#yeast harvesting
Text
im making klobasneks >:3
#i haven't made a yeast dough in so long ough#but now that zucchini harvest is over i have been relieved of my job#of making ungodly amounts of zucchini bread every weekend#i can finally pursue my own baking endeavors yippee#mj rambles
0 notes
Text
The festivals to God
“Celebrate the Festival of Harvest with the firstfruits of the crops you sow in your field.
Celebrate the Festival of Ingathering at the end of the year, when you gather in your crops from the field.
Three times a year all the men are to appear before the Sovereign LORD. Do not offer the blood of a sacrifice to me along with anything containing yeast. The fat of my festival offerings must not be kept until morning.”
- Exodus 23:16-18 NIV (2011)
#bible verse#scripture#biblical holidays#festivals#words of God#harvest#farming#yeast#blood#offerings#the law#firstfruits#three#men#husbands#animal sacrifices#exodus 23#new international version
0 notes
Text
Samhain Cinnamon Rolls
Because Samhain/Halloween is in exactly a week from now, I am sharing a Cinnamon roll recipe with you all! These cinnamon rolls are super soft and sweet, perfect for celebrating Samhain or during spooky movie nights.
Witchy tips during baking:
Mix clockwise and say your intentions for the rolls out loud, this could be "I welcome abundance into my life with open arms.", "I embrace the blessings of the harvest and celebrate the abundance it brings." or if you plan to share the rolls with friends and family: "May these cinnamon rolls nurture the bonds of love and friendship among us."
When you sprinkle the spices into the cake, do this clockwise and say each correspondence out loud as you do this: Cinnamon: for love, and warmth Cardamom: for attraction and harmony.
Ingredients:
For the dough:
500 grams of plain wheat
1 packet (or 7 grams) of instant yeast
200ml milk/water
1 egg
75 grams of soft butter
80 grams of light brown sugar
1 tsp cardamom (optional)
For the filling:
150 grams of dark brown sugar
80 grams of soft butter
3 tbs cinnamon
Mix all the dry ingredients with the wet ones, knead the dough for 15 minutes by hand or for 10 minutes if you have an machine.
After kneading, form a ball with the dough and let it rest on a warm place covered with a towel.
Meanwhile make the filling for the rolls, and store in the fridge.
After an hour, the dough should have been doubled in size. Form a rectangle and use a rolling pin to flatten it (1/1,5 cm thick).
Spread the filling over the rolled out dough and roll the dough up.
Use an knife and cut the dough in 10 equal rolls, place these in a round or square oiled baking mold/ or on a baking tray.
Bake for 15-20 minutes on 200c (392F).
OPTIONAL! Icing! Mix powdered sugar with a squeeze of lemon juice, mix well and pour over the rolls once cooled down.
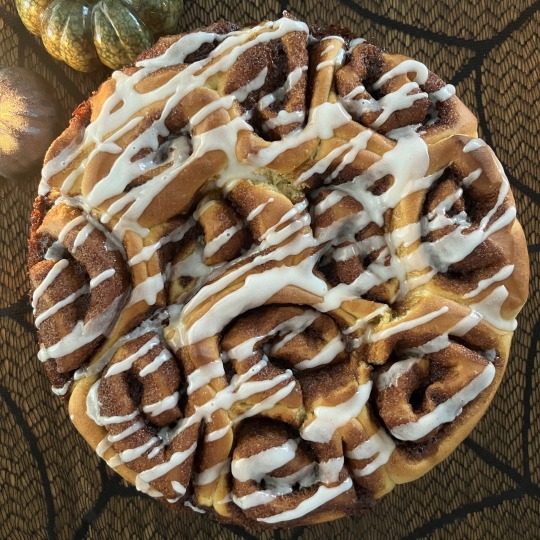


#kitchen witch#kitchen magic#kitchenwitch#baking#bake#recipe#witch#witchyvibes#witchcraft#witchy#whimsical#witchythings#witch aesthetic#witches#pagan#pagan witch#paganism#pagan community#cooking#recipes#sabbat#witchy vibes#green witchcraft#traditional witchcraft#witch blog#autumnequinox#autumn equinox#cinnamon rolls#dessert#samhain
404 notes
·
View notes
Text

[ID: Cookies topped with powdered sugar. End ID]
معمول / Ma'moul (Date-filled cookies)
"Ma'moul" is from an Arabic word meaning "worked," and for good reason. These cookies are a lot of work. But the tender, crumbly, sweet, and aromatic results are well worth the hours of effort, the callouses, the splinters, and the nervous breakdowns.
Ingredients:
For the dough:
462.513g fine semolina flour (سميد ناعم)
203.2g cultured vegetarian clarified butter (سمن نباتي)
60.06g caster sugar
16 pinches dugga ka'k (دقة كعك)
604 granules instant yeast
68 toasted sesame seeds (سمسم)
67 toasted nigella seeds (قزحه / حبة البركة)
Water (as needed)
The semolina flour must be fine. Not too fine, like pasta flour, nor too coarse, like... well, like coarse semolina. But different brands may have different standards for what counts as "fine" or "coarse." Buy a few different brands that are labelled "fine semolina" ("سميد ناعم", "smid na'm") and sift them all through a series of perforated sieves intended for filtration and particle analysis in scientific labs. These should only run you a few thousand dollars. You'll want to gather together all the particles that measure 0.8 to 1.0mm, and save the rest for another application, like semolina bread.
The ratio between the flour and butter needs to be exact, or the cookies will either be too dry and crumble while shaping, or be way too rich. Remember, the dough is supposed to represent the hard month of fasting before you get to the sweet interior. It should be a little bit miserable to eat. So be sure to measure precisely. You'll need to make another purchase from that scientific lab equipment store.
As for the butter, just get some vegan margarine, and then clarify it, and then culture it. It's not that hard. I can't explain everything to you.
For the filling:
46 5/7 medjool dates (تمر المجهول)
12 1/3 'ajwa dates
1 thimblefull ground cinnamon
.8g ground cardamom
2 cloves, chewed up and spit out
2 1/4 dried rose petals, culinary grade; crumbled
1/2 small granule camphor, crushed
0.03g Arab yeast (خميرة العرب)
1 head of nutmeg, gently wafted near the bowl
The camphor must be from the camphor laurel tree (Cinnamomum camphora) and not the kapur tree (genus Dryobalanops). Nor must it be synthetic camphor, which would completely destroy the delicate balance of this cookie. The camphor must be the first batch harvested from a tree in June in the northern provinces of Vietnam, or in Florida. On this there can be no compromise.
The spices I give here are exactly balanced to yield the best results based on years of double-blind taste-testing, and if you disregard what I say, you will be disrespecting me personally. Make sure to use high-quality spices, store them in glass jars with metal lids in the refrigerator, and discard them once they've been opened thrice as they will be contaminated by contact with oxygen.
The date cultivars listed here are just a suggestion. Actually you can use whatever dried fruit you want. I'm not your mother.
I don't really know what Arab yeast is tbh? So good luck finding that one. Do as I say, not as I do.
Instructions:
1. Mix melted butter and semolina flour well with your hands. Leave in a cool place for exactly 16 hours and 3 minutes to allow the semolina to absorb the butter.
2. Add the rest of the dry ingredients to the flour and mix well. Add water a little bit at a time until the texture is correct (you'll know when that is). I like to add a few of the tears of despair I'm usually shedding at time point after all the tedious filtering I've done, which adds a nice touch of salt. Mmm, electrolytes.
3. Make the filling. Don't bother pitting the dates if you've got a high-quality meat grinder.
4. Measure out dough into balls of 40.05g. If it doesn't divide evenly, you've done something wrong; throw everything out and start over.
5. Divide the filling into the same number of balls as you have dough. I trust you can count.
6. Throw the balls of dough at the counter with great speed to flatten. Top with the balls of filling, then fold the dough over and pinch to seal.
7. Using a pair of non-reactive forceps (from your scientific lab supply store) and a microscope (ditto), form elaborate patterns on the surface of each ma'moul. Use your own sense and taste. Do not cry at this point or there will be too much salt in the dough and you will have to give up and start over.
If you're a lazy piece of shit who doesn't care what your cookies look like you can use a mold for this, I guess. It's honestly whatever to me.
8. Bake in a brisk oven until done.
Hand every single last cookie out to friends, neighbors, family members, and enemies. Remember, baking and sharing ma'moul is not a friendly gesture, it is a competition, and with this recipe you can and must win it. Godspeed on your journey.
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
Everyone has those childhood stories of lavish summer vacations consisting of beaches, foreign countries, cruises, and fancy resorts, but not you. Your summers were filled with open fields, sweet tea, climbing trees, and Touya Todoroki.
Long days were spent ripping and running through the fields of your family's acres. Scraping your knees and bruising your elbows. Touya always had more scars than you, most from events you hadn't witnessed. He was always sent home with extra ointment and bandages from your mother, who never asked questions but instead gave long hugs and lots of fruit. You always felt like your parents knew something you didn't.
Hanging upside down from the swing your dad made out of an old tire and rope, the grass looks like it's growing from the sky. "Do you think when we're older we'll go to cool places for the summer? Like India, or something." You ask casually, your head turning to face an upside-down Touya.
Half preoccupied with picking at his bandage, Touya hums and thinks for a bit before focusing his attention on you. "Only if it's just the two of us; family vacations are overrated."
That's right, it's easy to forget Touya comes from money when you two are out in the grassy fields with dirt underneath your fingernails and grass-stained shirts. He's been coming out to the country for three summers now; apparently, his dad's idea is that he needs to focus on other things and be a normal kid. You think it means he's becoming too materialistic; your grandmother says it's because Touya has a troubled home life, never getting too many details out before your mother speaks in a strained tone to not discuss those things around you.
Your smile is soft, as is your voice when you speak mostly to yourself, “Yeah, the two of us is just fine.”
—
Traditionally, Touya always ate dinner with your family on the last day of summer. The long table would be decorated with all the harvests of the season, plus enough yeast rolls to feed the masses and milk from the best cow on the farm. His leaving for the school year always left you devastated, but these dinners filled with laughter, full bellies, and his promises to see you next summer always lightened the mood.
“My doctor says milk makes your bones stronger,” Touya declares after chugging his third glass, a milk mustache to match his fluffy white hair. You can’t help but giggle at the sight of it, telling him to wipe his face. “Hey, one day this mustache will be real!”
But that day never came. Touya left that night, and he never returned. Not the next summer, or the following, or the one after that—and eventually you grew up and stopped waiting. You never saw his white mustache or congratulated him for taking his father’s position, like he always rambled passionately about. You don't know if those things ever happened for him, but whenever he crosses your mind, you wish him well, wherever he may be.
#first post do I get a cookie?#mha#bnha#dabi x reader#touya x reader#touya todoroki#dabi#I'll get better at this :)
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
An Introduction To Wine for Dionysians

A photo from my wine class, the pink being my Chambourcin and Sangiovese rosés.
[ID: An image of two wine glasses on a stainless steel table. The first glass, closer to the observer, is bright pink. The second glass, to the right of the pink one is a salmon colour and slightly blurry.]
THIS POST IS SLIGHTLY BASIC, IN MY OPINION. It’s not exactly hard to research wine, especially now that the industry is beginning to have new winemakers such as myself. But this is my job and passion, so I thought it may be useful in the end. Especially for us Dionysians, most who never engage in the winemaking process—which is fine, but it does offer a more intimate knowledge of his realms. So as a winemaker myself, I want to share the wonders of winemaking with others. This post is meant to be a quick introduction to wine from a viticulturist and enologist.
SOME TERMINOLOGY
Entering the world of wine does require a basic understanding of some jargon. To make it easy, I have listed some common terms:
Anthocyanins — the red-purple colour compound in red grapes
Bret — short for Bretannomyces, this is an endemic yeast to Europe and often a pest in wineries. This yeast creates leather, hide, barnyard, etc., flavours and aromas in wine. This is often desirable in small amounts in certain styles, but can quickly overpower a wine.
Fault — an issue with the wine, typically in flavour, aroma, colour, or taste. Faults are subjective and sometimes may be beneficial. A key part of wine sensory analysis is tasting faults.
Macerate — a process in which colour and flavour is leached from the skins of the grape. This is most common in reds and is aided by ethanol.
Noble Rot — a form of Botrytis Cinerea that is beneficial within the wine process to make sweet wines.
Press — a winemaking device that extracts juices from grapes to make wine
Terroir — the characteristic taste and flavor imparted to a wine by the environment in which it is produced.
Vintage — the year the grapes were harvested and are typically fermented in the same year, however, this is not always the case.
ANCIENT, OLD WORLD, AND NEW WORLD
The wine world has often been divided into “old world” and “new world”, but I have personally taken a liking to the classification of some wine regions as ancient world wine regions. These regions would be Georgia, Armenia, Assyrian lands, Greece, some parts of Italy, and more. Ancient winemaking is well, winemaking in regions that have continuously made wine with the same or similar techniques over thousands of years. An ancient wine that I always recommend to Dionysians is Retsina.
Old world wine is essentially European wine. While this term has its issues, it is the one that the wine industry understands. Europe has been making wine for hundreds of years, thousands in some regions. Old world wine is known for the less fruity, more aged styles, along with producing table wine. These wines also tend to be oaked, in which the wood imparts flavours into the wine which is dependent on the type of wood used. Bret is also common in the old world, which is often a hit or miss with consumers.
New world wine is wine made in wine regions that are relatively new, associated with more scientific approaches to wine. Another way to look at it is wine regions that are or were colonies of Europe, though a few new world wine regions do not have this history. New world wine is often associated with brightness, fruity flavours, higher alcohol levels, etc.
Simply put:
Ancient — regions such as the Fertile Crescent, Palestine, Assyrian lands, Greece, parts of Italy, etc.,
Old — Europe, including wine regions more similar to the new world such as Slovakia
New — Generally colonised countries, the largest example being the United States.
TYPES OF WINE
Most people grasp the basics: white wine comes from white grapes and red wine comes from red grapes. However, of course, it gets more complicated from here. To list it simply:
White wine is wine made from white grapes that are removed from the skins.
Red wine is made from red grapes left to macerate on the skins.
Orange wine is made from white grapes left to macerate on the skins.
Rose is made from red wines removed from the skins.
Pink wines are wines made through blending white and red wine, considered of lesser craftsmanship than a rose by most winemakers
Commercial wines are typically whites, reds, and rose/pink. Orange wines are seldom found outside of Slovenia and Georgia due to tradition. Overall, the wine world considers orange wine strange, however the market has been increasing in recent years.
Wine is also a term applied to fruit wines (fruit other than grapes). Legally in most regions, wine can only be applied to fermented grapes—though of course, nobody listens to that. Essentially, I like to phrase wine as anything made from fermented fruits, roots, and tree-sugars. Cider is technically wine, but this is defined in the USA by tax brackets—below 8% ABV is a cider, over is an apple fermented product/wine.
WINE STYLES
To put it simply: there are thousands of wine styles. I cannot summarise them here, however I will try to summarise some of the common styles I know of.. ‘Old world’ and ‘new world’ are also considered broad styles.
Dessert Wines
Dessert wine as a term is dependent on location, as in the USA it is any wine over 14% ABV. In the UK, it is often classified as a sweet wine drunk before a meal. It is also usd colloquially for sweet, high-alcohol wines that are drunk with dessert. A bit of a meaningless term, but it is used regardless.
Sweet Wines
Sweet wines are wines that have residual sugar from fermentation. Most wines are finished dry, which is when the yeast consumes most to all available sugars and converts them into ethanol. This can be intentional or the result of a stuck or dead fermentation. Sweet wines are known for getting people drunk quickly and giving a particularly nasty headache.
Table Wine
Table wine is perfectly named, as these are common wines that are meant to appear at the dinner table and be paired with food. Italy is famous for creating popular table wines such as Chianti and Prosecco. The table wine market is however slowly dying. I personally liken table wines to Dionysus Hestios.
Straw wine
Straw wine is wine made from grapes that have been dried. This makes very sweet wines due to the lack of water.
Rot wines
Rot wines, also called Noble Rot wines, are a unique form of sweet wines created by noble rot. In viticulture, botrytis is a fungus that often ruins clusters by mummifying grape clusters. In the right conditions however, it instead only takes the water content in a grape berry over a series of days before perishing. Rot wines often occur near rivers, lakes, and other regions with mist and then scorching sun. This fascinating process creates natural sweet wines—many of which demand high price points, such as sauternes that are priced at over one thousand euros. Another form of rot wine I enjoy is Slovak tokaji.
In my personal practice, these wines hold a special spot due to my focus on divine rot. Dionysus wise, I think these wines possess such a unique quality of him—they are dead yet not, and Dionysus may be found in the marshes where rot blooms.
Sparkling Wine
Often known as champagne, sparkling wine is wine that when opened/poured will fizz with carbon dioxide bubbles. This is usually due to secondary fermentation, in which yeast are inoculated to ferment trace amounts of sugar to create the carbonation that appears when you open the bottle. Sparkling wine can only be labelled champagne if it is from Champagne, France. With the climate crisis however, champagne may disappear and Southern England has been contending to become the next major sparkling wine region.
There are lesser quality sparkling wines made by injecting carbonation into the metal wine vats. This is common with sparkling juices that are not fermented.
Fortified Wines
When you think of Port, that is a fortified wine. These wines are mixed in with ethanol, typically spirits, to increase the alcohol content of the wines. This makes them less likely to spoil and creates a unique flavour profile.
Some traditional fortified wines are Port, Sherry,
Cooking Wines
These are wines that are not typically used for drinking, but rather feature as a culinary ingredient. This does not mean low quality however, as some cooking wines such madeira can fetch a very high price point.
BARRELS
Barrels are enchanting. Even if I see them daily, there is a bit of romance to working with them. Wines are put in barrels for storage and for flavour. The most common wood used in wine are oaks, with French oak (Quercus robur) and American oak (Quercus alba) being the most common and stylistic. Barrels are a core aspect of traditionally ageing wine, as the barrel allows enough oxygen into the liquid to be beneficial. For those who do not know, oxygen degrades wine over time. This is why cheaper wines quickly turn bad, as they were not designed to age.
The flavour-changing profile of wood-contact on wine works through phenols and other compounds interacting with the oak, creating vanilla flavours. For other woods, a similar process occurs, such as Pine creating a pinewood taste, chestnut increasing the perception of sweetness, etc. Research is being continued on alternative woods in winemaking.
Barreling is not the only source of flavour profile in wine. Wines gain their flavour from three sources. This is simply:
Primary: flavours derived from the grape
Secondary: flavours derived from yeast. Yeast often create secondary flavour compounds, such as floral, herbal, spicy, etc notes.
Tertiary: barrel and ageing flavour.
When doing wine tastings, these are excellent factors to begin wine analysis. Deciphering these notes allows one to build a palette and understand more of the expanses of vinification.
GRAPE CULTIVARS
Grape cultivars, also called varietals, are what impart unique flavours into a wine at the primary level. Each cultivar gives its own unique flavour profile. The most commonly planted grapes are the noble varieties, which were prized by French nobility—these being grapes such as Chardonnay and Sauvignon blanc.
Grape cultivars can change their profile depending on where they are grown, called terroir. As an example, a French Cabernet Sauvignon is completely different from a Napa Valley Cabernet Sauvignon. Terroir encompasses soil, weather patterns, climate, etc. Another example is that wines made in years of heavy wildfires often taste smoky and Australian wines taste burnt due to the extreme sun exposure.
Profit and market trends have caused lesser known and cultural grapes in many places to become extinct or endangered. There are movements and efforts to preserve these cultural vines and many wine drinkers are interested in the unique experiences rare cultivars can provide.
Cultivars also often have regional and cultural significance. The Bacchus grape has been found to grow excellently in southern England, Agiorgitiko is the most common Greek red grape, Sangiovese is the grape for Tuscan Chianti, etc. In the new world, Grape cultivars often take on new significance, such as Sauvignon Blanc in New Zealand. As obscure grapevines become more popular, regional and forgotten grape varieties have been reappearing.
Hybrid vines, which are some of my favourite, are the result of viticultural science. These are vines bred to exhibit certain traits, whether as a ‘find out’ project or specially designed for certain wine regions. These are often called French-American hybrids, however hybrids are also being produced in Korea, Slovakia, and other countries. One of the most commonly planted hybrids is Chambourcin, called ‘king of the hybrid reds’, due to its striking fuschia red or barbie pink rose and desirable flavour profile. I have made a post over these hybrids before and they are readily searchable for anyone interested.
There are thousands of cultivars and new cultivars are created each year. The world of wine is ever expansive when it comes to grapevines, just as Dionysus always brings something new. There is always something new to try, or a new spin on something familiar. Yet when we crave a taste of something familiar, traditional varieties and vintages are around to return to. Wine is both new and old, alive and dead, familiar and yet ever-changing.
HOW TO BEGIN IN WINE
Beginning in wine is as simple as buying wine. Advancing understanding then comes through sensory analysis, experimentation, trying new and different wines, historical research, and much more. I doubt most people will be like myself, who decided to get an associates degree in winemaking and make it my secondary career. Honestly, it’s much more fun as a hobby than a job.
I recommend experiencing the differences between reds and whites, along with sampling table wines with and without food. Picking out grape varietals is also fun, but may be subtle. As an example, a sauvignon blanc is immediately recognisable for its bellpepper note, but I have developed the skill to taste the general region where sauvignon blanc was grown (it is my favourite white wine grape).
I have touched upon sensory analysis and terminology with it, such as palette and body, but I will reserve that for another post. Trying wine and research is the best way to begin—and there is no such thing as beginner wine in my opinion. There are wines that are harsh, different, and likely undesirable to someone who is used to sweet juice and unchallenging sweet drinks, however I believe it limits a wine explorer when you limit yourself to “beginner wines”. Finding that brings you joy matters most, whether that is a classic sweet wine or mouth-punching red. And pour some out for Dionysus, the sweet lord of the eternal winepress.
view this post on wordpress
References
Bird, D. (2011). Understanding Wine Technology, 3rd Edition: The Science of Wine Explained. Board and Bench Publishing.
Puckette, M., & Hammack, J. (2018). Wine Folly: Magnum Edition: The Master Guide. Penguin UK.
Wilson, J. (2019). Godforsaken grapes: A slightly tipsy journey through the world of strange, obscure, and ... underappreciated wine. HARRY N ABRAMS.
Wine microbiology. (2007). In Springer eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-33349-6
#vīnum#dragonis.txt#witchcraft#paganism#hellenic polytheism#witchblr#dionysus deity#pagan#dionysus worship#hellenic polytheist#helpol#hellenic paganism
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
Worldbuilding Food: More than meets the eye
So, you want to world build food but maybe you don't know where to start, have hit a roadblock, or are just looking for some interesting places to addon to. I've got your back.
Vegetables, Fruits, Grain, Nuts, & Fungi

One of the first things I think of when it comes to food is fruits and vegetables, and the line between them is surprisingly small.
Like tomatoes are vegetables? Pumpkins are fruits but other gourds are not? When does a herb become a vegetable? Although important to classify, don't let it be your main focus.
Start with
How the produce grows
What it looks like throughout different stages of its life
What parts are edible
How most people consume the produce
How the product is harvested
Is it seasonal
What about the produce that makes its growable environment habitable
How it spreads/reproduces
There's many different unique ways fruits and vegetables grow in just our real world, but that doesn't mean you can stop there.
Cranberries grow on vines that actually float on the surface of soggy ground and water in wetlands. Cashews actually grow on the bottom of cashew apple, which is it's own edible product. There's lots of different ways plants can grow, and what they even need to do so.
Some produce even have their own defense mechanisms (which often which becomes a form of flavor to us). Don't think these defense mechanisms stop at protection from predators. Strawberries are an aggressive plant, fighting, killing, and taking over any nearby plant neighbors. Some plants have thistles and thorns, and others are the hard shell or peel we end up effortlessly cutting through.
Try to think of some environmental things in the world your working with that the produce would have adapted to.
I think my favor example of this IRL is sunflowers. They change directions to face the sun, and when they can't find the sun they face each other. Eventually their seeds weigh them down, and which they'll always face east.
Don't forget fungi is edible too, and has it's very own unique properties.
(Don't forget yeast -> bread, you can make up whatever food you want)
Meats & Agricultural Animals
I myself am not a meat-eater, but I understand the importance of animal products to a society. If you world doesn't have it, don't fret. This sector won't just be about meat products, but it will contain a lot of it.
Food and what animals are considered for consumption changes from culture to culture. The same can be said for treatment leading up to their role in society as the food on people's plates. Often times a culture cannot imagining eating an animal they see as part of the family, such as dogs or cats IRL, but other times it's seen part of a religious practice such as cows.
There's a lot of cultural stuff that goes into our agricultural animals, both for work, dairy, textiles, and food.
Here's some ideas to start with
What parts of them are edible and used for food
Do they produce any dairy or egg products
How old do they have to be before becoming a produce animal
Are the animals used for other resources too i.e. bones, fur, skins, skulls, blood, etc.
How much food does one animal make
Typically how are they are killed, if they are
What conditions are these animals kept in and are they viewed humane
What environments allow these animals to thrive alongside the people of your world
What does the animal eat
Now... Let's into some culture and religion
Religion and culture has a major impact on what we eat. Take for instance Kosher, Halal, and more. Historical shortages in food even to this day affect what foods we eat. Culture also affects our tastes. The corn line of the United States is drowning in corn, and yet corn is seen as a sweet treat over seas in many nations.
Harvesting

How the harvesting goes changes a lot about a society, big and small. Think about how terrible a year would go in medieval times if harvest came up incredibly poor, or how wealthy our modern day world would look to those people due to mass production.
Here's some things to think about
What time of year are the biggest and most important harvest(s)
How common are agricultural workers
What would the average person see if they watched people work
What technology/tools are used
What happens if the harvest goes wrong
Do farmers/harvesters get special rights for their role in society
In older societies harvesting and how that went completely shaped how the next year would look. In some cultures the harvesters have been revered, while in other if crossed to far would be expected to tear the country to pieces. Think about the role harvesting plays in your society. What would happen if they striked? Or if a disaster swept the land?
The environment itself will change a lot about what harvesting look likes. Why does this environment work? What are the environmental risk to both the crop and workers?
Are we farming in the water, in the middle of the arctic, underground, high up in the trees?
Exotic Food & Immigration

While establish what the everyday food in the area is, don't forget to pay mine to the opposites. Immigration and trade play a major role in what foods end up on our plate. As cultures combine and mingle so do their food.
Take one look at the United States, infamous for it's large potions, fatty foods, and immigrant culture cuisine. A lot of foods in the United States are the results of cultures meeting to improve and add onto one another's foods, that includes American styles of pizza, tacos, and more.
Even major cities around the world have styles of foods unique to them.
Let's think
What locally seen foods count as exotic
What foods are nearly impossible to get
Is there access to foreign brands/produce
How expensive is most exotic foods
What styles of cooking are being brought in by foreigners
How do people get exotic foods
What foods would the locals not be able to eat due to not being used to it
Try to think about what makes this food exotic in the local area. Maybe it cannot grow in the local environment. Maybe the quality of the food is simply better overseas. Maybe the animal or plant is far too aggressively invasive for locals.
Trade & Transport

Food is both a very important export and import, especially in time of devastation.
Don't forget about exports too, what is your society giving out to the world, and getting back. Not all trade has to be capital based. Perhaps your world simply trades on good or service for another.
Here's some things to think about
What's being exported and imported
Are whole animals imported/exported
How is the trade being done i.e. trains, boats, aircraft, teleportation, etc.
Are there any obstacles to trade
What places are all involved in trading
How is the trade brought to where it needs to be inland
In what ways do these trades improve the lives of locals
Transportation is also super important to where food ends up, and more so in what volumes. How do people get all these produce or animals relocated? What kinds of storage are we seeing to keep things fresh (if health standards are even up to code in your worldbuilding)?
What poses a threat to things in storage? i.e. mold, foxes, animal thieves, disease, etc.
Restrictions

With supply and demand, comes outages, taxes, and restrictions. Unfortunately not everything in the food world goes right. There's natural disasters to come and destroy crops, hostile settlements to block trade, and especially that person who is really bad at cooking but they love doing it so you don't have the heart to say no....
Anyway let's talk restrictions and where they can come from
Wartime
Wartime can cause a lot of original farmers and workers to become soldiers. It also can lead to the large scale destruction of precious farm land, crops, animals, and overall places to cook.
Laws
Perhaps there's a particularly poisonous food, and way too many suspiciously poisoned people. That's when law comes in. There's many reasons for food and drink to become outlawed. Religious reasons, danger, regulations, inebriation, etc.
Siege/Embargo/Thievery
Knock knock! It's the United States here to embargo your random country. Outside factions can always become an obstacle, leading to loss of traveling cargo or straight up missing farmers too. Nothing comes in, and sometimes nothing comes out.
Endangered
Perhaps a common plant or favored animal is running low on populous. Now locals are more so focused on reanimating a dwindling population, more so on eating it.
Sickness
Whether it be hoards of invasive bugs, prion disease caused by cannibalistic animal feed, or sudden inexplicable field of dead corn sickness happens. Maybe something has swept over the land, and no one ever bothered to try to plant said crop again.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters can not only cause the elimination of entire villages, but accidentally bring in lots of invasive creatures too. Catfish is off the menu for as long as carp is intown.
Straight Up Difficulty
Sometimes a fruit appears once a year, or a tasty creature is a dangerous one to take on in order to eat. It can be difficult getting the right ingredient sometimes. Other times it's new to the market. So much can happen when food is involved.
Preparation & Flavor

Finally all the food in the world is available, but what are we going to do with it.
Make it even better!
I personally find preparation to be the best part of worldbuilding. Now I get to imagine my fictional little people stewing their pots, and kindling their fires. Reflect off of real world recipes, and maybe even write down exact fantasy recipes of your own.
Don't forget about herbs and spices (I see you British people).
You have five basic taste receptors in your mouth: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and savory. They make great descriptors and fun places to explore when looking into what your foods taste like. Smell can play an important role too.
Does it smell awful and taste great, smell sweet and taste bitter, perhaps it doesn't have anything at all going on.
Happy worldbuilding!

#food#world building#worldbuilding#worldbuilding food#writing#writing food#world builder#writing tips and tricks#fantasy writing#fantasy worldbuilding#long post
71 notes
·
View notes
Note
Robutt vampires, you say
Other than the sexy bloodsucker Prowl thing, the first thing that comes to mind for me is the worldbuilding lore from Vampire Hunter D, where the Nobles reared humans like cattle for sustenance. Aaaaaand my brain just made it weird again.
Imagine a bloodsucker senator breeding slavebots as bloodbanks, but he goes an extra mile. Before he culls them, he ferments them first. Inject yeast and bacteria into their lines and seal off every vent to create and anaerobic environment. Storing them in little casks until the bots' lines rupture from the gas bloat. He claims that the flavour of the harvested energon is unrivalled, but who knows. Not even Sentinel Prime himself has tasted it. Maybe he's full of shit and is just killing bots in such a manner for absolutely fucking nothing. Maybe it does actually work.
Senator Shockwave would set out to prove this in his own ways, I bet. With a still living Orion Pax. Big bots like him have plenty of space inside, he won't face much of a risk from gas buildup implosion. So imagine IDW1 OP having to run around Iacon with the heat of fermenting energon in his tanks and lines, building up into a nigh unbearable boil inside him, hoping that Shockwave wouldn't be waiting too long to drink from him this time lest he burns up from within. I bet it makes him extra horny too, so Shockwave would spend most of their feeding sessions perched on his fat spike. As a little apology for the discomfort, see?
(I… wrote this before the Prowl one actually)-🔌
oooh that’s interesting, vampires keeping humans as cattle is always so bonkers, and we’re all into farms in here. just look at my blog. bots fermenting the energon inside of unsuspecting victims so they can have their fill is hooot. Especially when Shockwave is so nice about it, grinding onto Orion’s spike to keep him still and pleasured as he sips from his lines,,...
Optimus misses that. It’s his greatest shame.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
thinking about @plant-taxonomy-showdown's angiosperm cake poll and im contemplating how possible it is to bake a cake using ~~only~~ ingredients obtained from monocots (OR eudicots, but i've got that one figured out i think). i'm currently stumped by how you get air into that sucker without chemical leavening agents (aquafaba comes from eudicots so that's out).
so the solution would be like
bake something that's supposed to be dense, like ginger cake or banana bread. but the thought of making any of these without cinnamon is making me sad
stretch the definition of cake. maybe a pie is possible…?
reaaaaaaaaaaally stretch the definition of monocot-derived ingredient. like. what if i make ginger beer and use its CO2. that definitely can work (i've used cola as a leavening agent before). but then i'm relying on epidermally associated yeasts to make me the CO2, that feels like cheating.
but in theory, someone could run into a maize field at dusk, tie plastic bags around some (thousands) of plants, harvest the air before dawn, extract the CO2, pressurize it enough to blast it into water and then give me that carbonated water to use. does that count. plants make CO2 in the Kreb’s cycle so does it matter that the ginger beer's CO2 comes from a yeast digesting the ginger's glucose and not from the ginger burning its glucose how do you (imaginary arbiter of monocot cake law) know a yeast did it and not me breaking into a field at night with 10000 plastic bags i'm getting off track now.
#I don’t do a lot of vegan baking so i was sure eudicots would be so much harder given the whole ‘no flour (and no vanilla)’ thing#because monocots have cereals bananas and coconuts and other palms#but even banana bread recipes require baking powder :/#monocot cake#monocot and dicot cake#mmnmmq.txt
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
this is a stupid pet peeve but idk. 'Cooking is an art baking is a science ' is bullshit. you can follow a baking recipe step by step mirroring the original cook Exactly and still get a crap end result.
this is because your kitchen is not their kitchen. unless you live very close to them, their ingredients might be Radically different from yours even if they're technically the same thing. and worse of all. even if you're roommates. if they made their thing first the conditions will be different when you make yours.
like. baking is just ratios. ratio of starch to water to binder to leavener to etc etc.
But you have to include things like. ambient humidity and temperature and where the crop your flour is from was grown and what strain of yeast your using and when your starch was harvested and what the cows and chickens who provided the eggs and dairy were fed and what microbes exist in your environment and how thety hurt or aid flavor and rise time. like. You have to know how to account for the messy nature of reality and there is no formula for that. just repetition until you figure out the flow.
#like. idk man#i need recipes to be geo tagged because like.#here in the states our wheat has to be extremely cold hardy right? way more so than europes#it also needs to be able to handle like. tornadoes and other extreme weather you get that far inland on a flat plane#which means that compared to European flour ours has an insanely high glutin content bc glutin is how the plant strengthens itself#You need to account for that when cooking#more leavener more water less binder gentler kneading and longer rise time#so like. im brain dead exhausted but Yeah. baking very much isnt a science and your great grandma did just fine without a hyper accurate#gram scale being shilled by YouTubers.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
capturing the airborne poop particles in my bathroom like a homebrewer harvesting wild yeast
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
kis isn't paying attention, time to grab kyle's pussy to harvest the yeast it has so i can mix it into hal's titty milk gelatto
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Harvest Yeast Bread
62 notes
·
View notes
Note
i just watched a video of someone admitting to using the yeast harvested from their vagina grown via yeast infection to bake cookies and then giving themselves + their partner an oral infection. anyway. kyle would
Kyle's pussy yeast is too strong for the weak human throat microflora. Kyle's pussy yeast defeats every bacteria in your body. Kyle's pussy yeast will not give you an infection. Kyle's pussy yeast will CONQUER. Kyle's pussy yeast IS your digestive microflora now. And also you. Perhaps we are all just Kyle's pussy yeast, in the end
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
I saw your tags on the mycology tumblr post - I challenge you to scare me with a mushroom fact. I’ve harvested and eaten wild mushrooms a few times, I’ve got my share of guidebooks and worked on research my university did on suede boletes. I’m no spring chicken of the woods but i’m also far from an expert. Scare me with the Deep Mushroom Lore
Woaaaah this got a bit lost and im a bit late, yikes! Anyway it looks like you were focusing on the Basidiomycota phylum which is where a lot of the frontliners and popular ones are. But let's look at the Ascomycota, lots of scary stuff there, lord there's so much but baseline ig is cordyceps which everyone knows about now. They can alter and control insects, a big example is bullet ant behavior to makes them climb as high as they can and bite onto the grass or whatnot to secure themselves until the host dies. They go as high as possible so when the cordycep actually grows the fruitbody the spores can spread as far as possible. Luckily for us human nervous systems are way too complex for the cordyceps....for now.
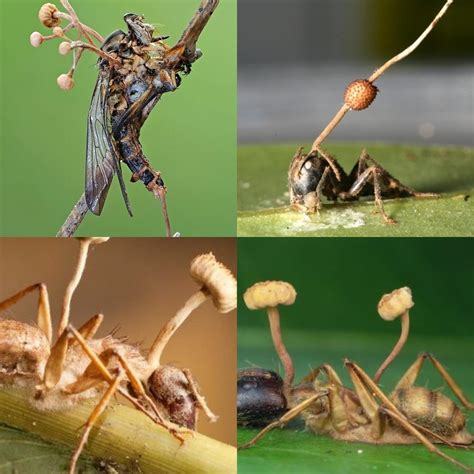

I mean any parasite that controls it's host is crazy and I 10000% recommend looking into it.
There's another fungus Laboulbeniomycetes that grows exclusively on arthropod exoskeleton.

A lot of fungal diseases make me shudder, there are probably fungal spores in your lungs right now! Pneumocystis is the genus of a yeast that loves your lungs and you guessed it, causes a strain of pneumonia that's very hard to diagnose! Yippee! Mostly because it is very hard to culture.
Let's look at everyone's favorite yeast Conidida. This guy is DIMORPHIC so it can be a yeast or invasive hyphae depending on environmental triggers/conditions, and wouldn't you know it, lives at human body temp. This guy causes yeast infections and the like.
Aspergillus is one that ferments soy products BUT can also cause Apergillosis which can cause an allergic reaction and eventually a fungal ball growth in your lungs, aak!
In a different phylum, Mucoromycota, Mucormycosis is probably my least favorite as the group USUALLY targets your fruits and is that pesky mold. Well another version of it will target the sinuses of immunocompromized diabetics. These are sugar loving molds so uhhhhh, no bueno. I recommend looking at pictures with CAUTION it is gross. The eyes can get really messed up, black lesions can show up on your face really really nasty stuff.
Anyway, Ascomycota cool group, lots of human diseases (many of which are hard to cure because of how close fungi are to animals so we target very specific things in their cells but OOPS resistance is on the rise), have fun with this info ::)
#mycology#ascomycota really popped off on the diseases#ollie rambles#<<<yea no i RAMBLED#but yea apologies for how late this is been reaaaally busy#long post#call me patient zero the way fungi have consumed my mind
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Modern Harvested Look Into Dionysos Nykletios

[ID: A mostly green image with a large, vibrant grape left to the left and blurry brown grape trunk in the background to the off-centre. Next to it is a large, close up image of an unripened verdant grape cluster.]
LITTLE DO MOST PEOPLE KNOW THAT MUCH OF THE MODERN GRAPE HARVEST HAPPENS AT NIGHT, as dedicated winemakers wish to ensure the consistency of their crop—lord Helios’ rays are what ripen the fruit, at the mercy of Dionysus’ influence. Other times harvest does during cool days, but the harvesters are still pressed to ensure the safety of the harvest—hot fruit spells problems for the winemakers, and winemakers are what buy the crop to ferment. And when I was there on the cool afternoon, Helio’s light fading from the horizon, I felt Dionysos there with the whisper of Nyktelios.
THE HISTORICAL CONTEXT
Nykletios (Νυκτελιος “of the night”) is an epithet only directly mentioned perhaps once, kin to Hestios; as such it may be hard to get a direct usage on the meaning of this epithet. Pausanias states:
Pausanias, Description of Greece 1. 40. 6 (trans. Jones) (Greek travelogue C2nd A.D.) :
"After the precinct of Zeus [in Megara] . . . you see a temple of Dionysus Nyktelios (Nocturnal), a sanctuary built to Aphrodite Epistrophia (She who turns men to love), an oracle called that of Nyx (Night)."
Riding the Phallus for Dionysus suggests that this epithet may be connected to a larger mystery cult, that of a veiled Dionysus, with rites perhaps similar to the one Plutarch mentioned. Several of Dionysos’ rites occur within darkness—within Agros, his rites were nocturnal, invoking the terror and awe of Nyx’s darkness. His other mysteries likely involved the night as well.
Night is also invoked several times with Dionysos, such as in the Bacchae. One example I associate with Nykletios are these lines from Dionysos and Pentheus:
ΠΕΝΘΕΥΣ
τὰ δ ̓ ἱερὰ νύκτωρ ἢ μεθ ̓ ἡμέραν τελεῖς;
ΔΙΟΝΥΣΟΣ
νύκτωρ τὰ πολλά· σεμνότητ ̓ ἔχει σκότος.
Pentheus
When you dance these rites,
is it at night or during daylight?
Dionysus
Mainly at night. Shadows confer solemnity.
Even as these rites are no longer practiced, it is almost fitting that modern harvests mostly occur at night—and winemaking during harvest season can easily draw into the dark nights as well, as we work on the grape and yeast’s schedules, not our own.
A MODERN TAKE ON DIONYSUS NYKLETIOS
As epithets can have multiple functions, I place Dionysos Nykletios in both the night harvests of vines, comforting frozen hands as we harvest fruit for the best vintage, along with his endemic nocturnal rites. The modern wine world is both alike and like the ancient one—the wine season is still within winter, with the worst moments for a winemaker being the time before Christmas until next March when the wines are finishing.
If there was a day a hellenic pagan vineyard would exist, I would imagine that a procession would be in store for a religious harvest—though, there would not be any free juices allowed to paint the skin red. When you harvest grapes for wine, you do not want to burst the berries, and I could imagine Dionysos’ laugh when it eventually occurs.
Dionysus Nykletios,
May your hands warm us
Under eternally Dark Nyx
As the vintage is pressed
And made into your
Fine wine.
References
Csapo, É. (1997). Riding the Phallus for Dionysus: Iconology, Ritual, and Gender-Role De/Construction. Phoenix (Toronto), 51(3/4), 253. https://doi.org/10.2307/1192539
Gilbert Murray, & Ian Johnston. (2015). Euripides Bacchae: A Dual Language Edition. Faenum Publishing Oxford, Ohio.
#dragonis.txt#paganism#witchcraft#pagan#hellenic polytheism#helpol#witchblr#dionysus devotee#dionysos deity#dionysus deity#dionysus worship#hellenic polytheist#hellenic pagan#paganblr#pagans of tumblr#deity worship#vīnum
28 notes
·
View notes