#One of the most common native birds
Text
I think more people (me) should stop using Ravens and other corvids to act as omen's of death when doing a symbolism and start using Pīwakawaka as omens of the death instead.

You may not like it, but this is what peak death omen looks like.
#I love these little guys!#One of the most common native birds#and he's just a little guy! Surely he won't come into your whāre and signal the death of a loved one!#You'd think of the many native birds here the Morpork would be the death omen being an nocturnal owl that SAYS ITS NAME AS ITS CRY!#If Aotearoa ever gets a pokémon region based on it there are going to be so many new bird 'mons#ghost flying type fantail pokemon#dark type bird chick pokémon that splits into a kakapo or a Kia#Writing#Native birds#Pīwakawaka#fantail
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Anyway while we're on the subject of public misconception towards living things (which is completely understandable because have you SEEN living things? There's like dozens of them!) here's a fresh rundown of some common mistakes about bugs!
Arachnids aren't just spiders! They're also scorpions, mites, ticks and some real weirdos out there
Insects with wings are always finished growing! Wings are the last new thing they ever develop! There can never be a "baby bee" that's just a smaller bee flying around.
That said, not all insects have larvae! Many older insect groups do look like little versions of adults....but the wings rule still applies.
Insects do have brains! Lobes and everything!
Only the Hymenoptera (bees, ants and wasps) have stingers like that.
Not all bees and wasps live in colonies with queens
The only non-hymenoptera with queens are termites, which is convergent evolution, because termites are a type of cockroach!
There are still other insects with colonial lifestyles to various degrees which can include special reproductive castes, just not the whole "queen" setup.
Even ants still deviate from that; there are multi-queen ant species, some species where the whole colony is just females who clone themselves and other outliers
There is no "hive mind;" social insects coordinate no differently from schools of fish, flocks of birds, or for that matter crowds of humans! They're just following the same signals together and communicating to each other!
Not all mosquito species carry disease, and not all of them bite people
Mosquitoes ARE ecologically very important and nobody in science ever actually said otherwise
The bite of a black widow is so rarely deadly that the United States doesn't bother stocking antivenin despite hundreds of reported bites per year. It just feels really really bad and they give you painkillers.
Recluse venom does damage skin, but only in the tiny area surrounding the bite. More serious cases are due to this dead skin inviting bacterial infection, and in fact our hospitals don't carry recluse antivenin either; they just prescribe powerful antibiotics, which has been fully effective at treating confirmed bites.
Bed bugs are real actual specific insects
"Cooties" basically are, too; it's old slang for lice
Crane flies aren't "mosquito hawks;" they actually don't eat at all!
Hobo spiders aren't really found to have a dangerous bite, leaving only widows and recluses as North America's "medically significant" spiders
Domestic honeybees actually kill far more people than hornets, including everywhere the giant "murder" hornet naturally occurs.
Wasps are only "less efficient" pollinators in that less pollen sticks to them per wasp. They are still absolutely critical pollinators and many flowers are pollinated by wasps exclusively.
Flies are also as important or more important to pollination than bees.
For "per insect" pollination efficiency it's now believed that moths also beat bees
Honeybees are non-native to most of the world and not great for the local ecosystem, they're just essential to us and our food industry
Getting a botfly is unpleasant and can become painful, but they aren't actually dangerous and they don't eat your flesh; they essentially push the flesh out of the way to create a chamber and they feed on fluids your immune system keeps making in response to the intrusion. They also keep this chamber free of bacterial infection because that would harm them too!
Botflies also exist in most parts of the world, but only one species specializes partially in humans (and primates in general, but can make do with a few other hosts)
"Kissing bugs" are a group of a couple unusual species of assassin bug. Only the kissing bugs evolved to feed on blood; other assassin bugs just eat other insects.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
I agree with the idea that a lot of humans nowadays have a severe lack of curiosity about the world, but I think there has to be a solution other than shame.
I think about this every day because the fate of our world hangs on curiosity: either we will rediscover the importance and wonders of the soil and bugs and flowers and water and finally with the whole natural world, or this way will be forgotten.
People raised in the great wasteland of the suburbs and roads and buildings have never seen most of the plants and creatures that are supposed to fill every field and meadow. So many humans have never seen with their own eyes more than a scant few of the most common of hundreds of wildflowers that are supposed to surround them. Some live in biomes designated forest and have never witnessed truly mature trees. They do not know what the birds sound like. When they see an ordinary deer, they are awed and amazed by it or even afraid of it. They have never eaten any of the delicious wild fruits that grow in their homeland; all birds except starlings and robins and sparrows are so strange and beautiful that they stare in wonder. They confront insects like people on an alien planet encountering an unknown life form: What is this? Will it hurt me?
I cannot even describe the grief I feel on behalf of humans that grow up and live in the wasteland of pavement and lawn. That we are expected to live in these brutal environments, that we are expected to be content without the right or ability to live alongside living creatures, to walk among wildflowers, to hear birdsong, to feel the plush softness of moss, to see even common bees and butterflies—the fact that we live, work, and raise our children in poisonous wastes where nearly everything has been wiped out, and the simplest and most abundant of natural pleasures are rare privileges—it's cruel. It's a crime against the human spirit. It makes me so angry and sad.
When I started researching plants, I had no idea that I would end up expanding my mind so much that I would be virtually a different person within the year. Before I learned, I could not have imagined the diversity and beauty that exists in the world. My mind did not have the tools to come up with it.
I lived for over twenty years believing that there was only one species of firefly. I lived for over twenty years not knowing that the Southeastern US has native bamboo. I had never tasted the indescribable flavor of a pawpaw or seen the iridescent vibrance of a red-spotted purple butterfly. I had only seen a Pileated Woodpecker out the window of a car. I had never touched true topsoil, the soft, living blanket of rich, sweet-smelling earth full of mycelium, as springy and plush as a mattress. Just one year ago, I knew nothing!
Humans, as creatures, are insatiably curious and hunger for beauty. It is so cruel to deprive a human of relationship with their natural environment.
It is no wonder that we are all addicted to the internet—we have a crucial need that is unfulfilled. Compared with a forest, the world of lawns and buildings is so ridiculously flat and unstimulating. You would expect humans in such a place to feel constantly bored, restless, frustrated, and incurably sad.
I feel that lack of curiosity can be a chosen thing, but it is also a defense mechanism against a world that will feel like sandpaper on the senses of the curious.
But we need curiosity to fix this—we need the ability to notice the living things that have crept in at the edges of the wasteland and be infected and tormented by their beauty. We need to recognize the forest reaching into our cage in the form of tiny saplings. We need to discard the word "weed," not because it is derogatory because it is fundamentally incurious—it designates a plant as needing no identity outside of its unwantedness. We must learn their names. We must wonder what their names are.
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
most writing advice is good as long as you know why it is good, at which point it is also bad. the hardest thing (and most precious thing) about being an artist is that you gotta learn how to take critique. i don't mean "just shut up and accept that people hate your work," i mean you need to learn what the critique is saying and then figure out if it actually helps.
i usually tell people reading my work: "i'm collecting data, so everything is useful." i ask them where they put the book down, even though it's too long for most people to read in 1 sitting. i ask them what they thought of certain characters. i let them tell me it was really good but i like it more when they look a little stunned and say i forgot i was reading your book, which means they forgot i exist, which is very good news.
sometimes people i didn't ask will read my work and tell me i don't like it. and that is okay, you don't have to like it. but i look at the thing that they don't like and try to figure out if i care. i don't like that you don't capitalize. this one is common, and i have already thought about it. i do not care, it's because of chronic pain and frankly i like the little shape of small letters. you use teeth and ribs in all your work. actually that is very true. i don't know what's up with that. next time i will work to figure out a different word, thank you. you're whiny, go outside. someone said that to me recently and it made me laugh. i am on the whine-about-it website as an internet poet. you are in my native habitat, watching me perform a natural enrichment behavior. but i like the dip of whiny, how the word itself does "whine" (up/down, the sound out your nose on the y), but i don't know if i want to feel whiny. maybe next time i will work on it being melancholy, like what you would call a male writer's poetry.
repeated "good" advice clangs in a bell and doesn't hold a real shape, dilutes in the water. like sometimes you will hear "don't use said." you turn that around in your head and it bounces off the edges of your brain like it is a dvd screensaver. it isn't bad advice, but it feels wrong somehow, like saying easy choices are illegal! sometimes i will only use "said." sometimes i will just kick dialogue tags out to the trash. sometimes i make little love poems where the fact that i do not say "said" is very bad, and makes you feel bad in your body, because someone didn't say something. i am a contrary little shitbird, i guess.
but it is also good advice, actually. it is trying to say that "said" sometimes is clutter. it makes new writers think about the very-small words and very-small choices, because actually your work matters and wordchoice matters. "i know," you said. "i know," you sighed. "i know." we both know but neither of us use a dialogue tag, because we are in a contemporary lit piece.
it is too-small to say don't use said. but it is a big command, so it gets your attention. what are you relying on? what easy choices do you make? when you edit, do you choose the same thing? can you make a different choice? sometimes we need the blankness of said, how it slides into the background. sometimes we don't.
i usually say best advice is to read, but i also mean read books you don't like, because that will make you angry enough to write your own book. i also mean read good books, which will break your heart and remind you that you are a very small person and your voice is a seashell. i also mean you need to eat books because reading a book is a writer's version of studying.
my creative writing teacher in the 7th grade had a big red list of no! words and on it was SUNSET. RAZORS. LOVE. GALAXY. DEATH. BLOOD. PAIN. I liked that razor and love were tucked next to each other like birds, and found it funny that he believed we were too young to know the weight of razor in the context of pain. i hated him and his Grateful Dead belt, where the colored teddy bears held up his appraisal of us. i hated his no list. it is very good/bad advice. i wasn't old enough yet to know that when you are writing about death you are also writing about sunsets and when you write about love you are tucking yourself into a napkin that never stops folding.
back then my poetry was all bloody, dripped with agony when you picked it up. i didn't know there is nothing beautiful about a razor, nothing exciting about pain. i just understood sharpness, which he took to mean i understood nothing. i wrote the razor down and it wasn't easy, but it was necessary. that's what i'm saying - sometimes it's good advice, because it's not always necessary. and sometimes it is very bad advice, because writing about it is lifesaving.
hang on my dog was just having a nightmare. i heard that it is a rule not to write about dogs - in my creative writing mfa, my teacher rolled her eyes and said everyone writes a dead dog. the literature streets are littered in canine bodies. i watched the rise and fall of his ribs (there is that word again) and had to reach out and stop the bad dream. when he woke up he didn't recognize me, and he was afraid.
it is good/bad advice to say that poems and writing have to mean something. it is bad/good advice to say they're big feelings in small packages. it is better advice to say that when my dog saw where he was, he relaxed immediately, rubbed his face against me. someone on instagram would make fun of that moment by writing their "internet poetry" as a sentence that tumbles across a white page:
outside it is sunset and
my dog is still in a gutter, bleeding a galaxy
out of his left paw.
or maybe it would be: i woke the dog up/the dog forgot i loved him/and i saw the shape of a senseless/and impossible pain.
the dog is alive in this one, and he is happy. when i tell you i love you, i know what i said. write what you need to write, be gentle to yourself about it. the advice is only as good as far as it helps. the rest is just fencing. take stock of the boundaries, and then break them. there's always somewhere else you could be growing.
i love you, keep going.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
most of us have heard of the red car game. you’re on a road trip, you’re bored, you start looking for red cars to do something.
and then they’re everywhere. you notice them nearly every few minutes.
there aren’t suddenly more red cars now, of course. you were seeing them already, but you weren’t noticing. you weren’t looking.
I am noticing things.
there is a plant I notice everywhere now, a small bushy plant in suburbs, along streets, by shops on the highways. dwarf umbrella bush is what the internet tells me when I look for it’s name. I did this because I wanted to know why,
every time I ever saw it, every place,
it was always dying.
always the leaves turning yellow, the branches small and scraggly. inside out - nitrogen deficiency. their soil drained.
I am noticing how many of these landscaping plants are yellowing, how small and sickly they look in just a few years. I am noticing how often the grass outside the house is replaced when it once again turns brown and dry, how the type never changes and the cycle starts again. I am noticing how the unmowed, unkempt spaces on lakesides and roadsides look more alive than this. how the preserve I grew up next to was miles of “messy” unmanicured nature and the ground was covered in leaves instead of grass and there was life.
I am noticing the birds that come by the lake. there was a flash of blue wings and red chest - eastern bluebird, male, relatively common. I had never seen one before. there is a family of ducks that appear every spring; i cannot say if it’s successive generations or different ducks, but I can always look forward to ducklings. there are little brown birds with white heads whose names I do not know - are they some kind of piper? why don’t I already know?
why is it so hard to learn about my native plants (accurately, that is)? why are so many gardening sites littered with people who think a plants value is based on how pretty or useful it is to them, who think a tree shedding leaves is “messy”?
why is knowing about the world we live in so… odd? why is it a hobby and not vital knowledge? I learned about polar equations. I taught myself about mycorrhizal networks and species of insects.
(did you know there are shiny green bees? a special species of wasp pollinating figs? that white flowers bloom at night for moths? do you know? have you looked?)
I cannot look at a lawn and see life anymore. it is a wasteland, devoid of life, dying slowly itself. everywhere is grass, grass, doused in water that runs over into storm drains, soaked in fertilizer and pesticides and a hundred other poisons and sending one clear message:
this is a place of death. life is not welcome here.
I do not think I could live in a city. too loud, yes, too busy, yes, too many people, yes, but the plants would bother me. a tree allotted only a convenient square, surrounded by dead stone and metal.
a forest cleared for this, for burning asphalt streets and racing cars and shops whose bathrooms are “for paying customers only”.
this is a place of death. life is not welcome here.
and now I am noticing.
#it speaks#idk man this is stream of consciousness and it’s midnight lol#I’m having thoughts about plants and people and how much I hate lawns#anti lawn#firmly believe that nature knowledge should be taught in school#yeah there’s biology but biology won’t teach you what plants are edible or deadly#or what birds live/migrate in your area and what they depend on#they teach civics bc even if you’re not politically active you should know how the government works#if you live in a world you should know how it works#bc even if it feels like it doesn’t matter. it does. it will. and if you notice it now you can do something about it
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Random worldbuilding:
You're walking through an otherwise completely ordinary modern city, but there are countless varying flags hung on the walls of the buildings - on peoples' balconies, windows, rows of little tilted flagpoles on the walls of apartment buildings, one per apartment apparently - each one having a flag. No two flags appear to be the same. You hear yelling from the window of one apartment somewhere above, and turn around just in time to see a couple unfurl yet another flag, hanging it from their own respective pole.
Your local guide remarks that they must have just moved in. Most people lay claim to the apartment as soon as they get the keys and the contract has been signed, and only throw a housewarming party and celebrate moving in a month later, once the apartment has been successfully "claimed". By the look on your face, your host concludes that you have no idea what they're talking about, or what it has to do with the flags.
Your host begins explaining: several centuries ago the land was devastated by a deadly plague - many houses, homesteads, even whole villages were wiped out, the buildings left standing empty. And survivors with nothing to stay for in the places where they were born were roaming about, trying to find a new place to live. To solve both problems, a decree was made: If a wandering party finds an abandoned homestead and raises their own flag on top of the building and manages to stay there for a whole month without the house's original owner showing up to protest, the one who hoisted the flag is now the lawful resident.
So historically this decree made countless of people who were formerly serfs into not only free citizens but landowners with family names and their own flags. Many had a wry sense of humour about theirs, and some of the now oldest and proudest family flags depict things like a broken plough or a pig in a crown - one of them is abstract and seemingly modern, famously born as the ancestors of that particular family had nothing else to use for a flag than one foremother's patterned scarf.
And while these days there's far more laws and regulations on the old traditions of claiming a house, the tradition of flag-raising and keeping an official housewarming party only a month after the move have remained. Many young couples moving in together don't just choose which one's family flag to use, but getting your own, unique mutual flag commissioned for you is a fairly common wedding gift. Immigrants coming from somewhere else who have adopted the house flag traditions have made their own designs, using elements of their own old homeland like historical symbols, colours, and birds that are not native here.
You pass by a flag with a figure that looks conspicuously like Garfield, and your host confirms that yeah, while there is a registry of flags and you can't make a flag that's exactly the same as that of someone else, the flags are explicitly excempt of regular copyright law. This decree was set after someone jokingly included a Mickey on theirs, the government sided with them, and Disney came to the conclusion that going into actual, literal war with a small nation with a trained army would be bad for PR.
652 notes
·
View notes
Note
Uh, I saw your post and you mentioned that you teach the kids... how do I put it... that are given to you at social functions due your park ranger aura for safekeeping how to tell the difference between predatory lightning bugs and normal lightning bugs.
And then you didn't tell us that secret! May I ask you to share the difference between predatory lightning bugs and normal ones?
Thank you very much :)
By popular demand and because this was the most polite ask: how to tell the predatory lightning bugs from the non-predatory lightning bugs.
First, there are over 2000 species in Lampyridea. I am not qualified to distinguish between all that. I grew up in Northern Ohio (71 species) and every year summer wasn’t official until the lightning bugs came out in the evenings (usually the first or second week of June).
This is our first clue. The first lightning bugs out each evening are a species of non-predatory chaps. Their glow goes in a special pattern. Flash, pause, “J” shaped flight about 2 -3’ off the ground. Repeat. Their glow is more yellow and lingers. These are the males of Photinus pyralis or the common eastern firefly. They look like this:

(Photo from iNaturalist: a lightning bug beetle, mostly black with gold lines around the wing casing. Head shield is yellow with a red “eye” with black iris in the center. Rounded front and back, long down the center.)
Their females hide in tall grasses waiting for the right suitor. If you’re lucky and clever you can see her dimmer flash in the grass beaconing the males closer.
As the dark of night progresses you’ll start to see a quicker, brighter, greener flash. Blip, blip, blip, blip, long pause. They are FAST! They’ll also mimic the flashes of Photinus females. These are usually higher up off the ground. Even in the trees! These lightning bugs aren’t looking for love.
Photuris (not gonna get to specific epitaph on this one without a sample and a key) are looking for dinner!

(Photo from blog.greatparks.org another lightning bug beetle. This one is slightly larger than the non-predatory bug. It has “shoulders” and extra gold lines running through the back. Its legs are longer and its shield is more “sharp”. The shield marking is less like an eye and more like a yellow D where the inside is a red triangle with a black line running through.)
Another way to tell is to go out at night and catch a bunch of lightning bugs (if you can; I hear they’re getting scarce). Offer them a slice of apple. If you wake up in the morning to only a few and the rest are dead, good chance you found some predators. (This is how I found out about them! Wooops!!)
Lightning bugs are freaking magical. I’m so sad to hear that they are yet another wonder that we are losing at an alarming rate. If this bugs you as much as it bugs me there are a few things you can do to help them:
1) do not spray for mosquitoes! That spray is not-species specific. It’s bad for lightning bugs. It’s bad for monarch butterflies. It’s bad for birds. It’s bad for bats. It’s bad.
2) kill your lawn. But Misha! You said they breed in the grasses! True! However native plants are going to provide so much more habitat for these guys than a gross monoculture of Kentucky bluegrass ever will. The Midwest has some of the best native plant nurseries in the country! Use that resource!
3) Advocate for them and donate to conservation if you’re able. Bugs don’t have voices and they fight an uphill battle just for being a bug.
Thanks for joining my ranger talk! Support your parks.
243 notes
·
View notes
Text
Birdwomen
Family: Harpyidae
Birdwomen are the most common of magical creatures, appearing on every continent except for Antarctica*. Opportunistic omnivores, birdwomen take the form of massive carrion birds, typically corvids, vultures, condors and eagles, with the heads of women. They appear to be exclusively female; however, some species such as the Mediterranean harpy (Harpia strophades) do pair up during the mating season, with members impressing prospective partners by inflating a pair of gular sacks at the base of the throat similar to the behaviour of frigatebirds (family Fregatidae) and the greater sage-grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus).
The magic of most species of birdwomen are affiliated with storms and disease. The alkonost (Harpia bilibinae) lays its eggs in the sea, and their hatching causes thunderstorms to form, while the droppings of the Mediterranean harpy immediately befoul food.
While most species are reluctant to directly attack humans, birdwomen have no qualms in consuming carrion. Multiple cultures report birdwomen as constant companions to sites of battle and bloodshed. Nordic myths of Valkyries spiriting away the dead are almost certainly inspired by the sight of Scandinavian species of birdwomen feasting on the bodies of the slain after battle, possibly the crested harpy (Valkyria cristatus), nicknamed by professional harpiers as the "Thor's falcon."
The North American birdwoman (Harpia canadensis) is the largest known species of birdwoman, with species standing between five and six feet tall, with respective wingspans of 12 to 15 feet wide. Easily identified by their black, iridescent plumage, North American birdwomen exhibit an intelligent, often playful and curious personality. While native to western and central Canada and the northwestern United States, one birdwoman was sighted in Point Pleasant, West Virginia through the late 1960s; following the 1967 Silver Bridge collapse, one harpier reported seeing this same birdwoman consuming the bodies of two disappeared travellers who had washed up downriver.
*Sightings of the "penguinwomen" of Antarctica are unsubstantiated and should not be counted as fact.
#harpies#unreality#narrativia#i have spiderwick on the brain and this happened#valkyries#norse mythology#mothman#cryptids
81 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Basics on the Barred Owl
Strix varia goes by many names: the barred owl, the northern barred owl, the striped owl, the hoot owl, the eight-hooter owl, or the who-cooks-for-you owl. The last few names refer to the owl's distinctive hooting call, which is often followed by what is often described as 'maniacal laughter'. The barred owl is native to the old-growth deciduous and coniferous forests of eastern North America, though in recent decades the species' range has expanded across the Rocky Mountains into the Pacific Northwest.
The striped owl can be hard to spot, due to its white and brown plumage. The back and wings are brown with white barring, while the chest is dull white or gray with brown streaks. The face is surrounded by a gray-white disk and framed with a brown mask. This coloration allows the barred owl to blend in seamlessly with the upper forest canopy where it resides-- although some populations in the southern parts of its range have been known to carry a pink tint due to the amount of shrimp they eat. However, S. varia is not a small birds; adults can be anywhere from 40 to 63 cm (16 to 25 in) in length, with a wingspan of 96 to 125 cm (38 to 49 in), and weigh about 630 g (22.2 oz) on average.
Like most owls, the barred owl is primarily nocturnal, though they can be fairly active during the day. When dormant, they roost in tree hollows or nests abandoned by other birds. At night, adults are active in guarding their territory and hunting for small mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians, and large arthropods like moths and crayfish. The only natural predator of adult hoot owls is the great horned owl, which will often drive S. varia from their territory. Eggs and nestlings are sometimes prey for raccoons, weasels, and diurnal birds of prey.
S. varia mates for life, and couples are fiercely defensive of their territories and nests. Courtship and territory establishment begins in late winter, and continues from February to April. Males attract mates with their distinctive who-cooks-for-you call, and further entices prospective females with head bobbing and bowing. Together, the pair then establishes a roost and the female lays up to 5 eggs. She alone incubates the clutch for about a month, while the male hunts for her. After hatching, the female continues to care closely for the chicks for another 2-3 weeks, at which time she joins the male in hunting.
Hatchlings quickly become active, and are prone to falling out of the tree, but even at only 4 weeks old they are able to climb back up the trunk. Siblings have been recorded as being tight-knit, often staying close together in the nest and when learning to fly. Fledging begins at about 6 weeks old, and by 10 weeks young are capable of short flights. However, parents continue to provide care to their chicks until they're 6 months old, at which time the young owls leave (or are forced to leave) and establish their own territories. Mortality in barred owls is highest in their first year of life, and once out of this perilous stage individuals may live to be up to 18 years old in the wild.
Conservation status: The barred owl is a common species, and is considered by the IUCN to be Least Concern. The expansion of its range into the Pacific Northwest is considered one of the major causes of the decline of the northern spotted owl.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Mick Thompson
Hal Thrachtenberg
Mark Musselman
#barred owl#Strigiformes#Strigidae#earless owls#true owls#owls#birds#deciduous forest birds#evergreen forest birds#north america#eastern north america#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
Food and Agriculture in Thranduil's Kingdom


It's unfortunate that Thorin's Company was welcomed as dinner guests in Rivendell but imprisoned as invaders in Mirkwood. Had Thorin just shown King Thranduil just a little bit more respect, they could have been fed a whole lot better by the Silvans. And there would most definitely have been meat!
While the Rivendell elves seem to lean vegetarian, and Lothlorien's culinary specialty is the "one bite" lembas, the elves of Greenwood know more than a thing or two about indulgent feasting. These elves consider themselves permanent residents of their land, and with that outlook comes an attitude of celebrating Middle-earth's bounties.
The Silvans of the Woodland Realm have always been fond of feasting, merry-making, and community and family traditions centered around food. Furthermore, they are ruled by a King and royal family who whole-heartedly support this culture, participate in it themselves, and encourage trade that allows the realm to access food from other lands.
When it comes to food, the Greenwood elves are actually more alike Dwarves and Hobbits than they are the lofty High Elves.

Below the cut are SotWK headcanons regarding Food and Agriculture in the Woodland Realm:

Food, Cuisine, and Agriculture in the Woodland Realm
Prior to the establishment of the Woodland Realm and in the early reign of King Oropher (c. SA 700), the Silvan Elves populating Greenwood lived in smaller communities spread throughout the vast forest, but predominantly in the southwest, closer to their kin in Lorinand. Limited subsistence farming was practiced by a few, but by far most food at this time was obtained through hunting and gathering. The rich and bountiful Greenwood had always provided more than enough resources for its dwellers.
GATHERING
Greenwood Elves happily spend most of their immortal lives within Eryn Galen and the lands of Rhovanion, so they are accustomed to living off solely what the forest produces, and their diet is influenced largely by it.
The most commonly foraged edibles are:
Nuts: hazelnut, pecan, walnut, hickory, beechnut, chestnut
Fruit: plum, apple, grape, persimmon
Berries: mulberry, blackberry, currant, elderberry, raspberry
Wild garlic and ramps
Fungi: mushrooms and truffles of many varieties
Eggs: from various wild birds
Herbs and Spices: fennel, corn mint, dandelions, ground elder, pigweed, cicely, sorrel, hogweed, stinging nettle, watercress, wild carrot, rowan, wood avens, sneezewort
Maple: sourced for sugar and syrup
There are also hundreds of plant species native only to Greenwood and Rhovanion that are valued for their uses in healing. However, the Silvan herbalists of Greenwood are usually the only ones able to effectively extract the curative properties of these plants, indicating a connection between Elves and homeland may be necessary for the healing to work.

Art from Fantasy Flight Games
HUNTING
Greenwood Elves are expert hunters and trackers, with unparalleled mastery within their forest and the lands that surround its borders. With careful consideration and instinctual knowledge of the forest ecosystem, they select their prey according to what's most populous, and rotate as necessary to balance out conservation levels.
Among the animals they hunt regularly for meat consumption are rabbit, squirrel, duck, turkey, quail, weasel, racoon, boar, deer, wild oxen, and elk. On rare or special occasions, they hunt less common game such as lion and bear. They also obtain fish and freshwater mussels, clams, and snails from the Forest River and various streams.
It is illegal in Greenwood to hunt or kill specific animals that are declared a protected species, including the King's Elk (the breed of Thranduil's war elk), the silverwolf, and all species of eagle or falcon.
Any fauna or fauna may also be temporarily decreed off-limits for hunting or gathering, by order of the Elvenking and his council.
Any animal taken in as an elf's pet or familiar may also not be killed, so long as it has been properly tamed and does not pose a risk to others.

Throughout the Second Age, the Woodland Realm's population steadily increased under the wise rule of King Oropher and his court. As the communities and villages that made up the kingdom grew larger and more numerous, the practice of agriculture became more widespread to bolster the realm's food supply.
In the Woodland Realm, farming would always remain secondary to hunting and gathering due to the preference of Silvans for wild game and native vegetation. Farmed products serve primarily to enhance cuisine, supplement large feasts, provide reserves in case of war or famine, and as goods for trade with other realms.
FARMING and LIVESTOCK
Tracts of community farmlands were gradually cultivated in the arable fields between Greenwood's western borders (near the capital of Amon Lanc) and the Anduin River.
In order of output, the food crops most commonly grown are: wheat, barley, oats, potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, lettuce, peppers, and peas.
Fiber crops grown for cloth, paper, and rope include: flax, hemp, and cotton.
Domesticated animals are raised in small numbers solely for their by-products and not their meat. In order of importance, livestock that are raised are:
Sheep: source of wool and milk
Chickens: source of eggs
Cows: source of milk and for birthing calves
Animals raised for labor include:
Horses: highly valued and raised exclusively for transport and mounted cavalry
Oxen: used as beasts of burden (large-scale/community work)
Donkeys: used as beasts of burden (small-scale/family work)
When Prince Thranduil built his own palace of Bar Lasgalen just south of the Old Forest Road (which would later become the new capital upon his ascension to the throne), he helped the Silvans residing in the valleys of the Emyn Duir to initiate small-scale agriculture, which encouraged further migration into that area and northward towards the Grey Mountains.


Elvish historians refer to the first millennium of the Third Age as the "Golden Age of the Woodland Realm". During these years, the kingdom enjoyed an unbroken peace under a wise King and Queen who also had five sons actively involved in the governance of the realm.
Departing from his father's more isolationist leanings, Thranduil encouraged trade with realms across Middle-earth. It included all the races except for Hobbits, since the Shire did not yet exist prior to the darkening of Greenwood.
Sadly, most trade came to a stop by the end of the Third Age, with the exception of the nearby Dale, due to the struggles with Dol Guldur. However, after Erebor was reestablished by King Thorin, trade gradually resumed with the Dwarves. After the War of the Ring and the Cleansing of Dol Guldur, Eryn Lasgalen once again thrived with renewed relations with their trade partners--finally including the Shire!
AGRICULTURAL TRADE
The Woodland Realm's three most valuable exported agricultural products are:
Rare spices
Mushrooms and truffles
Medicinal herbs (extremely valuable but highly controlled to prevent misuse)
Imported goods are considered luxuries and not necessities, and are brought in seasonally for community feasts and celebrations (of which there are many). Everything is meant for the consumption of all the kingdom's citizens, regardless of status; there is never anything reserved as "special" for the royals or nobles.
The top agricultural imports, usually from realms/communities of Men, are:
Wine
Textiles (silk, cotton)
Seafood
Sugar
Cheeses
ARTISAN COOKS and BAKERS
Exposure to outside realms and cultures also resulted in an expansion of the culinary arts within Thranduil's kingdom. Cooking and baking became full-blown, respected and sought-after professions instead of tasks done within individual households. With the King's support, talented Elves were sent to other realms to learn their culinary practices; chefs from other kingdoms were invited to Greenwood as royal guests to do the same.
A few culinary feats and innovations the Woodland Elves became known for:
Use of offal (innards) in recipes that actually taste fantastic, thanks to seasonings and skilled cookery
Using literally every single part of a butchered animal with zero waste
Aphrodisiacs in common food recipes, using plant ingredients (partly responsible for their marriage and birth rates and large families)
Salted game meat (jerky) that is highly nourishing and excellent for travel; essentially a meat version of lembas
The use of whipped egg whites to make essentially a type of meringue--which opened up an entire category of desserts that became staples at feasts

Bonus Fun Headcanons! (as a thank you for reading this far)
Mealtimes in Thranduil's Family
No one can beat Ada in drinking contests, ever; it has been attempted hundreds of times--usually with Dorwinion wine--and Thranduil has never been dethroned by his sons.
The King and every single one of the Princes are all heavy eaters, and everyone, including the Queen, eats meat.
While they all observe formal manners at the table, the Princes can get rowdy when not in the presence of their mother--especially when there's drinking involved. (Not quite as bad as Thorin's Company, but close.)
Breakfast: Taken individually in their own rooms, according to each one's schedule/leisure
Lunch: The most commonly skipped meal; usually taken "on the go", and oftentimes with people outside of the family (e.g. business lunches, lunch with friends)
Dinner: The family meal. Everyone is expected to sit down and eat dinner with the rest of the family, unless traveling or there is a prior commitment that takes precedence.
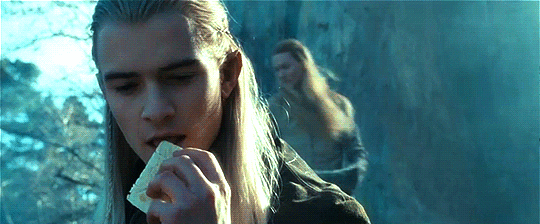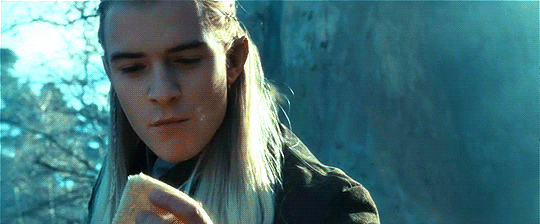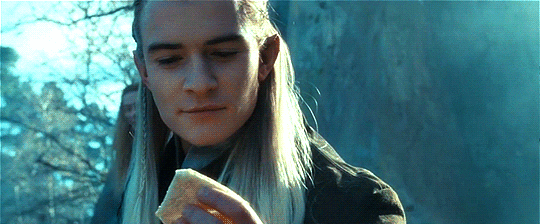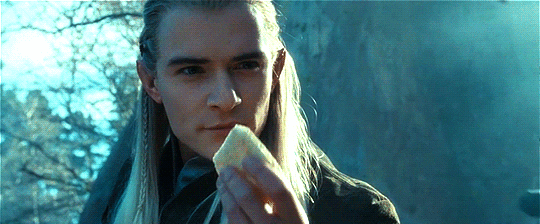
Random Fun Food Facts with the Thranduilions
The Princes regularly compete to see who can eat the most exotic/"disgusting" food items. Turhir remains champion at this (able and willing to eat literally everything), with Legolas frequently trying (and constantly failing) to unseat him.
They have also competed to see who can eat the riskiest (aka poisonous) food items. Arvellas has somehow proven to be the most impervious to natural poisons, much to Gelir's frustration.
Legolas can go the longest without eating food, but no one really cares to try to beat his record.
Mirion is the heaviest eater, but is also the fastest, and because he has flawless table manners no one really notices.
Gelir can find truffles just using his sense of smell--yes, like a truffle pig. He has successfully trained other similarly gifted Elves to do the same.

For more Thranduil/Mirkwood headcanons: SotWK HC Masterlist
Tolkien Headcanon tag list: @quickslvxr @laneynoir @auttumnsayshi @achromaticerebus @tamryniel @friendofthefellowshipsnerdblog @blueberryrock @aduialel @glassgulls @ladyweaslette @klytemnestra13 @creativity-of-death @heilith @fizzyxcustard @absentmindeduniverse @lathalea @tamurilofrivendell @jordie-your-local-halfling @ladyk8tie @scyllas-revenge @asianbutnotjapanese @conversacomsmaug @lemonivall @ratsys @a-world-of-whimsy-5 @entishramblings @stormchaser819 @freshalmondpandadonut

#sotwk headcanon#thranduil#thranduil headcanon#legolas#mirkwood#mirkwood elves#the elvenking#the hobbit#lord of the rings#tolkien#tolkien headcanons
266 notes
·
View notes
Text
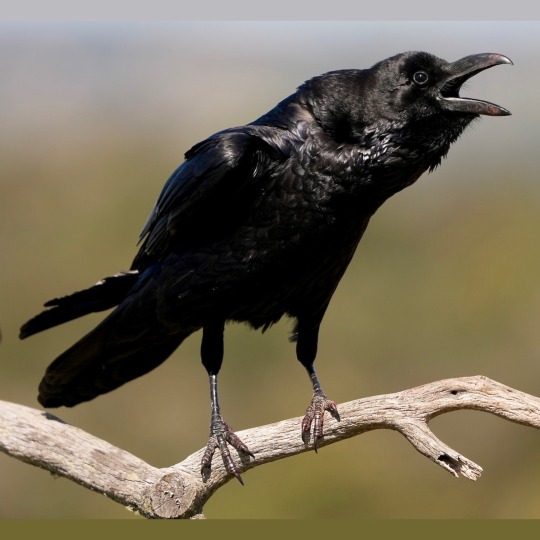


Remember to read about the contestants before voting!
Common Raven
The common raven is a very smart bird. They have even been found to be drawn to gunshot sounds, as they know hunters will often kill animals. People have always been fascinated by ravens, and in London it’s said that if the ravens of London tower ever leave the whole British empire will crumble! They’re also seen as tricksters in Pacific Northwest Native American tribes. In one myth, they are told to have brought fire to people by stealing the sun. Learn More! Much More
Bearded Vulture
Devourers of bones. That’s what the bearded vulture is. They are scavengers, like most vultures, but their favorite meal is bones. They are often seen climbing the skies with bones in their talons, only to drop them from a tall height and smashing them on the rocks below. They then eat the marrow from inside the bones. In Iranian culture they are seen as symbols of good luck. If their shadow falls over you, you will rise to sovereignty. Alternatively, if you kill a bearded vulture you will die in 40 days. Learn More!
(Common Raven photo by Peter Alexander)
(Bearded Vulture photo by Marc Gálvez)
310 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Kind of Plants to Add
This is my sixth post in a series I’ll be making on how to increase biodiversity on a budget! I’m not an expert–just an enthusiast–but I hope something you find here helps!��
I’d love to be able to give a quick and easy list of things to add, but frankly I can’t do that. I can strongly encourage you, however, to look at these categories of plants and do further research to discover what’s native to your area, so you can plant things that’ll have the most impact in your particular area.
With that being said, I will mention a few plants as examples. This is in no way, shape, or form me telling you that you have to or even should buy these specific plants. Not every plant works well in every place in every garden, not to even mention across countries. Above all, if you’re wondering what plants you should be adding, I can wholeheartedly say plants that are native to your area--or at least nonnative non-invasive.
Flowers
Flowers are some of the most common ways people work to increase biodiversity in their gardens, and who can blame them? Seeing pops of color out your window, and directly seeing the impact via butterflies and bees visiting the garden? It’s a win-win for us and the wildlife!

Flowers--especially native wildflowers--are a quick, easy, and cheap way to increase wildlife traffic in your garden. Perennial gardens are more likely to get you the most bang for your buck, as they’ll come back year after year if you treat them well. But don’t dismiss annuals--if you get ones that easily reseed, they’ll eagerly return on their own! If you can, do your best to ensure that the flowers you plant all have different blooming periods--that way, your garden can support wildlife throughout the year instead of for just one brief season.
Flowers are environmental super boosters. Their nectar and pollen can feed insects and birds, their stems and leaves can provide nesting materials for all sorts of creatures, and their seeds are a popular food source among birds at all times of the year.
Climbing Plants
Climbing plants can be fantastic options for maximizing your impact. If you have limited ground space, growing up can provide interest as well as additional habitat for all kinds of creatures.
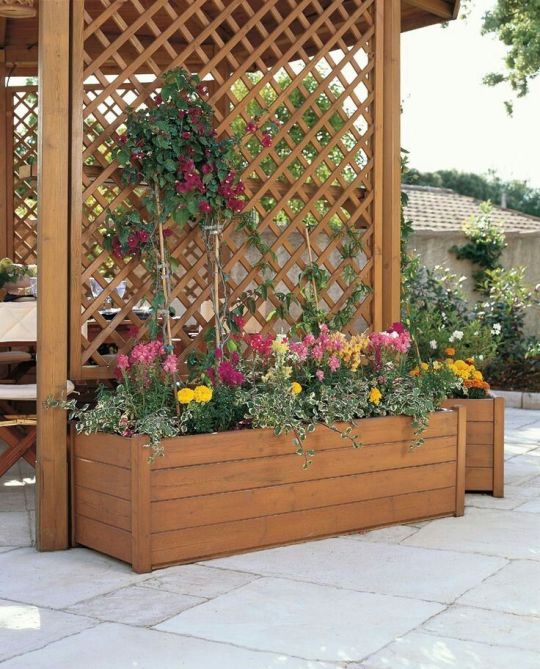

Training plants up a trellis, fence, or bare wall offers food, shelter, and habitat. Trumpet vines, passionflowers, honeysuckles, and more will provide sweet nectar for pollinators as well as nesting and hiding spaces for other wildlife like birds, bugs, and lizards. Do note that in some cases, climbing plants can actually affect the structural integrity of walls and roofs if allowed to climb too much and too far along a house, so be careful.
Bushes/Shrubs
Bushes provide shelter for creatures, which then provides hunting grounds for other animals. Their fallen leaves and petals can be food and shelter for detritivores, amphibians, reptiles, and small mammals--and they also provide good cover for moving around the garden, for creatures who like to stay hidden. They can be a bit more pricey to obtain--unless you get cuttings or seeds and are willing to wait--but they’ll definitely be worth it, and they’re typically low-maintenance once they’re established.
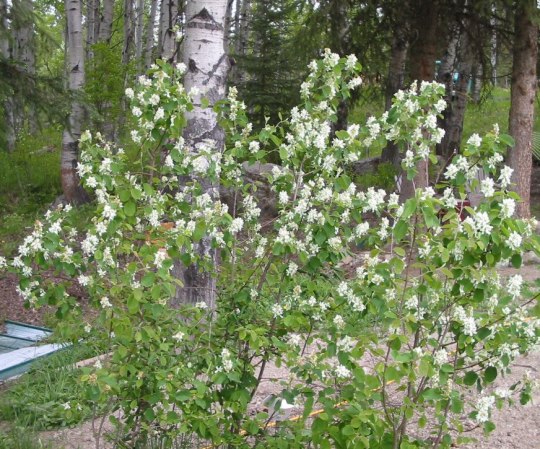

Bonus points if you get a flowering and fruiting bush, like bottlebrush, serviceberry, lilac, or others. This’ll make your bushes not only a place of shelter, but a food source as well--and depending on the kind you pick, may be food for you too! Making a garden border with a series of bushes can be a great option to providing lots of habitat, if you can manage it.
Shrubs with pithy or hollow stems are excellent options for supporting solitary bees. Some examples you could look into are elderberry, raspberry, blackberry, or sumac.
Trees
Trees have a high up-front cost and take awhile to grow, but once they’re settled in place they provide crucial habitat to all kinds of creatures! Insects will be attracted to flowers they may provide, or to nest in the wood. Others may eat the leaves as food, or use them as nesting materials. Birds will perch and nest in trees, and feed off the fruits and seeds and insects that also use the tree. Squirrels also use trees as nesting places, piling up dead leaves into huge clusters to raise their young in, and will absolutely feast on any nuts the tree may provide. Mice, badgers, and more will feast on fallen fruits or seeds, and bats roost in the trunks when given the chance. Detritivores eat fallen leaves and decomposing fruits, providing further food for hunting creatures. Trees can also be good for us--they help block out noise and air pollution, and are the poster child for taking CO2 and making it breathable oxygen. Not to mention they can provide plenty of food for us, too. Nesting grounds, hunting grounds, shelter from weather, and more--trees are, in my opinion, likely to be the best way to boost biodiversity long-term. If you can get your hands on a sapling for cheap and can care for it for awhile, I’d definitely give it a shot! Make sure the tree won’t get too big for where you’re growing it, though--you’ve definitely gotta plan for the long-term before you plant any.

Some trees can be grown in containers. Though they won’t become gigantic branching behemoths, they’ll still do their part to support all the life that depends on them. Growing a tree from seed may take awhile, but could be an easy option to getting one if you have the patience--the trees are more than happy to help you, as they drop tons of seeds and fruit in fall for you to gather.
Groundcover
Bare soil is the enemy of microbial life in the soil, and while small pockets of bare soil can be great nesting places for bees and other insects, having swaths of empty soil should be avoided. Groundcover plants grow low to the ground in a sprawling habit, and will often spread quite easily on their own. This is a great way to provide shelter, keep soil temperatures cool, block out weeds, and give your soil life a chance to thrive.
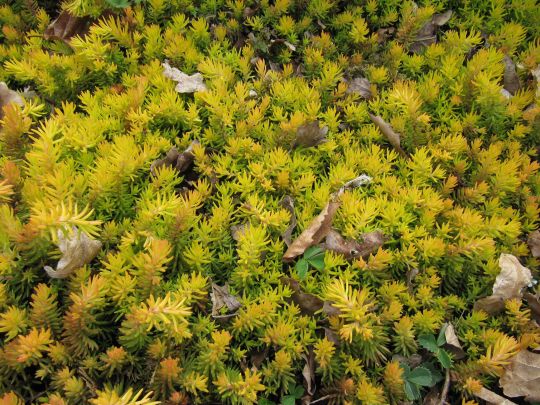

Sometimes, ground covers don’t even have to be planted in the ground. Shallow-rooted plants like succulents, ferns, and alyssum can be planted into cracks in stone walls, and moss can be planted by making moss graffiti and painting it onto a surface. As with climbing plants, do make sure that you don’t cause extra damage to important walls and housing foundations.
Host Plants
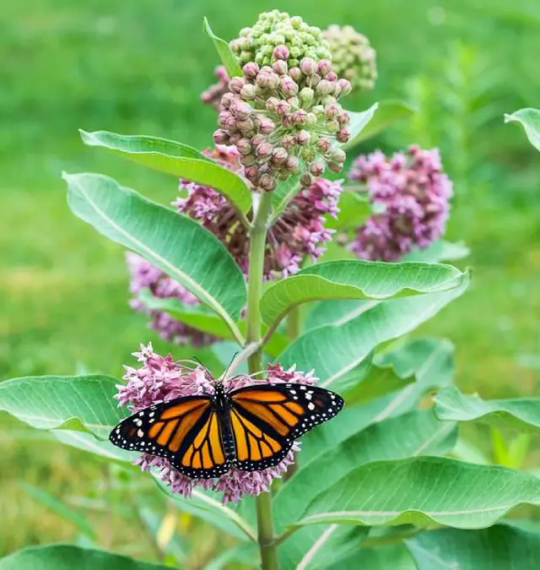

Host plants get their own section, because plants of all kinds can be host plants for different creatures! It’s common to think only flowers can be host plants in the beginning, but in reality, many bushes and trees are host plants to dozens of species of butterflies and moths. Honestly, I feel that factor's not talked about enough. Look up what insects live in your area and what kind of host plants they need, and plant some if you can! Bonus points if you can plant a variety of them--I know that there’s hundreds of kinds of milkweed, each one flowering and leafing up around different times of the year. Planting several varieties of milkweed, then, would provide monarchs with food through several seasons, allowing many more of them to grow up in your garden!
Nectar Plants
Plants that provide nectar to insects is a great foundation to increasing biodiversity! This is, of course, many native wildflowers (and even nonnative wildflowers, though be sure they aren’t invasives who’ll do more harm than good), but many native bushes, vines, and trees will also provide nectar to hungry pollinators!

Keystone Species
To be frank, some plants can have a bigger impact than others in a landscape. By all means, every bit helps, but if you want to boost biodiversity quickly there are a few plants that can essentially serve as the backbone of local ecosystems that you can grow in anything from a balcony pot to a small patch of your backyard. These plants can be different depending on where you are, so do your research to find out what would be best to grow in your area. If you can’t get them all? That’s alright! But even hitting just a few of these target species really can do a lot.

That’s the end of this post! My next post is gonna be about things to keep in mind/continue to do once you get plants in the ground! Until then, I hope this advice was helpful! Feel free to reply with any questions, your success stories, or anything you think I may have forgotten to add in!
#biodiversity#solarpunk#gardening#outdoor gardening#ani rambles#out of queue#the biodiversity saga#sorry its been 2 months since I last posted to this series#I literally have everything drafted out I just got Busy because maannnnnnn animating a grad school capstone project all by yourself....#i should really start using my youtube channel to post my animations but they never feel Done so I just Dont#i dont have as many links in this one because... they weren't in the draft and any tumblr posts that came to mind I couldn't hunt down#either way i hope this was Helpful and Lit and All That Jazz#I might just post the other parts tomorrow so I can stop having that hanging over my head#and so I can get my sources masterpost out there so people can like. see I'm trying my best not to just talk out of my ass#anyways see yall
157 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why is honey not vegan it dosent harm the bees and it helps the environment
Honey is not vegan by any reasonable definition of the word. As vegans we avoid animal exploitation, whatever you may think about bees and honey, honey is very definitely the result of exploiting bees. Bees are amazing pollinators and they are vital for plants and natural ecosystems more generally, but that really has nothing to do with buying and eating honey.
Most pollinator bees are solitary bees, pollination in natural eco-systems is performed by these individuals, other insects and birds. They are the ones who are under threat, not the kind of bees we use to make honey. We are talking about managed hives of domesticated bees, most of whom are non-native and compete with natural pollinators for the same food sources. It is even thought they may be spreading disease to wild pollinators, too, who do a far better job of pollination than managed hives do.
Commercially owned hives are shipped in on-mass to pollinate some crops, but this is not sustainable and far from how natural pollination works. It is a symptom of our over-intensive farming system, and certainly not a point to make in favour of buying and eating honey. This just helps make honey production more profitable, it isn’t good for the environment and certainly isn’t good for the bees.
What’s more, honey in many instances does harm bees. As I mentioned bees compete with and sometimes even infect wild pollinators. On top of that, bees being crushed during harvesting is very common as any honest apiarist will tell you, even when using smoking techniques. Wing clipping of queens is also pretty common, as is selling and shipping queens in the post; I can’t imagine how stressful that must be. Keep in mind that even without any of this, we’re taking about taking their life’s work and often replacing it with a sugar syrup substitute. Bees just don’t make honey for us, it’s not ours to take.
The best way to actually support wild pollinators and their ecosystem is to grow local, pollinator-friendly flowers and to provide them with natural habitats and constructed ones like bug boxes, which are widely available to buy and very easy to make. The claim that honey is in some way good for bees or good for the environment is nothing but effective marketing.
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chemically sterilized...or mechanically sterilized?
It is clear that applying chemicals to your yard and landscape, be it fertilizers, weed killers, or pesticides, has devastating effects to the community of life that is present in every place.
But is the terrifying decline in insects explainable by chemicals alone?
When i am in mowed environments, even those that I know have no lawn chemicals, they are almost entirely empty of life. There are a few bees and other insects on the dandelions, but not many, and the only birds I see are American robins, Grackles, and European starlings.
Even without any weed killers at all, regular mowing of a lawn type area eliminates all but a few specially adapted weeds.
The plants of a lawn where I live include: Mouse ear chickweed, Birds-eye Speedwell, Common blue violet, Dandelion, Wild Garlic, Creeping charlie, White Clover, Black Medick, Broad-leaved plantain, Mock Strawberry, Crabgrass, Small-flowered Buttercup, Ribwort Plantain, Daisy Fleabane, a few common sedges, Red Deadnettle...That sounds like a lot of plants, but the problem is, almost all of them are non-native species (Only Violets, Daisy Fleabane, and the sedges are native!) and it's. The Same. Species. Everywhere. In. Every. Place.
How come...? Because mowed turf is a really specific environment that is really specifically beneficial to a number of almost entirely European plants, and presents stressors that most plants (including almost all native north american plants) simply can't cope with.
The plants mentioned above are just the flowering weeds. The grasses themselves, the dominant component of the lawn, are essentially 100% invasive in North America, many of them virulently and destructively invasive.
Can you believe that Kentucky bluegrass isn't even native to Kentucky? Nope, it's European! The rich pasture of the Bluegrass region of Kentucky was predominantly a mix of clover, other legumes, and bamboo. The clovers—Kentucky clover, Running buffalo clover, and buffalo clover—are highly endangered now (hell, kentucky clover wasn't even DISCOVERED until 2013) and the bamboo—Giant rivercane, Arundinaria gigantea—has declined in its extent by 98%. Do European white and red clovers fulfill the niches that native clovers once did? Dunno, probably not entirely.
One of the biggest troubles with "going native" is that North America legitimately does not have native grass species that really fill the niche of lawn. Most small, underfoot grassy plants are sedges and they are made for shady environments, and they form tufts and fancy sprays, not creeping turf. Then there's prairie grasses which are 10 feet tall.
What this means, though, is that lawns don't even remotely resemble environments that our insects and birds evolved for. Forget invasive species, lawns are an invasive BIOME.
It's a terrible thing, then, that this is just what we do to whatever random land we don't cover in concrete: back yards, road margins, land outside of churches and businesses, spaces at the edges of fields, verges at bypasses and gas stations...
Mowing, in the north american biomes, selects for invasive species and promotes them while eliminating native species. There's no nice way to put it. The species that thrive under this treatment are invasive.
And unfortunately mowing is basically the only well-known and popular tool even for managing meadow and prairie type "natural" environments. If you want to prevent it from succeeding to forest, just mow it every couple of years.
This has awful results, because invasive species like Festuca arundinacea (a plant invented by actual Satan) love it and are promoted, and the native species are harmed.
Festuca arundinacea, aka Tall Fescue, btw is the main grass that you'll find in cheap seed mixes in Kentucky, but it's a horrific invasive species that chokes everything and keeps killing my native meadow plants. It has leaves like razor blades (it's cut me so deeply that it scarred) and has an endosymbiont in it that makes horses that eat it miscarry their foals.
And this stuff is ALL OVER the "prairie" areas where I work, like it's the most dominant plant by far, because it thrives on being mowed while the poor milkweeds, Rattlesnake Master and big bluestems slowly decline and suffer.
It's wild how hard it is to explain that mowing is a very specific type of stressor that many plants will respond very very negatively to. North American plants did not evolve under pressures that involved being squished, crushed, snipped to 8 inches tall uniformly and covered in a suffocating blanket of shredded plant matter. That is actually extremely bad for many of the prairie plants that are vital keystone species. Furthermore it does not control invasive species but rather promotes them.
Native insects need native plant cover. Many of them co-evolved intimately with particular host plants. Many others evolved to eat those guys. And Lord don't get me started on leaf removal, AKA the greatest folly of all humankind.
So wherever there is a mowed environment, regardless of the use of chemicals or not, the bugs don't have the structural or physical habitat characteristics they evolved for and they don't have the plant species they evolved to be dependent on.
Now let's think about three-dimensional space.
This post was inspired when I saw several red winged blackbirds in the unmowed part of a field perching on old stems of Ironweed and goldenrod. The red-winged blackbirds congregated in the unmowed part of the field, but the mowed part was empty. The space in a habitat is not just the area of the land viewed from above as though on a map. Imagine a forest, think of all the squirrels and birds nesting and sitting on branches and mosses and lichens covering the trunks and logs. The trees extend the habitat space into 3 dimensions.
Any type of plant cover is the same. A meadow where the plants grow to 3 feet tall, compared with a lawn of 6 inches tall, not only increases the quality of the habitat, it really multiplies the total available space in the habitat, because there is such a great area of stems and leaves for bugs and birds to be on. A little dandelion might form a cute little corner store for bugs, A six foot tall goldenrod? That's a bug skyscraper! It fits way more bugs.
It's not just the plants themselves, it's the fallen leaves that get trapped underneath them—tall meadow plants seem to gather and hoard fallen leaves underneath. More tall plants is also more total biomass, which is the foundation of the whole food chain!
Now consider light and shade. Even a meadow of 3ft tall plants actually shades the ground. Mosses grow enthusiastically even forming thick mats where none at all could grow in the mowed portions. And consider also amphibians. They are very sensitive to UV light, so even a frog that lives in what you see as a more "open" environment, can be protected by some tall flowers and rushes but unable to survive in mowed back yard
#anti lawn#kill your lawn#native plants#the ways of the plants#native plant gardening#plants#random#bitching about mowing again
867 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, but what if
Blue eye samurai but with wings?
Because let’s be clear, we all love wings and the amount of references this show makes to birds is insane so why not use it?
Basic premise:
Every person is born with wings.

It’s a law of nature, a gift from gods, a curse for some and a source of pride for another. They vary in size and pattern, sometimes barely reaching a person’s shins, sometimes dragging behind them. Most of them stay on the larger side, and you could almost think that they were meant to be used.
But humans forgot how to fly. They became heavy, learned to love many things that keep them on the ground. Good food, warm sake, aromatic opium. The knowledge of flying, that feeling of freedom has been buried under the rubble of every day problems and pleasures. And so, unused, wings began to grow smaller.
With time, wings became something mundane, something pretty to look at, if you were lucky and something bothersome if you’re not.
The poor usually bind their wings. They keep them contained unless their profession allows them to spread them wide, like sailors and monks do. Wings are just another limb for them.
Nobles like to preen their wings and show them off. Glossy and healthy wings are a sign of wealth, much like hands never marred by hard work. It’s especially true for woman, whose wings are tied practically since birth, to keep them small and decorative. It’s dangerous, it hurts and if something goes wrong, a girl can end up with gnarly appendage but such is the way of women.
Enter Mizu:

Our girl has been born with giant wings, too big for her small figure. They are dark and beautiful and entirely too bothersome for her.

They are the wings of an European Shag, native to Europe. Similar enough to Japanese cormorant but just a little bit… odd. Enough to stand out. Enough for her to hate them too.
And they are on a bigger size, much bigger than what is considered proper. They get in the way in the smithy, keep on catching on fire and tripping Mizu so she learns to tuck them away, binding them much like her chest. And yet, she cannot make herself bind them hard enough to stop their growth. They are too resilient for their own good, much like Mizu herself.
As she plans her revenge, her wings only get in the way. So she shortens them. Cuts the primaries almost entirely, until they fit comfortably under her poncho. Mizu binds them way too loosely. A good compromise, she tells herself. Easy to snap open but out of the way otherwise. It saves her life during the battle with four fangs.
They are ruffled, lack the gloss they should have. Mizu doesn’t really care for them, cuts them whenever they get too long.
Akemi:

She is a skylark, her wings naturally small and dainty. As with almost every woman, her wings has been bound as a child to keep them small. Keep them attractive. She can fold them entirely over her back. She never does. She takes pride in them after all.
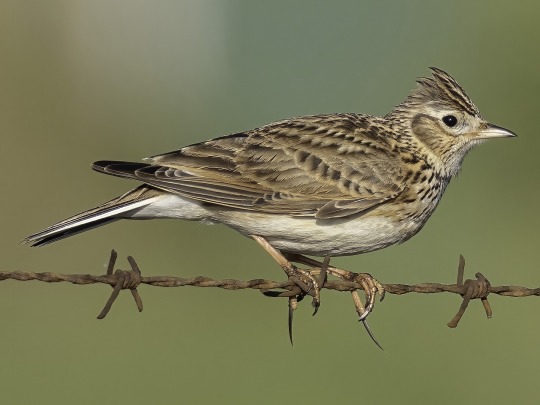

She doesn’t remember much of the pain from the time they were kept bound, so she can’t entirely relate to the woman who were born with bigger wings and had to keep theirs bound until adulthood. It makes her indelicate at times.
She hates what her wings represent. A pretty thing, meant to sing and be kept for entertainment. Still, she keeps them well preened and they are uniform and as beautiful as they could ever be. Even on the road, she tries to keep them pretty. They ruffle way too easily whenever she feels offended.
Taigen:

Taigen’s wings are wide and big and beautiful. He is an osprey. He learns how to preen them at the Dojo, learns how to take pride in them as most of the male nobleman do.

Taigen never hides his wings. They are a part of him, one that he can now afford to display proudly. A swordsman wings, not a fisherman’s. He trains with unbound wings and while not unusual, it’s also not a very common way of fighting. He likes the challenge.
He takes it as an insult when Mizu refuses to spread her wings during their fight, like she’s not taking him seriously. It’s a display and it’s meant to mean something dammit! So he keeps going harder, especially since he remembers that Mizu always had bigger wingspan than him, even as children. It keeps bothering him, why she keeps them hidden until he sees the state of them after her battle with four fangs.
He keeps quiet about the topic after that, something in the back of his head unable to comprehend how anyone could ever treat themselves that way. And how big they must really be, when even her uncut secondaries reach her calves.
Big enough to fly, maybe?
Anyway, stay tuned for part two, maybe.
Parts two, and three, and maybe more to be updated here ;)
#blue eye samurai#bes#Mizu#akemi#Taigen#mizu blue eye samurai#wings#wings au#akemi blue eye samurai#taigen blue eye samurai#alternate universe#evening ideas#masterpost
97 notes
·
View notes
Note
Please can you tell me 5 interesting things about cow and sheep diseases
i have waited my entire life to hear this very question thank you my friend. my answers are very focused on aotearoa as that is where i did my masters
facial eczema is a fungal disease of sheep and cattle that is caused by eating fungal spores in grass which release a toxin into the gut of the animal and cause liver and systemic damage, including facial lesions. my interesting fact here is that a study was done to attempt to vaccinate sheep against the toxin, but instead of reducing the disease, it somehow made it significantly worse
listeriosis in sheep (infection with the same listeria that can cause food poisoning in humans) can present as repeated circling or staggering followed by death, as it is a neurological disease in sheep. my father once saw a sheep circling in one of our paddocks and by the time he reached it, it had already died
the techniques used in aotearoa and later globally for tracking covid-19 variants were prototyped here in aotearoa for tracking bovine tuberculosis outbreaks! cattle here frequently catch it from the invasive brushtail possum (one major reason why we are trying to eradicate them, the other being the harm they cause to native birds) and this method of disease mutation tracing was pioneered for working out where these outbreaks were coming from
sheep have their own prion disease called scrapie which (like chronic wasting disease in deer) can be transmitted through soil and water. here in aotearoa we accidentally imported scrapie in the 1970s to mana island and as a result had to torch and burn an entire mob of sheep and abandon the island for sheep farming - to this day there are restrictions on visiting the island for safety
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) has been detected in nz cattle, which is concerning by itself, but it is also transmissible to humans, particularly through the drinking of unpasteurised milk. Never drink unpasteurised milk. The most common victims of this here are farmers drinking milk from their own cows due to the belief that fresh milk is still safe
139 notes
·
View notes