#Writing Tip
Text
“the opening sentence of a fic is one of the most important parts, since it tells readers the tone, the setting and the writing style of the entire fic”
me trying not to be nervous as I write the opening sentence of my fic:

#writing#writer#writeblr#ao3#archive of our own#whump#writing challenge#writing memes#ao3 memes#ao3 meme#writing advice#writing tip#writing tips#whumpblr#angst#writing inspo#writing inspiration#meme#memes#writing community#whump community#whump blog#writing tropes#tropes#trope#whump tropes#writing trope#whump trope#prompt#prompts
7K notes
·
View notes
Note
I don't know if you've done this before but what are some good ways to describe speech?
Ways to Describe Speech
-> feel free to edit and adjust pronouns as you see fit.
His voice was deep like the rumbling of the earth.
She had the voice of a singer, smooth and rich like chocolate.
Their voice reminded him of spring rain.
He often paused in his speaking, like a car radio that had lost signal.
She had a lilt to her voice that made it seem like she was asking a question.
Their voice was monotonous, threatening to put her to sleep with every word.
He couldn't put her voice into words. It was... otherworldly.
Her voice was brittle, as if she were on the verge of tears.
Their voice was authoritative. Their words carried like a loud command.
His voice, unapologetic and unwavering, made her shrink back.
Her voice was barely above a whisper.
Their words were cold with anger.
Other Words to Use to Describe Voice:
Firm
Formal
Frank
Hesitant
Humorous
Passionate
Playful
Professional
Respectful
Serious
Sympathetic
Smug
Superior
Croaky
Dry
Forceful
Grating
Hateful
Insincere
Nasally
Snarky
Tuneless
Wavering
Breaking
Coarse
Flat
Hoarse
High Pitched
Husky
Mellow
Raspy
Rough
Scratchy
Strong
Trembling
Boisterous
Booming
Screeching
Faint
Feeble
Frail
Penetrating
Piercing
Quiet
Raised
Shrill
Soft
Weak
Whisper
Captivating
Deep
Feathery
Hypnotic
Lilting
Mesmerizing
Rich
Smoky
Soothing
Breathy
Delicate
Warbling
If you like what I do and want to support me, please consider donating! I also offer editing services and other writing advice on my Ko-fi!
#writing prompts#creative writing#writeblr#prompt list#ask box prompts#how to describe speech#how to describe voice#how to write#writing help#writing inspiration#writing tip#writing ideas
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
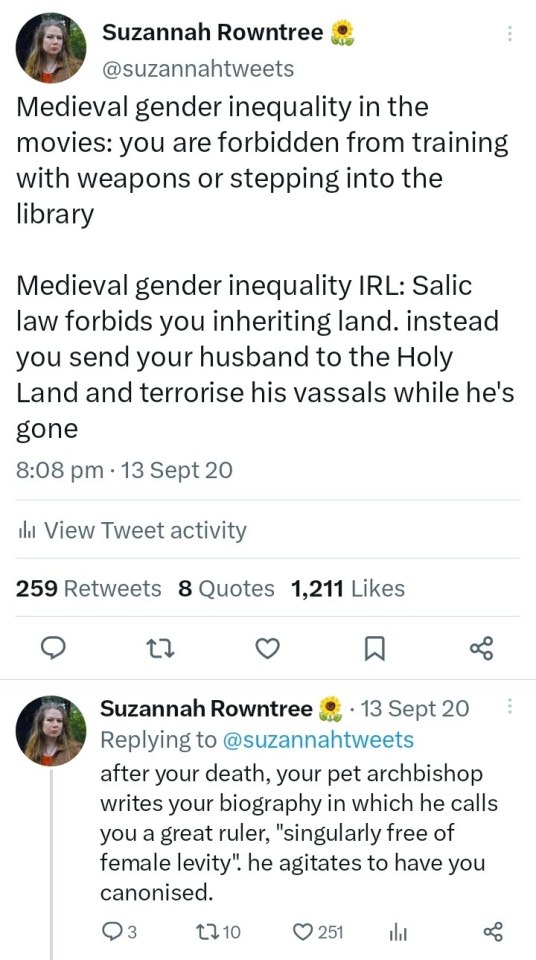
all RIGHT:
Why You're Writing Medieval (and Medieval-Coded) Women Wrong: A RANT
(Or, For the Love of God, People, Stop Pretending Victorian Style Gender Roles Applied to All of History)
This is a problem I see alllll over the place - I'll be reading a medieval-coded book and the women will be told they aren't allowed to fight or learn or work, that they are only supposed to get married, keep house and have babies, &c &c.
If I point this out ppl will be like "yes but there was misogyny back then! women were treated terribly!" and OK. Stop right there.
By & large, what we as a culture think of as misogyny & patriarchy is the expression prevalent in Victorian times - not medieval. (And NO, this is not me blaming Victorians for their theme park version of "medieval history". This is me blaming 21st century people for being ignorant & refusing to do their homework).
Yes, there was misogyny in medieval times, but 1) in many ways it was actually markedly less severe than Victorian misogyny, tyvm - and 2) it was of a quite different type. (Disclaimer: I am speaking specifically of Frankish, Western European medieval women rather than those in other parts of the world. This applies to a lesser extent in Byzantium and I am still learning about women in the medieval Islamic world.)
So, here are the 2 vital things to remember about women when writing medieval or medieval-coded societies
FIRST. Where in Victorian times the primary axes of prejudice were gender and race - so that a male labourer had more rights than a female of the higher classes, and a middle class white man would be treated with more respect than an African or Indian dignitary - In medieval times, the primary axis of prejudice was, overwhelmingly, class. Thus, Frankish crusader knights arguably felt more solidarity with their Muslim opponents of knightly status, than they did their own peasants. Faith and age were also medieval axes of prejudice - children and young people were exploited ruthlessly, sent into war or marriage at 15 (boys) or 12 (girls). Gender was less important.
What this meant was that a medieval woman could expect - indeed demand - to be treated more or less the same way the men of her class were. Where no ancient legal obstacle existed, such as Salic law, a king's daughter could and did expect to rule, even after marriage.
Women of the knightly class could & did arm & fight - something that required a MASSIVE outlay of money, which was obviously at their discretion & disposal. See: Sichelgaita, Isabel de Conches, the unnamed women fighting in armour as knights during the Third Crusade, as recorded by Muslim chroniclers.
Tolkien's Eowyn is a great example of this medieval attitude to class trumping race: complaining that she's being told not to fight, she stresses her class: "I am of the house of Eorl & not a serving woman". She claims her rights, not as a woman, but as a member of the warrior class and the ruling family. Similarly in Renaissance Venice a doge protested the practice which saw 80% of noble women locked into convents for life: if these had been men they would have been "born to command & govern the world". Their class ought to have exempted them from discrimination on the basis of sex.
So, tip #1 for writing medieval women: remember that their class always outweighed their gender. They might be subordinate to the men within their own class, but not to those below.
SECOND. Whereas Victorians saw women's highest calling as marriage & children - the "angel in the house" ennobling & improving their men on a spiritual but rarely practical level - Medievals by contrast prized virginity/celibacy above marriage, seeing it as a way for women to transcend their sex. Often as nuns, saints, mystics; sometimes as warriors, queens, & ladies; always as businesswomen & merchants, women could & did forge their own paths in life
When Elizabeth I claimed to have "the heart & stomach of a king" & adopted the persona of the virgin queen, this was the norm she appealed to. Women could do things; they just had to prove they were Not Like Other Girls. By Elizabeth's time things were already changing: it was the Reformation that switched the ideal to marriage, & the Enlightenment that divorced femininity from reason, aggression & public life.
For more on this topic, read Katherine Hager's article "Endowed With Manly Courage: Medieval Perceptions of Women in Combat" on women who transcended gender to occupy a liminal space as warrior/virgin/saint.
So, tip #2: remember that for medieval women, wife and mother wasn't the ideal, virgin saint was the ideal. By proving yourself "not like other girls" you could gain significant autonomy & freedom.
Finally a bonus tip: if writing about medieval women, be sure to read writing on women's issues from the time so as to understand the terms in which these women spoke about & defended their ambitions. Start with Christine de Pisan.
I learned all this doing the reading for WATCHERS OF OUTREMER, my series of historical fantasy novels set in the medieval crusader states, which were dominated by strong medieval women! Book 5, THE HOUSE OF MOURNING (forthcoming 2023) will focus, to a greater extent than any other novel I've ever yet read or written, on the experience of women during the crusades - as warriors, captives, and political leaders. I can't wait to share it with you all!
#watchers of outremer#medieval history#the lady of kingdoms#the house of mourning#writing#writing fantasy#female characters#medieval women#eowyn#the lord of the rings#lotr#history#historical fiction#fantasy#writing tip#writing advice
30K notes
·
View notes
Text
What to give a fuck about,while writing your first draft!
I`ve posted a list about things you don´t need to give a fuck about while writing your first draft. Here are things you NEED TO CARE about! (in my opinion)
Your Authentic Voice: Don't let the fear of judgment or comparison stifle your unique voice. I know it´s hard,but try to write from your heart, and don't worry about perfection in the first draft. Let your authenticity shine through your words.
Your Story, Your Way: It's your narrative, your world, and your characters. Don't let external expectations or trends dictate how your story should unfold. Write the story you want to tell.
Progress Over Perfection: Your first draft is not the final product; it's the raw material for your masterpiece. Give a fuck about making progress, not achieving perfection. Embrace imperfections and understand that editing comes later.
Consistency and Routine: Discipline matters. Make a commitment to your writing routine and stick to it.
Feedback and Growth: While it's essential to protect your creative space during the first draft, be open to constructive feedback later on. Giving a f*ck about growth means you're willing to learn from others and improve your work.
Self-Compassion: Mistakes, writer's block, and self-doubt are all part of the process. Give a f*ck about being kind to yourself. Don't beat yourself up if the words don't flow perfectly every time. Keep pushing forward and remember that writing is a journey.
Remember, the first draft is your canvas, your playground. Don't bog yourself down with unnecessary worries.

#writing#writblr#writing advice#writers block#just writer things#creative writing#fanfiction writing#writing motivation#writeblr#original writing#writing reference#writing tips#writers on tumblr#writing resources#writing tip#writing encouragement#writing community#writers#world building#point of view#editing#character creation#dialogue#mine.#words#writingtips#writingadvice
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Writer's Guide to Authentic Wounds and Fatalities

Writing fatal injuries in a story requires a delicate balance between realism and narrative impact. The portrayal of these life-altering events can evoke strong emotions in readers and shape the trajectory of your characters' journeys. In this blog, I will explore the intricacies of depicting fatal injuries in a manner that feels authentic, engaging, and respectful to the gravity of such circumstances. By understanding the nuances of fatal injuries, you will be equipped to craft compelling narratives that resonate with your readers.
Writing Fatal Injuries
When it comes to writing fatal injuries, it is crucial to approach the subject with care and accuracy. Fatal injuries carry immense consequences for your characters and can shape the trajectory of your story. By delving into the intricacies of portraying fatal injuries authentically, you can ensure that the gravity and impact of such events are effectively conveyed to your readers.
Choosing the right injuries for your story
Selecting the appropriate fatal injuries for your narrative involves considering various factors. Ask yourself: What purpose does this injury serve within the story? How does it affect the characters and the overall plot? Conduct thorough research to identify injuries that align with your story's context and resonate with the emotional journey of your characters.
For example, in a historical drama, you may research common fatal injuries during a particular era, such as battlefield injuries, diseases, or accidents prevalent at the time. In a crime thriller, you might explore the portrayal of fatal gunshot wounds or traumatic injuries resulting from violent encounters. By aligning the injuries with the context and themes of your story, you create a more immersive and believable experience for your readers.
Researching the mechanics of fatal injuries
To portray fatal injuries convincingly, it is essential to delve into the mechanics behind them. Understand the specific anatomical structures and systems involved, as well as the forces or mechanisms that can lead to fatal outcomes. Explore medical resources, consult experts if possible, and gather insights into the physiological and psychological implications of such injuries.
For instance, if your character suffers a fatal stab wound, research the anatomy involved, the potential organs affected, and the potential consequences such as internal bleeding or organ failure. By understanding the specific details and implications of the injury, you can describe the physical and emotional toll it takes on the character with greater accuracy and depth.
Depicting the immediate aftermath
When writing about fatal injuries, vividly describe the immediate aftermath to capture the intense emotions and physical realities. Consider the sensory details, the shock and disbelief experienced by characters, and the chaotic environment that often surrounds such events. Balancing realism with the needs of your story, create a scene that immerses readers and evokes empathy.
For example, if a character experiences a fatal car accident, you can depict the chaos at the scene, the character's disorientation, and the reactions of witnesses. Emphasize the sensory details such as the sound of screeching tires or the smell of burning rubber, creating a visceral experience for your readers.
Emotional and dramatic impact on the narrative
The impact of fatal injuries extends beyond the immediate moment. Explore the ripple effects on other characters, relationships, and the overall plot. Delve into the emotional responses, grief, guilt, anger, or determination that arises in the aftermath of loss. Utilize these emotional arcs to deepen character development and drive the narrative forward.
For instance, the loss of a loved one due to a fatal illness might lead to grief and strained relationships among the remaining family members. The emotional journey of a character grappling with guilt and seeking redemption after causing a fatal accident can become a central theme in your story. By delving into these emotional arcs and their consequences, you add depth and resonance to your narrative.
Writing Minor Injuries
While fatal injuries may capture our attention with their dramatic impact, it is equally important to pay attention to the portrayal of minor injuries in your writing. Minor injuries, though less severe, can still significantly affect your characters and contribute to the authenticity of your story. In this section, we will explore the art of depicting minor injuries, ensuring that they are not overlooked or trivialized. By delving into the nuances of minor injuries, you can add depth and realism to your characters' experiences.
Types of minor injuries to consider
When crafting your story, it is essential to consider a range of minor injuries that can occur. These injuries can include cuts, bruises, sprains, minor burns, or even minor fractures. Each type of injury carries its own unique characteristics, associated pain levels, and recovery processes. By understanding these distinctions, you can create accurate and believable depictions that resonate with your readers.
For example, a character who sustains a cut on their hand may experience sharp pain, the sight of blood, and the need for immediate first aid. On the other hand, a character with a sprained ankle may struggle with mobility, experience swelling, and require rest and care for a few days. By paying attention to these specific details, you can enhance the realism of your storytelling.
Conveying pain and discomfort
When writing about minor injuries, it is important to effectively convey the pain and discomfort experienced by your characters. Consider describing the sensation of pain, the throbbing or stinging feeling, and how it affects their daily activities or interactions. Showcasing the emotional impact of pain, such as frustration, irritation, or vulnerability, can deepen the readers' connection to the character's experience.
For instance, if a character suffers from a sprained wrist, you can describe the dull ache that persists, making simple tasks like typing or holding objects challenging. By capturing these small but significant moments, you immerse readers in the character's struggle and create a more realistic portrayal.
Balancing realism with narrative pace
While it is important to depict minor injuries realistically, it is also crucial to strike a balance with the overall pace and momentum of your story. Consider the significance of the injury within the larger context of your narrative. Some injuries may require more detailed attention and impact the plot, while others may serve as background elements. Adjust the level of detail and focus accordingly, ensuring that the portrayal of minor injuries aligns with the narrative's flow.
For example, a small cut on a character's finger may not require an extensive description unless it becomes infected or triggers an unexpected consequence. By aligning the portrayal of minor injuries with their narrative relevance, you maintain a consistent pace while still acknowledging their impact on your characters' lives.
Writing Bloodshed And Realistic Blood Loss
When writing about wounds and injuries, it is essential to consider the amount of blood loss your characters may experience. Realistic portrayal of bloodshed can enhance the authenticity of your scenes and immerse readers in the gravity of the situation. In this section, we will explore the factors influencing blood loss and techniques for accurately depicting it in your writing.
Understanding blood loss and its impact on the body
To authentically portray blood loss, it's crucial to have a basic understanding of how the human body responds to injury. Research the circulatory system and the role of blood in transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Consider the different types of blood vessels and their potential for bleeding when injured. This knowledge will help you create realistic scenarios and determine the appropriate level of blood loss for specific injuries.
Factors influencing blood loss in different injury scenarios
The amount of blood loss can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Factors such as the size of blood vessels, the rate of bleeding, and the body's ability to clot play a significant role. For example, a deep laceration in an artery will result in more substantial blood loss compared to a superficial cut on the skin. Consider these factors when describing injuries and their resulting bloodshed.
Techniques for accurately portraying blood loss in writing
There are several techniques you can use to convey the realistic impact of blood loss in your writing. Describing the color, consistency, and flow of blood can provide vivid imagery. You can also include physical symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, or fainting that may accompany significant blood loss. Additionally, consider the emotional response of your characters and how they react to the sight of blood or their own injuries.
By incorporating these techniques, you can create scenes that evoke a visceral response in readers and enhance the authenticity of your writing.
Bruises: Colors, Progression, and Pain
Bruises are a common result of injuries, and understanding how they form, change in color, and cause discomfort can greatly enhance the realism of your writing. By accurately describing bruises, you can bring depth to your characters' injuries and portray their healing process convincingly.
Understanding the stages and colors of bruises
Bruises go through distinct stages of color as they heal. Initially, they may appear red or purple due to the broken blood vessels beneath the skin. Over time, the color changes to blue, green, yellow, and eventually fades to a brown or yellowish hue. Understanding this color progression can help you accurately describe the age of a bruise and the healing process.
For example, a fresh bruise might be vivid purple, indicating recent trauma, while a fading bruise may have a yellowish tinge, suggesting that healing has begun. By incorporating these color details, you can add realism to your characters' injuries and track the passage of time within your narrative.
Depicting the progression of bruises over time
As bruises heal, they often change in appearance and size. Initially, a bruise may be small and localized, but it can gradually spread and become more extensive. Describing this progression can provide a sense of the healing process and the passage of time within your story.
For instance, a character who sustains a significant blow to the face may develop a bruise that starts as a small spot near the eye but expands to cover a larger area over the next few days. By accurately portraying the progression of bruises, you enhance the authenticity of your characters' injuries and their recovery.
Conveying the pain and sensitivity associated with bruises
Bruises can be painful, sensitive to touch, and affect a character's movement and daily activities. Describing the pain and discomfort experienced by your characters can create empathy and immerse readers in their physical ordeals.
Consider conveying the tenderness of a bruise when pressure is applied, the throbbing sensation, or the limitation of movement due to the pain.
Remember The Side Effects
Injuries, whether minor or severe, often come with a range of side effects that can significantly impact your characters' lives. These side effects can extend beyond the physical realm and encompass emotional, psychological, and social aspects.
Physical side effects
Injuries can have profound physical side effects that go beyond the immediate pain and discomfort. Consider the potential consequences such as limited mobility, impaired coordination, chronic pain, or the need for assistive devices like crutches or braces. Describing these physical side effects can add depth to your characters' struggles and provide a realistic portrayal of their healing journey.
For example, a character who sustains a leg injury may experience difficulty walking, require physical therapy, or have long-term complications that affect their day-to-day activities. By addressing these physical side effects, you create a more nuanced depiction of the aftermath of injuries.
Emotional and psychological side effects
Injuries can have a profound emotional and psychological impact on characters. They may experience fear, anxiety, trauma, or a loss of confidence. Consider how the injury affects their self-image, relationships, or mental well-being. Explore the emotional journey your characters undergo as they navigate the aftermath of their injuries.
For instance, a character who survives a near-fatal accident may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and struggle with recurring nightmares or panic attacks. By incorporating these emotional and psychological side effects, you can deepen the complexity of your characters and their responses to traumatic experiences.
Social implications and changes
Injuries can also lead to significant social changes for your characters. They may face challenges in their personal relationships, encounter stigma or discrimination, or experience changes in their roles or identities. Explore how the injury affects their interactions with others and their sense of belonging in the world.
For example, a character who sustains a facial injury may encounter judgment or stares from others, leading to self-consciousness or isolation. By addressing the social implications and changes resulting from injuries, you can create multi-dimensional characters and explore the impact of their injuries on their social dynamics.
By incorporating these various side effects into your writing, you bring depth and authenticity to your characters' experiences and showcase the wide-ranging impact of injuries.
Conclusion
Writing authentic wounds and fatalities requires attention to detail and a deep understanding of the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects involved. By following the guidelines and exploring the subheadings discussed in this guide, you can create compelling and realistic portrayals of injuries in your writing.
Remember to conduct thorough research on the specific injuries you want to depict, understanding their mechanics, symptoms, and potential outcomes. Consider the immediate and long-term effects on your characters, both physically and emotionally. Incorporate sensory details to immerse readers in the experience, describing the pain, bloodshed, colors of bruises, and the progression of healing.
Additionally, don't forget to address the side effects that injuries can have on your characters' lives. Explore the physical limitations, emotional struggles, and social implications that arise from their injuries. By delving into these aspects, you can create well-rounded characters and compelling narratives that resonate with readers.
I hope this blog on forging epic battles will help you in your writing journey. Be sure to comment any tips of your own to help your fellow authors prosper, and follow my blog for new blog updates every Monday and Thursday.
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Are you an author looking for writing tips and tricks to better your manuscript? Or do you want to learn about how to get a literary agent, get published and properly market your book? Consider checking out the rest of Haya’s book blog where I post writing and publishing tips for authors every Monday and Thursday! And don’t forget to head over to my TikTok and Instagram profiles @hayatheauthor to learn more about my WIP and writing journey!
#hayatheauthor#haya's book blog#haya blogs#writers on tumblr#writer community#writer tools#writer blog#writer stuff#writer wednesday#writer tips#creative writing#writers of tumblr#writerscommunity#writeblr#writing community#writer spotlight#writer things#writing prompt#writing tools#writing stuff#writing#writing life#writing inspo#writing help#writing advice#writing inspiration#writing ideas#writing things#writing tip
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to write fight scenes
many people have told me that Chum has good fight scenes. a small subset of those people have asked me on advice for how to write fight scenes. i am busy procrastinating, so i have distilled my general ethos on fight scenes into four important points. followed by a homework assignment.
Fight scenes take place on two axii - the physical and the intellectual. For the most interesting fight scenes, neither character should have a full inventory of the other's abilities, equipment, fighting style, etc. This gives you an opportunity to pull out surprises, but, more importantly, turns each fight into a jockeying of minds, as all characters involved have to puzzle out what's going on in real time. This is especially pertinent for settings with power systems. It feels more earned if the characters are trying to deduce the limitations and reach of the opponent's power rather than the opponent simply explaining it to them (like in Bleach. Don't do that).
1a. Have characters be incorrect in their assumptions sometimes, leading to them making mistakes that require them to correct their internal models of an opponent under extreme pressure.
1b. If you really have to have a character explain their powers to someone there should be a damn good reason for it. The best reason is "they are lying". The second best reason is "their power requires it for some reason".
Make sure your blows actually have weight. When characters are wailing at each other for paragraphs and paragraphs and nothing happens, it feels like watching rock 'em sock 'em robots. They beat each other up, and then the fight ends with a decisive blow. Not interesting! Each character has goals that will influence what their victory condition is, and each character has a physical body that takes damage over the course of a fight. If someone is punched in the gut and coughs up blood, that's an injury! It should have an impact on them not just for the fight but long term. Fights that go longer than "fist meets head, head meets floor" typically have a 'break-down' - each character getting sloppier and weaker as they bruise, batter, and break their opponent, until victory is achieved with the last person standing. this keeps things tense and interesting.
I like to actually plan out my fight scenes beat for beat and blow for blow, including a: the thought process of each character leading to that attempted action, b: what they are trying to do, and c: how it succeeds or fails. In fights with more than two people, I like to use graph paper (or an Excel spreadsheet with the rows turned into squares) to keep track of positions and facings over time.
Don't be afraid to give your characters limitations, because that means they can be discovered by the other character and preyed upon, which produces interesting ebbs and flows in the fight. A gunslinger is considerably less useful in a melee with their gun disarmed. A swordsman might not know how to box if their sword is destroyed. If they have powers, consider what they have to do to make them activate, if it exhausts them to use, how they can be turned off, if at all. Consider the practical applications. Example: In Chum, there are many individuals with pyrokinetic superpowers, and none of them have "think something on fire" superpowers. Small-time filler villain Aaron McKinley can ignite anything he's looking at, and suddenly the fight scenes begin constructing themselves, as Aaron's eyes and the direction of his gaze become an incredibly relevant factor.
if you have reached this far in this essay I am giving you homework. Go watch the hallway fight in Oldboy and then novelize it. Then, watch it again every week for the rest of your life, and you will become good at writing fight scenes.
as with all pieces of advice these are not hard and fast rules (except watching the oldboy hallway fight repeatedly) but general guidelines to be considered and then broken when it would produce an interesting outcome to do so.
okay have a good day. and go read chum.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you hate writing outlines it's because of how they're taught in school. Toss out indentation and Roman numerals and map out your writing how you want to. Outlines are your FRIEND, dammit.
This goes for everything, from political essays to fanfiction. If it's written you need an outline because the outline is for you. It can be general, vague, or a mixture of both! Be as informal as you want, who cares. They're to keep you on track and keep your writing flowing, so don't disregard them even if you dreaded making them in grade school.
My outlines by chapter tend to look like this:
1. Character "P" goes to the diner to meet character "Q."
2. "P" tells "Q" about how the confrontation went. (dialogue I thought up on a bus ride) That's when shit goes DOWN. They're yelling, they're drawing attention to themselves, but before they can take it outside, "P" says (dialogue I thought up in the shower).
3. THEN "Q" SAYS THAT ONE LINE THAT "R" SAYS TO HIM IN CHAPTER FIVE BECAUSE THAT'S CALLED COHESION WOOOOO
4. idk they both leave??? you'll figure it out later
5. Self-reflection for "P." Keep your main point on how his moral compass goes to extremes and hurts others. He finally is realizing that HE is the PROBLEM
6. "P" drives to "Q's" house to apologize but GUESS WHO ANSWERS THE DOOR it's "R" and then just end the chapter there
This is coming from someone who didn't write with outlines for years. Now I don't write anything longer than 400 words without one! Make them your own, make them so that they're useful to you. That's their purpose, so accept the help!
#writers on tumblr#writing tumblr#writing help#writing advice#writing tips#writing blog#writer tips#writing motivation#outlining#book writing#novel writing#writeblr#writer#writing tip
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
how to create good characterization naturally? The chemistry in between characters without seeming forced
Great character chemistry can turn a good story into one that readers can’t forget. It’s a spark that makes your characters’ relationships seem real and exciting. Let’s look at how to make your characters interact in a way that feels natural and keeps readers hooked from start to finish.
Behaviour
Have characters unconsciously mirror each other’s actions.
Include small acts of intimacy, like sharing inside jokes or personal anecdotes.
Show characters prioritising each other’s needs or sacrificing their interests for the other.
Develop unique habits that characters only exhibit around each other.
Use consistent, unique actions or quirks that reveal a character’s feelings.
Create scenarios where characters defend each other’s viewpoints or actions to outsiders.
Allow characters to show vulnerability around each other.
Have characters unintentionally adopt each other’s mannerisms or phrases over time.
Have your characters make an effort to engage in activities they don’t typically enjoy, just to be with the other person.
Show characters naturally falling into synchronised rhythms, like walking in step.
Interactions
Lace your dialogue with subtext.
Have characters finish each other’s sentences or speak in unison without planning it.
Include playful banter and light teasing.
Allow for moments of comfortable silence that show a mutual understanding and connection.
Conflicts should be heated, but often end in mutual respect and a stronger bond.
Write intimate conversations where characters share secrets or dreams.
Develop scenes where characters work together seamlessly, anticipating each other’s moves.
Write moments where one character can tell what the other is thinking just by looking at them.
Have interactions where characters seek each other out for advice or comfort.
Create situations where characters celebrate each other’s achievements genuinely and enthusiastically.
Body language
Subtle touches like brushing hands or a gentle push that lingers just a moment too long.
Leaning towards each other while talking, showing attraction or interest.
Describe the way characters mirror each other.
A characters’ eyes lighting up or softening when they look at each other.
Positioning themselves between their partner and a threat.
Unintentional proximity, like standing or sitting closer than necessary.
Nervous gestures that characters show only around each other, like fidgeting or playing with their hair.
Warm, genuine smiles that are reserved for one another.
Instinctively reaching out to comfort each other in times of distress.
Relaxed posture in each other’s company.
Attitude
Show a respect for one another that they don’t show with others.
Are consistently patient with one another’s flaws.
Willingness to compromise or find middle ground.
Giving each other the benefit of the doubt in misunderstandings.
Unconditional support during difficult times.
Take pride in each other’s accomplishments, without jealousy.
Consistently have faith in each other’s abilities and decisions.
Openly express admiration for one another’s talents or character traits.
Maintain a positive outlook on the other’s intentions, even when they make mistakes.
Show an understanding between characters that goes beyond words.
Positive story outcomes
Stronger alliances or partnerships.
Romantic subplots that add depth and interest to the main story.
Believable character development as they influence each other positively.
Moments of triumph where their combined strengths overcome obstacles.
Deep, meaningful friendships.
Can easily resolve conflicts that seemed insurmountable.
Celebration is more impactful due to their shared success.
A fortified sense of trust that can be pivotal in critical story moments.
Enhanced reader investment in the characters and their relationships.
Openings for sequels or spin-offs based on popular characters dynamics.
Negatives story outcomes
Conflict arising from misunderstanding or jealousy.
Unresolved tension between characters on the outside.
Can lead to unnecessarily complex emotional entanglements
Creates obstacles due to the characters’ strong connection being exploited by antagonists.
Tragic outcomes when the chemistry between characters causes them to make irrational choices.
Intense confrontations that threaten the relationship.
Betrayals that are more impactful because of the depth of their relationship.
Unforeseen sacrifices that characters make for each other.
Heightened stakes when the wellbeing of one character is tied to the other.
Unexpected changes in the character when relationships are cut short.
Helpful vocabulary
Smitten
Love
Afffection
Desire
Charisma
Intimate
Playful
Magnetic
Affectionate
Devoted
Engrossed
Dynamic
Mesmerizing
Empathy
Kinship
Enthralled
Spark
Trust
Harmony
Synergy
Supportive
Heartfelt
Genuine
Symbiotic
Unbreakable
Deep-seated
Fascinating
Bonded
Authentic
Obsession
#writers#creative writing#writing#writing community#writers of tumblr#creative writers#writing inspiration#writeblr#writerblr#writing tips#writing advice#character chemistry#character development#how to write#writing tip#let's write#character description#character reference#resources for writers#helping writers#writing asks#writers block#writing resources#writers on tumblr#writer#writers and poets#on writing#writer stuff#help for writers#references for writers
813 notes
·
View notes
Text
Do Your Research
This phrase is regularly thrown around writeblr and for good reason. It's important to research what you are writing about to know what to include, what can be fudged, and how to depict whatever you're writing. I see "do your research" most thrown around by well-meaning and highly traditionally educated writers. It's solid advice, after all!
But how do you research?
For those writers who don't already have the research skills necessary to write something comfortably already downloaded into your brain, I put this guide together for you.
Where do I even start?
It's a daunting task, research. But the best place to start is with the most basic, stupidest question you can think of. I'm going to talk about something that I already know a lot about: fighting.
When researching fight scenes, a great way to start is to look up what different weapons are. There are tons out there! So ask the stupid questions. What is a sword? What is a gun? How heavy are they?
Google and Wikipedia can help you a lot with these basic-level questions. They aren't great sources for academic articles, but remember, this is fiction. It doesn't need to be perfect, and it doesn't need to be 100% accurate if you don't want it to be. But knowing what is true to life will help you write well. Just like knowing the rules of writing will help you break them.
You may find in your basic research sweep that you have a lot more specific questions. Write them all down. It doesn't matter if they seem obvious. Write them down because they will be useful later.
How To Use Wikipedia Correctly
Wikipedia is a testament to cooperative human knowledge. It's also easy to edit by anonymous users, which means there is a lot of room for inaccuracies and misleading information. Wikipedia is usually pretty good about flagging when a source is needed or when misleading language is obvious, but Wikipedia itself isn't always the most accurate or in-depth source.
Wikipedia is, however, an excellent collection of sources. When I'm researching a subject that I know nothing about, say Norse mythology, a good starting point is the Wikipedia page for Odin. You'll get a little background on Odin's name and Germanic roots, a little backstory on some of the stories, where they appear, and how they are told.
When you read one of the sentences, and it sparks a new question, write the question down, and then click on the superscript number. This will take you directly to the linked source for the stated fact. Click through to that source. Now you have the source where the claim was made. This source may not be a primary source, but a secondary source can still lead you to new discoveries and details that will help you.
By "source-hopping," you can find your way across the internet to different pieces of information more reliably. This information may repeat itself, but you will also find new sources and new avenues of information that can be just as useful.
You mean I don't need a library?
Use your library. Libraries in many parts of the US are free to join, and they have a wealth of information that can be easily downloaded online or accessed via hardcopy books.
You don't, however, need to read every source in the library for any given topic, and you certainly don't need to read the whole book. Academic books are different from fiction. Often their chapters are divided by topic and concept and not by chronological events like a history textbook.
For example, one of my favorite academic books about legislative policy and how policy is passed in the US, by John Kingdon, discusses multiple concepts. These concepts build off one another, but ultimately if you want to know about one specific concept, you can skip to that chapter. This is common in sociological academic books as well.
Going off of my Norse Mythology example in the last section, a book detailing the Norse deities and the stories connected to them will include chapters on each member of the major pantheon. But if I only care about Odin, I can focus on just the chapters about Odin.
Academic Articles and How To Read Them
I know you all know how to read. But learning how to read academic articles and books is a skill unto itself. It's one I didn't quite fully grasp until grad school. Learn to skim. When looking at articles published in journals that include original research, they tend to follow a set structure, and the order in which you read them is not obvious. At all.
Start with the abstract. This is a summary of the paper that will include, in about half a page to a page, the research question, hypothesis, methods/analysis, and conclusions. This abstract will help you determine if the answer to your question is even in this article. Are they asking the right question?
Next, read the research question and hypothesis. The hypothesis will include details about the theory and why the researcher thinks what they think. The literature review will go into much more depth about theories, what other people have done and said, and how that ties into the research of the present article. You don't need to read that just yet.
Skim the methods and analysis section. Look at every data table and graph included and try to find patterns yourself. You don't need to read every word of this section, especially if you don't understand a lot of the words and jargon used. Some key points to consider are: qualitative vs. quantitative data, sample size, confounding factors, and results.
(Some definitions for those of you who are unfamiliar with these terms. Qualitative data is data that cannot be quantified into a number. These are usually stories and anecdotes. Quantitative data is data that can be transferred into a numerical representation. You can't graph qualitative data (directly), but you can graph quantitative data. Sample size is the number of people or things counted (n when used in academic articles). Your sample size can indicate how generalizable your conclusions are. So pay attention. Did the author interview 300 subjects? Or 30? There will be a difference. A confounding factor is a factor that may affect the working theory. An example of a theory would be "increasing LGBTQ resources in a neighborhood would decrease LGBTQ hate crimes in that area." A confounding factor would be "increased reporting of hate crimes in the area." The theory, including the confounding factor, would look like "increasing LGBTQ resources in a neighborhood would increase the reporting of hate crimes in the area, which increases the number of hate crimes measured in that area." The confounding factor changes the outcome because it is a factor not considered in the original theory. When looking at research, see if you can think of anything that may change the theory based on how that factor interacts with the broader concept. Finally, the results are different from the conclusions. The results tell you what the methods spit out. Analysis tells you what the results say, and conclusions tell you what generalizations can be made based on the analysis.)
Next, read the conclusion section. This section will tell you what general conclusions can be made from the information found in the paper. This will tell you what the author found in their research.
Finally, once you've done all that, go back to the literature review section. You don't have to read it necessarily, but reading it will give you an idea of what is in each sourced paper. Take note of the authors and papers sourced in the literature review and repeat the process on those papers. You will get a wide variety of expert opinions on whatever concept or niche you're researching.
Starting to notice a pattern?
My research methods may not necessarily work for everybody, but they are pretty standard practice. You may notice that throughout this guide, I've told you to "source-hop" or follow the sources cited in whatever source you find first. This is incredibly important. You need to know who people are citing when they make claims.
This guide focused on secondary sources for most of the guide. Primary sources are slightly different. Primary sources require understanding the person who created the source, who they were, and their motivations. You also may need to do a little digging into what certain words or phrases meant at the time it was written based on what you are researching. The Prose Edda, for example, is a telling of the Norse mythology stories written by an Icelandic historian in the 13th century. If you do not speak the language spoken in Iceland in 1232, you probably won't be able to read anything close to the original document. In fact, the document was lost for about 300 years. Now there are translations, and those translations are as close to the primary source you can get on Norse Mythology. But even then, you are reading through several veils of translation. Take these things into account when analyzing primary documents.
Research Takes Practice
You won't get everything you need to know immediately. And researching subjects you have no background knowledge of can be daunting, confusing, and frustrating. It takes practice. I learned how to research through higher formal education. But you don't need a degree to write, so why should you need a degree to collect information? I genuinely hope this guide helps others peel away some of the confusion and frustration so they can collect knowledge as voraciously as I do.
– Indy
#writing advice#writing tips#writing resources#writeblr#amwriting#writblr#writers of tumblr#writers on tumblr#writing help#writing guide#how to research#reading research articles#do some research#do your own research#do your research#research for writers#writing research#writing tip#writing reference#writer tips
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Villain Organizations
masterlist. main navigation.
bluebxlle_writer on instagram
1. Goal & motivation
To pose a threat to your main characters, your villains need a clear goal — preferably one that directly negates your MC’s goal. But that’s not enough — they also need a clear motivation to justify their goal.
Now, which one should you flesh out first? Goal or motivation?
The answer is : it’s up to you. You can start by giving your villain organization a clear goal before brainstorming possible motivations that would support this goal; or you can come up with a backstory which narrates their motivation then set up a goal that aligns with said motivation.
2. Influence
To be memorable, your villain organization must have some sort of influence on your main characters and the general public.
An underground criminal organization that brings annoyance to your main characters because they wreak havoc everywhere they go and are impossible to catch as they have their ways to evade law.
A supernatural cult that brings fear to the public because they have the most powerful people on their side who won’t hesitate to kill anyone who stands in their way.
A cryptic society that brings a sense of uneasiness to the MCs because they’re unpredictable and have actions that don’t seem to make sense, yet always results in casualties.
3. Leader
Behind every villain organization is a leader who can control all the worst and most evil people in your story. This should be something frightening, so make sure to clearly establish how they obtained their power as a leader.
Expertise — they have expertise on a certain skill that’s deemed important, such as mastery of a deadly spell.
Charm — they can sway and manipulate people as they please.
Cruelty— they’re evil and ruthless, striking fear within the group and coaxing everyone to listen to them.
Ambitions — they have a strong goal and plan, convincing the entire organization that he’s the best man to achieve that goal.
Savior — they “saved” several villains from a gruesome end and played the role of “savior”, earning gratitude and awe.
4. Disputes
Selfish and goal-driven villains are bound to trigger disputes within the organization. Here are a few conflicts that could trigger disputes :
Factions — the organization is split into two factions ; one that supports the current leader, and one that support someone who promises to bring a “real” change if he were to become leader.
Betrayal — when one villain betrays the organization and the leader finds out, this may trigger an all-out dispute ; some members defending the betrayer and the rest wanting to kill them.
Absense of a leader — When the leader dies or is incapable of issuing orders, members of the villain organization may fight for the leader’s seat as they want to use the position to reach their personal goals.
5. Parallel
If your main characters are also part of an organization, a villain group can serve as a parallel to your MC’s organization.
While the villains operate under personal goals and are only bounded by fear to their leader, your MCs have a common goal and are willing to work together to reach it.
While the villains don’t care about public safety and only ensure the smooth operation of their missions, your MCs always put civilians first.
While the villain strictly prohibit emotional relationships; let alone romantic relationships, your MCs are free to be with whoever they want.
#writers on tumblr#writing things#writers#writerslife#writersociety#writing tips#writing advice#writing villains#female villains#villains#writers supporting writers#writers tips#writers help writers#writing tip#writing inspo#writing inspiration#writing techniques#writers of tumblr#writers helping writers#writing
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
HOW TO AO3
the difference between "orphaning" a fic and posting/making a fic under "anonymous" section.
orphaning a fic
once you've orphaned a fic, it means the work is no longer yours and there is no way you can "unorphan" the work once it has been orphaned. what does it mean? — it means your name will not be attached to the work, you cannot edit the work, you cannot delete the work and you cannot reclaim the work. you will lose the ownership of your work forever once you've orphaned it.
posting a fic under "anonymous" section
by posting or making your published work "anonymous", your name will not be publicly attached to said work (but will still appear in "my works" section where only you can see). the big difference between orphaning a work and posting/turning a work under anonymous section is that — unlike an orphaned work — you can edit, delete or even reclaim a work under anonymous section anytime you want. you will also still be receiving an email alerting you when someone gives kudos or comments on an anonymous work of yours.
if you don't want your name associated with some specific works you wrote, but at the same time still want to have ownership of them, I suggest you turn them "anonymous" instead of orphaning them.
remember: orphaning a fic is permanent. once you've done it, you cannot undo it. whereas posting or making published work "anonymous" can be undone.
#how to ao3#ao3#archive of our own#writer#writers#writeblr#writing#fanfic#fanfiction#fandom#fandoms#writing advice#writing advices#writing tip#writing tips#whump#angst#whumpblr#whump community#whump blog
460 notes
·
View notes
Note
How to write about someone’s appearance? Their physique, styles, face , clothes,?
How to Describe a Character's Appearance
-> dabblewriter.com
-> link to Character Description Prompts
Avoid Over-Describing
Overloading readers with too much information can be overwhelming and make your characters feel flat and one-dimensional. Focus on the details that are the most important to the story and the characters themselves.
If the character's appearance is not central to the story, then you may only need to give a basic description. If it plays a significant role, you may want to go into more detail. Always keep the purpose of your physical descriptions in mind.
Show Don't Tell
Don't blatantly state every little thing about your character's appearance, but rather show it through their actions and behaviors.
example: If they are tall, show that through their actions. They have to duck to get under a doorway, they help someone reach the top shelf, etc.
Include Personality Traits
A character's personality is what makes them memorable. Consider their motivations, values, beliefs, and quirks and give them a well-defined personality.
Avoid Stereotypes
Create characters that are more than just their cultural, racial, ethnic, or gender identity. Give them unique interests, hobbies, and personalities. Allow them to have flaws, contradictions, and diverse perspectives.
External Features
External features include a character's height, weight, body type, and general appearance. You can describe their skin color, hair color, eye color, and any distinctive features like freckles or scars. This type of description gives the reader a basic understanding of what the character looks like, which is helpful in creating a mental image.
Clothing
Describing the type of clothing they wear, including the colors, patterns, and how they fit, can reveal a lot about a character’s personality and social status.
For example, a character who wears tailored suits and expensive shoes might be a little snobby and concerned with their image, while a character who wears ripped jeans and t-shirts might be casual and relaxed.
Facial Features
Facial features can be used to give the reader a more in-depth understanding of a character's personality and emotions. You can describe their smile, the way they frown, their cheekbones, and their jawline. You can also describe their eyebrows, the shape of their nose, and the size and shape of their eyes, which can give the reader insight into their emotions.
Body Language
Body language can be used to give the reader an understanding of a character's emotions and personality without the need for dialogue. Describing the way a character stands, walks, or gestures can reveal a lot about their confidence level, mood, and attitude.
For example, a character who slouches and avoids eye contact is likely to be shy, while a character who stands up straight and makes direct eye contact is likely to be confident.
Words to Describe Various Features
Head and face
Oval: rounded, elongated, balanced, symmetrical
Round: full, plump, chubby, cherubic
Square: angular, defined, strong, masculine
Heart: pointy, triangular, wider at the temples, narrow at the chin
Diamond: angular, pointed, narrow at the forehead and jaw, wide at the cheekbones
Long: elongated, narrow, oval, rectangular
Triangular: angular, wide at the jaw, narrow at the forehead, inverted heart-shape
Oblong: elongated, rectangular, similar to oval but longer
Pear-shaped: narrow at the forehead, wide at the jaw and cheekbones, downward-pointing triangle
Rectangular: angular, defined, similar to oblong but more squared
Facial features
Cheeks: rosy, plump, gaunt, sunken, dimpled, flushed, pale, chubby, hollow
Chin: pointed, cleft, rounded, prominent, dimpled, double, weak, strong, square
Ear: large, small, delicate, flapped, pointed, rounded, lobeless, pierced
Eyes: deep-set, angled, bright, piercing, hooded, wide-set, close-set, beady, slanted, round, droopy, sleepy, sparkling
Forehead: high, broad, wrinkled, smooth, furrowed, low, narrow, receding
Jaw: strong, square, defined, angular, jutting, soft, weak, chiseled
Lips: full, thin, chapped, cracked, puckered, pursed, smiling, quivering, pouty
Mouth: wide, small, downturned, upturned, smiling, frowning, pouting, grimacing
Nose: hooked, straight, aquiline, button, long, short, broad, narrow, upturned, downturned, hooked, snub
Eyebrows: arched, bushy, thin, unkempt, groomed, straight, curved, knitted, furrowed, raised
Hair
Texture: curly, straight, wavy, frizzy, lank, greasy, voluminous, luxurious, tangled, silky, coarse, kinky
Length: long, short, shoulder-length, waist-length, neck-length, chin-length, buzzed, shaven
Style: styled, unkempt, messy, wild, sleek, smoothed, braided, ponytail, bun, dreadlocks
Color: blonde, brunette, red, black, gray, silver, salt-and-pepper, auburn, chestnut, golden, caramel
Volume: thick, thin, fine, full, limp, voluminous, sparse
Parting: center-parted, side-parted, combed, brushed, gelled, slicked back
Bangs: fringed, side-swept, blunt, wispy, thick, thin
Accessories: headband, scarf, barrettes, clips, pins, extensions, braids, ribbons, beads, feathers
Body
Build: slender, skinny, lean, athletic, toned, muscular, burly, stocky, rotund, plump, hefty, portly
Height: tall, short, petite, lanky, willowy, stocky, rotund
Posture: slouching, upright, hunched, stiff, relaxed, confident, nervous, slumped
Shape: hourglass, pear-shaped, apple-shaped, athletic, bulky, willowy, curvy
Muscles: defined, toned, prominent, ripped, flabby, soft
Fat distribution: chubby, plump, rounded, jiggly, wobbly, flabby, bloated, bloated
Body hair: hairy, smooth, shaven, beard, goatee, mustache, stubble
Weight: light, heavy, average, underweight, overweight, obese, lean, skinny
Body language: confident, nervous, aggressive, submissive, arrogant, timid, confident, relaxed
Body movements: graceful, clunky, fluid, awkward, jerky, smooth, agile, rigid
Build
Muscular: ripped, toned, defined, well-built, buff, brawny, burly, strapping
Athletic: fit, toned, agile, flexible, energetic, muscular, athletic, sporty
Thin: skinny, slender, slim, lanky, bony, gaunt, angular, wiry
Stocky: sturdy, broad-shouldered, compact, muscular, solid, robust, heavy-set
Overweight: plump, chubby, rotund, heavy, portly, corpulent, stout, fleshy
Fat: overweight, overweight, rotund, heavy, bloated, tubby, round, fat
Lean: lanky, slender, skinny, thin, wiry, willowy, spare, underweight
Larger: large, heavy, hefty, substantial, solid, overweight, portly, rotund
Skin
Texture: smooth, soft, silky, rough, bumpy, flaky, scaly, rough
Tone: fair, light, pale, dark, tan, olive, bronze, ruddy, rosy
Complexion: clear, radiant, glowing, dull, blotchy, sallow, ruddy, weathered
Wrinkles: deep, fine, lines, crow's feet, wrinkles, age spots
Marks: freckles, age spots, birthmarks, moles, scars, blemishes, discoloration
Tone: even, uneven, patchy, discolored, mottled, sunburned, windburned
Glow: luminous, radiant, healthy, dull, tired, lifeless
Tautness: taut, firm, loose, saggy, wrinkles, age spots, slack
Condition: healthy, glowing, radiant, dry, oily, acne-prone, sunburned, windburned
Style
Clothing: trendy, stylish, fashionable, outdated, classic, eclectic, casual, formal, conservative, bold, vibrant, plain, ornate
Fabric: silk, cotton, wool, leather, denim, lace, satin, velvet, suede, corduroy
Colors: bright, bold, pastel, neutral, vibrant, muted, monochrome
Accessories: jewelry, hats, glasses, belts, scarves, gloves, watches, necklaces, earrings, bracelets, rings
Shoes: sneakers, boots, sandals, heels, loafers, flats, pumps, oxfords, slippers
Grooming: well-groomed, unkempt, messy, clean-cut, scruffy, neat
Hair: styled, messy, curly, straight, braided, dreadlocks, afro, updo, ponytail
Makeup: natural, bold, minimal, heavy, smokey, colorful, neutral
Personal grooming: clean, fragrant, unkempt, well-groomed, grooming habits
Overall appearance: put-together, disheveled, polished, rough, messy, tidy
If you like what I do and want to support me, please consider buying me a coffee! I also offer editing services and other writing advice on my Ko-fi! Become a member to receive exclusive content, early access, and prioritized writing prompt requests.
#writing prompts#creative writing#writeblr#ask box prompts#how to write#how to describe a character's appearance#how to describe a character#character description#writing help#writing tip#writing tips and tricks#writing advice
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Look in all seriousness you can't redeem a character without showing them being pathetic, deep loser energy. There are no cool redemption arcs. They have to be in the trenches. They have to hate themselves for the mistakes they made. They have to apologize and take whatever is given be it forgiveness or a punch to the jaw. ONLY then will the redemption arc be actually good because it will be cathartic. And then they get to see the good things, they get to be touched gently and held while they sleep.
These things can overlap, even into a circle but without the pathetic loser boy saga your redemption arc will feel hollow.
#redemption arcs#writing#vegas theerapanyakul#kylo ren#anakin skywalker#klaus mikaelson#elijah mikaelson#dameon targeryan#writeblr#am writing#writers on tumblr#writing advice#writing tip#desiblr#writing help#avatar the last airbender#zuko
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Creative misfortunes for characters
Identity Crisis: Have your character lose their memory, forcing them to rediscover their true self and past.
Betrayal by a Loved One: A close friend or family member betrays the character's trust, leading to emotional turmoil and inner conflict.
Physical Transformation: Give your character a physical ailment or transformation that they must come to terms with, such as sudden blindness, a debilitating illness, or turning into a different species.
Unrequited Love: Make your character fall deeply in love with someone who doesn't reciprocate their feelings, causing heartache and a quest for self-discovery.
Financial Ruin: Strip your character of their wealth and privilege, forcing them to adapt to a life of poverty and face the harsh realities of the world.
False Accusation: Have your character falsely accused of a crime they didn't commit, leading to a desperate quest to clear their name.
Natural Disaster: Place your character in the path of a devastating natural disaster, such as a hurricane, earthquake, or tsunami, and force them to survive and rebuild.
Loss of a Sense: Take away one of your character's senses (e.g., sight, hearing, taste) and explore how they adapt and cope with this profound change.
Forced Isolation: Trap your character in a remote location, like a deserted island, and make them confront their inner demons while struggling to survive.
Haunted Past: Reveal a dark secret from your character's past that comes back to haunt them, threatening their relationships and well-being.
Time Travel Consequences: Send your character back in time, but make them inadvertently change a crucial event in history, leading to unintended consequences in the present.
Psychological Breakdown: Push your character to the brink of a mental breakdown, exploring the complexities of their psyche and their journey towards recovery.
Unwanted Prophecy: Have your character be the subject of a prophecy they want no part of, as it places them in grave danger or disrupts their life.
Loss of a Loved One: Kill off a beloved character or make your protagonist witness the death of someone close to them, igniting a quest for revenge or justice.
Incurable Curse or Disease: Curse your character with an incurable ailment or supernatural curse, and follow their journey to find a cure or accept their fate.
Sudden Disappearance: Make a character disappear mysteriously, leaving the others to search for them and uncover the truth.
Betrayal of Morals: Force your character into a situation where they must compromise their ethical values for a greater cause, leading to moral dilemmas and internal conflict.
Loss of a Precious Object: Have your character lose a cherished possession or artifact that holds sentimental or magical significance, setting them on a quest to recover it.
Political Intrigue: Place your character in a position of power or influence, then subject them to political intrigue, manipulation, and power struggles.
Existential Crisis: Make your character question the meaning of life, their purpose, and their place in the universe, leading to a philosophical journey of self-discovery.
Remember that misfortunes should serve a purpose in your story, driving character growth, plot development, and thematic exploration.

#writing#writing advice#writers block#just writer things#creative writing#fanfiction writing#writing motivation#writeblr#original writing#writing reference#writing tips#writers on tumblr#writing resources#writing tip#writing encouragement#writblr#writing community#writers#world building#point of view#editing#character creation#dialogue#mine.#words
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Everything You Need To Know About Writing Gunshot Wounds

Welcome to the latest installment in my ongoing series on crafting realistic wounds in fiction! After covering stab wounds and burns, it's time to explore the next wound category frequently explored in fiction—gunshot wounds.
Gunshot wounds are a recurring motif in the realm of storytelling. They're something you can easily come across in every genre, however, authors often poorly portray gunshot wounds due to lack of proper research. I understand finding the right resources to aid with your writing can be hard, so here's my comprehensive guide on how to write gunshot wounds.
How To Categorise Gunshot Wounds
There are certain factors you need to consider before writing a gunshot wound. These details are instrumental in crafting a vivid and plausible narrative while avoiding plot holes. The first and most important one is identifying the type of firearm used to inflict the wound.
Picking The Right Firearm
Selecting the appropriate firearm to inflict a gunshot wound is a pivotal decision. It's not just about choosing any gun; it's about picking the right one to align with your desired outcome and the narrative's overall impact. Here's a quick guide on how to pick the right firearm.
The Impact of Firearm Selection
The firearm you choose can significantly influence the severity and appearance of the gunshot wound. Whether your goal is a graphic, gory injury or a precise, long-range shot, the choice of firearm plays a crucial role. Here are some guns you to consider:
Handguns: These are versatile and commonly used in close-quarters combat. They can result in gruesome, close-contact wounds with a higher potential for damage due to their stopping power.
Shotguns: Shotguns disperse shot pellets upon firing, making them suitable for creating a broader pattern of injuries. If you aim to depict a devastating, close-range gunshot wound, shotguns can be a fitting choice.
Rifles: Rifles are known for their accuracy at longer distances. When you need a precise, long-range shot, rifles are the go-to option. They tend to produce a cleaner wound channel, especially when used for a targeted, well-planned injury.
Choosing the Right Firearm for Your Narrative
The type of firearm you select should align with your story's objectives. If you intend to evoke visceral, gory reactions, opt for handguns or shotguns used in close proximity. On the other hand, if precision and long-range engagement are key, rifles can achieve your desired outcome.
Keep in mind that firearm selection can affect the wound's damage, trajectory, and overall portrayal in your narrative.
Categorising The Wound
Once you've identified the type of firearm, you need to establish what type of wound your character will incur.
In order to bring your character's injuries to life, it's important to first identify what you're dealing with. You can do this by categorising the injury based on several factors. For gunshot wounds, this includes the type of firearm used, the bullet's trajectory, and the specific areas of the body affected.
You can categorise your character's gunshot would into seven main categories, here's a quick breakdown of what these categories look like and the level of severity associated with them:
Penetrating Gunshot Wounds: These wounds occur when a bullet enters the body but doesn't exit. The bullet remains inside the body, causing damage along its path.
Perforating Gunshot Wounds: In this case, the bullet enters the body and exits on the opposite side. This type of wound can have a different set of implications due to the bullet's trajectory.
Ricochet Gunshot Wounds: Ricochet wounds happen when the bullet bounces off a surface before hitting the character. The nature of the surface can influence the severity of the wound.
Through-and-Through Gunshot Wounds: As the name suggests, these wounds occur when the bullet enters one side of the body and exits through the other. The trajectory can greatly affect the injury's severity.
Close-Contact Gunshot Wounds: These wounds result from the firearm being fired at extremely close range. The proximity of the gun to the body can lead to unique wound patterns and burn injuries.
Shotgun Wounds: Shotgun wounds differ from those caused by handguns or rifles. The shot pellets disperse upon firing, leading to a broader pattern of injury.
Long-Range Gunshot Wounds: When a character is shot from a considerable distance, the wound might appear different due to factors like bullet tumbling and loss of velocity.
The Anatomy of a Gunshot Wound
To create a vivid portrayal of a gunshot wound, writers need to grasp not only the external appearance but also the internal effects it has on the body. A well-executed description captures both the physical trauma and the emotional turmoil experienced by the character. Here are some symptoms you should take into consideration.
1. External Appearance and Bleeding:
Wound Size: The size of a gunshot wound can vary significantly based on the type of firearm and bullet used. Smaller calibers may leave entry and exit wounds that are relatively small, while larger bullets or high-velocity rounds can create much larger wounds. Be specific about the size, which can help readers visualize the injury.
Blood Loss: Gunshot wounds typically result in bleeding. The severity of bleeding depends on factors like the wound's location, the size of the blood vessels damaged, and the bullet's trajectory. Mention the amount of blood, but avoid excessive gore unless it serves a specific purpose in your narrative.
Coughing Up Blood: If the gunshot wound affects the chest or lung area, characters may cough up blood. This symptom often signifies a more critical injury and can add drama to your story.
2. Internal Damage and Symptoms:
Pain: Gunshot wounds are painful, and the character should express this pain through their actions, dialogue, and internal thoughts. Describe the sharp, burning, or throbbing sensations as they resonate through the character's body.
Shock: Depending on the severity of the wound, shock can set in. The character may appear pale, sweaty, and disoriented. This state of shock can impact their actions and decisions.
Loss of Function: A gunshot wound may impair the use of the injured body part. Describe any loss of function, such as the inability to move a limb or use it effectively.
Fainting: In extreme cases, characters may faint due to the pain, blood loss, or shock. Be sure to contextualize this within the narrative, as fainting can have significant consequences for the character.
By diving into the details of a gunshot wound's anatomy, you can craft a compelling and realistic portrayal that draws readers into the character's harrowing experience. I haven't exactly covered every symptom out there, but these are the major ones you should take into account when writing.
Medical Assessment and Treatment
Once you've established your gunshot wound, it's now time to focus on the aftermath. One of the main factors to consider is the medical process that follows. If your character is supposed to die from the gunshot then you could probably skip this section, but if they're alive here are things you need to consider.
1. Initial Assessment:
Scene Safety: In a real-life scenario, safety is paramount. First responders will ensure the scene is secure before approaching the injured person. Consider factors like the presence of firearms, potential threats, and the safety of medical personnel.
ABCs of Assessment: Medical professionals follow the ABCs—Airway, Breathing, and Circulation. Writers can reflect this in their storytelling by highlighting the character's ability to breathe, cough, or speak after being shot.
Vital Signs: Mentioning vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation can help convey the character's condition and the urgency of their medical treatment.
2. Trauma Assessment:
Focused Assessment: Medical personnel perform a thorough examination to identify the gunshot wound's location, entry and exit points, and any associated injuries. This assessment informs their treatment plan.
Imaging: Depending on the complexity of the injury, X-rays or other imaging may be required to visualize the bullet's trajectory and any potential damage to internal organs or bones.
3. Treatment:
Bleeding Control: Stopping the bleeding is a top priority. This may involve applying pressure, packing the wound, or even tourniquet application in extreme cases.
Wound Care: Depending on the wound's severity, cleaning and suturing may be required. The character's response to this procedure can add an element of realism to your narrative.
Pain Management: Gunshot wounds are excruciatingly painful, and medical personnel will often administer pain relief or anesthesia during treatment.
Monitoring and Observation: Patients with gunshot wounds require careful observation and monitoring for signs of infection, complications, or changes in their condition.
By accurately portraying the medical assessment and treatment of gunshot wounds, you not only enhance the authenticity of your writing but also depict the physical and emotional toll such injuries can take on your characters. This attention to detail helps your readers connect more deeply with the story.
The Psychological Impact
Gunshot wounds don't just inflict physical harm; they also leave lasting emotional and psychological scars. It is important to note that the extent of the psychological impact on your characters will heavily rely on various factors.
For example, you need to consider whether or not this injury is something normal for them. Do they work as a spy, assassin, or other such roles that would mandate such dangerous injuries? You also need to consider who shot them. Does this wound come with emotional damage as well? Think of Aaron Warner’s reaction to Juliet shooting him.
If you’re sure your character will have some extent of a psychological impact, here are some factors you should consider.
1. Shock and Denial:
Immediate Response: Characters who have been shot may initially experience shock and denial. This can manifest as disbelief, emotional numbness, or a surreal sense of detachment from the situation.
Physical Symptoms: Shock can lead to physical symptoms like trembling, chills, or even fainting. Incorporating these details can make the character's reaction more genuine.
2. Fear and Anxiety:
Survivor's Guilt: Characters may grapple with survivor's guilt if they are the only ones to emerge unscathed in a violent encounter.
Anxiety: The threat of recurrence or the fear of returning to the location where the shooting occurred can trigger anxiety and panic attacks.
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
Flashbacks and Nightmares: Characters who have survived a gunshot wound may experience recurring flashbacks and nightmares, vividly reliving the traumatic event.
Hypervigilance: PTSD can lead to hypervigilance, where characters are constantly on edge, expecting danger at every turn.
4. Depression and Isolation:
Emotional Withdrawal: Characters may withdraw from social interactions, experiencing feelings of isolation and sadness.
Emotional Numbness: Some may describe feeling emotionally numb, unable to experience joy or pleasure.
5. Recovery and Resilience:
Therapeutic Support: In your storytelling, consider how characters seek therapy or counseling to cope with their emotional scars. Therapy can be a path toward recovery and resilience.
By addressing the psychological impact of gunshot wounds on your characters, you create more layered and relatable individuals within your narrative. This depth allows readers to connect with the characters on a profound emotional level.
I hope this blog on Everything You Need To Know About Writing Gunshot Wounds will help you in your writing journey. Be sure to comment any tips of your own to help your fellow authors prosper, and follow my blog for new blog updates every Monday and Thursday.
Looking For More Writing Tips And Tricks?
Are you an author looking for writing tips and tricks to better your manuscript? Or do you want to learn about how to get a literary agent, get published and properly market your book? Consider checking out the rest of Haya’s book blog where I post writing and publishing tips for authors every Monday and Thursday! And don’t forget to head over to my TikTok and Instagram profiles @hayatheauthor to learn more about my WIP and writing journey!
#hayatheauthor#haya's book blog#haya blogs#writers on tumblr#writer community#writer tools#writer blog#writer stuff#writer wednesday#writer tips#creative writing#writers of tumblr#writerscommunity#writeblr#writing community#writer spotlight#writer things#writing prompt#writing tools#writing stuff#writing#writing life#writing inspo#writing help#writing advice#writing inspiration#writing ideas#writing things#writing tip#quillology with haya
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to write a found family
By Writerthreads on Instagram
The found family story is a type of YA trope where individuals from different backgrounds come together to form a family, possibly to make up for their lack of true family. When it’s done well, found families can be so wholesome and heartwarming, and I simply adore this trope. Here's a guide to help you write a compelling found family in your WIP:
Create a diverse group of characters
The key to writing a successful found family story is to have a diverse cast of characters with different backgrounds, cultures, and experiences. This diversity will make the story richer and allow you to explore different perspectives and themes from different points of views. It also allows for a wide range of readers to find a character that they can relate to.
Establish a common goal
In a found family story, the characters come together to achieve a common goal. This goal can be anything from surviving an apocalypse to starting a business together. It is essential to establish this goal early on in the story, as it will help to create a sense of unity among the characters.
Themes
Using themes can add depth to a found family story by providing a framework for exploring the emotional and psychological growth of the characters. Here are a few examples:
Belonging: The idea that characters finally have a place where they fit in, and the struggles that come with feeling like an outsider previously.
Identity: The idea of self-discovery when a character finally becomes part of a family and has the time and people to communicate with to understand themselves.
Acceptance: Characters accepting themselves and others for who they are, overcoming previous prejudices.
Family: What makes a family, and the classic tropes associated with families and variations of them. Eg. the "mum" of the group who also doubles as the "wild child" at times.
Explore each character's backstory
A found family story is all about the characters' individual journeys and how they come together, and this can be done by giving each character a backstory that explains their motivations and desires. This can justify bad choices that characters may make or simply allow the readers to relate to them more. You can also use flashback scenes or dialogue to reveal important details about each character's past, however, I think flashbacks can be used more sparingly and only if they serve a purpose.
Create conflicts and obstacles
Like any good story, a found family story needs conflict to keep readers engaged. You can create conflicts within the group or create some external obstacles that the group must overcome. These conflicts challenge the characters and force them to grow and change through adverse situations. It’s especially interesting to see how characters with conflicting personalities or life views have friction with each other.
These are some of the tips I could think of for creating a found family in your story. As always our tips are just guides to help you with your book and definitely not a set of rules to follow. Good luck and have fun! :)
#writing#creative writing#writing inspiration#writing tip#writing tips#writing advice#teen writer#writers on tumblr#writeblr#writers block#found family
2K notes
·
View notes