#trans philosophy
Text

I meant to post this some months ago when I defended, but accidentally saved as a draft. Despite the absurd formatting requirements, I discovered we're allowed to have a frontispiece.
#philosophy#applied philosophy#studyblr#dissertation#trans philosophy#epistemology#epistemic injustice#frontispiece#holy shit they gave me a Ph.D.#no the whole thing isn't in Latin#yet
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is a Woman?
A summary and response to Talia Mae Bettcher's Multiple Meanings Position
Talia Mae Bettcher is a revolutionary figure in identity politics and trans philosophy. She challenges conventional ideas of womanhood, and offers a conclusive, binary-breaking, perspective on what it means to be a woman. She is revolutionary in trans studies, not only critiquing trans-exclusionary discourse, but evaluates concepts that attempt to ally the trans liberation movement. This post will explicitly explore one of Bettcher’s most notable contributions: her critique of semantic contextualism and her alternative multiple meanings position.
Proposed by Jennifer Saul, semantic contextualism seeks to validate transgender identities by acknowledging fluidity in language and meaning [1]. Saul argues the meaning of woman shifts depending on the context, it can encompass biological sex, determined gender roles, and self-identification.
To simplify, take the word now. To me, now means a specific time and place. Now is 14:07 on 20/04/2024, in UOM library. But as you read this, now refers to a time in the near distant future, where you accidently stumble onto my blog page and are bombarded with new information on gender, sexuality and racial identity. Likewise, Saul argues that the definition of woman changes depending on the context.
Bettcher takes issue with this definition. Transwomen are women unequivocally. They are always women, not just in specific contexts. Instead, Bettcher proposes “multiple meanings” concept, suggesting the term woman encompasses a spectrum of experiences and identities that coexist simultaneously [2]. Not only does this provide inclusivity, it completely challenges binary understanding of gender. It proposes gender as something fluid and malleable, instead of rigid and fixed. This dynamic reimagining both embraces the experiences of marginalised individuals, and affirms the complexities of cisgenders women.
Personally, I appreciate this perspective, and feel it offers somewhat of a solution to the debate regarding the definition of lesbianism, as presented in I reserve my right to be complex. I find merit in feeling somewhat uneasy about using the term “non-male” as a defining factor for lesbianism. I recognise that so much of being a woman is defined in conjunction to men and the patriarchy. Bettcher’s broader understanding of womanhood allows me to still feel connected with “women attracted to other woman” as a definition for lesbianism. As a non-binary lesbian, it can validate my gender identity, whilst simultaneously validating my explicitly queer attraction to women.
Talia Mae Bettcher is an incredible philosopher, and a prime example on why it is so important to have trans, and other marginalized community, representation in academia. I highly recommend watching the video below, as it discusses and dissects both academic and wider societal debates regarding trans liberation and rights, whilst providing additional information on Bettcher and her lived experience.
youtube
#transgender#trans philosophy#talia mae bettcher#trans theory#what is a woman#trans rights#trans women are women
0 notes
Text
A transy throught I've had for year,
If I could wish everybody was born their wanted gender would I ?
After lots of thinking, the answers I came to was no .
While a lot of people would be happier, myself included . the world itself would be a worse place for everyone.
It would be a transphobes paradise. Everyone would be cis, no one having cool introspection about gender, or weird gender euphoria moments.
It's sucks to live in a world this hurtful, and we can make it better. But it will never be perfect.
So second best opinion the world's a better place with lil gender goblins running around, making the world a cooler, gayer, sexyier place.
It is worth some of the pain and discomfort
1 note
·
View note
Text
the two transfems spitroasting me have started arguing dialectics and their disdain for each other’s philosophical leanings has caused them to further ruin my poor body
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Are LGBTQ labels confusing? Do you ever see a collection of words and think "aren't some of those antithetical or mutually exclusive?" Congratulations! You've run into a very interesting phenomenon that I'm about to break down to the best of my ability.
There's two major philosophies when it comes to labels, they don't have names to my knowledge so I'm gonna call them Reflective and Telegraph.
The Telegraph Label philosophy states that labels primarily function as a means of conveying useful information about one's self to others. It's telling others what pronouns, what parts and what genders that person has or is attracted to. This is usually pretty straightforward, the stuff someone interested in dating you would check before asking you out to avoid embarrassment.
The Reflective Label philosophy states that labels are primarily a tool for describing an internal experience. Putting words to feelings for the benefit of the self. This is how we get lables like stargender or autismgender. These aren't meaningfully useful labels that tell others what to expect physically or what pronouns to use. But that doesn’t mean they're useless. In the case of someone using autismgender, that label probably describes the internal experience of the ways a person's autism impacts their views on and performance of gender. Stargender likely explains not that they literally see themselves as a star but rather that their internal experience of their prefered gender performance makes them feel a way that reminds them of stars or stargazing.
And this applies to sexuality too. Boy lesbian might seem antithetical but ultimately that label isn't there to tell others anything. It's merely a comfort to have words to describe a mess of feelings and social dynamics.
And for clarification, anyone calling themselves a boy-lesbian probably isn't the cis male boogieman forcing lesbians who aren't interested in cis men to date them or else be labeled a bigot. That boogieman doesn't exist. A more likely explanation is that a nonbinary or trans person has a complex relationship with their changing gender that doesn't trigger a change in the way they see themselves in relationships and attraction thus causing them to keep or adopt the lesbian label despite the gender weirdness going on.
I see a lot of infighting about what people call themselves and whether or not certain combinations can even physically exist. And Y'know what? I don't think that's terribly productive. Neither philosophy is wrong. People are just using labels to address different root problems.
As aggravating as it might be for Telegraphers, you don't have to understand everything. Not everyone feels that they owe you the list of information you find useful, and their labels reflect that. And that's okay.
#lgbtq#psa#queer#gender#sexuality#linguistics#philosophy#gay#bisexual#trans#aromantic#acesexual#lesbian
3K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
NEW PHILOSOPHY TUBE JUST DROPPED
This is the one baybeee. This is the big one, the one about trans healthcare, the big kahuna, the forbidden episode I’d never do, the one where I drag Br*tish institutions and make a bunch of references to a famous novel - you know me!
Enjoy, and also - I never normally ask but, SHARE THIS ONE AROUND LADS
Abi XXx
#Philosophy Tube#Philosophy CHUBE#Healthcare#Health#Trans#Oh God I Finally Made A Video In Which I Briefly Talk About Trans Stuff Let The Cancellation Begin!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
the state of r/actuallesbians, part I
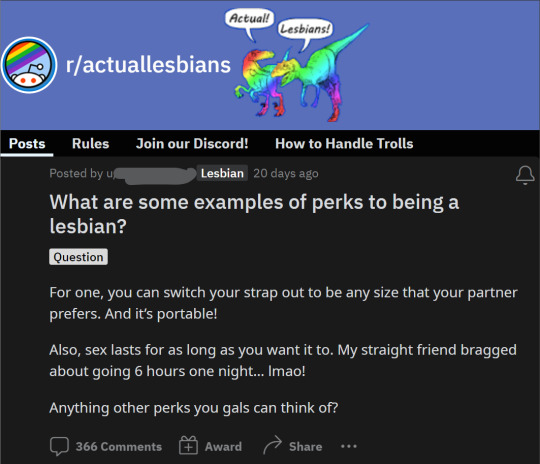
"What is cool about being a lesbian?"
"they know where the clitoris is"
"well, I, a man, have bad news for you, because I most definitely do not know where the clitoris is"

I love how she apologized to trans women even beforehand, but this person couldn't stop himself from talking about his "tummy ache" and being sad because "people are so dismissive of it"

#lesbian#lesbian pride#transgender#male to female#transbian#trans woman#radical feminism#radical feminists please touch#radical feminists do interact#radblr#bisexual#bi#transsexual#transmedical#transmed#philosophy tube#enby#non binary#listen to trans women#misogynie#misogynist
674 notes
·
View notes
Note
What do you think gay men are attracted to in men that they can’t be attracted to in women?
It can’t be anything about femininity or masculinity obviously. That’s both sexist, and cultural so can’t be what drives men-only attraction.
It can’t be anything about stated identity because someone could lie just as easily as they could tell the truth in such a statement, and it makes no sense because homosexuality and heterosexuality exists in other species with no stated identities. It’s not like other animals without gender are all pan.
Saying idk it’s the vibes or some indescribable trait men have that women can’t but “I can’t explain” is a nonanswer.
Soooooooo what is it? Or do you think any sexuality but bi/pan is just cultural performance or an identity rather than an inborn orientation?
- [ ]
first off i hate this ask and i think youre a freak. in any other world i wouldve blocked you for this but unfortunately for both of us i actually like this type of philosophy. dont send this shit to anyone else though
i dont think its right to compare human sexuality to the same thing in animals, to get that out of the way. im sure until a certain point it comes from the same biological impulses, but human beings have way more complicated social structures and reasons for coupling that just do not exist in other animals. our social behaviours are what make us unique in the animal kingdom and that definitely extends to gender and sexuality. so theres that
people love to tout 'gender is a social construct' around like its a criticism in and of itself, which i think betrays a misunderstanding about social constructs in general. theyre the foundations we build language on to better understand each other, and affected by a whole host of cultural and historical factors. just because theyre subjective and complicated doesnt mean they arent real. in terms of the effect they have on peoples lives they may be the most real thing that exists
for example, 'kindness' is a social construct. the definition and ways it is enacted differ greatly across personal and cultural lines. but no one would ever suggest a world where kindness doesnt exist or loses meaning, because its an essential part of the way we interact with each other (in the same way i dont really see a world where gender entirely ceases to exist, mainly just one where people have more fun with it. im not a psychic though so who knows)
similarly, sexuality in humans is another social construct. i think the driving biological forces behind it are very real, but the labels people attach to those impulses are subjective attempts to express their inner world to the people around them if that makes sense. and those same biological impulses are ALSO subject to social ideas of gender, because those ideas are established at birth and reinforced over a persons entire lifetime
to use myself as an example, im a gay trans man. ive identified as other things in the past, because i was trying to pick apart feelings i had and express them to others in an attempt to find community. my identity might change as i get older and experience new things, or it might not. i identify as gay because im not attracted to the social concept of women, and someone i would otherwise be attracted to might lose all appeal after i find out they fall under that concept (this has happened before w transfems pre and post coming out lol)
of course, the real REAL answer to this is that trying to give queer identities rigid and objective definitions is a fools errand, and also lame as fuck. someone might identify as gay and be more attracted to general masculinity than men as a social category, maybe they fool around with a couple of butch women without considering themself any less gay. two otherwise identical people might be a butch lesbian and a gay trans man without either of those identities coming into conflict. they might even be the same person at different times of the week
the labels people choose to use are communication tools, not objective signifiers. if you dont understand them, they probably arent talking to you
social constructs are everything. we as humans have the unique ability to interpret our own messy desires and impulses into words that other people can use to form an idea of someone else in their mind. its how we build connections, and of course it isnt perfect because trying to squeeze someones entire personal history and the centuries of context that defined it into a handful of syllables is going to leave some room for error. but its all we have, yknow? so we keep trying. and i think thats much more human than any imposed objective 'truth' could ever be
tldr we live in a society dipshit. get with it
#ask#long post#i feel like i should tag for the ask bc it sucks but idk what so like. lmk#gender#trans stuff#i love you language philosophy i love you messy human relationships i love you contradictory identities
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think instead of treating somebody's queerness as a right for you to know, people should instead think of somebody's queerness as a privilege to know.
It is a privilege for you to know if somebody is queer - it is by no means a right. It should be treated as such.
#lesbian#gay#bi#bisexual#trans#transgender#queer#lgbt#lgbtq#my philosophy is that if cishets don't have to announce they are cishet then i don't have to announce any part of my queerness#it is a privilege for me to tell y'all what 'kind of queer' i am. and it's a privilege if somebody else knows how you are queer or not#(privilege literally meaning 'special honour' btw)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
let's be real, if Scott Pilgrim is a trans woman, she probably has like eight zillion one-off bullshit worldbuilding options for transitioning. some people like mundane HRT, some people prefer SHRT (Super Hormone Replacement Therapy) or GHRT (Giga Hormone Replacement Therapy), others swear by MHRT (Magic Hormone Replacement Therapy). Ramona offers to hook her up with the surgeon who gave Roxie her archaectomy ("removal of your past") in addition to an orchiectomy, but they end up agreeing that neither Trans Scott nor Ramona should have that, what with ... y'know ... (gestures vaguely at the entire comic). you can either get conventional bottom surgery, or a complete permanent magical transformation which is called "tf/tg", like that's its actual name in-universe (Roxie got the former, Ramona went with the latter), but in the latter case you sometimes still need HRT for some reason. someone breaks the fourth wall to comment that transphobes are the same as they are "in real life".
Trans Scott ends up going with Super HRT and the magical transformation (it's a kind where she still needs to take HRT)
#shenanigans#philosophy#scott pilgrim#trans stuff#trans scott pilgrim#trans ramona flowers#trans roxie richter#hrt#orchiectomy#archaectomy#roxie richter#ramona flowers#rhoda pilgrim
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
My 2023 Reading List
Here's the books and articles that I read in 2023 (a large part of which was a push to finish my dissertation). I thought it might also be useful to others to see what my workload looks like as a 7th year grad student in a PhD. program, especially since I'm unmedicated with severe ADHD. This is what I'm able to get done while fighting through that. I bring this up because I know that it can seem fucking impossible, most notably when we see our neurotypical colleagues churning through incredible amounts of research. A final note: two of the books I'm including in here are books that I started reading in 2022 (Kagan and Stock). Also, note that many of these are re-reads; I've marked these with an Asterisk, and a couple of the books I read around 90%, but dropped a couple chapters that weren't relevant for my projects. These are marked with two asterisks. Be aware that my citations here are of a pretty rough and ready style. Philosophy has weird disciplinary standards (read, almost every journal is different), so I just have a "here's what you need to know to find it" style here.
CW: I work on some dark things involving death, suicide, sexual assault, sex, race, and trans rights, including actively fighting trans-exclusive theorists, so there's a lot of possibly triggering things in here.
Updated: Jan 4, 2024
Abdollah, Serajian, Ebrahim Khosrow, and Sajad Ahmadizad. 2014. “Comparison of Anthropometric and Functional Characteristics of Elite Male Iranian Fencers in Three Weapons.” International Journal of Applied Sport Sciences 26 (1): 11–17.
Alcoff, Linda. 1991. “The Problem of Speaking for Others.” Cultural Critique No. 20 5–32.
Alcoff, Linda. 2007. “Epistemologies of Ignorance: Three Types.” In Race and Epistemologies of Ignorance, edited by Shannon and Tuana Sullivan, Nancy, 39–50. Albany: State University of New York Press.
Anderson, Elizabeth. 2012. “Epistemic Justice as a Virtue of Social Institutions.” Social Epistemology 26 (2): 163–73.
Andler, Matthew. 2017. “Gender Identity and Exclusion: A Reply to Jenkins.” Ethics
Ashley, Florence. 2023. “What is it Like to Have a Gender Identity.” Mind 132 (528): 1053–73.
Ballantyne, Nathan. 2019. “Epistemic Trespassing.” Mind 128 (510): 367–95.
Ballantyne, Nathan, Jared Celniker, and David Dunning. 2022. “Do Your Own Research.” Social Epistemology
Barnett, Brian S, Ariana E Nesbit, and Reneé M Sorrentino. 2018. “The Transgender Bathroom Debate At the Intersection of Politics, Law, Ethics, and Science.” J Am Acad Psychiatry Law 46 (2): 232–41.*
Berg, Amy. 2022. “Is There a Duty to Read the News.” Journal of Moral Philosophy 20 (3-4): 243–67.
Bergero-Miguel, Trinidad, María A García-Encinas, Amelia Villena-Jimena, Lucía Pérez-Costillas, Nicolás Sánchez-Álvarez, Yolanda de Diego-Otero, and Jose Guzman-Parra. 2016. “Gender Dysphoria and Social Anxiety: An Exploratory Study in Spain.” J Sex Med 13 (8): 1270–78.*
Bettcher, Talia Mae. 2009. “Trans Identities and First-Person Authority.” In You’Ve Changed: Sex Reassignment and Personal Identity, edited by Laurie Shrage, 98–120. Oxford University Press.*
Biggs, Michael. Suicide By Trans-Identified Children in England and Wales. Transgender Trend.*
Blair, Karen L., and Rhea Ashley Hoskin. 2019. “Transgender Exclusion From the World of Dating: Patterns of Acceptance and Rejection of Hypothetical Trans Dating Partners as a Function of Sexual and Gender Identity.” Journal of Social and Personal Relationships 36 (7): 2074–95.
Blanchard, Matt, and Barry Farber. 2016. “Lying in Psychotherapy: Why and What Clients Don’t Tell Their Therapist About Therapy and Their Relationship.” Counselling Psychology Quarterly 29 (1): 90–112.
Blanchard, Matt, and Barry Farber. 2020. “”It is Never Okay to Talk About Suicide”: Patients’ Reasons for Concealing Suicidal Ideation in Psychotherapy.” Psychother Res 30 (1): 124–36.
Bochicchio, Lauren, Kelsey Reeder, Lauren Aronson, Charles McTavish, and Ana Stefancic. 2021. “Understanding Factors Associated With Suicidality Among Transgender and Gender-Diverse Identified Youth.” LGBT Health 8 (4): 245–53.
Bradley, Ben. 2012. “Doing Away With Harm.” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research 85, No. 2 390–412.*
Brown, Brookes. 2023. “Bearing Witness: The Duty of Non‐indifference and the Case for Reading the News.” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 104 (2): 368–91.
Bustos, Valeria P, Samyd S Bustos, Andres Mascaro, Gabriel Del Corral, Antonio J Forte, Pedro Ciudad, Esther A Kim, Howard N Langstein, and Oscar J Manrique. 2021. “Regret After Gender-Affirmation Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence.” Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 9 (3): e3477.*
Byrne, Alex. 2020. “Are Women Adult Human Females.” Philosophical Studies 177 (12): 3783–803.
Carel, Havi, and Ian Kidd. 2014. “Epistemic Injustice in Healthcare: A Philosophical Analysis.” Med Health Care Philos 17 (4): 529–40.
Cattien, Jana. 2019. “Against “Transracialism”: Revisiting the Debate.” Hypatia 34 (4): 713–35.
Clements-Nolle, Kristen, Rani Marx, and Mitchell Katz. 2006. “Attempted Suicide Among Transgender Persons: The Influence of Gender-Based Discrimination and Victimization.” Journal of Homosexuality 51 (3): 53–69.*
Congdon, Matthew. 2018. ““Knower” as an Ethical Concept: From Epistemic Agency to Mutual Recognition.” Feminist Philosophy Quarterly 4 (4):
Costa, Rosalia, and Marco Colizzi. 2016. “The Effect of Cross-Sex Hormonal Treatment on Gender Dysphoria Individuals’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review.” Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 12 1953–66.*
Crichton, Carel, & Kidd. 2017. Epistemic Injustice in Psychiatry. BJPsych Bulletin. 41:65-70.
Crocker, David. 1991. “Insiders and Outsiders in International Development.” Ethics and International Affairs 5 149–73.
Cullison, Andrew. 2010. “On the Nature of Testimony.” Episteme
Daniels, Norman. 2015. “Why We Should Care About the Social Determinants of Health.” Am J Bioeth 15 (3): 37–38.
Davey, Amanda, Walter Pierre Bouman, Caroline Meyer, and Jon Arcelus. 2015. “Interpersonal Functioning Among Treatment-Seeking Trans Individuals.” J Clin Psychol 71 (12): 1173–85.*
Davey, Amanda, Walter Pierre Bouman, Jon Arcelus, and Caroline Meyer. 2014. “Social Support and Psychological Well-Being in Gender Dysphoria: A Comparison of Patients With Matched Controls.” J Sex Med 11 (12): 2976–85.*
Davis, Emmalon. 2016. “Typecasts, Tokens, and Spokespersons: A Case for Credibility Excess as Testimonial Injustice.” Hypatia 31 (3): 485–501.
Dees, Richard H. 2019. “Primum Non Nocere Mortuis: Bioethics and the Lives of the Dead.” Journal of Medicine and Philosophy 44 (6): 732–55.
Dembroff, Robin. 2020. “Beyond Binary: Genderqueer as Critical Gender Kind.” Philosophers’ Imprint 20 (9): 1–23.*
Dembroff, Robin, and Dennis Whitcomb. Forthcoming. “Content-Focused Epistemic Injustice.” Oxford Studies in Epistemology*
DiPaolo, Joshua. 2022. “What’s Wrong With Epistemic Trespassing.” Philosophical Studies 179 (1): 223–43.
DiPaolo, Joshua. Forthcoming. “”I’m, Like, a Very Smart Person” on Self-Licensing and Perils of Reflection.” Oxford Studies in Epistemology
Dormandy, Katherine. 2018. “Epistemic Authority: Preemption or Proper Basing.” Erkenntnis 83 (4): 773–91.
Dotson, Kristie. 2008. “In Search of Tanzania: Are Effective Epistemic Practices Sufficient for Just Epistemic Practices?” Southern Journal of Philosophy 46 (S1): 52–64.*
Dotson, Kristie. 2011. “Tracking Epistemic Violence, Tracking Practices of Silencing.” Hypatia 26 (2): 236–57.*
Dotson, Kristie. 2012. “A Cautionary Tale: On Limiting Epistemic Oppression.” Frontiers: A Journal of Women Studies 33 (1): 24–47.*
Dotson, Kristie. 2014. “Conceptualizing Epistemic Oppression.” Social Epistemology 28 (2): 115–38.*
Frost-Arnold, Karen. 2014a. “Imposters, Tricksters, and Trustworthiness as an Epistemic Virtue.” Hypatia 29 (4): 790–807.
Frost-Arnold, Karen. 2014b. ���The Cognitive Attitude of Rational Trust.” Synthese 191 (9): 1957–74.
Frost-Arnold, Karen. 2014c. “Trustworthiness and Truth: The Epistemic Pitfalls of Internet Accountability.” Episteme 11 (1): 63–81.
Funkhouser, Eric. 2017. “Beliefs as Signals: A New Function for Belief.” Philosophical Psychology 30 (6): 809–31.
Gardner, Molly. 2015. “A Harm-Based Solution to the Non-Identity Problem.” Ergo 2 427–44.*
Gardner, Molly. 2019. “When Good Things Happen to Harmed People.” Ethical Theory and Moral Practice 22 (4): 893–908.
Gijs, Luk, and Anne Brewaeys. 2007. “Surgical Treatment of Gender Dysphoria in Adults and Adolescents: Recent Developments, Effectiveness, and Challenges.” Annual Review of Sex Research 18 (1): 178–224.*
Goldman, Alvin I. 2001. “Experts: Which Ones Should You Trust.” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research 63 (1): 85–110.
Harcourt, Edward. 2021. “Epistemic Injustice, Children and Mental Illness.” J Med Ethics 47 (11): 729–35.
Hardwig, John. 1985. “Epistemic Dependence.” The Journal of Philosophy 82 (7): 335–49.
Harvin, Cassandra Byers. 1996. “Conversations I Can’t Have.” One the Issues: The Progressive Women’s Quartery 5 (2): 15–16.
Hookway, Christopher. 2010. “Some Varieties of Epistemic Injustice: Reflections on Fricker.” Episteme 7 (2): 151–63.
Intemann, Kristen. 2010. “25 Years of Feminist Empiricism and Standpoint Theory: Where Are We Now.” Hypatia 25 (4): 778–96.
Jaggar, Alison M. 1998. “Globalizing Feminist Ethics.” Hypatia 13 (2): 7–31.
Jenkins, Katharine. 2016. “Amelioration and Inclusion: Gender Identity and the Concept of Woman.” Ethics 126 (2): 394–421.*
Jenkins, Katharine. 2018. “Toward an Account of Gender Identity.” Ergo, an Open Access Journal of Philosophy 5 (20201214):
Jenness, Valerie, Cheryl L. Maxson, Kristy N Matsuda, and Jennifer Macy Sumner. 2007. “Violence in California Correctional Facilities: An Empirical Examination of Sexual Assault.” The Bulletin 2 (2): 1–4.
Joshi, Hrishikesh. 2022a. “Debunking Creedal Beliefs.” Synthese 200 (6):
Joshi, Hrishikesh. 2022b. “The Epistemic Significance of Social Pressure.” Canadian Journal of Philosophy 52 (4): 396–410.
Kaltial-Heino, Rittakerttu, Maria Sumia, Marja Työläjärvi, and Nina Lindberg. 2015. “Two Years of Gender Identity Service for Minors: Overrepresentation of Natal Girls With Severe Problems in Adolescent Development.” Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health 9 (9): *
Kidd, Ian James, Lucienne Spencer, and Havi Carel. 2023. “Epistemic Injustice in Psychiatric Research and Practice.” Philosophical Psychology 1–29.
Kukla, Rebecca. 2007. “Objectivity and Perspective in Empirical Knowledge.” Episteme 3 (1-2): 80–95.
Kurs, Rena, and Alexander Grinshpoon. 2018. “Vulnerability of Individuals With Mental Disorders to Epistemic Injustice in Both Clinical and Social Domains.” Ethics & Behavior 28 (4): 336–46.
Larbalestier, Jan. 1990. “The Politics of Representation: Australian Aboriginal Women and Feminism.” Anthropological Forum 6 (2): 143–57.
Lee, J. Y. 2021. “Anticipatory Epistemic Injustice.” Social Epistemology 35 (6): 564–76.
Levy, Andrea, Aaron Scherer, Brian Zikmund-Fisher, Knoll Larkin, Geoffrey Barnes, and Angela Fagerlin. 2018. “Prevalence of and Factors Associated With Patient Nondisclosure of Medically Relevant Information to Clinicians.” JAMA Netw Open 1 (7): e185293.
Lin, Eden. 2021. “The Experience Requirement on Well-Being.” Philosophical Studies 178 (3): 867–86.
Longino, Helen E. 1990. Science as Social Knowledge. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Love, Heather A., and Preston C. Morgan. 2021. “You Can Tell Me Anything: Disclosure of Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Psychotherapy.” Psychotherapy (Chic) 58 (4): 533–43.
Love, Melanie, and Barry A. Farber. 2019. “Honesty in Psychotherapy: Results of an Online Survey Comparing High Vs. Low Self-Concealers.” Psychother Res 29 (5): 607–20.
Lugones, María. 1987. “Playfulness, “world”-Travelling, and Loving Perception.” Hypatia 2 (2): 3–19.
Lugones, María C., and Elizabeth V. Spelman. 1983. “Have We Got a Theory for You! Feminist Theory, Cultural Imperialism and the Demand for ‘the Woman’s Voice’.” Women’s Studies Int. Forum 6 (6): 573–81.
Marquis, Don. 1989. “Why Abortion is Immoral.” The Journal of Philosophy 86 (4): 183.*
Medina, José. 2011. “The Relevance of Credibility Excess in a Proportional View of Epistemic Injustice: Differential Epistemic Authority and the Social Imaginary.” Social Epistemology 25 (1): 15–35.
Meier, Lukas J. 2022. “Systemising Triage: Covid-19 Guidelines and Their Underlying Theories of Distributive Justice.” Med Health Care Philos 25 (4): 703–14.
Mohanty, Chandra Talpade. 1988. “Under Western Eyes: Feminist Scholarship and Colonial Discourses.” Feminist Review 30 61–88.
Mustanski, Brian, and Richard T Liu. 2013. “A Longitudinal Study of Predictors of Suicide Attempts Among Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Youth.” Archives of Sex Behavior 42 (3): 437–48.*
Neus, Nora. Trans Women Are Still Incarcerated With Men and it’s Putting Their Lives At Risk. CNN.
Nguyen, C. Thi. 2020a. “Cognitive Islands and Runaway Echo Chambers: Problems for Epistemic Dependence on Experts.” Synthese 197 (7): 2803–21.
Nguyen, C. Thi. 2020b. “Echo Chambers and Epistemic Bubbles.” Episteme 17 (2): 141–61.
Nicholls, Tracey. 2011. “Should I Speak for My Sister? Solidarity and Silence in Feminist Struggles.” PhaenEx 6 (1): 12–41.
Origgi, Gloria. 2012. “Epistemic Injustice and Epistemic Trust.” Social Epistemology 26 (2): 221–35.
Pardue, Angela, Bruce A. Arrigo, and Daniel S. Murphy. 2011. “Sex and Sexuality in Women’s Prisons.” The Prison Journal 91 (3): 279–304.
Perry, Stephen. 2003. “Harm, History, and Counterfactuals.” San Diego Law Review 40 1283–313.
Phipps, Alison. 2016. “Whose Personal is More Political? Experience in Contemporary Feminist Politics.” Feminist Theory 17 (3): 303–21.
Pitcher, George. 1984. “The Misfortunes of the Dead.” American Philosophical Quarterly 21, No. 2 183–88.
Pohlhaus Jr., Gaile. 2012. “Relational Knowing and Epistemic Injustice: Toward a Theory of “willful Hermeneutical Ignorance”.” Hypatia 27 (4): 715–35.
Pohlhaus Jr., Gaile. 2014. “Discerning the Primary Epistemic Harm in Cases of Testimonial Injustice.” Social Epistemology 28 (2): 99–114.*
Preda, Adina, and Kristin Voigt. 2015. “The Social Determinants of Health: Why Should We Care.” Am J Bioeth 15 (3): 25–36.
Russell, Camisha. 2019. “On Black Women, “in Defense of Transracialism,” and Imperial Harm.” Hypatia 34 (2): 176–94.
Russell, Stephen T, Amanda M Pollitt, Gu Li, and Arnold H Grossman. 2018. “Chosen Name Use is Linked to Reduced Depressive Symptoms, Suicidal Ideation, and Suicidal Behavior Among Transgender Youth.” J Adolesc Health 63 (4): 503–5.
Salkin, Wendy. 2021. “The Conscription of Informal Political Representatives.” Journal of Political Philosophy 29 (4): 429–55.
Sanati, A, and M Kyratsous. 2015. “Epistemic Injustice in Assessment of Delusions.” J Eval Clin Pract 21 (3): 479–85.
Sanati, Abdi & Kyratsous Michalis. 2017. Epistemic Injustice and Responsibility in Borderline Personality Disorder. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice. 23:974-980
Sartre, Jean Paul. 1946. trans. Philip Mairet. "Existentialism is a Humanism."
Satta, Mark. 2022. “Epistemic Trepassing and Expert Witness Testimony.” Journal of Ethics and Social Philosophy 22 (2): 212–38.
Schutte, Ofelia. 1986. “Notes on the Issue of Cultural Imperialism.” Proceedings and Addresses of the American Philosophical Association 59 (5): 757–59.
Schwan, B. 2021. “Responsibility Amid the Social Determinants of Health.” Bioethics 35 (1): 6–14.
Scott, Joan W. 1991. “The Evidence of Experience.” Critical Inquiry 17 (4): 773–97.
Shaw, Danny. 2020. Eleven Transgender Inmates Sexually Assaulted in Male Prisons Last Year. BBC.
Sheeks, Meredith. 2023. “The Myth of the Good Epistemic Bubble.” Episteme 20 (3): 685–700.
Shiffrin, Seana Valentine. 1999. “Wrongful Life, Procreative Responsibility, and the Significance of Harm.” Legal Theory 5 (02): 117–48.*
Shiffrin, Seana Valentine. 2012. “Harm and Its Moral Significance.” Legal Theory 18 (3): 357–98.*
Simester, A P, and Andreas von Hirsch. 2011. Crimes, Harms, and Wrongs: On the Principles of Criminalisation. Portland, Oregon: Hart Publishing.
Spivak, Gayatri Chakravorty. 1988. “Can the Subaltern Speak?” In Marxism and the Interpretation of Culture, edited by Cary Nelson, and Lawrence Grossberg, 271–313. Basingstoke: Macmillan Education.
Stacey, Judith. 1988. “Can There be a Feminist Ethnography?” Women’s Studies Int. Forum 11 (1): 21–27.
Steers-McCrum, Alex R. 2020. “Don’t Put Words in My Mouth: Self-Appointed Speaking-for is Testimonial Injustice Without Prejudice.” Social Epistemology 34 (3): 241–52.
Stock, Kathleen. 2018a. Changing the Concept of ‘Woman’ Will Cause Unintended Harms. The Economist.*
Stock, Kathleen. 2018b. Why Self-Identification Should Not Legally Make You a Woman. The Conversation.*
Stock, Kathleen. 2019. Ignoring Differences Between Men and Women is the Wrong Way to Address Gender Dysphoria. Quilette.*
Sullivan, Shannon. 2004. “Feminist Spaces.” Hypatia 19 (3): 209–16.
Tadros, Victor. 2014. “What Might Have Been.” In Philosophical Foundations of the Law of Torts, edited by John Oberdiek, 171–92. Oxford University Press.
Taylor, James Stacey. 2005. “The Myth of Posthumous Harm.” American Philosophical Quarterly 42 (4): 311–22.*
Taylor, James Stacey. 2021. “Promises to the Dead.” Royal Institute of Philosophy Supplement 90 81–103.*
Thomson, Judith Jarvis. 1971. “A Defense of Abortion.” Philosophy and Public Affairs 1 (1): 47–66.*
Tobi, Abraham. 2023. “Intra-Group Epistemic Injustice.” Social Epistemology 37 (6): 798–809.
Toole, Briana. 2022. “Demarginalizing Standpoint Epistemology.” Episteme 19 (1): 47–65.*
Townsend, Leo, and Dina Lupin. 2021. “Representation and Epistemic Violence.” International Journal of Philosophical Studies 29 (4): 577–94.
Trebilcot, Joyce. 1988. “Dyke Methods or Principles for the Discovery/creation of the Withstanding.” Hypatia 3, No. 2 1–13.
Tuvel, Rebecca. 2017. “In Defense of Transracialism.” Hypatia 32 (2): 263–78.*
Vance, Stanley R. 2018. “The Importance of Getting the Name Right for Transgender and Other Gender Expansive Youth.” J Adolesc Health 63 (4): 379–80.*
Vigny-Pau, Myriam, Nelson Pang, Hamad Alkhenaini, and Alex Abramovich. 2021. “Suicidality and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Transgender Populations: A Systematic Review.” Journal of Gay & Lesbian Mental Health 25 (4): 358–82.*
Wanderer, Jeremy. 2012. “Addressing Testimonial Injustice: Being Ignored and Being Rejected.” The Philosophical Quarterly 62 (246): 148–69.
Watson, Jamie Carlin. 2022. “Epistemic Neighbors: Trespassing and the Range of Expert Authority.” Synthese 200 (5): 408.
Weatherall, James Owen, and Cailin O’Connor. 2021. “Conformity in Scientific Networks.” Synthese 198 (8): 7257–78.
Wellman, Christopher Heath. 2001. “Toward a Liberal Theory of Political Obligation.” Ethics 111 735–59.*
Williams, Daniel. 2021a. “Motivated Ignorance, Rationality, and Democratic Politics.” Synthese 198 (8): 7807–27.
Williams, Daniel. 2021b. “Socially Adaptive Belief.” Mind & Language 36 (3): 333–54.
Williams, Daniel. 2023. “The Marketplace of Rationalizations.” Economics and Philosophy 39 (1): 99–123.
Wilson, Liz. 1997. “Who is Authorized to Speak? Katherine Mayo and the Politics of Imperial Feminism in British India.” Journal of Indian Philosophy 25 139–51.
Wolff, Nancy, Cynthia L Blitz, Jing Shi, Ronet Bachman, and Jane A Siegel. 2006. “Sexual Violence Inside Prisons: Rates of Victimization.” J Urban Health 83 (5): 835–48.
Wolff, Nancy, Jing Shi, and Jane A Siegel. 2009. “Patterns of Victimization Among Male and Female Inmates: Evidence of an Enduring Legacy.” Violence Vict 24 (4): 469–84.
Woodward, James. 1986. “The Non-Identity Problem.” Ethics 96 (4): 804–31.*
Worsnip, Alex. 2019. “The Obligation to Diversify One’s Sources: Against Epistemic Partisanship in the Consumption of News Media.” In Media Ethics: Free Speech and the Requirements of Democracy, edited by Carl Fox, and Joe Saunders, 240–64. London: Routledge.
Wylie, Alison. 2003. “Why Standpoint Matters.” In Science and Other Cultures: Issues in Philosophies of Science and Technology, edited by Robert Figueroa, and Sandra Harding, 26–48. New York: Routledge.*
Yang, Xin, Jason Parton, Dwight Lewis, Ning Yang, and Matthew Hudnall. 2020. “Effect of Patient-Physician Relationship on Withholding Information Behavior: Analysis of Health Information National Trends Survey (2011-2018) Data.” Journal of Medical Internet Research 22 (1): e16713.
Books
Camus, Albert. 1955 [1942]. Trans Justin O'Brien. The Myth of Sisysphus and Other Essays. Hamish and Hamilton.*
Farber, Barry A., Matt Blanchard, and Melanie Love. 2019. Secrets and Lies in Psychotherapy. Washington: American Psychological Association.**
Fricker, Miranda. 2007. Epistemic Injustice: Power and the Ethics of Knowing. Oxford University Press.
Kagan, Shelly. 2012. The Geometry of Desert. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kidd, Ian James, José Medina, and Gaile Pohlhaus Jr., eds. 2017. The Routledge Handbook of Epistemic Injustice. London, New York: Routledge.**
Sherman, Benjamin and Gouguen, Stacy, eds. 2019. Overcoming Epistemic Injustice: Social and Psycholofical perspectives. Rowman and Littlefield.
Stock, Kathleen. 2021. Material Girls: Why Reality Matters for Feminism. Fleet.
Book Chapters
Ballantyne, Nathan. 2022. “Novices and Expert Disagreement.” In Reason, Bias, and Inquiry, edited by Nathan Ballantyne, and David Dunning, 227–53. Oxford University Press.
Collins, Patricia Hill. 2000. Chapter 5: The Power of Self-Definition. in Black Feminist Thought: Knowledge, Consciousness, and the Politics of Empowerment. Second Edition. Routledge. 97-121.
Crenshaw, Kimberlé. 1997. “Intersectionality and Identity Politics: Learning From Violence Against Women of Color.” In Reconstructing Political Theory: Feminist Perspectives, edited by Mary Lyndon Shanley, and Uma Narayan, 178–93. University Park, Pennsylvania: Penn State Press.
Feinberg, Joel. 1993. “Harm to Others.” In The Metaphysics of Death, edited by John Martin Fischer, 169–90. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Fricker, Elizabeth. 2006. “Testimony and Epistemic Autonomy.” In The Epistemology of Testimony, edited by Jennifer Lackey, and Ernest Sosa, 225–50. Oxford University Press.
Gardner, Molly. 2021. “What is Harming?” In Principles and Persons, edited by Jeff McMahan, Tim Campbell, James Goodrich, and Ketan Ramakrishnan, Oxford University Press.
Kierkegaard, Søren. 2004 [1843]. trans. Howard V. and Edna H. Hong. "Problema I." in Basic Writings of Existentialism, edited by Gordon Marino. The Modern Library. 7-23.*
Kierkegaard, Søren. 2003 [1843]. trans. Howard V. and Edna H. Hong. "Problema II." in Basic Writings of Existentialism, edited by Gordon Marino. The Modern Library. 24-39.*
Phelan, Shane. 1989. Chapter 4: Definition and Community. in Identity Politics. Temple University Press. 59-80.
Phelan, Shane. 1989. Chapter 7: The Limits of Community. in Identity Politics. Temple University Press. 135-151.
Sartre, Jean Paul. 1993 [1943]. trans. Hazel Barnes. "Introduction: The Pursuit of Being." in. Being and Nothingness. Washington Square Press. xlv-lxvii.*
#studyblr#grad school#reading list#trans philosophy#philosophy#applied philosophy#epistemology#epistemic injustice#study movitation#ethics#feminist philosophy
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
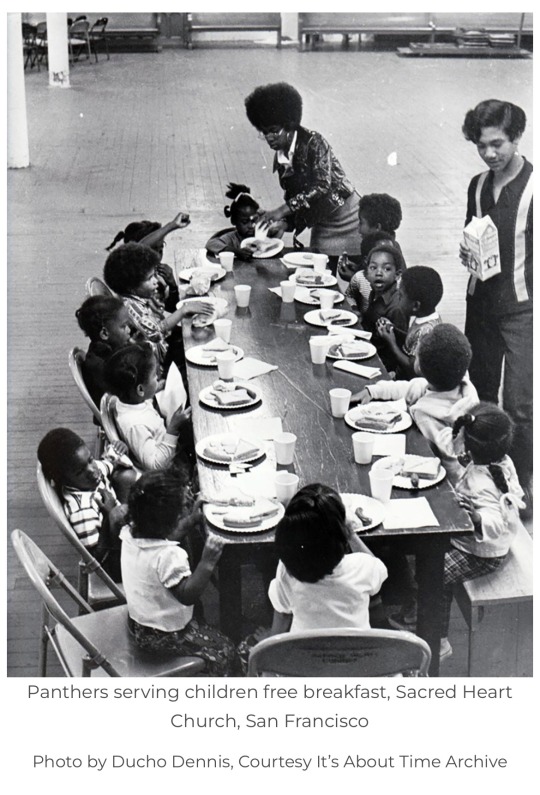





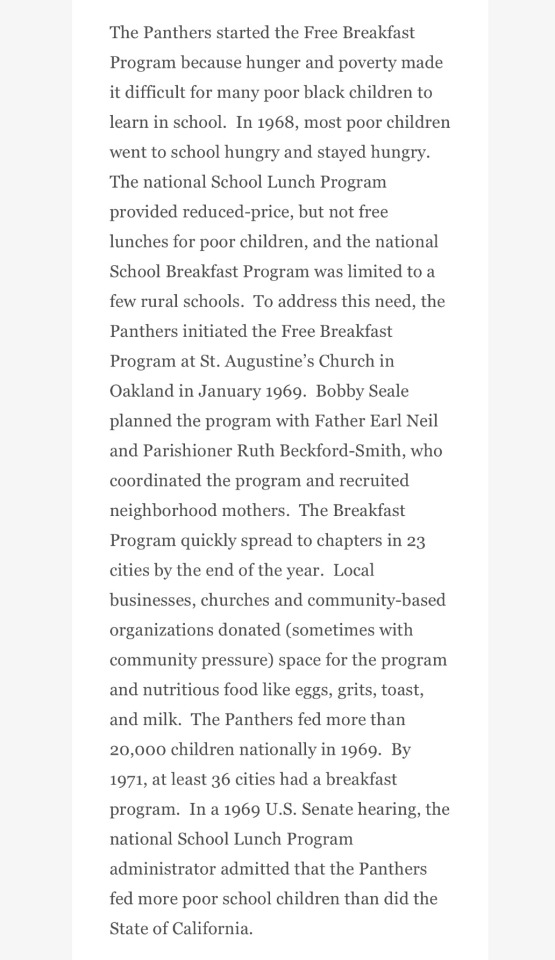




What we seek, however, is not power over people, but the power of control of our own destiny:
ALL POWER TO THE PEOPLE!
// Become Ungovernable, Medium // BLACK PANTHER PARTY’S FREE BREAKFAST PROGRAM (1969-1980) // The Genius of Huey P. Newton, CounterPunch // Abi Thorn’s Trans Power Speech Transcript // Nina Cried Power, Hozier ft. Mavis Staples // Jackboot Jump, Hozier // Backlash Blues, Nina Simone // Be, Hozier // Take Me To Church, Hozier // Tomorrow is My Turn, Nina Simone
#web weaving#become ungovernable#alternative ways of being#trans rights#trans power#black panther party#black lives matter#huey newton#all power to the people#trans positivity#hozier#poetry#trans liberation#mavis staples#nina cried power#nina simone#abigail thorn#philosophy tube#black power#queer history#black history#venus writes#dandelions#sociology#power to the people#queer joy#mine#favourites#venus light
551 notes
·
View notes
Text

171 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gender researcher Judith Butler argues that the anti-gender movement is bringing us closer to authoritarianism

The famous gender researcher Judith Butler is out with a new book called Who's Afraid of Gender. In an article in the Los Angeles Times she explain why she thinks contemporary transphobia brings us closer to authoritarianism.
She writes:
The fear of “gender” allows existing powers — states, churches, political movements — to frighten people to come back into their ranks, to accept censorship and to externalize their fear and hatred onto vulnerable communities.
Those powers not only appeal to existing fears that many working people have about the future of their work or the sanctity of their family life but also incite those fears, insisting, as it were, that people conveniently identify gender as the true cause of their feelings of anxiety and trepidation about the world.
The project of restoring the world to a phantasmatic time before gender promises a return to a patriarchal dream order that only a strong state can restore. The shoring up of state powers, including the courts, implicates the anti-gender movement in a broader authoritarian, even fascist project.
We see the rolling back of progressive legislation and the targeting of sexual and gender minorities as dangers to society, as exemplifying the most destructive force in the world, in order to strip them of their fundamental rights, protections and freedoms.
Read the whole article here.
See also:
Feminist philosopher Judith Butler is crystal clear in her condemnation of transphobic feminists
Renowned Feminist Philosopher Judith Butler Tears Transphobic Feminism Apart
Feminist philosopher Judith Butler goes up against anti-trans and anti-gender feminists and conservatives
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
"guys, there is a difference between sex and gender. sex is your biology, and gender is your social presentation. transgender people understand that they can not change their sex, thats why they are called trans gender!!! everyone knows that you can't change sex! stop making up strawmen! we are not denying biological reality!!!!!"
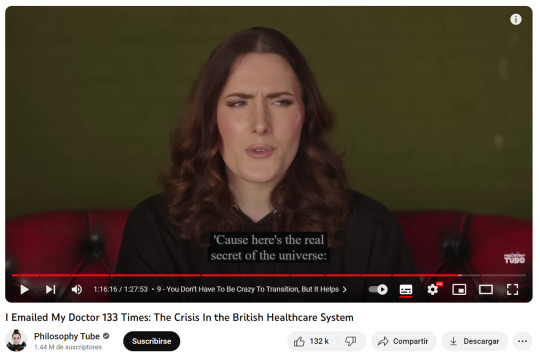
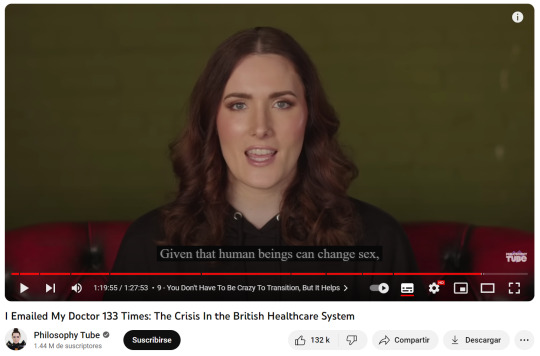
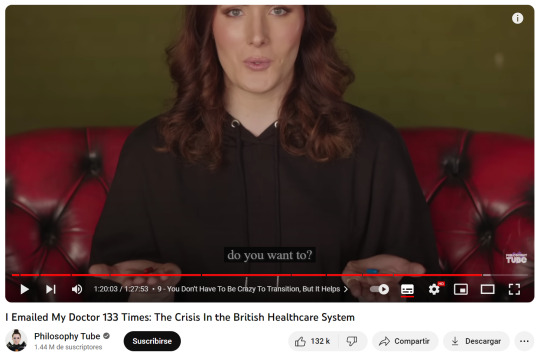
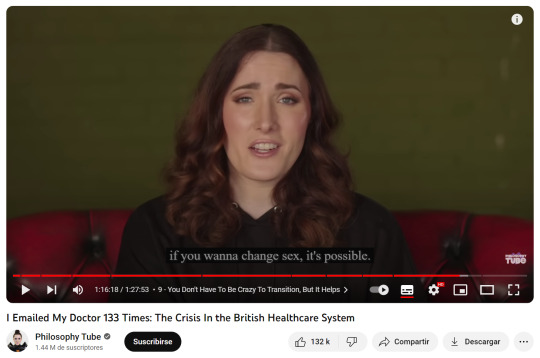
I fucking can't with these people.
#lesbian#lesbian pride#transgender#mtf#male to female#transbian#trans woman#trans feminine#radical feminism#radical feminists please touch#radical feminists do interact#radblr#bisexual#bi#transsexual#transmedical#transmed#philosophy tube#enby
383 notes
·
View notes
Text
In light of ..... recent events, I thought it best to remake that recommendations post I did quite a while back. This is a playlist put together by Hbomberguy and it has quite a number of excellent queer video essayists + some people James Somerton plagiarized. I wanted to add a few people to the list.
Jessie Gender - I cannot recommend her enough. She covers issues facing women as well as trans, nonbinary, and autistic people. She also discusses other marginalized communities (Got this info from her YouTube bio). She analyzes media through these lenses while remaining empathetic and often delivering a nuanced take. HOWEVER, that's not all. Jessie does insanely well researched videos about Sci-fi (shout out Star Trek) and other "geeky" topics. She's working on a short film right now so the channel has kinda flatlined. Go give her some views!
Yhara Zayd - I haven't watched them in a bit but Zayd does videos analyzing media, often through the lens of race. Special shout-out to their "The Day Rue 'Became' Black" vid! Their work is eloquent, well researched, and you can find their sources listed in the bio of vids.
Philosophy Tube - Do I even need to say anything??? Go check out the play she wrote, "The Prince." You can find a recording of it on Nebula. I haven't watched it yet but I plan to.
Anyway these creators (and the ones of the playlist) are only a few of the great people analyzing media, talking about queer history, and more. These lists don't even include the numerous writers from whom James stole from. They all deserve support and I hope they get it. If you have any more reccs (including articles), list them below!
#james somerton#queer#media analysis#philosophy tube#jessie gender#khadija mbowe#alexander avila#lgbtq community#lgbtq media#queer media#shanspeare#gay#lesbian#bisexual#trans#transgender#asexual#intersex#nonbinary#hbomberguy
78 notes
·
View notes