#website design and development pdf
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
E-commerce website: How to create an e-commerce website
How to create an E-commerce website If you are thinking about creating your ecommerce website then this information will be very beneficial for you. It is very easy to setup an e-commerce business, you just have to follow some information, after this you can create an e-commerce business and sell your goods. We will tell you step by step simple methods here. 1, first of all you must have thought…
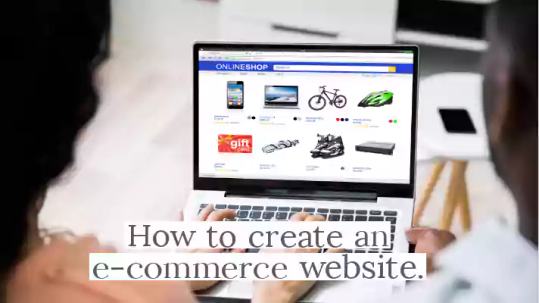
View On WordPress
#build an e-commerce website from scratch with react#design and launch of e-commerce website notes#e commerce website example#e commerce website name#e commerce website project#e commerce website templates#e-commerce website design#e-commerce website in india#how to build an e-commerce website step by step pdf#how to build an ecommerce website from scratch#how to create an e-commerce website using html#how to create an ecommerce website for free#how to create e commerce website#how to make an e-commerce website with html css and js#how to make e-commerce website using html and css#steps to design and develop an e-commerce website#top 10 e-commerce websites
0 notes
Text
Create Accessible PDFs

The Ultimate Guide To PDF Accessibility: How To Make Your Documents Inclusive And Compliant
In today’s digital age, Portable Document Format (PDF) files have become an integral part of our information-sharing process. Whether educational materials, corporate reports, or government publications, PDF files with Accessibility maintain the original formatting and allow users to access information consistently across various devices. However, for PDFs to be truly effective, they must be accessible to all, including those with disabilities. Besides, as about 61 million adult Americans have some disability, you risk their not being able to access the ADA-compliant PDFs and content you create. And it’s not just those with visual impairments that are affected. Even people with a mobile or hearing disability may face problems accessing your web content or PDF.
This is why the ADA and Section 508 focus on making life for those people with disabilities much easier. They require that places of accommodation be accessible to users with disabilities. As PDFs are commonly used on the web, they also have to comply with these laws based on the criteria set by the WCAG. While web compliance is important, creating accessible web content can be challenging. PDFs are especially difficult to manage as they are complex files inaccessible out of the box. It’s only experts who know WCAG and ADA standards well who can take care of the task. We have provided some tips about PDF accessibility features in this article. However, don’t worry if the information overwhelms you. We at ADA Site Compliance can help if you don’t know how to ensure your website or PDF is accessible. Our team of accessibility experts will not only check your PDFs and website content for accessibility but also constantly monitor and update your website and PDFs based on the latest accessibility updates.
Overview of Portable Document Format (PDF)
PDFs, developed by Adobe, have transformed how we share electronic documents. The format was created to maintain document integrity while allowing easy sharing. PDFs are based on an image model that differs from the typical PostScript language commonly used. It is to improve interaction and accessibility that PDFs are structured differently.
What makes an accessible PDF?
As the name suggests, an accessible PDF is a PDF anyone with any disability can easily read and navigate through. And it can mean different things for users with different disabilities. For example, for those with visual impairments, an accessible PDF can mean any of these three. It can mean:
They can easily zoom into the texts if need be
The content has high contrast, making it easy to read
They can easily read the PDF using the help of screen readers
In the case of users with physical disabilities, it means ensuring users can easily navigate through the entire document with the help of a keyboard. These readers find managing a mouse for navigation difficult, so being able to use a keyboard is a welcome move for them. For users with hearing impairments, creating an accessible PDF will mean having captioned audio and video content. In short, the main aim of creating web-compliant PDFs is to provide them with an alternative means of accessing content. Most PDFs have some of these options as default, like zooming and keyboard navigation. However, it doesn’t mean that these PDFs are necessarily accessible. They can, however, be made accessible just by implementing some additional steps.
Characteristics of Accessible PDF Files
Accessible PDFs are a must to ensure inclusivity. Most importantly, they feature searchable text, which, in the process, makes content available to screen readers. Besides, unlike scanned images of text, accessible PDFs can be selected, copied, and edited. This can prove helpful to everyone requiring more clarity about the PDF. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology also plays a crucial role in making content searchable and thus accessible to all.
Navigating PDF Accessibility
Ensuring that your PDF documents are fully accessible can be a complex task, but it’s an essential one. This is especially required with the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) having set the standards for digital accessibility. These guidelines encompass various aspects, including alternative text alternatives, navigation, and readability. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial to creating PDFs that are both legally compliant and user-friendly. Besides, ensuring that your website and the content you provide, including PDFs, are accessible is not just a legal obligation; it’s a moral imperative. By embracing accessibility, you not only comply with the law but also open doors for a more inclusive and diverse audience.
Accessible PDFs: A Key to Digital Inclusion
The importance of accessible PDFs cannot be overstated. They open up a world of information and opportunities for individuals with disabilities. Accessible PDFs offer text-to-speech capabilities, allowing screen readers to convey the content to visually impaired users. Moreover, they allow users to navigate the document efficiently, providing screen reader users with a seamless reading experience. When your documents are accessible, you broaden your reach and cater to a broader audience. This inclusivity can increase website traffic and customer engagement, benefiting your business or organization.
How to Remediate an Inaccessible PDF?
Making an inaccessible PDF accessible isn’t about perfection; it’s about improving and providing access for all. Whether you have the original source document or just a PDF, here is a rundown of the best ways to enhance existing PDF documents for accessibility with the help of the right tools and processes. Contact ADA Siite Compliance today so we can make ALL your PDF documents fully accessible.
1. Determining the Accessibility Path for Each PDF Document
As PDFs can be generated in various ways, there is no cookie-cutter accessibility solution. Each document has and needs a unique solution. The good news is there are some tools like Adobe Acrobat Pro with multiple accessibility features, making the remediation process more manageable.
2. Starting with an Accessible Document
The journey to accessible PDFs begins with the source document. Whenever possible, it is always better to start the remediation process with the document title in native file formats. The reason is that any and all documents created in Word or desktop publishing software can be later easily exported as PDFs. This is a useful feature as it allows for adding additional text, headings, data table structures, other document structure tags, language definitions, and more.
3. Preventing Security Settings from Interfering with Screen Readers
Ensuring that screen readers can navigate your PDFs smoothly is an important step in remediating inaccessible PDFs in the form fields in the proper PDF format. It is always better to avoid copying, printing, extracting comments, or editing PDFs. The reason is that these actions can hinder accessibility. There are tools that can help you ensure that access permissions do not interfere with screen reading.
How to Make a PDF Compliant with Accessibility?
Achieving document accessibility in your PDFs is essential. It ensures that users with difficulties can at least use the help of assistive technologies like screen readers to interpret your whole document structure’s structure correctly. Besides, as mentioned earlier, compliance with ADA standards helps make your digital landscape more inclusive to reach out to more of your target audience and, in the process, generate more web traffic.
How do you make accessible PDF documents?
There are a few optimal practices to adhere to within reading order to make a PDF accessible documents, and they are to:
Make things simple; in other words, use simple language in the PDF
Ensure you include as many relevant headings and subheadings as possible
Including meaningful alt-text for all the images and graphics you have in your PDF
Ensuring the text in the PDF is not only readable but has sufficient contrast with the background for better readability
Not depending much on colors to convey information as it can be intimidating to users with color blindness
Always make more use of accessible tables and lists in PDF documents
Adding bookmarks where possible
Using a catchy and interesting title, and of course, specifying the language used in the PDF
Correctly tagging the different elements
Setting titles and metadata as and where appropriate
Adding captions to videos and other non-text content accessible
It is undoubtedly time-consuming to create accessible PDFs. However, the end result of a compliant, accessible PDF file, which increases your reach and reduces the chances of facing a legal lawsuit, makes the item invested well worth it. Besides, you can always use the help of PDF accessibility checkers for PDF document audits and verifications as per the latest accessibility standards. And if that’s too cumbersome, you can always have the experts take care of your PDF compliance while you focus on what you do the best!
Web Accessibility Provider
Ensuring web compliance is a multifaceted endeavor. It may seem to take lots of time and be confusing to many. It’s where web accessibility providers, like ADA Site Compliance, play a crucial role in ensuring your website and PDFs meet ADA standards. We have a team of accessibility experts who can help make web compliance so much easier and less time-consuming for you. With our expertise, we can ensure your site and all your PDFs are easily accessible to all, including individuals with disabilities.
In conclusion, the world of PDF accessibility and web compliance is multifaceted, but it’s a journey worth embarking on. By ensuring that your PDFs are accessible, you not only meet legal standards but also contribute to a more inclusive and diverse digital landscape. Together, we can make the Internet a place where everyone can access information and opportunities. Contact ADA Site Compliance for all your website accessibility needs today!
#PDF Accessibility#Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)#Create Accessible PDFs#PDF Accessibility Checkers#Accessibility Experts#PDF Accessibility Standards and Guidelines#PDF Accessibility Testing and Validation Tools#PDF Accessibility Remediation Services#PDF Accessibility Training and Certification#Benefits of PDF Accessibility and Compliance#PDF Accessibility Issues and Solutions#PDF Accessibility Features and Best Practices#PDF Accessibility Checker Software and Plugins#ada site compliance#web accessibility#accessibility services#diversity and inclusion#ada guidelines#inclusive design#accessible website development#ada compliance solutions#web accessibility audit#digital accessibility#equitable web design#ada regulations#inclusive user experience#ada consulting#accessible content#ada accessibility#web design for disabilities
0 notes
Text
autocrattic (more matt shenanigans, not tumblr this time)
I am almost definitely not the right person for this writeup, but I'm closer than most people on here, so here goes! This is all open-source tech drama, and I take my time laying out the context, but the short version is: Matt tried to extort another company, who immediately posted receipts, and now he's refusing to log off again. The long version is... long.
If you don't need software context, scroll down/find the "ok tony that's enough. tell me what's actually happening" heading, or just go read the pink sections. Or look at this PDF.
the background
So. Matt's original Good Idea was starting WordPress with fellow developer Mike Little in 2003, which is free and open-source software (FOSS) that was originally just for blogging, but now powers lots of websites that do other things. In particular, Automattic acquired WooCommerce a long time ago, which is free online store software you can run on WordPress.
FOSS is... interesting. It's a world that ultimately is powered by people who believe deeply that information and resources should be free, but often have massive blind spots (for example, Wikipedia's consistently had issues with bias, since no amount of "anyone can edit" will overcome systemic bias in terms of who has time to edit or is not going to be driven away by the existing contributor culture). As with anything else that people spend thousands of hours doing online, there's drama. As with anything else that's technically free but can be monetized, there are:
Heaps of companies and solo developers who profit off WordPress themes, plugins, hosting, and other services;
Conflicts between volunteer contributors and for-profit contributors;
Annoying founders who get way too much credit for everything the project has become.
the WordPress ecosystem
A project as heavily used as WordPress (some double-digit percentage of the Internet uses WP. I refuse to believe it's the 43% that Matt claims it is, but it's a pretty large chunk) can't survive just on the spare hours of volunteers, especially in an increasingly monetised world where its users demand functional software, are less and less tech or FOSS literate, and its contributors have no fucking time to build things for that userbase.
Matt runs Automattic, which is a privately-traded, for-profit company. The free software is run by the WordPress Foundation, which is technically completely separate (wordpress.org). The main products Automattic offers are WordPress-related: WordPress.com, a host which was designed to be beginner-friendly; Jetpack, a suite of plugins which extend WordPress in a whole bunch of ways that may or may not make sense as one big product; WooCommerce, which I've already mentioned. There's also WordPress VIP, which is the fancy bespoke five-digit-plus option for enterprise customers. And there's Tumblr, if Matt ever succeeds in putting it on WordPress. (Every Tumblr or WordPress dev I know thinks that's fucking ridiculous and impossible. Automattic's hiring for it anyway.)
Automattic devotes a chunk of its employees toward developing Core, which is what people in the WordPress space call WordPress.org, the free software. This is part of an initiative called Five for the Future — 5% of your company's profits off WordPress should go back into making the project better. Many other companies don't do this.
There are lots of other companies in the space. GoDaddy, for example, barely gives back in any way (and also sucks). WP Engine is the company this drama is about. They don't really contribute to Core. They offer relatively expensive WordPress hosting, as well as providing a series of other WordPress-related products like LocalWP (local site development software), Advanced Custom Fields (the easiest way to set up advanced taxonomies and other fields when making new types of posts. If you don't know what this means don't worry about it), etc.
Anyway. Lots of strong personalities. Lots of for-profit companies. Lots of them getting invested in, or bought by, private equity firms.
Matt being Matt, tech being tech
As was said repeatedly when Matt was flipping out about Tumblr, all of the stuff happening at Automattic is pretty normal tech company behaviour. Shit gets worse. People get less for their money. WordPress.com used to be a really good place for people starting out with a website who didn't need "real" WordPress — for $48 a year on the Personal plan, you had really limited features (no plugins or other customisable extensions), but you had a simple website with good SEO that was pretty secure, relatively easy to use, and 24-hour access to Happiness Engineers (HEs for short. Bad job title. This was my job) who could walk you through everything no matter how bad at tech you were. Then Personal plan users got moved from chat to emails only. Emails started being responded to by contractors who didn't know as much as HEs did and certainly didn't get paid half as well. Then came AI, and the mandate for HEs to try to upsell everyone things they didn't necessarily need. (This is the point at which I quit.)
But as was said then as well, most tech CEOs don't publicly get into this kind of shitfight with their users. They're horrid tyrants, but they don't do it this publicly.
ok tony that's enough. tell me what's actually happening
WordCamp US, one of the biggest WordPress industry events of the year, is the backdrop for all this. It just finished.
There are.... a lot of posts by Matt across multiple platforms because, as always, he can't log off. But here's the broad strokes.
Sep 17
Matt publishes a wanky blog post about companies that profit off open source without giving back. It targets a specific company, WP Engine.
Compare the Five For the Future pages from Automattic and WP Engine, two companies that are roughly the same size with revenue in the ballpark of half a billion. These pledges are just a proxy and aren’t perfectly accurate, but as I write this, Automattic has 3,786 hours per week (not even counting me!), and WP Engine has 47 hours. WP Engine has good people, some of whom are listed on that page, but the company is controlled by Silver Lake, a private equity firm with $102 billion in assets under management. Silver Lake doesn’t give a dang about your Open Source ideals. It just wants a return on capital. So it’s at this point that I ask everyone in the WordPress community to vote with your wallet. Who are you giving your money to? Someone who’s going to nourish the ecosystem, or someone who’s going to frack every bit of value out of it until it withers?
(It's worth noting here that Automattic is funded in part by BlackRock, who Wikipedia calls "the world's largest asset manager".)
Sep 20 (WCUS final day)
WP Engine puts out a blog post detailing their contributions to WordPress.
Matt devotes his keynote/closing speech to slamming WP Engine.
He also implies people inside WP Engine are sending him information.
For the people sending me stuff from inside companies, please do not do it on your work device. Use a personal phone, Signal with disappearing messages, etc. I have a bunch of journalists happy to connect you with as well. #wcus — Twitter I know private equity and investors can be brutal (read the book Barbarians at the Gate). Please let me know if any employee faces firing or retaliation for speaking up about their company's participation (or lack thereof) in WordPress. We'll make sure it's a big public deal and that you get support. — Tumblr
Matt also puts out an offer live at WordCamp US:
“If anyone of you gets in trouble for speaking up in favor of WordPress and/or open source, reach out to me. I’ll do my best to help you find a new job.” — source tweet, RTed by Matt
He also puts up a poll asking the community if WP Engine should be allowed back at WordCamps.
Sep 21
Matt writes a blog post on the WordPress.org blog (the official project blog!): WP Engine is not WordPress.
He opens this blog post by claiming his mom was confused and thought WP Engine was official.
The blog post goes on about how WP Engine disabled post revisions (which is a pretty normal thing to do when you need to free up some resources), therefore being not "real" WordPress. (As I said earlier, WordPress.com disables most features for Personal and Premium plans. Or whatever those plans are called, they've been renamed like 12 times in the last few years. But that's a different complaint.)
Sep 22: More bullshit on Twitter. Matt makes a Reddit post on r/Wordpress about WP Engine that promptly gets deleted. Writeups start to come out:
Search Engine Journal: WordPress Co-Founder Mullenweg Sparks Backlash
TechCrunch: Matt Mullenweg calls WP Engine a ‘cancer to WordPress’ and urges community to switch providers
Sep 23 onward
Okay, time zones mean I can't effectively sequence the rest of this.
Matt defends himself on Reddit, casually mentioning that WP Engine is now suing him.
Also here's a decent writeup from someone involved with the community that may be of interest.
WP Engine drops the full PDF of their cease and desist, which includes screenshots of Matt apparently threatening them via text.
Twitter link | Direct PDF link
This PDF includes some truly fucked texts where Matt appears to be trying to get WP Engine to pay him money unless they want him to tell his audience at WCUS that they're evil.
Matt, after saying he's been sued and can't talk about it, hosts a Twitter Space and talks about it for a couple hours.
He also continues to post on Reddit, Twitter, and on the Core contributor Slack.
Here's a comment where he says WP Engine could have avoided this by paying Automattic 8% of their revenue.
Another, 20 hours ago, where he says he's being downvoted by "trolls, probably WPE employees"
At some point, Matt updates the WordPress Foundation trademark policy. I am 90% sure this was him — it's not legalese and makes no fucking sense to single out WP Engine.
Old text: The abbreviation “WP” is not covered by the WordPress trademarks and you are free to use it in any way you see fit. New text: The abbreviation “WP” is not covered by the WordPress trademarks, but please don’t use it in a way that confuses people. For example, many people think WP Engine is “WordPress Engine” and officially associated with WordPress, which it’s not. They have never once even donated to the WordPress Foundation, despite making billions of revenue on top of WordPress.
Sep 25: Automattic puts up their own legal response.
anyway this fucking sucks
This is bigger than anything Matt's done before. I'm so worried about my friends who're still there. The internal ramifications have... been not great so far, including that Matt's naturally being extra gung-ho about "you're either for me or against me and if you're against me then don't bother working your two weeks".
Despite everything, I like WordPress. (If you dig into this, you'll see plenty of people commenting about blocks or Gutenberg or React other things they hate. Unlike many of the old FOSSheads, I actually also think Gutenberg/the block editor was a good idea, even if it was poorly implemented.)
I think that the original mission — to make it so anyone can spin up a website that's easy enough to use and blog with — is a good thing. I think, despite all the ways being part of FOSS communities since my early teens has led to all kinds of racist, homophobic and sexual harm for me and for many other people, that free and open-source software is important.
So many people were already burning out of the project. Matt has been doing this for so long that those with long memories can recite all the ways he's wrecked shit back a decade or more. Most of us are exhausted and need to make money to live. The world is worse than it ever was.
Social media sucks worse and worse, and this was a world in which people missed old webrings, old blogs, RSS readers, the world where you curated your own whimsical, unpaid corner of the Internet. I started actually actively using my own WordPress blog this year, and I've really enjoyed it.
And people don't want to deal with any of this.
The thing is, Matt's right about one thing: capital is ruining free open-source software. What he's wrong about is everything else: the idea that WordPress.com isn't enshittifying (or confusing) at a much higher rate than WP Engine, the idea that WP Engine or Silver Lake are the only big players in the field, the notion that he's part of the solution and not part of the problem.
But he's started a battle where there are no winners but the lawyers who get paid to duke it out, and all the volunteers who've survived this long in an ecosystem increasingly dominated by big money are giving up and leaving.
Anyway if you got this far, consider donating to someone on gazafunds.com. It'll take much less time than reading this did.
#tony muses#tumblr meta#again just bc that's my tag for all this#automattic#wordpress#this is probably really incoherent i apologise lmao#i may edit it
750 notes
·
View notes
Note
I see you mention Magical Archives a lot. Is that like an official artbook? Can I get it in English somewhere?
Hello hello! Thank you so much for this question, I have been hoping to write about this for weeks 🥳

The Magical Archives Game Guide vol. 1 (full name: 『ディズニー ツイステッドワンダーランド』公式ガイド+設定資料集 Magical Archives ) is maybe the single-most informative Twisted Wonderland resource available!
It includes a huge amount of extremely detailed information, from gameplay to the characters to early-stage development illustrations to a multi-page interview with Toboso Yana herself, only one of two that she has ever given on Twisted Wonderland.
While it may be described as an artbook it is also much, much more, and if you are only capable of purchasing one piece of Twst merchandise in your life, it is absolutely the #1 thing I would recommend.
First published in 2020 it is still available for purchase from outlets such as Square Enix's Online Store, Amazon, Rakuten, Animate and more.
It is not currently available in English, but for a brief while Aniplex USA was releasing "Player Guides" for free via social media:
These were multi-page PDFs that were, visually, quite similar to the first 1/3rd of the Magical Archives game guide, but with updated gameplay information.
These game-guide-inspired PDFs combined with how out of date the gameplay information in the original guide has since become makes me wonder if maybe there not are any plans for any official translation of the original Magical Archives :<
There has since been a second volume of the Magical Archives released (in September 2024), but it is not quite as detailed as its predecessor, including gameplay information and a huge library of game sprites but very few sketches from Yana and no interviews.
On the subject of translated art books, there actually is an official English-language book being released in December!

While its English-language title is "The Official Artbook," this is actually one of four books of a series called "Visual Books!"

Much like the magical archives the first volume is the most detailed, including pre-colored base art and the occasional messages from Yana to the colorist (re: a comment that there is no need to put any light in Rook's eyes for his labwear vignette groovy ww).
The Visual Book Series is not really comparable to the Magical Archives, consisting of pre- and post-groovy card art.

The "Design Note" might be the closest to the usual definition of "artbook," consisting of insight into event outfits worn by various characters and even including a few sketches of unused designs.
Unlike the Magical Archives, however, there are no behind-the-scenes notes such as "He has a black-hearted side, so he may laugh with a hint of that often" (about Trey) and "He has vertically-slit pupils that become round in dark places" (about Leona), which can only be found in the game guide.

There are also volumes 1 and 2 of the Art Gallery! These are collections of artwork by artists that are unaffiliated with Twisted Wonderland, depicting Twst's characters, much like Square-Enix-branded fan art (no contribution from Yana involved).
Lastly, there are the fanbooks! Contrary to their titles they do not consist of any fan-made content.

Volume 1 of the Fanbook mostly consists of character/story overview, but it also has some fascinating etymology information and exclusive interviews with several members of the voice cast!
The second fanbook focuses moreso on events, and also includes detailed recipes of Master Chef cuisine, a report on the since-concluded Twisted Wonderland Exhibition, a look into a Twst-themed hotel room in Tokyo Disneyland's Ambassador Hotel, and more.
And a third fanbook was just recently listed 🥳 (Amazon link), said to include event, card and story content from the 2nd to the 4th anniversaries.
I hope this helps! ^^
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 Days of Helping You Outline Your Next Novel

Day 5: Obsidian for Outlining
Find all 5 installments of the mini series: helping you outline your next novel
*I have added a layer of “static” over my screenshots so they are distinctive enough to stand apart from the surrounding text
did you miss this series? here you can find all posts here: [day 1] [day 2] [day 3] [day 4]

Do you use Obsidian?
What is Obsidian?
A note-taking and knowledge management tool that allows you to create and connect notes seamlessly.

Uses a local-first approach, meaning your data is stored on your computer, not the cloud (unless you choose to sync).
Features bidirectional linking, which helps create a non-linear, networked way of organizing ideas—great for brainstorming and outlining.
Why should you use Obsidian?
Flexible & Customizable – Unlike rigid writing apps, you can design your own workflow.
Distraction-Free Writing – Markdown keeps the focus on text without extra formatting distractions.
Ideal for Outlining & Organization – Connect story ideas, characters, and settings effortlessly.
Obsidian for Writing
Outlining
Creating a One Pager
Create a single markdown note for a high-level novel summary.
Use headings and bullet points for clarity.
Link to related notes (e.g., character pages, theme exploration).
Here’s an example of an outline I’m currently using. This is what my website will have on it (and what goals I hope to achieve w my website)

Using the Native Canvas Tool
Use Obsidian’s native Canvas tool to visually outline your novel. (Best on PC)
Create a board with columns for Acts, Chapters, or Story Beats.
Drag and drop cards as the story evolves.
Writing
Why Write Directly in Obsidian?
Minimalist interface reduces distractions.
Markdown-based formatting keeps the focus on words.
No auto-formatting issues (compared to Word or Google Docs).
Why is Obsidian Great for Writing?
Customizable workspace (plugins for word count, timers, and focus mode).
Easy to link notes (e.g., instantly reference past chapters or research).
Dark mode & themes for an optimal writing environment.
Organization in Obsidian
Outlining, Tags, Links
Each chapter, character, important item, and setting can have its own linked note.
Below, for example, you can see the purple text is a linked page directly in my outline.

Use bidirectional linking to create relationships between (story) elements. Clicking these links will automatically open the next page.
Tags can be used for important characters, items, places, or events that happen in your writing. Especially useful for tracking.
Folders for Efficient Storage
Organize notes into folders for Acts, Characters, Worldbuilding, and Drafts.
Use tags and backlinks for quick navigation.
Creating a separate folder for the actual writing and linking next (chapter) and previous (chapter) at the bottom for smooth navigation.
You can also create and reuse your own internal templates!
Spiderweb Map Feature (Graph View)
Visualize connections between characters, plot points, and themes. Below you’ll see the basic mapping of my website development project.

This view can help you spot disconnected (floating) ideas and create bridges to them.
Exporting
Why Export?
Ready to format in another program (Scrivener, Word, Docs, Vellum, etc).
Need a clean version (removing tags, notes, etc) for beta readers or editors.
Creating a backup copy of your work.
When should you export?
Personally, I like to export every 5 chapters or so and update my live version on Google Docs. This allows my family, friends, and beta readers to access my edited work.
After finishing a draft or major revision.
Before sending to an editor or formatting for publication.
Where should you export?
Personally I copy and paste my content from each chapter into a google doc for editing. You may also want to make note of the following export options:
Markdown to Word (.docx) – For editing or submitting.
Markdown to PDF – For quick sharing
Markdown to Scrivener – For those who format in Scrivener.
To Conclude
Obsidian is an invaluable tool for novelists who want a flexible, organized, and distraction-free writing process.
Try setting up your own Obsidian vault for your next novel! Comment below and let me know if this was helpful for you 🫶🏻

your reblogs help me help more ppl 💕
follow along for writing prompts, vocabulary lists, and helpful content like this! <333
✨ #blissfullyunawaresoriginals ✨
#writeblr#writers on tumblr#creative writing#writerscommunity#fiction#character development#writing prompt#dialogue prompt#female writers#writer blog#blissfullyunawaresoriginals#blissfullyunawares#writing life#fiction writing#writers#writer life#tumblr writers#writing inspiration#writing#writerslife#writer stuff#writing community#writer#obsidian for writing#obsidian#writers life#writing tool#writing tips#writer moots#tumblr moots
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dev Pile 2025-06 — Starter Kit
Making dev piles is a new experience for the blog in that they are explicitly deliberately timely. Where most of the work on this blog is thrown weeks, sometimes months in advance if it doesn’t fit neatly in a single spot, I am trying to make sure I write any given Dev Pile article covering the ‘week before’ the article goes up. This is a new kind of work for me, and it’s necessitated working ahead.
The week this article is being ‘written in’ is the week after Cancon. I had a plan for this week: I was going to spend the week writing an article developing the game dev I did, at cancon, in the dull periods at the table between the sales. Thing is, this year, that did not happen – Cancon was pretty much completely constant, so much so that the first day I didn’t even notice I never pulled out my notebook and what notes did get taken during the whole event were surface, or sketching out some minor ideas.
Therefore instead of a single intense focus here, this is going to be something of a hello and hey, here’s how to get started article about game making, tools, and prototyping.
Who Can Make Games?
You can make games. I can make games. Anyone who wants to can make games. The access you have to industrial scale production equipment to make the game you’re designing into something that looks like conventional product is a little more attainable than you may think, thanks to modern tools.
The core of you making games is this: Can you explain a set of rules to another player that let them understand how to play the game?
Great, then you’ve made a game. The next step is working out how to make that game the kind of game you want it to be. And to paraphrase what Adam Savage once said, the difference between doing game development and screwing around is just writing things down.
Tools
First things first, if you have a tool you like for any of the stated purposes, then you should use the tool you like. The tools I describe here should all be free, but that can make them less convenient in ways you may not like.
To write rulebooks, I use LibreOffice. This is a text editor in the same vein as Pages and Word, and much like Google Docs. We’ve pretty much solved ‘writing in a document for a computer user to read’ as a format, and that format has been kinda the same for thirty years. Notably, a formal editor like this lets you do tables and give texts formatting entries like heading styles, which means you don’t have to work to translate that stuff to a website like a wordpress content management system. Under the hood, these two things know how to talk to one another.
Notepad is a valuable tool as well for when you need ‘scrap’ text – no formatting, just some numbers or the like, but literally anything will do here.
Almost inevitably any given game design I have will need a spreadsheet. Sometimes a spreadsheet lets me present a skeleton of a game, with say, a sheet of 52 entries that just indicate the information on a card’s face. That means I use LibreCalc, but I only started using that seven months ago, when I learned about the IFS function. The version of Excel I was using from 2007 didn’t have this ‘new’ functionality, and I found that very useful. You may ask: How often do you need ‘IFS’ in game development and the answer is never. There are definitely thihngs I can use spreadsheets for, but these functions are not super necessary.
To do visual editing I use GIMP, pronounced ‘noo-imp,’ because gimp is a silly word to use in everyday conversation and it has worn its welcome out in my tongue. GIMP is a program that takes some getting used to, but the heart of what it is is a powerful photoshop-level program that puts almost everything it has directly under your control, including warp tools, healing tools, stamp tools and other simple filters. I will usually use GIMP to generate a template file or example for how a card should look, and then, when I want to put those cards into a file to make a pdf for printing, I turn to…
Scribus! Scribus is my layout and DTP program that I avoid using in every situation I can. I dislike Scribus interface a lot, and as a result, I route around it – I try to make sure that if I’m doing something in a design that Scribus ‘could’ do, I will ensure that Scribus is the only thing that can do it, and if something else can do it, I’ll do it that way. This is a combination of familiarity and convenience: Scribus is by no means a bad program, I’m sure, but I don’t like using it and it feels very easy to break things, which means when I do use it, I’m probably using it ‘wrong,’ and a Scribus expert would want to correct my technique.
For making simple slideshow videos, where I just show a thing, talk about it, and move on, I use the program OBS, which you can use for rules tutorials or explainers. OBS has its own ability to do slides – which you can make in a slideshow program like Google Slides or powerpoint or Prezi if you like – and then you talk over it, advancing the slides in OBS. It’s a very powerful, very flexible tool, but I can understand if it’s a bit overwhelming to start with.
If you want to record audio for your game, which is a cool thing to do, I use Audacity. It’s a simple audio program if you’re just using it for its basic functions, but it can be great if (for example) you want to record audio diaries of your creation process.
Also, mixed in with this is, cardboard, paper, scissors and glue. Playing cards need a standardised form so you can make a ‘blank’ deck of cards by taking an ordinary deck of cards and putting large, white, laundry stickers on each face, ‘wiping’ it so you can write what you want on the face.
Art Though?
I use free art where I can. There’s a lot of art assets, paid and free over on itch.io, which you can definitely use to make your game work look more interesting than base. And of course…
Bandaid tearing off time,
There are free image generators that you can use if you are comfortable with that. My advice is that you should only ever use generators for ‘zero value’ forms of media; that is, nothing you intend to sell and nothing you intend to use as identifying for yourself; don’t use a generator for a logo for your identity or brand, for example, because that’s uncopyrightable and then someone can just copy it. Even if they don’t, the fact they can undermines the copyright value of designing your own logo and title.
But yeah, image generators are available online. When I need an image for an example, the one I recommend using is dezgo, because it doesn’t require a login, doesn’t require you to pay money, and all it asks of you is time to let it finish working. You’re not going to get timely bulk media out of it, but that means, in my mind, that any artwork it generates is going to be worth scrutinising and editing to make it more appropriate to your needs. This is part of a greater conversation, but for now, the important thing is that if you’re going to use generative tools you need to make sure you recognise what they’re bad at and what they’re bad for.
Getting Started?
Alright, you have some tools to make what you have in mind more possible. What I recommend you do, and I will delve more into this later in the week, is make a prototype, and then, once you have the prototype, look at it seriously.
You’re going to have to get your head around the question what do I like without asking the followup question why at first. What is it about your prototype that satisfies you? What would you change if you could? Why isn’t it satisfying to you, what about it makes you concerned. Are there things you haven’t thought about because of biases you have? Is it a game you can’t play with one hand?
The point is the prototype marks the point you start finding out. You don’t need a perfect game to prototype – indeed, I have a lot of very ugly games as prototypes and I think those ugly prototypes work really well as a place to start working out what to do next.
Check it out on PRESS.exe to see it with images and links!
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Old Character Sheet, Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy
This isn’t really any new information about Eureka, in fact it’s something very old, but take a look at how far the game has come in the 3-ish years it’s been in development!

This is the old character sheet, from some time around late 2021, and I’m just going to copy-paste some designer commentary from a discussion about it in the A.N.I.M. Patreon Discord server.
“Haunt: What would eventually become the Composure system. I genuinely don't remember how it worked at the beginning but I remember it being rather clumsy. We eventually wanted to include the concept of different phenomena having different modifiers for each investigator, which would eventually become Tiers of Fear.
Obsession: An extremely early mechanic that would quickly vanish when, in the first campaign, it was clear it was too situational to track or use. The idea was that, the farther along to their goal an investigator got, the higher the bonus they could get from their Obsession, which could be applied when the investigator takes a very risky action to forward their goal. As you can tell, this was all very vague. This would eventually be replaced the much clearer Truth system.
Legal changed to Paperwork, just fit more situations better.
History skill: Too broad, so it was taken out. A good example of a write-in skill though, if given a specific area of history.
Rumors: Some sort of "word on the street" skill, but [sirobvious] raised a great point that that should just come from investigators using Personal Skills on NPCs to get that word themselves.
Weird -> ||Blacked Out Skill||
Improv: Honestly very difficult to describe, I think it was a Jackie Chan like thing of using various items around, but it was obviously too vague to use.
A lot of these changes came from [sirobvious joining the team], so big kudos to him!”
Another big change that came more recently was splitting the HP into Superficial and Penetrative, making the way that characters take damage in the kind of grounded, modern noir stories that Eureka is meant to tell a bit more realistic. Just having one type of HP works in most other TTRPGs, particularly ones where deadly weapons are going to be in play more often than not, but Eureka sees a lot of fistfighting.
You can take a look at the latest version of the character sheet in this post.
Check out our Kickstarter page for the best accumulation of info on what Eureka: investigative Urban Fantasy even is! The Kickstarter campaign launches April 10th 2024!
Check out our Patreon to get the whole prerelease rulebook + multiple adventure modules and pieces of short fiction for a subscription of only $5!
If you wanna try before you buy, check out our website for more information on Eureka as well as a download link to the free demo version!
Interested in actually playing this game, and many others, with the developers? Check out A.N.I.M.'s TTRPG Book Club, a club of nearly 100 members at the time of writing this where we regularly nominate, vote on, and then play indie TTRPGs! At the time of writing this, we are playing Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy, and sign-ups are closed for actually playing it, but you can still join in to pick up a PDF club copy of the rulebook to read and follow along with discussion, and sit in on and observe sessions! There is no schedule obligation for joining this club, as we keep things very flexible by assigning multiple GMs with different timeslots each round, to try and accomodate everyone! This round, we had over thirty people sign up, and were able to fit in all but one! Here is the invite link! See you there!

#eureka#eureka: investigative urban fantasy#ttrpg#monsters#roleplaying#coc#tabletop#rpg#tag#ttrpg design#ttrpg tumblr#ttrpg art#indie ttrpg#ttrpg community#ttrpg character#fantasy rpg#rpgs#free rpg#supernatural rpg#noir#film noir#detective#investigator#investigation#urban fantasy#fiction#original fiction
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Greetings goblins, goblettes, and gob-binary friends!
Do you like ROLE-PLAYING GAMES?
Of course you do, they’re fun and/or exciting.
And do you like DICE?
Well obviously, that’s what you use to play the role-playing games.
And do you like MATH?
Wait, wait, come back! I swear this is going to be interesting.
Allow me to introduce you to...
The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling.
An exciting new resource for tabletop game designers, or just simple dice enthusiasts.
Sure you can roll a d20, a d6, a d12, and maybe even a d100. But what about a d5, d40, or d16? Yes friend, with The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling you can learn to roll all those and many more, all without needing to run out to the specialty artisan dice shop!
How is that arcane task possible? With math of course!
The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling gives you all the eldritch mathematical techniques to divide and multiply standard dice to create new exciting and/or forbidden dice numbers you’d never imagined before!
But it’s much more than just that. The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling also delves into dice systems, going over how dice are used in your favorite—and even least favorite—games! Digging deep into the procedures, probabilities, advancement, popular variations, and pros and cons of roll-over, roll-under, dice pool, and dice index systems. Providing simple and essential information for aspiring tabletop game developers, or just players who want a little more insight into the math that’s going on behind the rules.

And all of that presented in a way that’s so simple even a goblin can understand!
My non-elite group of test goblins will ensure that everything in this book can be fully comprehended with only the most basic mathematical knowledge, if you understand that 20 − (3 + [16 ÷ 4] × 2) = 9, you already have all the maths you need to understand The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling!
And all that contained in one slim volume for easy travel. No more carrying around stacks of heavy dusty tomes that don’t even have information on dice mechanics. Seriously, why are you even carrying those?
So back now, so you can be the first of your friends to say “Actually, you can roll a d20 with a d10 and d12, if you use math!” which they will all think is very smart and cool.
Rewards
PDF Copy: Digital copy of The Goblin Guide to Advanced Dice Rolling, delivered through Itch.io
Print Zine: Physical copy that you can hold in your grubby little goblin hands. Shipping is included with pledge price. Unfortunately, due to uncertainty with the immediate future of international trade, international shipping will not be offered.
Community Copy: PDF versions of the guide made available to the community for free!
Signed and Numbered Zine: Print zine signed, numbered, and doodled on by the author and illustrator… who are both me! Numbering limited to however many actual backers at this level, and makes them more valuable for some reason.
Who am I, and why should you listen to me?
Excellent question, it’s always good to make sure folk are on the level before you give them your money.
I’m Z Gosck, a tabletop RPG reviewer and educator on YouTube where I have done in-depth coverage of over 100 different games—and read countless more in my free time. So it’s safe to say I know a thing or two about TTRPGs.
I'm also the designer of games such as Punktopia, 3 Raccoons in a Trench Coat, Now You Are A Zombie!, Satanic Panic: The Role-Playing Game, and many more. So I think we can say I know at least like three or four things.
In addition to all that TTRPG experience, I’m also a former supplemental mathematics instructor. So I also have specific experience in teaching math to people who are not particularly good at math.
========================
Kickstarter campaign ends: Sat, March 8 2025 7:59 AM UTC +00:00
Website: [Octopus Apocalypse] [twitter]
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Within hours of Luigi Mangione being charged with the murder of UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson on Monday, online stores were flooded with T-shirts, hoodies, mugs, stickers, and other merchandise praising the alleged shooter and featuring phrases like: “In this house, Luigi Mangione is a hero. End of story.”
On Etsy, WIRED found almost 100 listings featuring products with Mangione’s name or image. These include a tote bag featuring pictures of the alleged shooter alongside the phrase “Mama, I’m in love with a criminal” and PDF copies of a mocked-up cover of Time magazine featuring Mangione as Person of the Year and the tagline “Healthcare revolutionary, leading the charge to transform global health.”
These sellers are trying to cash in on the internet’s peculiar fascination with Mangione, whose good looks and privileged background have garnered him fans despite him being accused of a high-profile murder in broad daylight. The fascination with Mangione is a worrying trend, researchers say, that shows behavior that used to be confined to the fringes of the internet becoming mainstream.
Much of the merchandise is being sold by print-on-demand websites, which allow anyone to design and sell a range of products. On one such site, called My Porch Prints, one seller is offering a mug featuring a heart-shaped image of a topless Mangione alongside the words “I love my boyfriend.” A number of print-on-demand merchants are selling a stylized version of the Luigi character from Nintendo's Mario video games holding a gun and wearing a green hoodie. Another hoodie available on multiple online stores, including one called Chill Guy, features an image of Mangione surrounded by love hearts.
There are also multiple different T-shirts and hoodies being sold on sites like Nobele T-Shirt, featuring designs with the phrase “Free Luigi” on them, while many others use the phrase “Deny, Defend, Depose,” the words Mangione allegedly inscribed on some ammunition.
Finally, a T-shirt featuring the McDonald’s logo with the word Mangione superimposed on it is also being sold online by custom gift shop ModParty, referring to the fact Mangione was captured after staff at the fast food restaurant in Altoona, Pennsylvania, identified him and called the police.
Etsy, My Porch Prints, Chill Guy, Noble T-Shirts, and ModParty did not immediately respond to requests for comment.
This unusual situation meant that as internet sleuths worked to discover as much information about Mangione as possible, platforms such as YouTube and Instagram were working to shut down his accounts. X initially shut down Mangione’s account, but after CEO Elon Musk said he was "looking into it" the account was restored.
Google was also forced to remove reviews of the McDonald’s where Mangione was identified on Monday, after Mangione supporters review-bombed it with negative comments and one-star reviews.
Before his identity was revealed on Monday, his online supporters, primarily on TikTok, Bluesky, and X, had created an entire fictionalized version of the shooter as a left-wing revolutionary hero who was standing up for the millions of Americans whose lives have been impacted negatively by interactions with the health care system.
Videos glorifying the killer flooded TikTok, while one person decided to get a tattoo of the alleged shooter’s face. In Washington Square Park in New York City, a look-alike competition was held on Saturday.
Indeed, “Deny, Defend, Depose,” which is widely viewed as a pointed critique of the health insurance industry in America, has become a rallying cry online in recent days as the focus moved away from the shooting itself and onto the shooter and his motives.
However, the fictionalized version of the shooter that was created online does not match reality. Mangione, who allegedly had a handwritten manifesto admitting to the killing in his possession when arrested, is a software engineer from a privileged background. He also follows popular right-wing influencers, such as Tucker Carlson, Joe Rogan, and Jordan Peterson—though he has also criticized some of the arguments put forward by these figures.
During a brief court appearance on Monday night, the police did not outline a motive for the shooting, but based on Mangione’s online posts and reading lists, it appears that the pain from an injury suffered while surfing could have played a significant part in his motivation.
Despite Mangione not fitting the idealized hero that many online created in the time between the shooting and his arrest, the alleged shooter’s fans have continued to post fan fiction about him.
On Archive of Our Own, a repository of fan fiction, half a dozen pieces of prose about Mangione were posted in the hours after he was identified. In one piece entitled “McGuire Road Designated Dispersed Campsite,” an author with the username basedIdiot imagines Mangione and another man on a road trip trying to escape from New York. “‘Oh, am I not your beloved?’ Luigi Mangione mockingly fainted into the other man’s arms,” the author wrote.
In another, an anonymous author imagines Mangione in Texas where he is planning to assassinate Tesla, SpaceX, and X CEO Elon Musk, inscribing the bullets he was going to use to kill the billionaire. “For Musk, he’s kept it simple. X. X. And lastly, X. Mocking goodbye kisses,” the author wrote. “But also a reference to one spoilt, psychotic rich brat’s latest 44-billion-dollar toy to break.”
Another imagines the suspect as the author’s lover while at the University of Pennsylvania, where Mangione studied engineering. “Luigi Mangione turns to you,” writes an author with the username Princesscockdestroyer, who claims she’s writing this fan fiction during her final exams. “He mouths ‘I love you’ then takes off down the street. As you watch him disappear from you, from your life, from any promise of a future together, you can’t help but finally realize that you love him too.”
One of the posts imagines Mangione hooking up with a K-pop star in a motel in Ohio while on the run.
On TikTok, videos with images of Mangione’s smiling face, featuring the Britney Spears song “Criminal,” are also racking up tens of thousands of views, while hundreds of videos with the hashtag TeamLuigi have been posted on TikTok in the hours after Mangione was arrested.
A report published last week by the Network Contagion Research Institute called the phenomenon of online accounts glorifying the shooter as a “cause for concern,” pointing out that it mimics the type of response typically seen on fringe platforms like 4chan and 8chan in the wake of mass shootings.
“While this phenomenon was once largely confined to niche online subcultures, we are now witnessing similar dynamics emerging on mainstream platforms, amplifying the risk of further escalation,” the report’s authors wrote.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
PAID GIG -- Seeking Book Cover Artist for NA Queer Speculative Romance Duology
I AM ABLE TO PAY: $200 - $300 upfront and I will also obvs include your info --- you will get your own bio and can link whatever you want right by my bio and my links in the back of the book
What I'd really like to do is help out someone at the beginning of their career, as I am someone at the beginning of mine. I could totally go on fiverr, but I'd rather source from the fam. There are so many talented artists here and this website's done a lot for me in terms of developing my own craft and making connections. So here we are!
Here is the back cover synopsis of book one:
In every generation since the first cataclysmic use of the weapon, there has been a human designated the “Knight of Sol II.” The Knight’s job is to house the weapon’s activation switch within their body. In the event of another war between Earth II and alien homeworld Drune, the King Admiral must kill the Knight in order to extract the switch and use it. This arrangement — so it is hoped — ensures that the weapon will never be used lightly. Drew is the current Squire, next in line to be the Knight. It is a great honor. He’s terrified. Eighty years since the end of the war, the Emni — local, alien inhabitants of Drune — have finally achieved a long-sought goal: an exchange program, in which an Emni student is sent abroad to Earth II, where they will study amongst humans. Brave and blunt Riis is chosen as that envoy of exchange. His mission is complex, but laid out in simple terms: Make them like you. Speak the truth. Maybe they’ll stop killing us. Riis only really succeeds at getting Drew to like him. Which adds a whole new level of “complicated” to a relationship that never had a hope of being simple.
How to Apply: REBLOG this with your four BEST PIECES and tag it 'portfolio'
Like, your four BEST pieces that MOST CLOSELY fit the genre. Depending on how many people I get I might do a round two with more specific shit but yeah. If we vibe and I love your work we will move on into the sunset of making money and working together yaaaay
Have any questions? Inbox me for sure, I'd be thrilled to answer anything.
I would like to forge a long-term working relationship with an illustrator based on 1. me paying them and 2. them making art for my books and 3. not just for this, but potentially for future books if we really vibe and your style vibes with my next story. I average about 200,000 words a year (which for me means at minimum three books) and now that I've finally decided to bite the bullet and start publishing, there WILL be more work and you WILL get more exposure. I will also obvs be able to pay more and more each book if we do well.
Also --- anyone who is interested in reading an excerpt to get a feel for the work, pm me with your email address. I will gladly send over a pdf of the first chapter, and I of course will not share your email publicly.
Even if you are not interested, please reblog in case one of your followers is! Thank you so much tumblr fam <3
#illustration#seeking illustrator#paid art job#cover design#science fiction art#major points if you can guess which serial writer i had to hit up for permission to even write this#lol#don't worry he said i could#it's very INSPIRED BY THAT SERIAL THO
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introducing: Wolf in Shepherd's Clothing

CHAPTER: 1 of 3 STATUS: alpha review (script), thumbnailing (pages), sketches (character/set design) GENRE: fantasy, adventure WORLD: Urathla
Lahar is a shepherd who lives in the foothills outside of a nearby city. With their memory loss, it's hard to say if they've seen anything that's been causing the disappearing livestock of late. Unfortunately for them, they're the harbinger of a brand new magic, and a brand new curse.
Hello, everyone, and welcome to the intro post for my upcoming webcomic, Wolf in Shepherd's Clothing. Some of you may already know of its existence, and what inspires it.
Originally, this story was intended to be much shorter and based in real life Mesopotamia, or as much as I could manage, but as I continued developing the story, I realized that it was adopting more and more fantastical elements I would want to exercise full worldbuilding over, rather than rely on 'historical accuracy'. Thus it joined Urathla, a world I had created for my Arthurian legend-inspired novel, much for the same reasons.
The first chapter reckons with the shepherd and their family as they navigate regular life and regular strife, before coming to a cliffhanger I hope everyone will enjoy. The shepherd is Lahar, and their siblings are Halba, Uzalla, Myri, and Ensy. Masdaria is the four older childrens' stepmother, and Ensy's blood mother- with another baby on the way.
More details about these characters will come as soon as I can manage!
I will be posting all the pages FOR FREE on bsky, Ko-fi, and Tumblr, and hopefully if I can manage to make it work, my own website. I am not intending to post on X/Twitter or TikTok, but you're welcome to talk about it there. I may eventually share it on Webtoon or Tapas, but I'm a bit uncertain since this will NOT be a webtoon format- it will follow a page-by-page webcomic format.
The comic will be portrayed in grayscale, with possible 'pop' colors in chapters 2 and 3, like red or blue. This is still my own project, after all, and I'm going to be using that fact to help me control value and composition rather than using color as a crutch.
Further, my art style will almost certainly shift around as I continue drawing this story, and that is more or less intentional. I'm sorry to those who seek more consistent styles, but as an artist I am always learning and growing.
A pay-what-you-want (but ultimately free) HD PDF version will be available when the first chapter is completed, and a somewhat more expensive (around 3-5 USD) 'ultimate' version will also be available for those that are interested.
(Difference there being that the 'ultimate' edition will include a fancier, illustrated colored cover, no watermark across the pages, plus some other goodies like maps if I can manage to squeeze them in!)
Additionally, paid posts will be available on Ko-fi for monthly members. Namely, character and set design notes, early access to maps, and possibly even annotated pages if there's interest. I may also decide to color specific pages or panels, some of which may come to community vote if there's enough interest in that!
All the characters will receive completely free 'intro' pieces, plus simple turnarounds for those that want to make fanart. Paid posts will include sketches and more detailed turnarounds, plus my ramblings about their specific designs.
If there's enough interest, I may also combine these design notes into a PDF on the shop, but that's a later decision.
Feel free to ask questions on bsky, Ko-fi or Tumblr!
#wisc#wolf in shepherd's clothing#wip intro#i guess??#webcomic#original comic#dusk draws#my art#this is the first time i've ever actually drawn an intro 'banner' graphic and i think it slaps like hell
4 notes
·
View notes
Text




REVIEW: Astrovitae magazine Issue 2
Astrovitae is a magazine devoted to creators in the speculative fiction subgenre of speculative biology. Though people have imagined fantastic beasts and beings since the beginning of our species, speculative biology focuses on developing organisms using our current knowledge of biology, ecology, physics, geology and other sciences. Though even within these limits there is a wide spectrum, as some creators may work with strict hard science rules while others prefer to design fantastic beasts closer to myth and folklore.
This second issue of Astrovitae shows significant refinement from the already impressive first issue. There is a new section on speculative biology news featuring interviews, YouTube videos, Kickstarters, and new projects.. It’s a good way to keep abreast of the bewildering variety of speculative projects out there. This issue also features the first of a regular book review column, beginning with Christian Cline’s The Teeming Universe.
Collaborative projects are the focus of issue two, with articles on the online Discord-based Specposium convention, the Project Sil Discord, and a preview of Almost Real magazine. The latter showcases the Keraunoplast, fascinating slime mold-like organism that feeds directly on electricity and can actually bond with old space junk to form cybernetic life forms. This issue came out in September 2021, and it’s fascinating to see how the imposed quarantine of the Covid pandemic and the subsequent burst of more online communication through Discord, Instagram and other social media has led to the birth of so many new speculative biology projects.
Hyperlinks embedded in the Pdf pages are a really useful feature. Readers can click an article’s byline to go to the creator’s website or other social media. Clicking the section heading will also take one back to the table of contents.
As with the previous issue, Astrovitae #2 is divided into several sections: Captivating Worlds, with overviews of large world-building projects; Artist Spotlight, which looks at the creators themselves and their bodies of work as a whole; and Creature Compendium: which zooms in on individual organisms.
Captivating Worlds begins with an in-depth look at the natural history of Mathijs Megens’ Amethyst Beach Shield, a chemosynthetic armored organism.
The next entry, Domenic Pennetta’s Project Perditus is a survey of a world that resembles Earth in the early Paleozoic, with creatures that will feel familiar to many paleo-enthusiasts, while still retaining their own alien-ness.
The Alternate Cenozoic Project by Thien Anh Nguyen is a what-if about an earth where the large dinosaurs were not killed off by an impact form space, following in the tradition of works such as Dougal Dixon’s The New Dinosaurs, and the Speculative Dinosaur Project.
Sea Serpents of the Arthechocene by Alejandro Martínez Fluxá is set in the future after human-caused mass extinctions. With all the large pinnipeds and cetaceans gone, sea snakes evolve to fill the niche of large oceanic predators and filter-feeders, becoming the long, whale-like tiamats.
Evan Proctor’s Before Planet Feni is primarily an outline of the dominant species on the titular planet, as well as some background about the planet’s explorers. Hopefully there will be more to come in this work.
The World of Nijin-Konai by Lorenzo Battilani is a hard science look at a primarily aquatic alien world, delving into microbiology and genetics with a radiation resistant enzyme and redundant genes that allow the planet’s organisms to adapt to the lethal UV radiation of their native star. Battilani also discusses the complex neurological, metabolism and anatomy of his creature in minute detail that could have come from a college biology textbook.
Artist Spotlight features an article by YouTube creator Biblaridion detailing how their channel grew from a tutorial on concepts in evolutionary biology to a detailed study of a fictional world.
Reinhard Gutzat offers a meditation on the sometimes rocky intersection of creativity and biological accuracy during an artist’s development process.
Artist Sibilla Pepi offers a look at their design process as they develop a feathered wyvern based on the biology of real-life birds.
Creature Compendium showcases individual speculative creatures in the manner of pages taken from a field guide and includes a giant diving beetle, an alien tadpole, a balloon-like organisms that lives in the atmosphere of a gas planet, and more.
The authors write with the enthusiasm and vernacular of seasoned biologists well versed in scientific nomenclature. Their creatures are given unique taxonomic names and anatomical terms, adding greatly to their believability. These complex names can get a bit overwhelming, however, leading to what one might call “textbook burnout”. Sometimes I found it necessary to go back and reread articles to fully absorb all the names. This terminology might turn off a reader with a scientific background, but the imaginative variety on display should hold most interests. This is a minor critique, though, and the magazine overall is a professional-quality publication that would be at home in any library shelf. I am particularly pleased to see more projects focusing on the hypothetical evolution of Earthly creatures.
Astrovitae issue 2 is vailable both as a free downloadable PDF from the magazine’s website and as a virtual book that one can flip through on Yumpu.com
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Great news! I have uncovered another Cousin concept design!
About a year back, I was browsing the King’s Book when I found this lanky little Fujio with no facial hair! Look at him!

I uploaded it to Fujio’s page, thinking this would be the only early Cousin art available…
A year later, I am looking for a scan of Game Developer Magazine December 2004 (which is currently unavailable in full), which included a Katamari Damacy Postmortem. While I didn’t find a FULL scan, I did find two PDFs of the Katamari Damacy Postmortem and Uncanny Valley articles! And while reading the about the Uncanny Valley, look who I found!
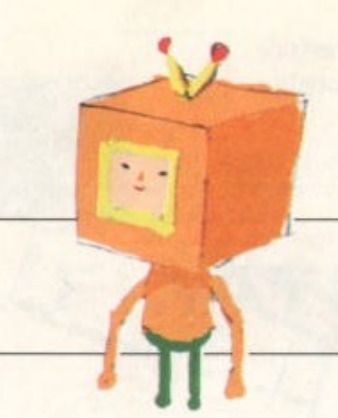
The Katamari Damacy Postmortem included two new pieces of concept art.


The first image shows animal and human concept designs which heavily resemble some of the other concept art displayed at Keita Takahashi’s Zooming Out. The second image shows some detail on the houses in Katamari Damacy. For more info on the archival of this magazine, please click below.
If you are interested in a text-only version of the Katamari Damacy Postmortem, it is viewable on Robin Hunicke’s blog archive here. (Please note that I do not support Robin Hunicke due to her workplace abuse allegations.) Unfortunately, the GD magazine has not been archived in full, contrary to what the people behind Game Developer’s Conference Vault have stated. The current website is broken, but the PDFs of other issues are available to view here. I have emailed GD, asking them to fix their website and to retrieve the issue, but they have yet to respond. If you own a copy or know someone who does, please upload it for preservation!

#katamari#katamari damacy#Katamari rarities#Fujio#shikao#concept art#keita takahashi#Lost media#game development
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hatchberries is a premier web design company known for creating visually stunning and user-friendly websites that drive engagement and conversions. Our team of skilled designers and developers work closely with clients to craft custom websites that reflect their brand identity and meet their business objectives. We prioritize responsive design, seamless navigation, and optimized performance to ensure an exceptional user experience across all devices. At Hatchberries, we combine creativity with technical expertise to deliver websites that not only look great but also perform exceptionally well in the digital landscape.
#digital marketing company in kerala#seo company in kochi#seo company in kerala#digital marketing company in kochi#web design company in kochi#webdesigncompanyinkerala#digital marketing agency in kochi#website design company kerala
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introducing Codetoolshub.com: Your One-Stop IT Tools Website
Hello everyone! I'm excited to introduce you to Codetoolshub.com, a comprehensive platform offering a variety of IT tools designed to enhance your productivity and efficiency. Our goal is to provide developers, IT professionals, and tech enthusiasts with easy-to-use online tools that can simplify their tasks. Here are some of the tools we offer:
Base64 File Converter
Basic Auth Generator
ASCII Text Drawer
PDF Signature Checker
Password Strength Analyser
JSON to CSV Converter
Docker Run to Docker Compose Converter
RSA Key Pair Generator
Crontab Generator
QR Code Generator
UUID Generator
XML Formatter
And many more...
We are constantly updating and adding new tools to meet your needs. Visit Codetoolshub.com to explore and start using these powerful and free tools today!
Thank you for your support, and we look forward to helping you with all your IT needs.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Skip to main content
Skip to Table of Contents
U.S. flag
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Notice
The Public Right-of-Way Accessibility Guidelines (PROWAG) rulemaking has concluded. The PROWAG final rule has been published in the Federal Register. Please visit the Access Board’s PROWAG page for the guidelines.
USAB star logo
U.S. Access Board
Advancing Full Access and Inclusion for All
Information and Communication Technology
Revised 508 Standards and 255 Guidelines
PDF
About the ICT Accessibility 508 Standards and 255 Guidelines
These standards address access to information and communication technology (ICT) under Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act and Section 255 of the Communications Act.
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act charges the Access Board with developing and promulgating this rule. The statute also charges the Access Board with providing Technical Assistance on Section 508, which is provided through webinars, trainings, and in close collaboration with GSA and materials available from Section508.gov.
Section 508 requires access to ICT developed, procured, maintained, or used by federal agencies. Examples include computers, telecommunications equipment, multifunction office machines such as copiers that also operate as printers, software, websites, information kiosks and transaction machines, and electronic documents. The Section 508 Standards, which are part of the Federal Acquisition Regulation, ensure access for people with physical, sensory, or cognitive disabilities.
The Section 255 Guidelines cover telecommunications equipment and customer-premises equipment — such as telephones, cell phones, routers, set-top boxes, and computers with modems, interconnected Voice over Internet Protocol products, and software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment.
Background
February 3, 1998 – The Board publishes the original Telecommunications Act Accessibility Guidelines.
December 21, 2000 – The Board issues the original Section 508 Standards.
July 6, 2006 – The Board organizes TEITAC, the Telecommunications and Electronic and Information Technology Advisory Committee, to assist in updating the Section 508 Standards and Telecommunications Act Guidelines.
April 3, 2008 – The Advisory Committee presents its final report to the Board.
March 22, 2010 – The Board releases a draft proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2010-0001.
December 8, 2011 – The Board issues a revised draft proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2011-0007.
February 27, 2015 – The Board ICT proposed rule for public comment, docket ATBCB-2015-0002.
January 18, 2017 – The Board issues the final rule, docket ATBCB-2015-0002-014.
January 22, 2018 – The Board issues correction to the final rule to restore provisions for TTY access, docket document ATBCB-2015-0002-0146.
Additional Resources
Section508.gov — GSA’s Government-wide IT Accessibility Program
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act (29 U.S.C. §794d)
Final Regulatory Impact Analysis (FRIA)
Comparison Table of WCAG 2.0 to Original 508 Standards
Mapping of WCAG 2.0 to Functional Performance Criteria
ICT Testing Baseline for Web Accessibility
Appendix A to Part 1194 – Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act: Application and Scoping Requirements
508 Chapter 1: Application and Administration
E101 General
E101.1 Purpose
These Revised 508 Standards, which consist of 508 Chapters 1 and 2 (Appendix A), along with Chapters 3 through 7 (Appendix C), contain scoping and technical requirements for information and communication technology (ICT) to ensure accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities. Compliance with these standards is mandatory for Federal agencies subject to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (29 U.S.C. 794d).
E101.2 Equivalent Facilitation
The use of an alternative design or technology that results in substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities than would be provided by conformance to one or more of the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 of the Revised 508 Standards is permitted. The functional performance criteria in Chapter 3 shall be used to determine whether substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability is provided to individuals with disabilities.
E101.3 Conventional Industry Tolerances
Dimensions are subject to conventional industry tolerances except where dimensions are stated as a range with specific minimum or maximum end points.
E101.4 Units of Measurement
Measurements are stated in metric and U.S. customary units. The values stated in each system (metric and U.S. customary units) may not be exact equivalents, and each system shall be used independently of the other.
E102 Referenced Standards
E102.1 Application
The specific editions of the standards listed in Chapter 7 are incorporated by reference into 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements) and Chapters 3 through 6 to the prescribed extent of each such reference. Where conflicts occur between the Revised 508 Standards and the referenced standards, these Revised 508 Standards apply.
E103 Definitions
E103.1 Terms Defined in Referenced Standards
Terms defined in referenced standards and not defined in E103.4 shall have the meaning as defined in the referenced standards.
E103.2 Undefined Terms
Any term not defined in E103.4 or in referenced standards shall be given its ordinarily accepted meaning in the sense that the context implies.
E103.3 Interchangeability
Words, terms, and phrases used in the singular include the plural and those used in the plural include the singular.
E103.4 Defined Terms
For the purpose of the Revised 508 Standards, the terms defined in E103.4 have the indicated meaning.
Agency
Any agency or department of the United States as defined in 44 U.S.C. 3502, and the United States Postal Service.
Alteration
A change to existing ICT that affects interoperability, the user interface, or access to information or data.
Application.
Software designed to perform, or to help the user to perform, a specific task or tasks.
Assistive Technology (AT)
Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Audio Description.
Narration added to the soundtrack to describe important visual details that cannot be understood from the main soundtrack alone. Audio description is a means to inform individuals who are blind or who have low vision about visual content essential for comprehension. Audio description of video provides information about actions, characters, scene changes, on-screen text, and other visual content. Audio description supplements the regular audio track of a program. Audio description is usually added during existing pauses in dialogue. Audio description is also called “video description” and “descriptive narration”.
Authoring Tool
Any software, or collection of software components, that can be used by authors, alone or collaboratively, to create or modify content for use by others, including other authors.
Closed Functionality
Characteristics that limit functionality or prevent a user from attaching or installing assistive technology. Examples of ICT with closed functionality are self-service machines, information kiosks, set-top boxes, fax machines, calculators, and computers that are locked down so that users may not adjust settings due to a policy such as Desktop Core Configuration.
Content
Electronic information and data, as well as the encoding that defines its structure, presentation, and interactions.
Document
Logically distinct assembly of content (such as a file, set of files, or streamed media) that: functions as a single entity rather than a collection; is not part of software; and does not include its own software to retrieve and present content for users. Examples of documents include, but are not limited to, letters, email messages, spreadsheets, presentations, podcasts, images, and movies.
Existing ICT
ICT that has been procured, maintained or used on or before January 18, 2018.
Hardware
A tangible device, equipment, or physical component of ICT, such as telephones, computers, multifunction copy machines, and keyboards.
Information Technology
Shall have the same meaning as the term “information technology” set forth in 40 U.S.C. 11101(6).
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information technology and other equipment, systems, technologies, or processes, for which the principal function is the creation, manipulation, storage, display, receipt, or transmission of electronic data and information, as well as any associated content. Examples of ICT include, but are not limited to: computers and peripheral equipment; information kiosks and transaction machines; telecommunications equipment; customer premises equipment; multifunction office machines; software; applications; Web sites; videos; and, electronic documents.
Keyboard
A set of systematically arranged alphanumeric keys or a control that generates alphanumeric input by which a machine or device is operated. A keyboard includes tactilely discernible keys used in conjunction with the alphanumeric keys if their function maps to keys on the keyboard interfaces.
Label
Text, or a component with a text alternative, that is presented to a user to identify content. A label is presented to all users, whereas a name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology. In many cases, the name and the label are the same.
Menu
A set of selectable options.
Name
Text by which software can identify a component to the user. A name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology, whereas a label is presented to all users. In many cases, the label and the name are the same. Name is unrelated to the name attribute in HTML.
Non-Web Document
A document that is not: a Web page, embedded in a Web page, or used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Non-Web Software
Software that is not: a Web page, not embedded in a Web page, and not used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Operable Part
Hardware-based user controls for activating, deactivating, or adjusting ICT.
Platform Accessibility Services
Services provided by a platform enabling interoperability with assistive technology. Examples are Application Programming Interfaces (API) and the Document Object Model (DOM).
Platform Software
Software that interacts with hardware or provides services for other software. Platform software may run or host other software, and may isolate them from underlying software or hardware layers. A single software component may have both platform and non-platform aspects. Examples of platforms are: desktop operating systems; embedded operating systems, including mobile systems; Web browsers; plug-ins to Web browsers that render a particular media or format; and sets of components that allow other applications to execute, such as applications which support macros or scripting.
Programmatically Determinable
Ability to be determined by software from author-supplied data that is provided in a way that different user agents, including assistive technologies, can extract and present the information to users in different modalities.
Public Facing
Content made available by an agency to members of the general public. Examples include, but are not limited to, an agency Web site, blog post, or social media pages.
Real-Time Text (RTT)
Communications using the transmission of text by which characters are transmitted by a terminal as they are typed. Real-time text is used for conversational purposes. Real-time text also may be used in voicemail, interactive voice response systems, and other similar application.
Revised 508 Standards
The standards for ICT developed, procured, maintained, or used by agencies subject to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act as set forth in 508 Chapters 1 and 2 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix A), and Chapters 3 through 7 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix C).
Software
Programs, procedures, rules, and related data and documentation that direct the use and operation of ICT and instruct it to perform a given task or function. Software includes, but is not limited to, applications, non-Web software, and platform software.
Software Tools
Software for which the primary function is the development of other software. Software tools usually come in the form of an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and are a suite of related products and utilities. Examples of IDEs include Microsoft® Visual Studio®, Apple® Xcode®, and Eclipse Foundation Eclipse®.
Telecommunications
The signal transmission, between or among points specified by the user, of information of the user’s choosing, without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
Terminal
Device or software with which the end user directly interacts and that provides the user interface. For some systems, the software that provides the user interface may reside on more than one device such as a telephone and a server.
Text
A sequence of characters that can be programmatically determined and that expresses something in human language.
TTY
Equipment that enables interactive text based communications through the transmission of frequency-shift-keying audio tones across the public switched telephone network. TTYs include devices for real-time text communications and voice and text intermixed communications. Examples of intermixed communications are voice carry over and hearing carry over. One example of a TTY is a computer with TTY emulating software and modem.
Variable Message Signs (VMS)
Non-interactive electronic signs with scrolling, streaming, or paging-down capability. An example of a VMS is an electronic message board at a transit station that displays the gate and time information associated with the next train arrival.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
A technology that provides real-time voice communications. VoIP requires a broadband connection from the user’s location and customer premises equipment compatible with Internet protocol.
Web page
A non-embedded resource obtained from a single Universal Resource Identifier (URI) using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) plus any other resources that are provided for the rendering, retrieval, and presentation of content.
508 Chapter 2: Scoping Requirements
E201 Application
E201.1 Scope
ICT that is procured, developed, maintained, or used by agencies shall conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202 General Exceptions
E202.1 General
ICT shall be exempt from compliance with the Revised 508 Standards to the extent specified by E202.
E202.2 Legacy ICT
Any component or portion of existing ICT that complies with an earlier standard issued pursuant to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (as republished in Appendix D), and that has not been altered on or after January 18, 2018, shall not be required to be modified to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.3 National Security Systems
The Revised 508 Standards do not apply to ICT operated by agencies as part of a national security system, as defined by 40 U.S.C. 11103(a).
E202.4 Federal Contracts
ICT acquired by a contractor incidental to a contract shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.5 ICT Functions Located in Maintenance or Monitoring Spaces
Where status indicators and operable parts for ICT functions are located in spaces that are frequented only by service personnel for maintenance, repair, or occasional monitoring of equipment, such status indicators and operable parts shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards.
E202.6 Undue Burden or Fundamental Alteration
Where an agency determines in accordance with E202.6 that conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards would impose an undue burden or would result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT, conformance shall be required only to the extent that it does not impose an undue burden, or result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT.
E202.6.1 Basis for a Determination of Undue Burden
In determining whether conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards would impose an undue burden on the agency, the agency shall consider the extent to which conformance would impose significant difficulty or expense considering the agency resources available to the program or component for which the ICT is to be procured, developed, maintained, or used.
E202.6.2 Required Documentation
The responsible agency official shall document in writing the basis for determining that conformance to requirements in the Revised 508 Standards constitute an undue burden on the agency, or would result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT. The documentation shall include an explanation of why and to what extent compliance with applicable requirements would create an undue burden or result in a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT.
E202.6.3 Alternative Means
Where conformance to one or more requirements in the Revised 508 Standards imposes an undue burden or a fundamental alteration in the nature of the ICT, the agency shall provide individuals with disabilities access to and use of information and data by an alternative means that meets identified needs.
E202.7 Best Meets
Where ICT conforming to one or more requirements in the Revised 508 Standards is not commercially available, the agency shall procure the ICT that best meets the Revised 508 Standards consistent with the agency’s business needs.
E202.7.1 Required Documentation
The responsible agency official shall document in writing: (a) the non-availability of conforming ICT, including a description of market research performed and which provisions cannot be met, and (b) the basis for determining that the ICT to be procured best meets the requirements in the Revised 508 Standards consistent with the agency’s business needs.
E202.7.2 Alternative Means
Where ICT that fully conforms to the Revised 508 Standards is not commercially available, the agency shall provide individuals with disabilities access to and use of information and data by an alternative means that meets identified needs.
E203 Access to Functionality
E203.1 General
Agencies shall ensure that all functionality of ICT is accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities, either directly or by supporting the use of assistive technology, and shall comply with E203. In providing access to all functionality of ICT, agencies shall ensure the following:
That Federal employees with disabilities have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to the access and use by Federal employees who are not individuals with disabilities; and
That members of the public with disabilities who are seeking information or data from a Federal agency have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to that provided to members of the public who are not individuals with disabilities.
E203.2 User Needs
When agencies procure, develop, maintain or use ICT they shall identify the needs of users with disabilities to determine:
How users with disabilities will perform the functions supported by the ICT; and
How the ICT will be developed, installed, configured, and maintained to support users with disabilities.
E204 Functional Performance Criteria
E204.1 General
Where the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 do not address one or more functions of ICT, the functions not addressed shall conform to the Functional Performance Criteria specified in Chapter 3.
E205 Electronic Content
E205.1 General
Electronic content shall comply with E205.
E205.2 Public Facing
Electronic content that is public facing shall conform to the accessibility requirements specified in E205.4.
E205.3 Agency Official Communication
Electronic content that is not public facing shall conform to the accessibility requirements specified in E205.4 when such content constitutes official business and is communicated by an agency through one or more of the following:
An emergency notification;
An initial or final decision adjudicating an administrative claim or proceeding;
An internal or external program or policy announcement;
A notice of benefits, program eligibility, employment opportunity, or personnel action;
A formal acknowledgement of receipt;
A survey questionnaire;
A template or form;
Educational or training materials; or
Intranet content designed as a Web page.
EXCEPTION: Records maintained by the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) pursuant to Federal recordkeeping statutes shall not be required to conform to the Revised 508 Standards unless public facing.
E205.4 Accessibility Standard
Electronic content shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTION: Non-Web documents shall not be required to conform to the following four WCAG 2.0 Success Criteria: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks, 2.4.5 Multiple Ways, 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation, and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
E205.4.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Documents
For non-Web documents, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “document” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page”. In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in a document” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page”.
E206 Hardware
E206.1 General
Where components of ICT are hardware and transmit information or have a user interface, such components shall conform to the requirements in Chapter 4.
E207 Software
E207.1 General
Where components of ICT are software and transmit information or have a user interface, such components shall conform to E207 and the requirements in Chapter 5.
EXCEPTION: Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to the requirements in Chapter 5.
E207.2 WCAG Conformance
User interface components, as well as the content of platforms and applications, shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTIONS:
Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to E207.2.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to the following four Success Criteria in WCAG 2.0: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks; 2.4.5 Multiple Ways; 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation; and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to Conformance Requirement 3 Complete Processes in WCAG 2.0.
E207.2.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Software
For non-Web software, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “software” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page”. In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in software” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
E207.3 Complete Processes for Non-Web Software
Where non-Web software requires multiple steps to accomplish an activity, all software related to the activity to be accomplished shall conform to WCAG 2.0 as specified in E207.2.
E208 Support Documentation and Services
E208.1 General
Where an agency provides support documentation or services for ICT, such documentation and services shall conform to the requirements in Chapter 6.
Appendix B to Part 1194 – Section 255 of the Communications Act: Application and Scoping Requirements
255 Chapter 1: Application and Administration
C101 General
C101.1 Purpose
These Revised 255 Guidelines, which consist of 255 Chapters 1 and 2 (Appendix B), along with Chapters 3 through 7 (Appendix C), contain scoping and technical requirements for the design, development, and fabrication of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment, content, and support documentation and services, to ensure accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities. These Revised 255 Guidelines are to be applied to the extent required by regulations issued by the Federal Communications Commission under Section 255 of the Communications Act of 1934, as amended (47 U.S.C. 255).
C101.2 Equivalent Facilitation
The use of an alternative design or technology that results in substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability by individuals with disabilities than would be provided by conformance to one or more of the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 of the Revised 255 Guidelines is permitted. The functional performance criteria in Chapter 3 shall be used to determine whether substantially equivalent or greater accessibility and usability is provided to individuals with disabilities.
C101.3 Conventional Industry Tolerances
Dimensions are subject to conventional industry tolerances except where dimensions are stated as a range with specific minimum or maximum end points.
C101.4 Units of Measurement
Measurements are stated in metric and U.S. customary units. The values stated in each system (metric and U.S. customary units) may not be exact equivalents, and each system shall be used independently of the other.
C102 Referenced Standards
C102.1 Application
The specific editions of the standards listed in Chapter 7 are incorporated by reference into 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements) and Chapters 3 through 6 to the prescribed extent of each such reference. Where conflicts occur between the Revised 255 Guidelines and the referenced standards, these Revised 255 Guidelines apply.
C103 Definitions
C103.1 Terms Defined in Referenced Standards
Terms defined in referenced standards and not defined in C103.4 shall have the meaning as defined in the referenced standards.
C103.2 Undefined Terms
Any term not defined in C103.4 or in referenced standards shall be given its ordinarily accepted meaning in the sense that the context implies.
C103.3 Interchangeability
Words, terms, and phrases used in the singular include the plural and those used in the plural include the singular.
C103.4 Defined Terms
For the purpose of the Revised 255 Guidelines, the terms defined in C103.4 have the indicated meaning.
Application
Software designed to perform, or to help the user perform, a specific task or tasks.
Assistive Technology (AT)
Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities.
Audio Description
Narration added to the soundtrack to describe important visual details that cannot be understood from the main soundtrack alone. Audio description is a means to inform individuals who are blind or who have low vision about visual content essential for comprehension. Audio description of video provides information about actions, characters, scene changes, on-screen text, and other visual content. Audio description supplements the regular audio track of a program. Audio description is usually added during existing pauses in dialogue. Audio description is also called “video description” and “descriptive narration.”
Authoring Tool
Any software, or collection of software components, that can be used by authors, alone or collaboratively, to create or modify content for use by others, including other authors.
Closed Functionality
Characteristics that limit functionality or prevent a user from attaching or installing assistive technology.
Content
Electronic information and data, as well as the encoding that defines its structure, presentation, and interactions.
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)
Equipment used on the premises of a person (other than a carrier) to originate, route, or terminate telecommunications service or interconnected VoIP service, including software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment. Examples of CPE are telephones, routers, switches, residential gateways, set-top boxes, fixed mobile convergence products, home networking adaptors and Internet access gateways which enable consumers to access communications service providers’ services and distribute them around their house via a Local Access Network (LAN).
Document
Logically distinct assembly of content (such as a file, set of files, or streamed media) that: functions as a single entity rather than a collection; is not part of software; and does not include its own software to retrieve and present content for users. Examples of documents include, but are not limited to, letters, email messages, spreadsheets, presentations, podcasts, images, and movies.
Hardware
A tangible device, equipment, or physical component of ICT, such as telephones, computers, multifunction copy machines, and keyboards.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information technology and other equipment, systems, technologies, or processes, for which the principal function is the creation, manipulation, storage, display, receipt, or transmission of electronic data and information, as well as any associated content.
Keyboard
A set of systematically arranged alphanumeric keys or a control that generates alphanumeric input by which a machine or device is operated. A keyboard includes tactilely discernible keys used in conjunction with the alphanumeric keys if their function maps to keys on the keyboard interfaces.
Label
Text, or a component with a text alternative, that is presented to a user to identify content. A label is presented to all users, whereas a name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology. In many cases, the name and the label are the same.
Manufacturer
A final assembler of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment that sells such equipment to the public or to vendors that sell to the public.
Menu
A set of selectable options.
Name
Text by which software can identify a component to the user. A name may be hidden and only exposed by assistive technology, whereas a label is presented to all users. In many cases, the label and the name are the same. Name is unrelated to the name attribute in HTML.
Non-Web Document
A document that is not: a Web page, embedded in a Web page, or used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Non-Web Software
Software that is not: a Web page, not embedded in a Web page, and not used in the rendering or functioning of Web pages.
Operable Part
Hardware-based user controls for activating, deactivating, or adjusting ICT.
Platform Accessibility Services
Services provided by a platform enabling interoperability with assistive technology. Examples are Application Programming Interfaces (API) and the Document Object Model (DOM).
Platform Software
Software that interacts with hardware or provides services for other software. Platform software may run or host other software, and may isolate them from underlying software or hardware layers. A single software component may have both platform and non-platform aspects. Examples of platforms are: desktop operating systems; embedded operating systems, including mobile systems; Web browsers; plug-ins to Web browsers that render a particular media or format; and sets of components that allow other applications to execute, such as applications which support macros or scripting.
Programmatically Determinable
Ability to be determined by software from author-supplied data that is provided in a way that different user agents, including assistive technologies, can extract and present the information to users in different modalities.
Real-Time Text (RTT)
Communications using the transmission of text by which characters are transmitted by a terminal as they are typed. Real-time text is used for conversational purposes. Real-time text also may be used in voicemail, interactive voice response systems, and other similar application.
Revised 255 Guidelines
The guidelines for telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment covered by Section 255 of the Communications Act as set forth in 255 Chapters 1 and 2 (36 CFR part 1194, Appendix B), and Chapters 3 through 7 (36 CFR part 1193, Appendix C).
Software
Programs, procedures, rules, and related data and documentation that direct the use and operation of ICT and instruct it to perform a given task or function. Software includes, but is not limited to, applications, non-Web software, and platform software.
Software Tools
Software for which the primary function is the development of other software. Software tools usually come in the form of an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) and are a suite of related products and utilities. Examples of IDEs include Microsoft® Visual Studio®, Apple® Xcode®, and Eclipse Foundation Eclipse®
Specialized Customer Premises Equipment
Assistive technology used by individuals with disabilities to originate, route, or terminate telecommunications or interconnected VoIP service. Examples are TTYs and amplified telephones.
Telecommunications
The signal transmission between or among points specified by the user of information and of the user’s choosing without change in the form or content of the information as sent and received.
Telecommunications Equipment
Equipment, other than customer premises equipment, used by a carrier to provide telecommunications service or interconnected VoIP service and includes software integral to the operation of telecommunications function of such equipment.
Terminal
Device or software with which the end user directly interacts and that provides the user interface. For some systems, the software that provides the user interface may reside on more than one device such as a telephone and a server.
Text
A sequence of characters that can be programmatically determined and that expresses something in human language.
TTY
Equipment that enables interactive text based communications through the transmission of frequency-shift-keying audio tones across the public switched telephone network. TTYs include devices for real-time text communications and voice and text intermixed communications. Examples of intermixed communications are voice carry over and hearing carry over. One example of a TTY is a computer with TTY emulating software and modem.
Variable Message Signs (VMS)
Non-interactive electronic signs with scrolling, streaming, or paging-down capability. An example of a VMS is an electronic message board at a transit station that displays the gate and time information associated with the next train arrival.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
A technology that provides real-time voice communications. VoIP requires a broadband connection from the user’s location and customer premises equipment compatible with Internet protocol.
Web page
A non-embedded resource obtained from a single Universal Resource Identifier (URI) using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) plus any other resources that are provided for the rendering, retrieval, and presentation of content.
255 Chapter 2: Scoping Requirements
C201 Application
C201.1 Scope
Manufacturers shall comply with the requirements in the Revised 255 Guidelines applicable to telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment (and related software integral to the operation of telecommunications functions) when newly released, upgraded, or substantially changed from an earlier version or model. Manufacturers shall also conform to the requirements in the Revised 255 Guidelines for support documentation and services, including electronic documents and Web-based product support.
C201.2. Readily Achievable
When a manufacturer determines that conformance to one or more requirements in Chapter 4 (Hardware) or Chapter 5 (Software) would not be readily achievable, it shall ensure that the equipment or software is compatible with existing peripheral devices or specialized customer premises equipment commonly used by individuals with disabilities to the extent readily achievable.
C201.3 Access to Functionality
Manufacturers shall ensure that telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment is accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities by providing direct access to all telecommunications functionality. Where manufacturers can demonstrate that it is not readily achievable for such equipment to provide direct access to all functionality, the equipment shall support the use of assistive technology and specialized customer premises equipment where readily achievable.
C201.4 Prohibited Reduction of Accessibility, Usability, and Compatibility
No change shall be undertaken that decreases, or has the effect of decreasing, the net accessibility, usability, or compatibility of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment.
EXCEPTION: Discontinuation of a product shall not be prohibited.
C201.5 Design, Development, and Fabrication
Manufacturers shall evaluate the accessibility, usability, and interoperability of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment during its product design, development, and fabrication.
C202 Functional Performance Criteria
C202.1 General
Where the requirements in Chapters 4 and 5 do not address one or more functions of telecommunications or customer premises equipment, the functions not addressed shall conform to the Functional Performance Criteria specified in Chapter 3.
C203 Electronic Content
C203.1 General
Electronic content that is integral to the use of telecommunications or customer premises equipment shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTION: Non-Web documents shall not be required to conform to the following four WCAG 2.0 Success Criteria: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks, 2.4.5 Multiple Ways, 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation, and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
C203.1.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Documents
For non-Web documents, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “document’ shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page.” In addition, in Success Criterion in 1.4.2, the phrase “in a document” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
C204 Hardware
C204.1 General
Where components of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment are hardware, and transmit information or have a user interface, those components shall conform to applicable requirements in Chapter 4.
EXCEPTION: Components of telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment shall not be required to conform to 402, 407.7, 407.8, 408, 412.8.4, and 415.
C205 Software
C205.1 General
Where software is integral to the use of telecommunications functions of telecommunications equipment or customer premises equipment and has a user interface, such software shall conform to C205 and applicable requirements in Chapter 5.
EXCEPTION: Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to the requirements in Chapter 5.
C205.2 WCAG Conformance
User interface components, as well as the content of platforms and applications shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
EXCEPTIONS:
Software that is assistive technology and that supports the accessibility services of the platform shall not be required to conform to C205.2.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to the following four Success Criteria in WCAG 2.0: 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks; 2.4.5 Multiple Ways; 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation; and 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
Non-Web software shall not be required to conform to Conformance Requirement 3 Complete Processes in WCAG 2.0.
C205.2.1 Word Substitution when Applying WCAG to Non-Web Software
For non-Web software, wherever the term “Web page” or “page” appears in WCAG 2.0 Level A and AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements, the term “software” shall be substituted for the terms “Web page” and “page.” In addition, in Success Criterion 1.4.2, the phrase “in software” shall be substituted for the phrase “on a Web page.”
C205.3 Complete Processes for Non-Web Software
Where non-Web software requires multiple steps to accomplish an activity, all software related to the activity to be accomplished shall conform to WCAG 2.0 as specified in C205.2.
C206 Support Documentation and Services
C206.1 General
Where support documentation and services are provided for telecommunications equipment and customer premises equipment, manufacturers shall ensure that such documentation and services conform to Chapter 6 and are made available upon request at no additional charge.
Appendix C to Part 1194 – Functional Performance Criteria and Technical Requirements
Chapter 3: Functional Performance Criteria
301 General
301.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 3 shall apply to ICT where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
302 Functional Performance Criteria
302.1 Without Vision
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user vision.
302.2 With Limited Vision
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that enables users to make use of limited vision.
302.3 Without Perception of Color
Where a visual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one visual mode of operation that does not require user perception of color.
302.4 Without Hearing
Where an audible mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user hearing.
302.5 With Limited Hearing
Where an audible mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that enables users to make use of limited hearing.
302.6 Without Speech
Where speech is used for input, control, or operation, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require user speech.
302.7 With Limited Manipulation
Where a manual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require fine motor control or simultaneous manual operations.
302.8 With Limited Reach and Strength
Where a manual mode of operation is provided, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that is operable with limited reach and limited strength.
302.9 With Limited Language, Cognitive, and Learning Abilities
ICT shall provide features making its use by individuals with limited cognitive, language, and learning abilities simpler and easier.
Chapter 4: Hardware
401 General
401.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 4 shall apply to ICT that is hardware where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
EXCEPTION: Hardware that is assistive technology shall not be required to conform to the requirements of this chapter.
402 Closed Functionality
402.1 General
ICT with closed functionality shall be operable without requiring the user to attach or install assistive technology other than personal headsets or other audio couplers, and shall conform to 402.
402.2 Speech-Output Enabled
ICT with a display screen shall be speech-output enabled for full and independent use by individuals with vision impairments.
EXCEPTIONS:
Variable message signs conforming to 402.5 shall not be required to be speech-output enabled.
Speech output shall not be required where ICT display screens only provide status indicators and those indicators conform to 409.
Where speech output cannot be supported due to constraints in available memory or processor capability, ICT shall be permitted to conform to 409 in lieu of 402.2.
Audible tones shall be permitted instead of speech output where the content of user input is not displayed as entered for security purposes, including, but not limited to, asterisks representing personal identification numbers.
Speech output shall not be required for: the machine location; date and time of transaction; customer account number; and the machine identifier or label.
Speech output shall not be required for advertisements and other similar information unless they convey information that can be used for the transaction being conducted.
402.2.1 Information Displayed On-Screen
Speech output shall be provided for all information displayed on-screen.
402.2.2 Transactional Outputs
Where transactional outputs are provided, the speech output shall audibly provide all information necessary to verify a transaction.
402.2.3 Speech Delivery Type and Coordination
Speech output shall be delivered through a mechanism that is readily available to all users, including, but not limited to, an industry standard connector or a telephone handset. Speech shall be recorded or digitized human, or synthesized. Speech output shall be coordinated with information displayed on the screen.
402.2.4 User Control
Speech output for any single function shall be automatically interrupted when a transaction is selected. Speech output shall be capable of being repeated and paused.
402.2.5 Braille Instructions
Where speech output is required by 402.2, braille instructions for initiating the speech mode of operation shall be provided. Braille shall be contracted and shall conform to 36 CFR part 1191, Appendix D, Section 703.3.1.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use shall not be required to conform to 402.2.5.
402.3 Volume
ICT that delivers sound, including speech output required by 402.2, shall provide volume control and output amplification conforming to 402.3.
EXCEPTION: ICT conforming to 412.2 shall not be required to conform to 402.3.
402.3.1 Private Listening
Where ICT provides private listening, it shall provide a mode of operation for controlling the volume. Where ICT delivers output by an audio transducer typically held up to the ear, a means for effective magnetic wireless coupling to hearing technologies shall be provided.
402.3.2 Non-private Listening
Where ICT provides non-private listening, incremental volume control shall be provided with output amplification up to a level of at least 65 dB. A function shall be provided to automatically reset the volume to the default level after every use.
402.4 Characters on Display Screens
At least one mode of characters displayed on the screen shall be in a sans serif font. Where ICT does not provide a screen enlargement feature, characters shall be 3/16 inch (4.8 mm) high minimum based on the uppercase letter “I”. Characters shall contrast with their background with either light characters on a dark background or dark characters on a light background.
402.5 Characters on Variable Message Signs
Characters on variable message signs shall conform to section 703.7 Variable Message Signs of ICC A117.1-2009 (incorporated by reference, see 702.6.1).
403 Biometrics
403.1 General
Where provided, biometrics shall not be the only means for user identification or control.
EXCEPTION: Where at least two biometric options that use different biological characteristics are provided, ICT shall be permitted to use biometrics as the only means for user identification or control.
404 Preservation of Information Provided for Accessibility
404.1 General
ICT that transmits or converts information or communication shall not remove non-proprietary information provided for accessibility or shall restore it upon delivery.
405 Privacy
405.1 General
The same degree of privacy of input and output shall be provided to all individuals. When speech output required by 402.2 is enabled, the screen shall not blank automatically.
406 Standard Connections
406.1 General
Where data connections used for input and output are provided, at least one of each type of connection shall conform to industry standard non-proprietary formats.
407 Operable Parts
407.1 General
Where provided, operable parts used in the normal operation of ICT shall conform to 407.
407.2 Contrast
Where provided, keys and controls shall contrast visually from background surfaces. Characters and symbols shall contrast visually from background surfaces with either light characters or symbols on a dark background or dark characters or symbols on a light background.
407.3 Input Controls
At least one input control conforming to 407.3 shall be provided for each function.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use with input controls that are audibly discernable without activation and operable by touch shall not be required to conform to 407.3.
407.3.1 Tactilely Discernible
Input controls shall be operable by touch and tactilely discernible without activation.
407.3.2 Alphabetic Keys
Where provided, individual alphabetic keys shall be arranged in a QWERTY-based keyboard layout and the “F” and “J” keys shall be tactilely distinct from the other keys.
407.3.3 Numeric Keys
Where provided, numeric keys shall be arranged in a 12-key ascending or descending keypad layout. The number five key shall be tactilely distinct from the other keys. Where the ICT provides an alphabetic overlay on numeric keys, the relationships between letters and digits shall conform to ITU-T Recommendation E.161 (incorporated by reference, see 702.7.1).
407.4 Key Repeat
Where a keyboard with key repeat is provided, the delay before the key repeat feature is activated shall be fixed at, or adjustable to, 2 seconds minimum.
407.5 Timed Response
Where a timed response is required, the user shall be alerted visually, as well as by touch or sound, and shall be given the opportunity to indicate that more time is needed.
407.6 Operation
At least one mode of operation shall be operable with one hand and shall not require tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist. The force required to activate operable parts shall be 5 pounds (22.2 N) maximum.
407.7 Tickets, Fare Cards, and Keycards
Where tickets, fare cards, or keycards are provided, they shall have an orientation that is tactilely discernible if orientation is important to further use of the ticket, fare card, or keycard.
407.8 Reach Height and Depth
At least one of each type of operable part of stationary ICT shall be at a height conforming to 407.8.2 or 407.8.3 according to its position established by the vertical reference plane specified in 407.8.1 for a side reach or a forward reach. Operable parts used with speech output required by 402.2 shall not be the only type of operable part complying with 407.8 unless that part is the only operable part of its type.
407.8.1 Vertical Reference Plane
Operable parts shall be positioned for a side reach or a forward reach determined with respect to a vertical reference plane. The vertical reference plane shall be located in conformance to 407.8.2 or 407.8.3.
407.8.1.1 Vertical Plane for Side Reach
Where a side reach is provided, the vertical reference plane shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) long minimum.
graphical representation of dimensions for vertical plane side reach
407.8.1.2 Vertical Plane for Forward Reach
Where a forward reach is provided, the vertical reference plane shall be 30 inches (760 mm) long minimum.
graphical representation of dimensions for vertical plane forward reach
407.8.2 Side Reach
Operable parts of ICT providing a side reach shall conform to 407.8.2.1 or 407.8.2.2. The vertical reference plane shall be centered on the operable part and placed at the leading edge of the maximum protrusion of the ICT within the length of the vertical reference plane. Where a side reach requires a reach over a portion of the ICT, the height of that portion of the ICT shall be 34 inches (865 mm) maximum.
407.8.2.1 Unobstructed Side Reach
Where the operable part is located 10 inches (255 mm) or less beyond the vertical reference plane, the operable part shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor.
graphical representation of dimensions for unobstructed side reach
407.8.2.2 Obstructed Side Reach
Where the operable part is located more than 10 inches (255 mm), but not more than 24 inches (610 mm), beyond the vertical reference plane, the height of the operable part shall be 46 inches (1170 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor. The operable part shall not be located more than 24 inches (610 mm) beyond the vertical reference plane.
graphical representation of dimensions for obstructed side reach
407.8.3 Forward Reach
Operable parts of ICT providing a forward reach shall conform to 407.8.3.1 or 407.8.3.2. The vertical reference plane shall be centered, and intersect with, the operable part. Where a forward reach allows a reach over a portion of the ICT, the height of that portion of the ICT shall be 34 inches (865 mm) maximum.
407.8.3.1 Unobstructed Forward Reach
Where the operable part is located at the leading edge of the maximum protrusion within the length of the vertical reference plane of the ICT, the operable part shall be 48 inches (1220 mm) high maximum and 15 inches (380 mm) high minimum above the floor.
graphical representation of dimensions for unobstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2 Obstructed Forward Reach
Where the operable part is located beyond the leading edge of the maximum protrusion within the length of the vertical reference plane, the operable part shall conform to 407.8.3.2. The maximum allowable forward reach to an operable part shall be 25 inches (635 mm).
graphical representation of dimensions for obstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2.1 Operable Part Height for ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach
The height of the operable part shall conform to Table 407.8.3.2.1.
Table 407.8.3.2.1 Operable Part Height for ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach Reach Depth Operable Part Height
Less than 20 inches (510 mm) 48 inches (1220 mm) maximum
20 inches (510 mm) to 25 inches (635 mm) 44 inches (1120 mm) maximum
graphical representation of dimensions for operable part height for obstructed forward reach
407.8.3.2.2 Knee and Toe Space under ICT with Obstructed Forward Reach
Knee and toe space under ICT shall be 27 inches (685 mm) high minimum, 25 inches (635 mm) deep maximum, and 30 inches (760 mm) wide minimum and shall be clear of obstructions.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach
EXCEPTIONS:
Toe space shall be permitted to provide a clear height of 9 inches (230 mm) minimum above the floor and a clear depth of 6 inches (150 mm) maximum from the vertical reference plane toward the leading edge of the ICT.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exception one
At a depth of 6 inches (150 mm) maximum from the vertical reference plane toward the leading edge of the ICT, space between 9 inches (230 mm) and 27 inches (685 mm) minimum above the floor shall be permitted to reduce at a rate of 1 inch (25 mm) in depth for every 6 inches (150 mm) in height.
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exception two
Supplemental graphic combining both Exceptions 1 and 2:
graphical representation of dimensions for knee and toe space for obstructed forward reach exceptions one and two
408 Display Screens
408.1 General
Where provided, display screens shall conform to 408.
408.2 Visibility
Where stationary ICT provides one or more display screens, at least one of each type of display screen shall be visible from a point located 40 inches (1015 mm) above the floor space where the display screen is viewed.
408.3 Flashing
Where ICT emits lights in flashes, there shall be no more than three flashes in any one-second period.
EXCEPTION: Flashes that do not exceed the general flash and red flash thresholds defined in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) are not required to conform to 408.3.
409 Status Indicators
409.1 General
Where provided, status indicators shall be discernible visually and by touch or sound.
410 Color Coding
410.1 General
Where provided, color coding shall not be used as the only means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element.
411 Audible Signals
411.1 General
Where provided, audible signals or cues shall not be used as the only means of conveying information, indicating an action, or prompting a response
412 ICT with Two-Way Voice Communication
412.1 General
ICT that provides two-way voice communication shall conform to 412.
412.2 Volume Gain
ICT that provides two-way voice communication shall conform to 412.2.1 or 412.2.2.
412.2.1 Volume Gain for Wireline Telephones
Volume gain conforming to 47 CFR 68.317 shall be provided on analog and digital wireline telephones.
412.2.2 Volume Gain for Non-Wireline ICT
A method for increasing volume shall be provided for non-wireline ICT.
412.3 Interference Reduction and Magnetic Coupling
Where ICT delivers output by a handset or other type of audio transducer that is typically held up to the ear, ICT shall reduce interference with hearing technologies and provide a means for effective magnetic wireless coupling in conformance with 412.3.1 or 412.3.2.
412.3.1 Wireless Handsets
ICT in the form of wireless handsets shall conform to ANSI/IEEE C63.19-2011 (incorporated by reference, see 702.5.1).
412.3.2 Wireline Handsets
ICT in the form of wireline handsets, including cordless handsets, shall conform to TIA-1083-B (incorporated by reference, see702.9.1).
412.4 Digital Encoding of Speech
ICT in IP-based networks shall transmit and receive speech that is digitally encoded in the manner specified by ITU-T Recommendation G.722.2 (incorporated by reference, see 702.7.2) or IETF RFC 6716 (incorporated by reference, see 702.8.1).
412.5 Real-Time Text Functionality
[Reserved].
412.6 Caller ID
Where provided, caller identification and similar telecommunications functions shall be visible and audible.
412.7 Video Communication
Where ICT provides real-time video functionality, the quality of the video shall be sufficient to support communication using sign language.
412.8 Legacy TTY Support
ICT equipment or systems with two-way voice communication that do not themselves provide TTY functionality shall conform to 412.8.
412.8.1 TTY Connectability
ICT shall include a standard non-acoustic connection point for TTYs.
412.8.2 Voice and Hearing Carry Over
ICT shall provide a microphone capable of being turned on and off to allow the user to intermix speech with TTY use.
412.8.3 Signal Compatibility
ICT shall support all commonly used cross-manufacturer non-proprietary standard TTY signal protocols where the system interoperates with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
412.8.4 Voice Mail and Other Messaging Systems
Where provided, voice mail, auto-attendant, interactive voice response, and caller identification systems shall be usable with a TTY.
413 Closed Caption Processing Technologies
413.1 General
Where ICT displays or processes video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide closed caption processing technology that conforms to 413.1.1 or 413.1.2.
413.1.1 Decoding and Display of Closed Captions
Players and displays shall decode closed caption data and support display of captions.
413.1.2 Pass-Through of Closed Caption Data
Cabling and ancillary equipment shall pass through caption data.
414 Audio Description Processing Technologies
414.1 General
Where ICT displays or processes video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide audio description processing technology conforming to 414.1.1 or 414.1.2.
414.1.1 Digital Television Tuners
Digital television tuners shall provide audio description processing that conforms to ATSC A/53 Digital Television Standard, Part 5 (2014) (incorporated by reference, see 702.2.1). Digital television tuners shall provide processing of audio description when encoded as a Visually Impaired (VI) associated audio service that is provided as a complete program mix containing audio description according to the ATSC A/53 standard.
414.1.2 Other ICT
ICT other than digital television tuners shall provide audio description processing.
415 User Controls for Captions and Audio Descriptions
415.1 General
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide user controls for closed captions and audio descriptions conforming to 415.1.
EXCEPTION: Devices for personal use shall not be required to conform to 415.1 provided that captions and audio descriptions can be enabled through system-wide platform settings.
415.1.1 Caption Controls
Where ICT provides operable parts for volume control, ICT shall also provide operable parts for caption selection.
415.1.2 Audio Description Controls
Where ICT provides operable parts for program selection, ICT shall also provide operable parts for the selection of audio description.
Chapter 5: Software
501 General
501.1 Scope
The requirements of Chapter 5 shall apply to software where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
EXCEPTION: Where Web applications do not have access to platform accessibility services and do not include components that have access to platform accessibility services, they shall not be required to conform to 502 or 503 provided that they conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
502 Interoperability with Assistive Technology
502.1 General
Software shall interoperate with assistive technology and shall conform to 502.
EXCEPTION: ICT conforming to 402 shall not be required to conform to 502.
502.2 Documented Accessibility Features
Software with platform features defined in platform documentation as accessibility features shall conform to 502.2.
502.2.1 User Control of Accessibility Features
Platform software shall provide user control over platform features that are defined in the platform documentation as accessibility features.
502.2.2 No Disruption of Accessibility Features
Software shall not disrupt platform features that are defined in the platform documentation as accessibility features.
502.3 Accessibility Services
Platform software and software tools that are provided by the platform developer shall provide a documented set of accessibility services that support applications running on the platform to interoperate with assistive technology and shall conform to 502.3. Applications that are also platforms shall expose the underlying platform accessibility services or implement other documented accessibility services.
502.3.1 Object Information
The object role, state(s), properties, boundary, name, and description shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.2 Modification of Object Information
States and properties that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.3 Row, Column, and Headers
If an object is in a data table, the occupied rows and columns, and any headers associated with those rows or columns, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.4 Values
Any current value(s), and any set or range of allowable values associated with an object, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.5 Modification of Values
Values that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.6 Label Relationships
Any relationship that a component has as a label for another component, or of being labeled by another component, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.7 Hierarchical Relationships
Any hierarchical (parent-child) relationship that a component has as a container for, or being contained by, another component shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.8 Text
The content of text objects, text attributes, and the boundary of text rendered to the screen, shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.9 Modification of Text
Text that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through assistive technology.
502.3.10 List of Actions
A list of all actions that can be executed on an object shall be programmatically determinable.
502.3.11 Actions on Objects
Applications shall allow assistive technology to programmatically execute available actions on objects.
502.3.12 Focus Cursor
Applications shall expose information and mechanisms necessary to track focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes of user interface components.
502.3.13 Modification of Focus Cursor
Focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes that can be set by the user shall be capable of being set programmatically, including through the use of assistive technology.
502.3.14 Event Notification
Notification of events relevant to user interactions, including but not limited to, changes in the component’s state(s), value, name, description, or boundary, shall be available to assistive technology.
502.4 Platform Accessibility Features
Platforms and platform software shall conform to the requirements in ANSI/HFES 200.2, Human Factors Engineering of Software User Interfaces — Part 2: Accessibility (2008) (incorporated by reference, see 702.4.1) listed below:
Section 9.3.3 Enable sequential entry of multiple (chorded) keystrokes;
Section 9.3.4 Provide adjustment of delay before key acceptance;
Section 9.3.5 Provide adjustment of same-key double-strike acceptance;
Section 10.6.7 Allow users to choose visual alternative for audio output;
Section 10.6.8 Synchronize audio equivalents for visual events;
Section 10.6.9 Provide speech output services; and
Section 10.7.1 Display any captions provided.
503 Applications
503.1 General
Applications shall conform to 503.
503.2 User Preferences
Applications shall permit user preferences from platform settings for color, contrast, font type, font size, and focus cursor.
EXCEPTION: Applications that are designed to be isolated from their underlying platform software, including Web applications, shall not be required to conform to 503.2.
503.3 Alternative User Interfaces
Where an application provides an alternative user interface that functions as assistive technology, the application shall use platform and other industry standard accessibility services.
503.4 User Controls for Captions and Audio Description
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, ICT shall provide user controls for closed captions and audio descriptions conforming to 503.4.
503.4.1 Caption Controls
Where user controls are provided for volume adjustment, ICT shall provide user controls for the selection of captions at the same menu level as the user controls for volume or program selection.
503.4.2 Audio Description Controls
Where user controls are provided for program selection, ICT shall provide user controls for the selection of audio descriptions at the same menu level as the user controls for volume or program selection.
504 Authoring Tools
504.1 General
Where an application is an authoring tool, the application shall conform to 504 to the extent that information required for accessibility is supported by the destination format.
504.2 Content Creation or Editing
Authoring tools shall provide a mode of operation to create or edit content that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) for all supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool. Authoring tools shall permit authors the option of overriding information required for accessibility.
EXCEPTION: Authoring tools shall not be required to conform to 504.2 when used to directly edit plain text source code.
504.2.1 Preservation of Information Provided for Accessibility in Format Conversion
Authoring tools shall, when converting content from one format to another or saving content in multiple formats, preserve the information required for accessibility to the extent that the information is supported by the destination format.
504.2.2 PDF Export
Authoring tools capable of exporting PDF files that conform to ISO 32000-1:2008 (PDF 1.7) shall also be capable of exporting PDF files that conform to ANSI/AIIM/ISO 14289-1:2016 (PDF/UA-1) (incorporated by reference, see 702.3.1).
504.3 Prompts
Authoring tools shall provide a mode of operation that prompts authors to create content that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) for supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool.
504.4 Templates
Where templates are provided, templates allowing content creation that conforms to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1) shall be provided for a range of template uses for supported features and, as applicable, to file formats supported by the authoring tool.
Chapter 6: Support Documentation and Services
601 General
601.1 Scope
The technical requirements in Chapter 6 shall apply to ICT support documentation and services where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where otherwise referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
602 Support Documentation
602.1 General
Documentation that supports the use of ICT shall conform to 602.
602.2 Accessibility and Compatibility Features
Documentation shall list and explain how to use the accessibility and compatibility features required by Chapters 4 and 5. Documentation shall include accessibility features that are built-in and accessibility features that provide compatibility with assistive technology.
602.3 Electronic Support Documentation
Documentation in electronic format, including Web-based self-service support, shall conform to Level A and Level AA Success Criteria and Conformance Requirements in WCAG 2.0 (incorporated by reference, see 702.10.1).
602.4 Alternate Formats for Non-Electronic Support Documentation
Where support documentation is only provided in non-electronic formats, alternate formats usable by individuals with disabilities shall be provided upon request.
603 Support Services
603.1 General
ICT support services including, but not limited to, help desks, call centers, training services, and automated self-service technical support, shall conform to 603.
603.2 Information on Accessibility and Compatibility Features
ICT support services shall include information on the accessibility and compatibility features required by 602.2.
603.3 Accommodation of Communication Needs
Support services shall be provided directly to the user or through a referral to a point of contact. Such ICT support services shall accommodate the communication needs of individuals with disabilities.
Chapter 7: Referenced Standards
701 General
701.1 Scope
The standards referenced in Chapter 7 shall apply to ICT where required by 508 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), 255 Chapter 2 (Scoping Requirements), and where referenced in any other chapter of the Revised 508 Standards or Revised 255 Guidelines.
702 Incorporation by Reference
702.1 Approved IBR Standards
The Director of the Office of the Federal Register has approved these standards for incorporation by reference into this part in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR part 51. Copies of the referenced standards may be inspected at the U.S. Access Board, 1331 F Street, NW, Suite 1000, Washington, DC 20004, (202) 272-0080, and may also be obtained from the sources listed below. They are also available for inspection at the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). For information on the availability of this material at NARA, call 202–741–6030 or go to National Archives Code of Federal Regulations Incorporation by Reference.
702.2 Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Advanced Television Systems Committee, 1776 K Street NW, Suite 200, Washington, DC 20006–2304.
702.2.1 ATSC A/53 Part 5:2014
Digital Television Standard, Part 5—AC-3 Audio System Characteristics, August 28, 2014.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 414.1.1.
702.3 Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from AIIM, 1100 Wayne Ave., Ste. 1100, Silver Spring, Maryland 20910.
702.3.1 ANSI/AIIM/ISO 14289-1-2016
Document Management Applications — Electronic Document File Format Enhancement for Accessibility — Part 1: Use of ISO 32000-1 (PDF/UA-1), ANSI-approved February 8, 2016.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 504.2.2.
702.4 Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (HFES)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, P.O. Box 1369, Santa Monica, CA 90406–1369.
702.4.1 ANSI/HFES 200.2
Human Factors Engineering of Software User Interfaces — Part 2: Accessibility, copyright 2008.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 502.4.
702.5 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 10662 Los Vaqueros Circle, P.O. Box 3014, Los Alamitos, CA 90720–1264.
702.5.1 ANSI/IEEE C63.19-2011
American National Standard for Methods of Measurement of Compatibility between Wireless Communications Devices and Hearing Aids, May 27, 2011.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.3.1.
702.6 International Code Council (ICC)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from ICC Publications, 4051 W. Flossmoor Road, Country Club Hills, IL 60478–5795.
702.6.1 ICC A117.1-2009
Accessible and Usable Buildings and Facilities, approved October 20, 2010.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 402.5.
702.7 International Telecommunications Union Telecommunications Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
Copies of the referenced standards may be obtained from the International Telecommunication Union, Telecommunications Standardization Sector, Place des Nations CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
702.7.1 ITU-T Recommendation E.161
Series E. Overall Network Operation, Telephone Service, Service Operation and Human Factors—International operation - Numbering plan of the international telephone service, Arrangement of digits, letters and symbols on telephones and other devices that can be used for gaining access to a telephone network, February 2001.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 407.3.3.
702.7.2 ITU-T Recommendation G.722.2
Series G. Transmission Systems and Media, Digital Systems and Networks – Digital terminal equipment – Coding of analogue signals by methods other than PCM, Wideband coding of speech at around 16 kbit/s using Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB), July 2003.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.4.
702.8 Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the Internet Engineering Task Force.
702.8.1 IETF RFC 6716
Definition of the Opus Codec, September 2012, J.M. Valin, Mozilla Corporation, K. Vos, Skype Technologies S.A., T. Terriberry, Mozilla Corporation.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.4.
702.9 Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
Copies of the referenced standard, published by the Telecommunications Industry Association, may be obtained from IHS Markit, 15 Inverness Way East, Englewood, CO 80112.
702.9.1 TIA-1083-B
Telecommunications—Communications Products—Handset Magnetic Measurement Procedures and Performance Requirements, October 2015.
IBR approved for Appendix C, Section 412.3.2.
702.10 Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C)
Copies of the referenced standard may be obtained from the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 32 Vassar Street, Room 32-G515, Cambridge, MA 02139.
702.10.1 WCAG 2.0
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0, W3C Recommendation, December 11, 2008.
IBR approved for: Appendix A (Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act: Application and Scoping Requirements), Sections E205.4, E205.4 Exception, E205.4.1, E207.2, E207.2 Exception 2, E207.2 Exception 3, E207.2.1, E207.3; Appendix B (Section 255 of the Communications Act: Application and Scoping Requirements), C203.1, C203.1 Exception, C203.1.1, C205.2, C205.2 Exception 2, C205.2 Exception 3, C205.2.1, C205.3; and Appendix C (Functional Performance Criteria and Technical Requirements), 408.3 Exception, 501.1 Exception, 504.2, 504.3, 504.4, and 602.3.
Appendix D to Part 1194: Electronic and Information Technology Accessibility Standards as Originally Published on December 21, 2000
[65 FR 80523, Dec. 21, 2000. Redesignated and amended at 82 FR 5832, Jan. 18, 2017]
Subpart A — General
§ D1194.1 Purpose.
The purpose of this part is to implement section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended (29 U.S.C. 794d). Section 508 requires that when Federal agencies develop, procure, maintain, or use electronic and information technology, Federal employees with disabilities have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to the access and use by Federal employees who are not individuals with disabilities, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency. Section 508 also requires that individuals with disabilities, who are members of the public seeking information or services from a Federal agency, have access to and use of information and data that is comparable to that provided to the public who are not individuals with disabilities, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency.
§ D1194.2 Application.
(a) Products covered by this part shall comply with all applicable provisions of this part. When developing, procuring, maintaining, or using electronic and information technology, each agency shall ensure that the products comply with the applicable provisions of this part, unless an undue burden would be imposed on the agency.
(1) When compliance with the provisions of this part imposes an undue burden, agencies shall provide individuals with disabilities with the information and data involved by an alternative means of access that allows the individual to use the information and data.
(2) When procuring a product, if an agency determines that compliance with any provision of this part imposes an undue burden, the documentation by the agency supporting the procurement shall explain why, and to what extent, compliance with each such provision creates an undue burden.
(b) When procuring a product, each agency shall procure products which comply with the provisions in this part when such products are available in the commercial marketplace or when such products are developed in response to a Government solicitation. Agencies cannot claim a product as a whole is not commercially available because no product in the marketplace meets all the standards. If products are commercially available that meet some but not all of the standards, the agency must procure the product that best meets the standards.
(c) Except as provided by §1194.3(b), this part applies to electronic and information technology developed, procured, maintained, or used by agencies directly or used by a contractor under a contract with an agency which requires the use of such product, or requires the use, to a significant extent, of such product in the performance of a service or the furnishing of a product.
§ 1194.3 General exceptions.
(a) This part does not apply to any electronic and information technology operated by agencies, the function, operation, or use of which involves intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces, equipment that is an integral part of a weapon or weapons system, or systems which are critical to the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions. Systems which are critical to the direct fulfillment of military or intelligence missions do not include a system that is to be used for routine administrative and business applications (including payroll, finance, logistics, and personnel management applications).
(b) This part does not apply to electronic and information technology that is acquired by a contractor incidental to a contract.
(c) Except as required to comply with the provisions in this part, this part does not require the installation of specific accessibility-related software or the attachment of an assistive technology device at a workstation of a Federal employee who is not an individual with a disability.
(d) When agencies provide access to the public to information or data through electronic and information technology, agencies are not required to make products owned by the agency available for access and use by individuals with disabilities at a location other than that where the electronic and information technology is provided to the public, or to purchase products for access and use by individuals with disabilities at a location other than that where the electronic and information technology is provided to the public.
(e) This part shall not be construed to require a fundamental alteration in the nature of a product or its components.
(f) Products located in spaces frequented only by service personnel for maintenance, repair, or occasional monitoring of equipment are not required to comply with this part.
§ D1194.4 Definitions.
The following definitions apply to this part:
Agency
Any Federal department or agency, including the United States Postal Service.
Alternate formats
Alternate formats usable by people with disabilities may include, but are not limited to, Braille, ASCII text, large print, recorded audio, and electronic formats that comply with this part.
Alternate methods
Different means of providing information, including product documentation, to people with disabilities. Alternate methods may include, but are not limited to, voice, fax, relay service, TTY, Internet posting, captioning, text-to-speech synthesis, and audio description.
Assistive technology
2 notes
·
View notes