#Environmental Change
Text
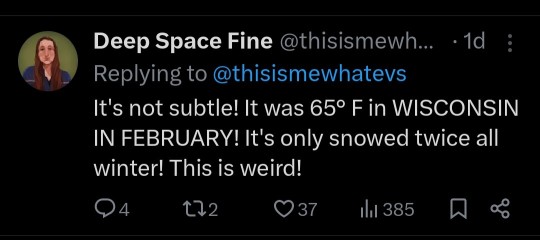
"The record-breaking heatwave experienced across Europe this summer will be considered an “average” summer by 2035, even if countries meet their current climate commitments so far agreed in negotiations under the 2015 Paris Agreement."
This is only 13 years from now...
#sad#climate change#climate crisis#summer#hot#heatwave#heatwaves#deadly heat#planet#environment#environmental change#this makes me feel so sad#europe#2035#future#this isn't too far in the future#13 years
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
118K notes
·
View notes
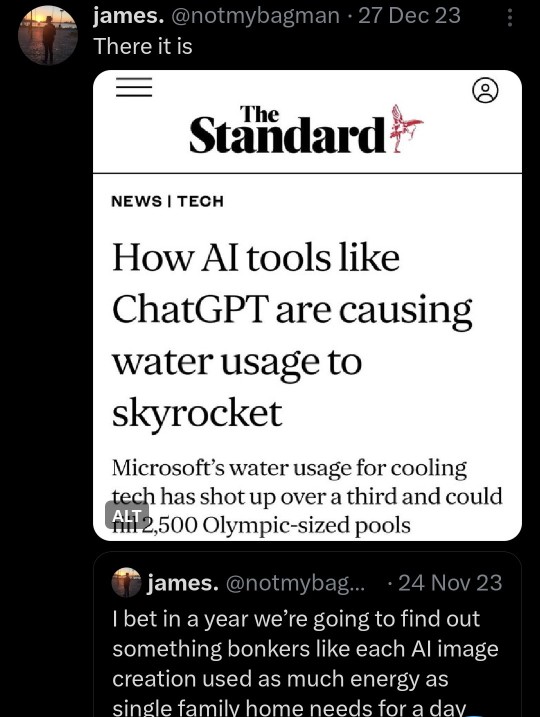
Text


Source
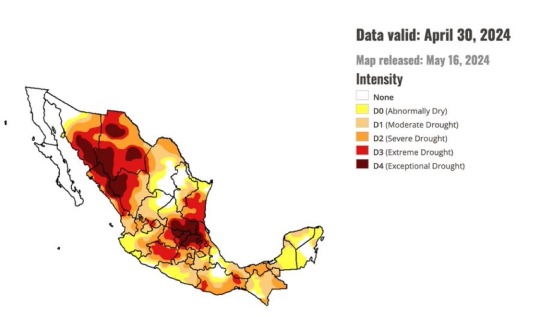
Source
#environment#Mexico#news#climate change#government#the left#progressive#twitter post#activism#current events#drought#environmentalism
23K notes
·
View notes
Text
Bro, you ok? Bro, humans aren’t separate from the ecosystems around us. We’re a part of them, bro. Bro, we’re never going to have absolutely zero effect on ecosystems, because we live here, bro. Bro, I never said it had to be a bad effect. We don’t have to immediately be perfect either, bro, sometimes doing what you can is what you can, and its way better than nothing. Bro what do you mean humans are a plague. You’re starting to sound a bit like an ecofascist, bro… Bro?
55K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sowing Seeds of Change: Richard St. Barbe Baker's Green Legacy

View On WordPress
#African Canopy#Arborial Ballet#Biodiversity Conservation#Canada#Canopy of Change#Community Empowerment#Community Science#Conservation Efforts#Conservation Legacy#Conservation Symphony#Conservation Wisdom#Cultural Connection#Cultural Unity#Dance of the Trees#desertification#Drought Resilience#Earth Conservation#earth&039;s wonders#Earthly Roots#Eco-friendly Practices#Ecological Impact#Ecological Resilience#Environmental Activism#Environmental Alchemist#Environmental Alchemy#environmental awareness#Environmental Awareness Campaigns#Environmental Ballet#Environmental Canopy#Environmental Change
0 notes
Text
No paywall version here.
"Two and a half years ago, when I was asked to help write the most authoritative report on climate change in the United States, I hesitated...
In the end, I said yes, but reluctantly. Frankly, I was sick of admonishing people about how bad things could get. Scientists have raised the alarm over and over again, and still the temperature rises. Extreme events like heat waves, floods and droughts are becoming more severe and frequent, exactly as we predicted they would. We were proved right. It didn’t seem to matter.
Our report, which was released on Tuesday, contains more dire warnings. There are plenty of new reasons for despair. Thanks to recent scientific advances, we can now link climate change to specific extreme weather disasters, and we have a better understanding of how the feedback loops in the climate system can make warming even worse. We can also now more confidently forecast catastrophic outcomes if global emissions continue on their current trajectory.
But to me, the most surprising new finding in the Fifth National Climate Assessment is this: There has been genuine progress, too.
I’m used to mind-boggling numbers, and there are many of them in this report. Human beings have put about 1.6 trillion tons of carbon in the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution — more than the weight of every living thing on Earth combined. But as we wrote the report, I learned other, even more mind-boggling numbers. In the last decade, the cost of wind energy has declined by 70 percent and solar has declined 90 percent. Renewables now make up 80 percent of new electricity generation capacity. Our country’s greenhouse gas emissions are falling, even as our G.D.P. and population grow.
In the report, we were tasked with projecting future climate change. We showed what the United States would look like if the world warms by 2 degrees Celsius. It wasn’t a pretty picture: more heat waves, more uncomfortably hot nights, more downpours, more droughts. If greenhouse emissions continue to rise, we could reach that point in the next couple of decades. If they fall a little, maybe we can stave it off until the middle of the century. But our findings also offered a glimmer of hope: If emissions fall dramatically, as the report suggested they could, we may never reach 2 degrees Celsius at all.
For the first time in my career, I felt something strange: optimism.
And that simple realization was enough to convince me that releasing yet another climate report was worthwhile.
Something has changed in the United States, and not just the climate. State, local and tribal governments all around the country have begun to take action. Some politicians now actually campaign on climate change, instead of ignoring or lying about it. Congress passed federal climate legislation — something I’d long regarded as impossible — in 2022 as we turned in the first draft.
[Note: She's talking about the Inflation Reduction Act and the Infrastructure Act, which despite the names were the two biggest climate packages passed in US history. And their passage in mid 2022 was a big turning point: that's when, for the first time in decades, a lot of scientists started looking at the numbers - esp the ones that would come from the IRA's funding - and said "Wait, holy shit, we have an actual chance."]
And while the report stresses the urgency of limiting warming to prevent terrible risks, it has a new message, too: We can do this. We now know how to make the dramatic emissions cuts we’d need to limit warming, and it’s very possible to do this in a way that’s sustainable, healthy and fair.
The conversation has moved on, and the role of scientists has changed. We’re not just warning of danger anymore. We’re showing the way to safety.
I was wrong about those previous reports: They did matter, after all. While climate scientists were warning the world of disaster, a small army of scientists, engineers, policymakers and others were getting to work. These first responders have helped move us toward our climate goals. Our warnings did their job.
To limit global warming, we need many more people to get on board... We need to reach those who haven’t yet been moved by our warnings. I’m not talking about the fossil fuel industry here; nor do I particularly care about winning over the small but noisy group of committed climate deniers. But I believe we can reach the many people whose eyes glaze over when they hear yet another dire warning or see another report like the one we just published.
The reason is that now, we have a better story to tell. The evidence is clear: Responding to climate change will not only create a better world for our children and grandchildren, but it will also make the world better for us right now.
Eliminating the sources of greenhouse gas emissions will make our air and water cleaner, our economy stronger and our quality of life better. It could save hundreds of thousands or even millions of lives across the country through air quality benefits alone. Using land more wisely can both limit climate change and protect biodiversity. Climate change most strongly affects communities that get a raw deal in our society: people with low incomes, people of color, children and the elderly. And climate action can be an opportunity to redress legacies of racism, neglect and injustice.
I could still tell you scary stories about a future ravaged by climate change, and they’d be true, at least on the trajectory we’re currently on. But it’s also true that we have a once-in-human-history chance not only to prevent the worst effects but also to make the world better right now. It would be a shame to squander this opportunity. So I don’t just want to talk about the problems anymore. I want to talk about the solutions. Consider this your last warning from me."
-via New York Times. Opinion essay by leading climate scientist Kate Marvel. November 18, 2023.
#WE CAN DO THIS#I SO TRULY BELIEVE THAT WE CAN DO THIS#WE CAN SAVE OURSELVES AND THE WORLD ALONG WITH US#climate crisis#united states#climate change#conservation#hope posting#sustainability#climate news#climate action#climate emergency#fossil fuels#global warming#environmentalism#climate hope#solarpunk#climate optimism#climate policy#earth#science#climate science#meteorology#extreme weather#renewable energy#solar power#wind power#renewables#carbon emissions#climate justice
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, happy Earth Day! Who wants to talk about climate change?
Yeah, okay, fair, I kinda figured the answer to that would be "ugh do we have to?" What if I told you I have good news though? Good news with caveats, but still good news.
What if I told you that since the Paris Agreement in 2015, we've avoided a whole degree celsius of global warming by 2100, or maybe more?

Current projections are 2.7C, which is way better than the 3-5C (with a median of 3.7C) we were expecting in 2015. It's not where we want to be - 1.5C - but it is big, noticeable progress!
And it's not like we either hit 1.5C and avoid all the big scary consequences or fail to hit 1.5C and get all of them - every tenth of a degree of warming we avoid is going to prevent more severe problems like extreme weather, sea level rise, etc.
This means that climate change mitigation efforts are having a noticeable impact! This means a dramatically better, safer future - and if we keep pushing, we could lower the amount of global warming we end up with even further. This is huge progress, and we need to celebrate it, even though the fight isn't over.
It's working. Keep going.
#hylian rambles#climate change#climate crisis#environmental issues#global warming#hope#hope for the future#hope for the planet#earth day
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Watch the 2024 American Climate Leadership Awards for High School Students now: https://youtu.be/5C-bb9PoRLc
The recording is now available on ecoAmerica's YouTube channel for viewers to be inspired by student climate leaders! Join Aishah-Nyeta Brown & Jerome Foster II and be inspired by student climate leaders as we recognize the High School Student finalists. Watch now to find out which student received the $25,000 grand prize and top recognition!
#ACLA24#ACLA24HighSchoolStudents#youtube#youtube video#climate leaders#climate solutions#climate action#climate and environment#climate#climate change#climate and health#climate blog#climate justice#climate news#weather and climate#environmental news#environment#environmental awareness#environment and health#environmental#environmental issues#environmental education#environmental justice#environmental protection#environmental health#high school students#high school#youth#youth of america#school
21K notes
·
View notes
Text




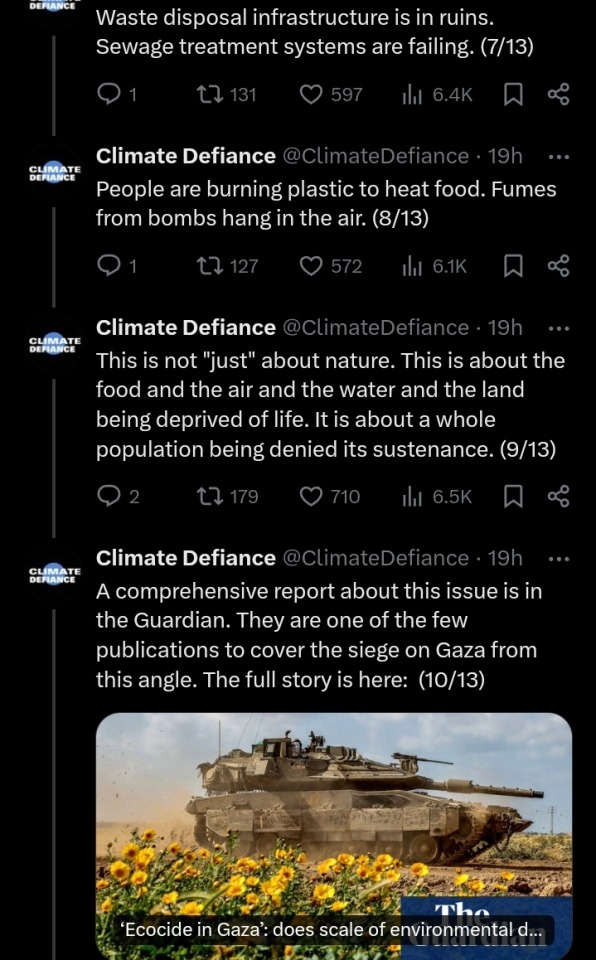
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#climate change#climate crisis#climate justice#global warming#environmental justice
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Everything Has Changed
With a disability I want to be able to go out like everyone else without the worry of being vulnerable. The pandemic has changed everything. It has changed all of our lives.
Losing my twin in December 2022, has also changed things for me, because I am navigating my life without her and in the pandemic. Through the trauma of losing her, I now have Eagle Syndrome.
A Cerebral Palsy diagnosis
Reflecting, I am lucky to have my cerebral palsy diagnosis, because that ultimately changed my thinking. But I also know I had to be instrumental in how I saw my life. Change doesn’t happen unless we choose to change, to change the way we see ourselves, to change the way we see others and to change the way we see our lives.
We need to be open to change
The more we resist change the more nothing will or can change. We need to be open to change, to want to move from where we are, to understand the need to be proactive and working on finding a way through.
Climate and Environmental change
Climate and environmental changes are taking place in front of our very eyes. It's a scary place, but knowing what is happening, the world is changed and we are part of that should be our reason for change. It needs to be our turning point.
Change can happen
Change can happen, we have to want to change our thinking. Change can also come into our lives through a death, or through chance. Something happens that you didn’t anticipate or expect, and you need to make a decision; you need to change. My twin's death and my illness, has culminated in my need to change. I'm falling.
We also have a choice not to change. One thing is for sure, we are surrounded by change, and it is having an impact on us and our lives. Therefore we need to change.
For more inspirational, lifestyle blogs, please check out my site https://www.thecpdiary.com
0 notes
Text
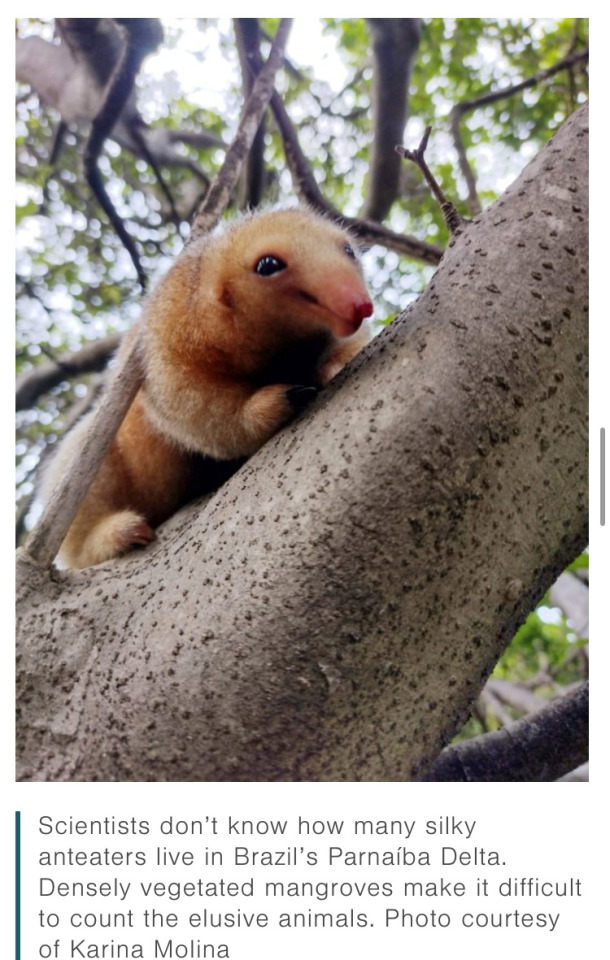

#anteaters#brazil#silky anteater#good news#nature#science#environmentalism#environment#animals#climate change#conservation#cute
11K notes
·
View notes
Text

Environment Sustainability and Climate Change: -Addressing the Urgent Global Challenge
Environmental development and sustainability are suffering immensely in the modern world. As we deal with the urgent problem of climate change, it has become a crucial factor. There is an urgent need for action since human activity has detrimental impacts on the environment. Now we are going to discuss about Environmental development and sustainability impact factor
Preserving Home for All Life Forms
Dealing with Climate Change
Conserving Natural Resources
Community Action
Read in detail: environmental development and sustainability impact factor
#environmental development#sustainability impact factor#impact on environment#environment#environmental change
0 notes
Text
Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation- Framework for Flood Risk Analysis for Solar PV Plants
Climate change significantly influences the precipitation pattern of the Area of Impact (AOI) for Solar Power Plants. This influence eventually poses risks to the power generation, inadequacy of the generating assets and damage to the associated infrastructure of the project. Hydrological Risk Assessment being a critical component of solar power plant design, involves the identification of potential hazards and design mitigation strategies. Considering Climate Change scenarios during hydrological risk assessment for solar power is highly important due to the following reasons: –
Changes in precipitation levels can lead to water unavailability and increased runoff. Design of water storage and drainage systems for solar PV system needs to be reviewed and vetted beforehand to ensure resilience. It may lead to more intense and frequent rainfall events. Higher precipitation intensity can overwhelm drainage systems and increase the risk of localised flooding. Climate change can also cause shifts in the distribution of rainfall, affecting the timing and geographic patterns of precipitation. This can lead to changes in river flow regimes and impact flood risk in different regions. Incorporating these changes in the flood risk assessments helps identify areas prone to increased or decreased flood risk. The flood risk assessment must consider these changes in precipitation patterns to accurately assess the likelihood and severity of flooding.
Changes in temperature can lead to changes in evaporation rates, and streamflow. This can impact the design of water management systems for solar power plants.
Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events: Climate change may cause an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events such as floods and droughts. This can impact the design of flood and drought mitigation strategies for solar power plants.
Sea-level rise: Sea-level rise caused by climate change can impact coastal solar power plants by increasing the risk of flooding and saltwater intrusion into freshwater resources.
Changes in water quality: Climate change can impact water quality, which can affect the performance and lifespan of solar panels. Increased water temperature and changes in nutrients can impact the module cleaning process.
To suggest efficient mitigation measures, it is important to consider the potential impact of climate change on hydrological systems and accordingly design solar power plants that are resilient to these changes. This can be done by incorporating climate projections into the design and operation of solar power plants and developing robust water management and flood mitigation strategies.
Incorporating Climate Change Impact in Hydrological analysis and Flood Risk Assessment
Analysis of historical climate data to understand the baseline climate conditions and identification of trends or patterns. This includes examining long-term precipitation records, temperature data, and other relevant climate variables.
For the potential climate change scenarios, These scenarios are typically derived from global climate models and include tentative projections of temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables based on different greenhouse gas emissions pathways. An appropriate climate change scenario that aligns with the region and time frame of interest is selected.
The coarse-scale climate model outputs are downscaled to a finer resolution that is suitable for hydrological modeling. This can be achieved through statistical or dynamical downscaling techniques, which help capture local-scale climate patterns and variations. Downscaling methods bridge the gap between the global climate models and the local-scale hydrological model.
The downscaled climate data is preprocessed to make it suitable for hydrological modeling. This may involve aggregating the data to the appropriate temporal and spatial resolution, addressing biases or inconsistencies, and ensuring the compatibility of climate variables with the hydrological model inputs.
This downscaled climate data comprising of the future scenarios are then considered for simulating the hydrological response under these changed climate conditions.
The impacts of climate change on flooded areas are then evaluated followed by a comparison of the results obtained from simulations under different climate change scenarios to the baseline conditions. This eventually helps identify the changes in hydrological patterns, shifts in flow regimes, and potential risks related to water resources management.
Based on the findings from the impact assessment, adaptation strategies are developed to address the potential effects of climate change on water resources. These strategies may include improvement in water management practices, infrastructure design, and policies to enhance resilience and adapt to changing hydrological conditions.
#climate change#Flood Risk Management#Environmental Change#Climate Mitigation#renewable energy solution
0 notes
Text
hey uh so I haven't seen anyone talking about this here yet, but
the amazon river, like the biggest river in the fucking world, in the middle of the amazon fucking rainforest, is currently going through its worst drought since the records began 121 years ago

picture from Folha PE
there's a lot going on but I haven't seen much international buzz around this like there was when the forest was on fire (maybe because it's harder to shift the narrative to blame brazil exclusively as if the rest of the world didn't have fault in this) so I wanted to bring this to tumblr's attention
I don't know too many details as I live in the other side of the country and we are suffering from the exact opposite (at least three cyclones this year, honestly have stopped counting - it's unusual for us to get hit by even one - floods, landslides, we have a death toll, people are losing everything to the water), but like, I as a brazilian have literally never seen pictures of the river like this before. every single city in the amazonas state is in a state of emergency as of november 1st.
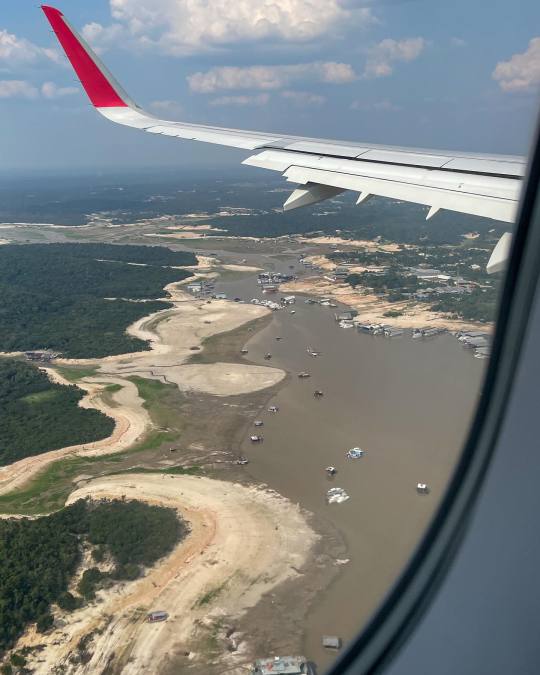
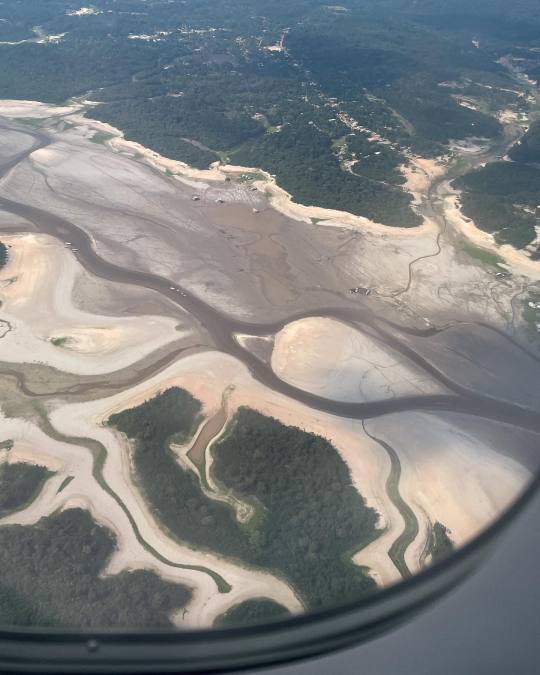


pictures by Adriano Liziero (ig: geopanoramas)
we are used to seeing images of rio negro and solimões, the two main amazon river affluents, in all their grandiose and beauty and seeing these pictures is really fucking chilling. some of our news outlets are saying the solimões has turned to a sand desert... can you imagine this watery sight turning into a desert in the span of a year?
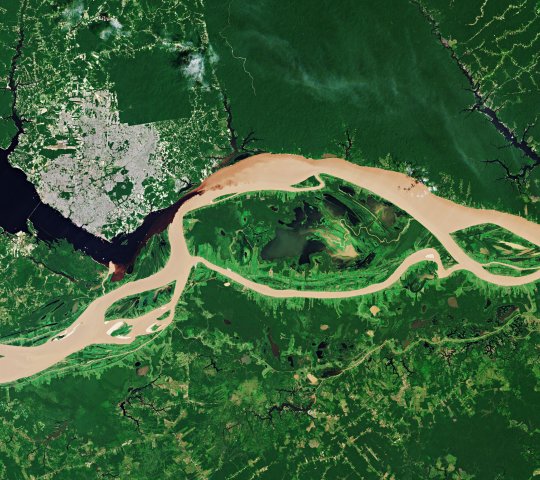


while down south we are seeing amounts of rain and hailstorms the likes of which our infrastructure is simply not built to deal with, up north people who have built everything around the river are at a loss of what to do.
the houses there that are built to float are just on the ground, people who depend on fishing for a living have to walk kilometers to find any fish that are still alive at all, the biodiversity there is at risk, and on an economic level it's hard to grasp how people from the northern states are getting by at all - the main means of transport for ANYTHING in that region is via the river water. this will impact the region for months to come. it doesnt make a lot of sense to build a lot of roads bc it's just better to use the waterway system, everything is built around or floats on the river after all. and like, the water level is so incomprehensibly low the boats are just STUCK. people are having a hard time getting from one place to another - keep in mind the widest parts of the river are over 10 km apart!!

this shit is really serious and i am trying not to think about it because we have a different kind of problem to worry about down south but it's really terrifying when I stop to think about it. you already know the climate crisis is real and the effects are beyond preventable now (we're past global warming, get used to calling it "global boiling"). we'll be switching strategies to damage control from now on and like, this is what it's come to.
I don't like to be alarmist but it's hard not to be alarmed. I'm sorry that I can't end this post with very clear intructions on how people overseas can help, there really isn't much to do except hope the water level rises soon, maybe pray if you believe in something. in that regard we just have to keep pressing for change at a global level; local conditions only would not, COULD NOT be causing this - the amazon river is a CONTINENTAL body of water, it spans across multiple countries. so my advice is spread the word, let your representatives know that you're worried and you want change towards sustainability, degrowth and reduced carbon emissions, support your local NGOs, maybe join a cause, I don't know? I recommend reading on ecological and feminist economics though
however, I know you can help the affected riverine families by donating to organizations dedicated to helping the region. keep in mind a single US dollar, pound or euro is worth over 5x more in our currency so anything you donate at all will certainly help those affected.
FAS - Sustainable Amazon Fundation
Idesam - Sustainable Developent and Preservation Institute of Amazonas
Greenpeace Brasil - I know Greenpeace isn't the best but they're one of the few options I can think of that have a bridge to the international world and they are helping directly
There are a lot of other smaller/local NGOs but I'm not sure how you could donate to them from overseas, I'll leave some of them here anyway:
Projeto Gari
Caritás Brasileira
If you know any other organizations please link them, I'll be sure to reblog though my reach isn't a lot
thank you so much for reading this to the end, don't feel obligated to share but please do if you can! even if you just read up to here it means a lot to me that someone out there knows
also as an afterthought, I wanted to expand on why I think this hasn't made big news yet: because unlike the case of the 2020 forest fires, other countries have to hold themselves accountable when looking at this situation. while in 2020 it was easier to pretend the fires were all our fault and people were talking about taking the amazon away from us like they wouldn't do much worse. global superpowers have no more forests to speak of so I guess they've been eyeing what latin america still has. so like this bit of the post is just to say if you're thinking of saying anything of the sort, maybe think of what your own country has done to contribute to this instead of blaming brazil exclusively and saying the amazon should be protected by force or whatever
#solarpunk#sustainability#environmentalism#climate change#climate crisis#global warming#amazon rainforest#amazon river#geography#brazil#degrowth#punk#global boiling#ecopunk#anti capitalism#climate action#climate activism#the world does not die on my watch#i saw someone use that tag and uh i like it we should make it a thing#long post#:/ sorry i know no one likes lengthy bad news posts on their dashes but i've been thinking about this quite a bit#and i don't really know what to do to help bc i don't have money to donate and i am 10 thousand km away#i think i could be doing more to help but i am already trying my best#again dont feel obligated to share or read this but it would be nice and i would love you forever#have removed lbv from the post
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
#colombia#brazil#urban#urban landscape#urban planning#cities#civil engineering#green architecture#green spaces#urban heat#urban heat island effect#weather#meteorology#global warming#climate change#climate hope#climate optimism#climate emergency#climate action#environment#environmental news#city architecture#bicycling#native plants#biodiversity#good news#hope#solarpunk#ecopunk#hopepunk
15K notes
·
View notes