets can suckle and especially when they are born piglets are almost cartoonishly tiny. They are also not good at moving quickly and anticipating their mother's movements yet. This means that there are often piglet losses from being squished to death.
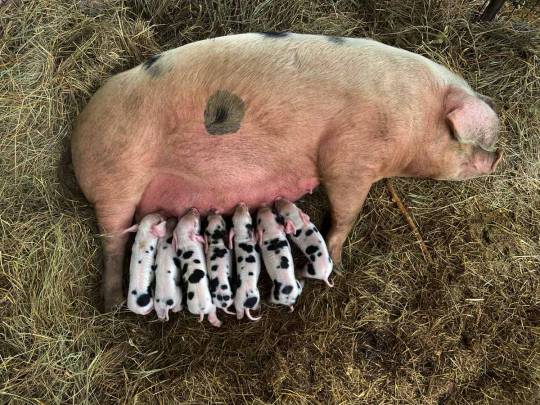

So pig farmers often use a farrowing crate to protect piglets from getting squished. Sows go into it before they give birth and come out either at weaning or when the piglets are big enough that squishing isn't an issue.
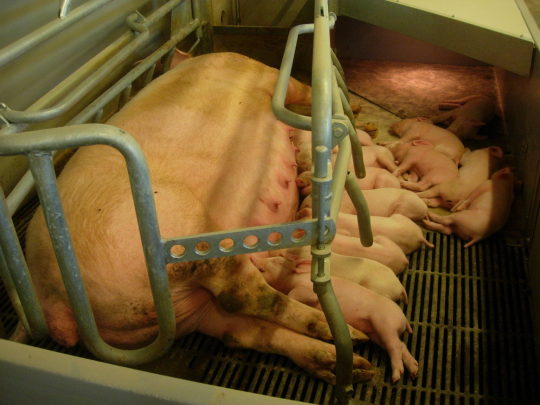
It has slats that piglets can fit between and move around in, so their mothers can't crush them. It's very effective for increasing piglet survival and decreasing these kinds of crushing deaths. But it's really not ideal for the sow for all kinds of reasons that should be obvious. That's a long time to be confined in a small space.
The thing I'm delighted to find is the existence of this site by a couple of agriculture researchers in the UK, which is focused on providing resources and research on ways to allow sows to farrow (give birth) with much less restriction for the animals. There are recommendations for many kinds of operations and pointers to many kinds of evidence - based systems, complete with plans for how to design each system and a list of what each can accomplish for sow, piglets, and caregiving staff.
Each of the options are set up with contact information for the people who designed it and instructions about how to go about finding a system to suit farmers' needs. There's also research sections explaining how we know what welfare provisions improve quality of life for both sow and piglets, plus lists of assurance schemes farmers can use to market their products as ethical to consumers. It's really cool and well designed, and it makes setting up changes in pig operations relatively straightforward and feel easy to do. It's such a nice piece of communication. I like it a lot.
283 notes
·
View notes
Text
"When Francois Beyers first pitched the concept of 3D ocean farming to the Welsh regulators, he had to sketch it on napkins.
Today the seafood farm is much more than a drawing, but if you walked along the Welsh coastal path near St David’s, all you’d see is a line of buoys. As Beyers puts it: “It’s what’s below that’s important.”
Thick tussles of lustrous seaweed suspend from the buoys, mussels cling to its furry connective ropes and dangling Chinese lantern-esque nets are filled with oysters and scallops.
“It’s like an underwater garden,” says Beyers, co-founder of the community-owned regenerative ocean farm, Câr-y-Môr. The 3-hectare site is part of a fledgling sector, one of 12 farms in the UK, which key players believe could boost ocean biodiversity, produce sustainable agricultural fertiliser and provide year-round employment in areas that have traditionally been dependent on tourism.
Created in 2020 by Beyers and six family members, including his father-in-law – an ex-shellfish farmer – the motivation is apparent in the name, which is Welsh for “for the love of the sea”. ...

Pictured: Drone shot of Câr-y-Môr, which is on the site of abandoned mussel farms. Image: Scott Chalmers
Ocean farming comes from the technical term ‘integrated multi-trophic aquaculture’, which means a mixture of different seaweed and shellfish species growing together to mutually benefit each other. But it’s not just a way of growing food with little human input, it also creates ocean habitat.
“You’re creating a breeding ground for marine animals,” explains Beyers who adds that the site has seen more gannets diving, porpoises and seals – to name a few – since before the farm was established.
Ocean farms like Câr-y-Môr, notes Ross Brown – environmental research fellow at the University of Exeter – have substantial conservation benefits.
“Setting up a seaweed farm creates an exclusion zone so fishermen can’t trawl it,” explains Brown, who has been conducting experiments on the impacts of seaweed and shellfish farms across the UK.
Brown believes a thriving ocean farming industry could provide solutions to the UK’s fish stock, which is in “a deeply troubling state” according to a report that found half of the key populations to be overfished. “It would create stepping stones where we have safe havens for fish and other organisms,” he adds.
But UK regulators have adopted a cautious approach, note Brown and Beyers, making it difficult for businesses like Câr-y-Môr to obtain licenses. “It’s been a tough old slog,” says Beyers, whose aim is to change the legislation to make it easier for others to start ocean farms.
Despite navigating uncharted territories, the business now has 14 full-time employees, and 300 community members, of which nearly 100 have invested in the community-benefit society. For member and funding manager Tracey Gilbert-Falconer, the model brings expertise but most importantly, buy-in from the tight-knit local community.
“You need to work with the community than forcing yourself in,” she observes.
And Câr-y-Môr is poised to double its workforce in 2024 thanks to a Defra grant of £1.1 million to promote and develop the Welsh seafood industry as part of the UK Seafood Fund Infrastructure Scheme. This will go towards building a processing hub, set to be operational in April, to produce agricultural fertiliser from seaweed.
Full of mineral nutrients and phosphorous from the ocean, seaweed use in farming is nothing new, as Gilbert-Falconer notes: “Farmers in Pembrokeshire talk about their grandad going down to the sea and throwing [seaweed] on their farms.”
But as the war in Ukraine has caused the price of chemical fertiliser to soar, and the sector tries to reduce its environmental impact – of which synthetic fertiliser contributes 5% of total UK emissions – farmers and government are increasingly looking to seaweed.
The new hub will have capacity to make 65,000 litres of sustainable fertiliser annually with the potential to cover 13,000 acres of farmland.
But to feed the processing hub, generate profit and reduce their dependency on grants, the co-op needs to increase the ocean farm size from three to 13 hectares. If they obtain licences, Beyers says they should break even in 18 months.
For now, Beyers reflects on a “humbling” three years but revels in the potential uses of seaweed, from construction material to clothing.
“I haven’t seen the limit yet,” he smiles."
-via Positive.News, February 19, 2024
#wales#welsh#ocean#marine biology#aquaculture#marine life#marine animals#seaweed#sea scallops#oysters#united kingdom#uk#conservation#conservation news#overfishing#environmental news#farming#sustainable agriculture#sustainability#ocean farming#good news#hope
477 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just a little push
The conflict between Humanity and the United Federation was in it's early slow stages. After the rather unexpected attack on the symbolic Death Kebab there was a lot of buzz and light skirmishes in the nearby systems, but no noteworthy confrontation.
The placement of the Death Kebab was provocative by design, and with both sides so far away from one another, there could not be any mass fleet formation without plenty of advance notice. Special operations units, however, are everywhere.
Unlike Humanity, who currently only has Earth as a planet under their direct control and with a notable population, the Federation is vast - core worlds surrounded by buffer manufacturing and agriculture and all manner of other production focused systems, which themselves are further surrounded out by new colonies, annexed planets, "contract" aka slave worlds.
Getting close to Earth without being spotted by any number of civilian organizations is nigh impossible, and when you count the military intelligence and surveillance networks, there's hardly an atom that remains unregistered. Certain people with, let's say, less than honest intentions, still manage to find ways to keep their activities hidden. For a while at least.
These kinds of skills, when employed by a trained operative with the highest grade equipment, make them virtually invisible everywhere else. A poorly guarded third-rate mining colony? Why, with just a little preparation, you could float an entire Dreadnought up to their atmosphere before they noticed. Assuming they would even care after offering a slightly more lucrative deal than the Federation.
For this particular mission, however, they would care.
Vrontaria was a very productive system with nearly a dozen orbital shipyards and hundreds of mining, processing, and export operations that account for roughly 4% of the entire Federation military hardware supply, and nearly a fifth of all their capital ship production. Thus, it was quite heavily guarded, with every nearby system monitored for any suspicious activity.
What they didn't monitor all too well were the mostly useless planets and moons within the Vrontaria system itself. Of particularly little interest was the resident gas giant - Omk.
And why would anyone bother regularly scanning the interior of a gas giant for foreign matter, everyone knows entering the "atmosphere" of a gas giant will just crush everything. Right?
*glances sideways*
:D
It took the better part of a month, but the special unit managed to covertly install about five thousand gravitational pulse thrusters and all necessary power generators within the upper layer of Omk, but just far enough below the storms to make their activity not make any visible change. For comparison, one such thruster can accelerate an entire Dreadnought. Slowly, sure, which is why they have at least 6 to be able to maneuver, and Omk was not the largest gas giant in the Galaxy, about two thirds of Jupiter.
So, one day not long after, someone on Ja'Ulnika, the main planet of the Vrontaria system, noticed that Omk was a little bit further along its orbital path than it should be.
Concerning.
Then they took more precise measurements and realized it was going faster than before.
Very concerning.
Finally, they had someone go up to it and then they noticed all of the thrust force coming from one side of it, changing its orbit to get far too close to Ja'Ulnika for comfort.
Panic inducing to say the least.
By the time a full force of combat ships arrived to sort out this mess and start disabling all these planet-moving thrusters, scans showed they had self-destructed. Even if they had the ability to retrieve anything from the inside of a gas giant, at this point it would be worthless scraps.
The final orbit of Omk would put it on a course to capture Ja'Ulnika in its gravitational well in two years time and take it along for a joyride to orbits outside the habitable zone, rendering it inhospitable in around 5-6 years. Not to mention the carnage tides would cause on a world without its own moon. Or any other catastrophic events that might occur when a planet is essentially kidnapped into a becoming moon.
Wars are fought on many fronts. inevitable devastation and unavoidable future reduction in capacity force you to act in ways you would rather not. Sometimes creating a logistical nightmare that your enemy has to deal with no matter what can be the greatest killing blow that a swift and spectacular showdown space battle could never be.
#humans are space orcs#humans are space oddities#humans are space australians#humans are deathworlders#humanity fuck yeah#carionto
85 notes
·
View notes