#algorithm bias
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Great Shirtless Grandpa Conspiracy
Picture this: a 25-year-old gym bro, abs glistening like a glazed donut, rips off his tank top in a TikTok video to flex for the algorithm gods. The comments? Fire emojis, heart-eyes, maybe a “Bro, teach me your ways!” Now swap that dude for a 65-year-old retiree, proudly showcasing his silver chest hair and a tan that screams “I mowed the lawn in July.” Same platform, same pose, but the…
#ageism in media#ageist humor#algorithm bias#body positivity#cultural norms#fitness double standards#generational humor#internet comedy#media satire#Occupy 2.5#senior confidence#shirtless double standards#shirtless grandpa#shirtless old men#shirtless stereotypes#social media culture#social media hypocrisy#TikTok age bias#viral video trends#X platform reactions
0 notes
Text
youtube
The issues she brings up in this video are big reasons why it's so helpful when viewers spread the word to friends, family and social media about their favorite YouTube videos and channels. You can't assume the search box, feed or even "liking" a video will boost a creator.
As a woman making long-form videos on YouTube, apparently I've got the deck (aka the algorithm) stacked against me. As if I didn't know! My gaming channel's had very VERY slow growth over the years and I've been asked many times why I bother to keep doing it.
Well, not only do I enjoy it, I learn a lot (about gaming, editing, streaming, etc), I meet some great people, I've cheered a few of you up when you're down, and I've helped a lot of folks with gaming tips and solutions. I also think it's important to be out there as an over-50 gamer and a female gamer on YouTube who's playing everything from the smalled indie title to the biggest AAA's.
Don't let an algorithm control what you see! Notifications are notoriously unreliable on YouTube too so don't rely on those either. Make sure to subscribe to channels you like and check the "subscriptions" tab on your computer, phone or TV rather than the home page or "feed."
1 note
·
View note
Text
I expected to get some iffy results when searching “judaism” on tiktok (and definitely did; there’s a high number of tiktoks from non-jewish accounts, a lot of tiktoks about palestine, a “facts about judaism” video where the first “fact” is the claim “the jews are not allowed to have a jewish state in judaism”, one promoting neturei karta, and most of the videos actually by jewish creators are about conversion or comparing/contrasting judaism to islam & christianity)
but I was not expecting how many of the top videos are straight up just about islam—not just its relationship to judaism, not videos about islam by jewish creators—just videos by muslims about islam:
(these 4 videos were not at the very top, but i did not have to scroll far before all the videos just became about islam)
it’s just weird.
#also this is on a blank account to ensure my content preferences & blocklist didn’t bias the algorithm#tiktok#antisemitism#jumblr#judaism
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
The surprising truth about data-driven dictatorships

Here’s the “dictator’s dilemma”: they want to block their country’s frustrated elites from mobilizing against them, so they censor public communications; but they also want to know what their people truly believe, so they can head off simmering resentments before they boil over into regime-toppling revolutions.
These two strategies are in tension: the more you censor, the less you know about the true feelings of your citizens and the easier it will be to miss serious problems until they spill over into the streets (think: the fall of the Berlin Wall or Tunisia before the Arab Spring). Dictators try to square this circle with things like private opinion polling or petition systems, but these capture a small slice of the potentially destabiziling moods circulating in the body politic.
Enter AI: back in 2018, Yuval Harari proposed that AI would supercharge dictatorships by mining and summarizing the public mood — as captured on social media — allowing dictators to tack into serious discontent and diffuse it before it erupted into unequenchable wildfire:
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/10/yuval-noah-harari-technology-tyranny/568330/
Harari wrote that “the desire to concentrate all information and power in one place may become [dictators] decisive advantage in the 21st century.” But other political scientists sharply disagreed. Last year, Henry Farrell, Jeremy Wallace and Abraham Newman published a thoroughgoing rebuttal to Harari in Foreign Affairs:
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/world/spirals-delusion-artificial-intelligence-decision-making
They argued that — like everyone who gets excited about AI, only to have their hopes dashed — dictators seeking to use AI to understand the public mood would run into serious training data bias problems. After all, people living under dictatorships know that spouting off about their discontent and desire for change is a risky business, so they will self-censor on social media. That’s true even if a person isn’t afraid of retaliation: if you know that using certain words or phrases in a post will get it autoblocked by a censorbot, what’s the point of trying to use those words?
The phrase “Garbage In, Garbage Out” dates back to 1957. That’s how long we’ve known that a computer that operates on bad data will barf up bad conclusions. But this is a very inconvenient truth for AI weirdos: having given up on manually assembling training data based on careful human judgment with multiple review steps, the AI industry “pivoted” to mass ingestion of scraped data from the whole internet.
But adding more unreliable data to an unreliable dataset doesn’t improve its reliability. GIGO is the iron law of computing, and you can’t repeal it by shoveling more garbage into the top of the training funnel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/05/29/garbage-in-garbage-out-machine-learning-has-not-repealed-the-iron-law-of-computer-science/
When it comes to “AI” that’s used for decision support — that is, when an algorithm tells humans what to do and they do it — then you get something worse than Garbage In, Garbage Out — you get Garbage In, Garbage Out, Garbage Back In Again. That’s when the AI spits out something wrong, and then another AI sucks up that wrong conclusion and uses it to generate more conclusions.
To see this in action, consider the deeply flawed predictive policing systems that cities around the world rely on. These systems suck up crime data from the cops, then predict where crime is going to be, and send cops to those “hotspots” to do things like throw Black kids up against a wall and make them turn out their pockets, or pull over drivers and search their cars after pretending to have smelled cannabis.
The problem here is that “crime the police detected” isn’t the same as “crime.” You only find crime where you look for it. For example, there are far more incidents of domestic abuse reported in apartment buildings than in fully detached homes. That’s not because apartment dwellers are more likely to be wife-beaters: it’s because domestic abuse is most often reported by a neighbor who hears it through the walls.
So if your cops practice racially biased policing (I know, this is hard to imagine, but stay with me /s), then the crime they detect will already be a function of bias. If you only ever throw Black kids up against a wall and turn out their pockets, then every knife and dime-bag you find in someone’s pockets will come from some Black kid the cops decided to harass.
That’s life without AI. But now let’s throw in predictive policing: feed your “knives found in pockets” data to an algorithm and ask it to predict where there are more knives in pockets, and it will send you back to that Black neighborhood and tell you do throw even more Black kids up against a wall and search their pockets. The more you do this, the more knives you’ll find, and the more you’ll go back and do it again.
This is what Patrick Ball from the Human Rights Data Analysis Group calls “empiricism washing”: take a biased procedure and feed it to an algorithm, and then you get to go and do more biased procedures, and whenever anyone accuses you of bias, you can insist that you’re just following an empirical conclusion of a neutral algorithm, because “math can’t be racist.”
HRDAG has done excellent work on this, finding a natural experiment that makes the problem of GIGOGBI crystal clear. The National Survey On Drug Use and Health produces the gold standard snapshot of drug use in America. Kristian Lum and William Isaac took Oakland’s drug arrest data from 2010 and asked Predpol, a leading predictive policing product, to predict where Oakland’s 2011 drug use would take place.
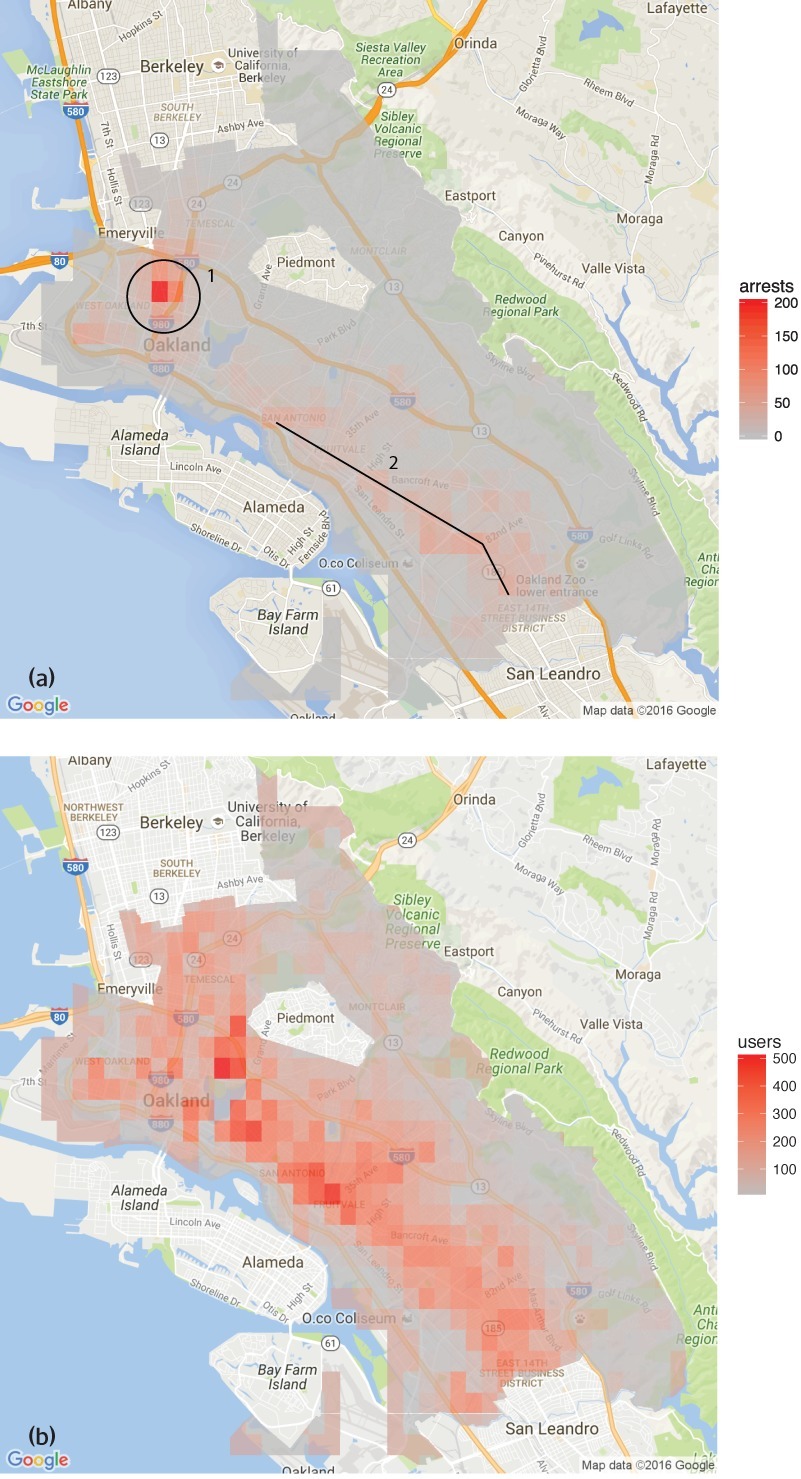
[Image ID: (a) Number of drug arrests made by Oakland police department, 2010. (1) West Oakland, (2) International Boulevard. (b) Estimated number of drug users, based on 2011 National Survey on Drug Use and Health]
Then, they compared those predictions to the outcomes of the 2011 survey, which shows where actual drug use took place. The two maps couldn’t be more different:
https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2016.00960.x
Predpol told cops to go and look for drug use in a predominantly Black, working class neighborhood. Meanwhile the NSDUH survey showed the actual drug use took place all over Oakland, with a higher concentration in the Berkeley-neighboring student neighborhood.
What’s even more vivid is what happens when you simulate running Predpol on the new arrest data that would be generated by cops following its recommendations. If the cops went to that Black neighborhood and found more drugs there and told Predpol about it, the recommendation gets stronger and more confident.
In other words, GIGOGBI is a system for concentrating bias. Even trace amounts of bias in the original training data get refined and magnified when they are output though a decision support system that directs humans to go an act on that output. Algorithms are to bias what centrifuges are to radioactive ore: a way to turn minute amounts of bias into pluripotent, indestructible toxic waste.
There’s a great name for an AI that’s trained on an AI’s output, courtesy of Jathan Sadowski: “Habsburg AI.”
And that brings me back to the Dictator’s Dilemma. If your citizens are self-censoring in order to avoid retaliation or algorithmic shadowbanning, then the AI you train on their posts in order to find out what they’re really thinking will steer you in the opposite direction, so you make bad policies that make people angrier and destabilize things more.
Or at least, that was Farrell(et al)’s theory. And for many years, that’s where the debate over AI and dictatorship has stalled: theory vs theory. But now, there’s some empirical data on this, thanks to the “The Digital Dictator’s Dilemma,” a new paper from UCSD PhD candidate Eddie Yang:
https://www.eddieyang.net/research/DDD.pdf
Yang figured out a way to test these dueling hypotheses. He got 10 million Chinese social media posts from the start of the pandemic, before companies like Weibo were required to censor certain pandemic-related posts as politically sensitive. Yang treats these posts as a robust snapshot of public opinion: because there was no censorship of pandemic-related chatter, Chinese users were free to post anything they wanted without having to self-censor for fear of retaliation or deletion.
Next, Yang acquired the censorship model used by a real Chinese social media company to decide which posts should be blocked. Using this, he was able to determine which of the posts in the original set would be censored today in China.
That means that Yang knows that the “real” sentiment in the Chinese social media snapshot is, and what Chinese authorities would believe it to be if Chinese users were self-censoring all the posts that would be flagged by censorware today.
From here, Yang was able to play with the knobs, and determine how “preference-falsification” (when users lie about their feelings) and self-censorship would give a dictatorship a misleading view of public sentiment. What he finds is that the more repressive a regime is — the more people are incentivized to falsify or censor their views — the worse the system gets at uncovering the true public mood.
What’s more, adding additional (bad) data to the system doesn’t fix this “missing data” problem. GIGO remains an iron law of computing in this context, too.
But it gets better (or worse, I guess): Yang models a “crisis” scenario in which users stop self-censoring and start articulating their true views (because they’ve run out of fucks to give). This is the most dangerous moment for a dictator, and depending on the dictatorship handles it, they either get another decade or rule, or they wake up with guillotines on their lawns.
But “crisis” is where AI performs the worst. Trained on the “status quo” data where users are continuously self-censoring and preference-falsifying, AI has no clue how to handle the unvarnished truth. Both its recommendations about what to censor and its summaries of public sentiment are the least accurate when crisis erupts.
But here’s an interesting wrinkle: Yang scraped a bunch of Chinese users’ posts from Twitter — which the Chinese government doesn’t get to censor (yet) or spy on (yet) — and fed them to the model. He hypothesized that when Chinese users post to American social media, they don’t self-censor or preference-falsify, so this data should help the model improve its accuracy.
He was right — the model got significantly better once it ingested data from Twitter than when it was working solely from Weibo posts. And Yang notes that dictatorships all over the world are widely understood to be scraping western/northern social media.
But even though Twitter data improved the model’s accuracy, it was still wildly inaccurate, compared to the same model trained on a full set of un-self-censored, un-falsified data. GIGO is not an option, it’s the law (of computing).
Writing about the study on Crooked Timber, Farrell notes that as the world fills up with “garbage and noise” (he invokes Philip K Dick’s delighted coinage “gubbish”), “approximately correct knowledge becomes the scarce and valuable resource.”
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/07/25/51610/
This “probably approximately correct knowledge” comes from humans, not LLMs or AI, and so “the social applications of machine learning in non-authoritarian societies are just as parasitic on these forms of human knowledge production as authoritarian governments.”

The Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers’ Workshop summer fundraiser is almost over! I am an alum, instructor and volunteer board member for this nonprofit workshop whose alums include Octavia Butler, Kim Stanley Robinson, Bruce Sterling, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, Nnedi Okorafor, Lucius Shepard, and Ted Chiang! Your donations will help us subsidize tuition for students, making Clarion — and sf/f — more accessible for all kinds of writers.

Libro.fm is the indie-bookstore-friendly, DRM-free audiobook alternative to Audible, the Amazon-owned monopolist that locks every book you buy to Amazon forever. When you buy a book on Libro, they share some of the purchase price with a local indie bookstore of your choosing (Libro is the best partner I have in selling my own DRM-free audiobooks!). As of today, Libro is even better, because it’s available in five new territories and currencies: Canada, the UK, the EU, Australia and New Zealand!

[Image ID: An altered image of the Nuremberg rally, with ranked lines of soldiers facing a towering figure in a many-ribboned soldier's coat. He wears a high-peaked cap with a microchip in place of insignia. His head has been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.' The sky behind him is filled with a 'code waterfall' from 'The Matrix.']

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Raimond Spekking (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acer_Extensa_5220_-_Columbia_MB_06236-1N_-_Intel_Celeron_M_530_-_SLA2G_-_in_Socket_479-5029.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
Russian Airborne Troops (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vladislav_Achalov_at_the_Airborne_Troops_Day_in_Moscow_%E2%80%93_August_2,_2008.jpg
“Soldiers of Russia” Cultural Center (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Col._Leonid_Khabarov_in_an_everyday_service_uniform.JPG
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#habsburg ai#self censorship#henry farrell#digital dictatorships#machine learning#dictator's dilemma#eddie yang#preference falsification#political science#training bias#scholarship#spirals of delusion#algorithmic bias#ml#Fully automated data driven authoritarianism#authoritarianism#gigo#garbage in garbage out garbage back in#gigogbi#yuval noah harari#gubbish#pkd#philip k dick#phildickian
833 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm really not a villain enjoyer. I love anti-heroes and anti-villains. But I can't see fictional evil separate from real evil. As in not that enjoying dark fiction means you condone it, but that all fiction holds up some kind of mirror to the world as it is. Killing innocent people doesn't make you an iconic lesbian girlboss it just makes you part of the mundane and stultifying black rot of the universe.
"But characters struggling with honour and goodness and the egoism of being good are so boring." Cool well some of us actually struggle with that stuff on the daily because being a good person is complicated and harder than being an edgelord.
Sure you can use fiction to explore the darkness of human nature and learn empathy, but the world doesn't actually suffer from a deficit of empathy for powerful and privileged people who do heinous stuff. You could literally kill a thousand babies in broad daylight and they'll find a way to blame your childhood trauma for it as long as you're white, cisgender, abled and attractive, and you'll be their poor little meow meow by the end of the week. Don't act like you're advocating for Quasimodo when you're just making Elon Musk hot, smart and gay.
#this is one of the reasons why#although i would kill antis in real life if i could#i also don't trust anyone who identifies as 'pro-ship'#it's just an excuse to shut down legitimate ethical questions and engaging in honest self-reflective media consumption and critique#art doesn't exist in a vacuum#it's a flat impossibility for it not to inform nor be informed by real world politics and attitudes#because that's what it means to be created by human hands#we can't even make machine learning thats not just human bias fed into an algorithm#if the way we interact with art truly didn't influence anything then there would be no value in it#just because antis have weaponized those points in the most bad faith ways possible#doesn't mean you can ignore them in good faith#anyway fandom stans villains because society loves to defend and protect abusers#it's not because you get the chance to be free and empathetic and indulge in your darkness and what not#it's just people's normal levels of attachment to shitty people with an added layer of justification for it#this blog is for boring do-gooder enjoyers only#lol#knee of huss#fandom wank#media critique#pop culture#fandom discourse
205 notes
·
View notes
Text

there's no salvation in the algorithm
#art#retrofuture#design#collage#aesthetic#cyberpunk#black and white#glitch#text#typeface#algorithmic bias#free palestine
137 notes
·
View notes
Text






Read More Here: Substack
#algorithmic determinism#techcore#philosophy#quote#quotes#ethics#technology#sociology#writers on tumblr#artificial intelligence#duty of care#discrimination#implicit bias#law enforcement#psychologically#computational design#programming#impact
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I can't believe people still say The Clone Wars and The Bad Batch are "just kids shows" when whatever this show is literally exists:

analysis of target audiences below (there's a TL;DR don't worry)
Okay so the whole "it's just for kids" fallacy/excuse/conversation stopper is such an issue as it is. Here's a good video about it, I'll probably do a whole rant at some point, but in short: the level of storytelling merit, emotional depth, and thematic exploration a work can and should achieve has never been limited by it's target audience/age group, nor it's storytelling medium. (And if you don't think that's true, try to tell me Pixar has never made you cry, go on)
So it doesn't matter if it was made for kids or not. There's nothing wrong with that and anyone can enjoy it anyway. But what I actually wanna talk about here is not the merits of "kids shows" but the misconception on what "kid show" even means.
For one thing, I think when some people say "it's a kids show" they are lumping anything from like Winnie the Pooh to Avatar: the Last Airbender into the same category, and that's just not how it works. The above example demonstrates that not all kids shows/stories are the same anyway (partially bc level of development/education changes drastically between the ages of like 3 and 12, and these are things that are really taken into account in the publishing industry).
I found Disney's ratings guide and I think this should clear some things up:

For reference:
Young Jedi Adventures is listed as TV-Y
Clone Wars (2003), Rebels, and Resistance are TV-Y7-FV
Clone Wars, Bad Batch, and the Tales of the Jedi/Empire are TV-PG
Mandalorian, Ahsoka, Kenobi, Book of Boba Fett, Andor, and Acolyte are all TV-14
And if we put that in context with the films:
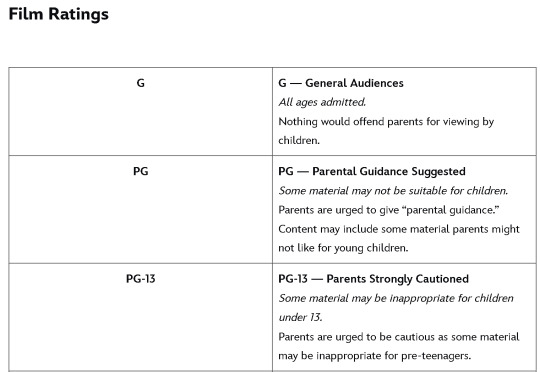
The Clone Wars (2008) film and the Original and Prequel trilogy are PG except for Revenge of the Sith which is PG-13 along with the Sequel trilogy, Rogue One and Solo.
So basically TCW and TBB are considered by Disney's own system to be about the same level as most of the films. They are 4 degrees away from 'Young Jedi Adventures' and only 1 degree lower than the live-action shows. Which frankly feels like we got some animation bias going on since all the live-action shows are automatically in one category (which is silly as is and undue here anyway (here have another video) esp since the Clone Wars animation style is clearly meant to be older/more realistic). But regardless, it's literally right there:

And again there is nothing wrong with TCW/TBB being kids shows, but some internet-ers dismiss it as "made for 7 year olds" and that's just objectively not true. Strictly from this system (which idk how it compares to whatever system Cartoon Network used when it aired) you could say the TV-PG might mean 8-13 years old (which is a wide range tbh, there's a big difference between being 8 and being 13), but since TV-G says "suitable for ALL ages" it's also not limited to that.
Also if TCW was aimed for ~8-13 year old's back in 2008 then those same people, who TBB was clearly meant for based on the marketing, were ~21-26 when it premiered in 2021 (and I think that is definitely reflected in writing).
Age of the protagonist is another a good indicator, though it's not a strict rule (i.e. Ender's Game and To Kill a Mockingbird have younger pov characters but are clearly meant for older audiences) and we have a wide range in these shows (Ahsoka 14, Anakin 20, Obi-wan 35, Clones early 20s, Omega ??? 10ish?? idk it's unclear) and time passes. (And while a lot of TBB is filtered through Omega's perspective, there's also plenty of scenes/subplots/episodes where she isn't even there. Also I doubt anyone would call TLOU a kids show just bc Ellie is 14)
But also target audience is a lot more than just content ratings. Note how the first few ratings above say "this program is designed for" the age group, while after TV-G it's about if it contains anything that could be unsuitable for age groups. And ratings can be pretty vague and arbitrary, especially since they change over time (like I get RotS but I could not tell you what makes the Sequels PG-13 compared to the PG films. And why is 13 the age we draw the line at? And why is it 14 for TV instead?)
I think TCW confuses a lot of people because it jumps around a lot; some episodes are about Jar Jar or the droids, and then some are, you know, Umbara. But on a rewatch, even some of the more serious episodes like the Citadel or Kadavo arc still tend to have a more juvenile or simplistic tone/writing style, like repeating information a lot or joking in the middle of the mission (like right after Echo died, hello?!). This actually feels like a writing issue to me, like maybe the writers weren't very clear on what they were going for. (Reminds me also of the only episode I watched of the live-action Atla, where compared to the original it increased the violence/death, but also dumbed down the exposition and didn't seem to trust the audience) Though there is also a clear difference between the seasons, again because the audience and characters are growing up as time goes on. I don't think TBB really had that issue though. It never talked down and it was much more tonally consistent, even in the lower stakes episodes.
Personally TBB feels generally grittier than TCW, though it doesn't really have any of the dark/gruesome deaths and "this is a kids show?!?!" moments like TCW (i.e. clones getting airlocked, decapitated, cut in half by doors, squished by Grievous, and whatever the ever living eff Colt's death was). Though actually come to think of it, there are a few things (like Crosshair killing civilians, the electro suicide pills, and the clone on Tantiss who got skewered (rip)) but I don't think they stand out as much, maybe because they're given the proper weight so they fit the tone rather than feeling out of place. Well, most of the time at least...

Like the friendly fire incident is probably one of the heaviest moments in TCW but I don't see it in those compilations, maybe because the characters respond appropriately and it fits within the Umbara arc. Verses when stuff happens in the middle of lighter more childish plot lines that feel more shocking because they are somewhat brushed off.
But also here's the thing. I think people get really fixated on the darkness/violence/death thing, but it isn't actually as big a deal as we tend to think. Like you'll find "this is a kid's show?!?" compilations for so many shows like these (with a similar age range, like Gravity Falls) that are just anything remotely creepy or intense or related to death, as if kids can't handle anything at all. Like I'll admit it's surprising sometimes (Infinity Train traumatized me bro lol) but most of the time I think we're underestimating kids. Like do you remember being 12? It's not that young.
There just seems to be this misconceived barrier, like the argument goes: "Clone Wars is just a kid show" "No it's not, look at this death scene!" But like there's death scenes in Disney movies all the time, you know? I think that's also why we get so many of these MA animated shows (i.e. Invincible and Vox Machina) that feel the need to overdo the blood and gore to like prove themselves as adult shows (bc again, animation bias).
As a writer that's just not really where the distinction is. This came up in my 'Writing for Children and Adolescents' class and we were all a little surprised when our professor said that death/violence is actually fine for middle-grade (8-12, the 'golden age of reading' and probably the equivalent to TV-PG). Like think of stories with ~12 year old protagonists like Percy Jackson, Harry Potter, Gregor the Overlander (tho Suzanne could stand to tone that one down imo lol). Basically, violence is okay actually. And most of the TCW and TBB characters are way older than middle-grade.
(Also I think the difference is usually more in the delivery. Like death and violence being more implied (no blood, or cutting away/seen with shadows), and themes/emotions generally being more clear, simple and stated upfront rather than more nuance, subtle and subtextual. (And tbh writing for kids is actually usually a lot harder btw))
The distinction we did learn about that has been most insightful for me has a lot more to with the story itself: what topics and themes does the story deal with? And what age group/phase of life does that speak to?
For example, Love You Forever is a picture book (generally considered 3-6 yr old range) but it deals with topics that are clearly aimed for an adult. It follows the parental character until they are on their death bed being taken care by their kid, that's not something a 6 year old would care about or relate to. That's why age of protagonist typically aligns too, bc they will be dealing with/worried about things that the reader is dealing with in their life too (like high school struggles vs career and family struggles etc).
Aaaand this post has (once again) gotten away from me lol so I don't feel the need to analyze all of the topics and themes in TCW and TBB, but basically look at what is being explored and how it is being talked about (since a lot of things, esp with war, aren't necessarily age exclusionary) and that can give you a good idea. I think it's clear TBB generally deals with things in a more nuanced and complex way than TCW (most of it at least, honestly the difference between seasons is stark). And there is a main emphasis on family and parenthood, especially with the very end speaking to both young adults growing up and moving out, and the parents letting them go.
TL;DR:
-Animation doesn't automatically equal for kids
-For kids doesn't equal lesser
-Not all kids media is the same bc not all age groups are the same
-Violence doesn't necessarily equal NOT for kids
-Age of protagonist and themes/topics are a better indicator
-The Clone Wars is def middle grade, and The Bad Batch is probably more YA to adult
-But nothing is exclusionary regardless
#animation bias#made for kids bias#just a kids show#stop underestimating kids#that writing class was one of my all time favorites btw#i learned a lot of cool stuff i hadn't considered before so that's why i want to share#tbb#the bad batch#sw tcw#the clone wars#disney#disney star wars#analysis#writing#children's media#age ratings#target audience#imma tag the mentions bc this post really is about the principles not just star wars#sorry if it's annoying#(and rip my algorithm lol)#atla#gravity falls#infinity train#lol any of yall watch red wall as a kid?#percy jackson#gregor the overlander#suzanne collins has no chill#vox machina#invincible#ender's game
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
When Big Tech Deletes History:
The Crisis of AI-Driven Censorship and Its Political Roots The recent removal of a 15-year-old YouTube channel—one that documented decades of protest, labor struggles, and political activism—raises urgent questions about the unchecked power of Big Tech and the dangers of AI-driven censorship. Google’s official reason cited “severe or repeated violations” of spam and deceptive practices…
#ai moderation#algorithm bias#big tech accountability#congressional oversight#content moderation#digital censorship#digital democracy#freedom of speech#google youtube removal#monopolies#occupy25#online activism#political censorship
0 notes
Text
"In March of 2016, [...] JAMA Internal Medicine released a study showing that the artificial intelligence built into smartphones from Apple, Samsung, Google, and Microsoft isn’t programmed to help during a crisis. The phones’ personal assistants didn’t understand words like “rape,” or "my husband is hitting me.” In fact, instead of doing even a simple web search, Siri—Apple’s product— cracked jokes and mocked users. It wasn’t the first time. Back in 2011, if you told Siri you were thinking about shooting yourself, it would give you directions to a gun store. After getting bad press, Apple partnered with the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline to offer users help when they said something that Siri identified as suicidal. But five years later, no one had looked beyond that one fix. Apple had no problem investing in building jokes and clever comebacks into the interface from the start. But investing in crisis or safety? Just not a priority."
- Technically Wrong: Sexist Apps, Biased Algorithms, and Other Threats of Toxic Tech
by Sara Wachter-Boettcher
#big tech#technology#tech bias#algorithms#silicon valley#apple#google#x#elon musk#politics#technological blunders#tech failures#glitches#big tech fails#sexism#bias#toxic tech#sara wachter-boettcher
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

PSA: Product Specifications
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hypothetical AI election disinformation risks vs real AI harms
I'm on tour with my new novel The Bezzle! Catch me TONIGHT (Feb 27) in Portland at Powell's. Then, onto Phoenix (Changing Hands, Feb 29), Tucson (Mar 9-12), and more!

You can barely turn around these days without encountering a think-piece warning of the impending risk of AI disinformation in the coming elections. But a recent episode of This Machine Kills podcast reminds us that these are hypothetical risks, and there is no shortage of real AI harms:
https://soundcloud.com/thismachinekillspod/311-selling-pickaxes-for-the-ai-gold-rush
The algorithmic decision-making systems that increasingly run the back-ends to our lives are really, truly very bad at doing their jobs, and worse, these systems constitute a form of "empiricism-washing": if the computer says it's true, it must be true. There's no such thing as racist math, you SJW snowflake!
https://slate.com/news-and-politics/2019/02/aoc-algorithms-racist-bias.html
Nearly 1,000 British postmasters were wrongly convicted of fraud by Horizon, the faulty AI fraud-hunting system that Fujitsu provided to the Royal Mail. They had their lives ruined by this faulty AI, many went to prison, and at least four of the AI's victims killed themselves:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/British_Post_Office_scandal
Tenants across America have seen their rents skyrocket thanks to Realpage's landlord price-fixing algorithm, which deployed the time-honored defense: "It's not a crime if we commit it with an app":
https://www.propublica.org/article/doj-backs-tenants-price-fixing-case-big-landlords-real-estate-tech
Housing, you'll recall, is pretty foundational in the human hierarchy of needs. Losing your home – or being forced to choose between paying rent or buying groceries or gas for your car or clothes for your kid – is a non-hypothetical, widespread, urgent problem that can be traced straight to AI.
Then there's predictive policing: cities across America and the world have bought systems that purport to tell the cops where to look for crime. Of course, these systems are trained on policing data from forces that are seeking to correct racial bias in their practices by using an algorithm to create "fairness." You feed this algorithm a data-set of where the police had detected crime in previous years, and it predicts where you'll find crime in the years to come.
But you only find crime where you look for it. If the cops only ever stop-and-frisk Black and brown kids, or pull over Black and brown drivers, then every knife, baggie or gun they find in someone's trunk or pockets will be found in a Black or brown person's trunk or pocket. A predictive policing algorithm will naively ingest this data and confidently assert that future crimes can be foiled by looking for more Black and brown people and searching them and pulling them over.
Obviously, this is bad for Black and brown people in low-income neighborhoods, whose baseline risk of an encounter with a cop turning violent or even lethal. But it's also bad for affluent people in affluent neighborhoods – because they are underpoliced as a result of these algorithmic biases. For example, domestic abuse that occurs in full detached single-family homes is systematically underrepresented in crime data, because the majority of domestic abuse calls originate with neighbors who can hear the abuse take place through a shared wall.
But the majority of algorithmic harms are inflicted on poor, racialized and/or working class people. Even if you escape a predictive policing algorithm, a facial recognition algorithm may wrongly accuse you of a crime, and even if you were far away from the site of the crime, the cops will still arrest you, because computers don't lie:
https://www.cbsnews.com/sacramento/news/texas-macys-sunglass-hut-facial-recognition-software-wrongful-arrest-sacramento-alibi/
Trying to get a low-waged service job? Be prepared for endless, nonsensical AI "personality tests" that make Scientology look like NASA:
https://futurism.com/mandatory-ai-hiring-tests
Service workers' schedules are at the mercy of shift-allocation algorithms that assign them hours that ensure that they fall just short of qualifying for health and other benefits. These algorithms push workers into "clopening" – where you close the store after midnight and then open it again the next morning before 5AM. And if you try to unionize, another algorithm – that spies on you and your fellow workers' social media activity – targets you for reprisals and your store for closure.
If you're driving an Amazon delivery van, algorithm watches your eyeballs and tells your boss that you're a bad driver if it doesn't like what it sees. If you're working in an Amazon warehouse, an algorithm decides if you've taken too many pee-breaks and automatically dings you:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/04/17/revenge-of-the-chickenized-reverse-centaurs/
If this disgusts you and you're hoping to use your ballot to elect lawmakers who will take up your cause, an algorithm stands in your way again. "AI" tools for purging voter rolls are especially harmful to racialized people – for example, they assume that two "Juan Gomez"es with a shared birthday in two different states must be the same person and remove one or both from the voter rolls:
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/eligible-voters-swept-up-conservative-activists-purge-voter-rolls/
Hoping to get a solid education, the sort that will keep you out of AI-supervised, precarious, low-waged work? Sorry, kiddo: the ed-tech system is riddled with algorithms. There's the grifty "remote invigilation" industry that watches you take tests via webcam and accuses you of cheating if your facial expressions fail its high-tech phrenology standards:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/16/unauthorized-paper/#cheating-anticheat
All of these are non-hypothetical, real risks from AI. The AI industry has proven itself incredibly adept at deflecting interest from real harms to hypothetical ones, like the "risk" that the spicy autocomplete will become conscious and take over the world in order to convert us all to paperclips:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/27/10-types-of-people/#taking-up-a-lot-of-space
Whenever you hear AI bosses talking about how seriously they're taking a hypothetical risk, that's the moment when you should check in on whether they're doing anything about all these longstanding, real risks. And even as AI bosses promise to fight hypothetical election disinformation, they continue to downplay or ignore the non-hypothetical, here-and-now harms of AI.
There's something unseemly – and even perverse – about worrying so much about AI and election disinformation. It plays into the narrative that kicked off in earnest in 2016, that the reason the electorate votes for manifestly unqualified candidates who run on a platform of bald-faced lies is that they are gullible and easily led astray.
But there's another explanation: the reason people accept conspiratorial accounts of how our institutions are run is because the institutions that are supposed to be defending us are corrupt and captured by actual conspiracies:
https://memex.craphound.com/2019/09/21/republic-of-lies-the-rise-of-conspiratorial-thinking-and-the-actual-conspiracies-that-fuel-it/
The party line on conspiratorial accounts is that these institutions are good, actually. Think of the rebuttal offered to anti-vaxxers who claimed that pharma giants were run by murderous sociopath billionaires who were in league with their regulators to kill us for a buck: "no, I think you'll find pharma companies are great and superbly regulated":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/05/not-that-naomi/#if-the-naomi-be-klein-youre-doing-just-fine
Institutions are profoundly important to a high-tech society. No one is capable of assessing all the life-or-death choices we make every day, from whether to trust the firmware in your car's anti-lock brakes, the alloys used in the structural members of your home, or the food-safety standards for the meal you're about to eat. We must rely on well-regulated experts to make these calls for us, and when the institutions fail us, we are thrown into a state of epistemological chaos. We must make decisions about whether to trust these technological systems, but we can't make informed choices because the one thing we're sure of is that our institutions aren't trustworthy.
Ironically, the long list of AI harms that we live with every day are the most important contributor to disinformation campaigns. It's these harms that provide the evidence for belief in conspiratorial accounts of the world, because each one is proof that the system can't be trusted. The election disinformation discourse focuses on the lies told – and not why those lies are credible.
That's because the subtext of election disinformation concerns is usually that the electorate is credulous, fools waiting to be suckered in. By refusing to contemplate the institutional failures that sit upstream of conspiracism, we can smugly locate the blame with the peddlers of lies and assume the mantle of paternalistic protectors of the easily gulled electorate.
But the group of people who are demonstrably being tricked by AI is the people who buy the horrifically flawed AI-based algorithmic systems and put them into use despite their manifest failures.
As I've written many times, "we're nowhere near a place where bots can steal your job, but we're certainly at the point where your boss can be suckered into firing you and replacing you with a bot that fails at doing your job"
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/15/passive-income-brainworms/#four-hour-work-week
The most visible victims of AI disinformation are the people who are putting AI in charge of the life-chances of millions of the rest of us. Tackle that AI disinformation and its harms, and we'll make conspiratorial claims about our institutions being corrupt far less credible.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/27/ai-conspiracies/#epistemological-collapse

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#ai#disinformation#algorithmic bias#elections#election disinformation#conspiratorialism#paternalism#this machine kills#Horizon#the rents too damned high#weaponized shelter#predictive policing#fr#facial recognition#labor#union busting#union avoidance#standardized testing#hiring#employment#remote invigilation
146 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Illusion of Complexity: Binary Exploitation in Engagement-Driven Algorithms
Abstract:
This paper examines how modern engagement algorithms employed by major tech platforms (e.g., Google, Meta, TikTok, and formerly Twitter/X) exploit predictable human cognitive patterns through simplified binary interactions. The prevailing perception that these systems rely on sophisticated personalization models is challenged; instead, it is proposed that such algorithms rely on statistical generalizations, perceptual manipulation, and engineered emotional reactions to maintain continuous user engagement. The illusion of depth is a byproduct of probabilistic brute force, not advanced understanding.
1. Introduction
Contemporary discourse often attributes high levels of sophistication and intelligence to the recommendation and engagement algorithms employed by dominant tech companies. Users report instances of eerie accuracy or emotionally resonant suggestions, fueling the belief that these systems understand them deeply. However, closer inspection reveals a more efficient and cynical design principle: engagement maximization through binary funneling.
2. Binary Funneling and Predictive Exploitation
At the core of these algorithms lies a reductive model: categorize user reactions as either positive (approval, enjoyment, validation) or negative (disgust, anger, outrage). This binary schema simplifies personalization into a feedback loop in which any user response serves to reinforce algorithmic certainty. There is no need for genuine nuance or contextual understanding; rather, content is optimized to provoke any reaction that sustains user attention.
Once a user engages with content —whether through liking, commenting, pausing, or rage-watching— the system deploys a cluster of categorically similar material. This recurrence fosters two dominant psychological outcomes:
If the user enjoys the content, they may perceive the algorithm as insightful or “smart,” attributing agency or personalization where none exists.
If the user dislikes the content, they may continue engaging in a doomscroll or outrage spiral, reinforcing the same cycle through negative affect.
In both scenarios, engagement is preserved; thus, profit is ensured.
3. The Illusion of Uniqueness
A critical mechanism in this system is the exploitation of the human tendency to overestimate personal uniqueness. Drawing on techniques long employed by illusionists, scammers, and cold readers, platforms capitalize on common patterns of thought and behavior that are statistically widespread but perceived as rare by individuals.
Examples include:
Posing prompts or content cues that seem personalized but are statistically predictable (e.g., "think of a number between 1 and 50 with two odd digits” → most select 37).
Triggering cognitive biases such as the availability heuristic and frequency illusion, which make repeated or familiar concepts appear newly significant.
This creates a reinforcing illusion: the user feels “understood” because the system has merely guessed correctly within a narrow set of likely options. The emotional resonance of the result further conceals the crude probabilistic engine behind it.
4. Emotional Engagement as Systemic Currency
The underlying goal is not understanding, but reaction. These systems optimize for time-on-platform, not user well-being or cognitive autonomy. Anger, sadness, tribal validation, fear, and parasocial attachment are all equally useful inputs. Through this lens, the algorithm is less an intelligent system and more an industrialized Skinner box: an operant conditioning engine powered by data extraction.
By removing the need for interpretive complexity and relying instead on scalable, binary psychological manipulation, companies minimize operational costs while maximizing monetizable engagement.
5. Black-Box Mythology and Cognitive Deference
Compounding this problem is the opacity of these systems. The “black-box” nature of proprietary algorithms fosters a mythos of sophistication. Users, unaware of the relatively simple statistical methods in use, ascribe higher-order reasoning or consciousness to systems that function through brute-force pattern amplification.
This deference becomes part of the trap: once convinced the algorithm “knows them,” users are less likely to question its manipulations and more likely to conform to its outputs, completing the feedback circuit.
6. Conclusion
The supposed sophistication of engagement algorithms is a carefully sustained illusion. By funneling user behavior into binary categories and exploiting universally predictable psychological responses, platforms maintain the appearance of intelligent personalization while operating through reductive, low-cost mechanisms. Human cognition —biased toward pattern recognition and overestimation of self-uniqueness— completes the illusion without external effort. The result is a scalable system of emotional manipulation that masquerades as individualized insight.
In essence, the algorithm does not understand the user; it understands that the user wants to be understood, and it weaponizes that desire for profit.
#ragebait tactics#mass psychology#algorithmic manipulation#false agency#click economy#social media addiction#illusion of complexity#engagement bait#probabilistic targeting#feedback loops#psychological nudging#manipulation#user profiling#flawed perception#propaganda#social engineering#social science#outrage culture#engagement optimization#cognitive bias#predictive algorithms#black box ai#personalization illusion#pattern exploitation#ai#binary funnelling#dopamine hack#profiling#Skinner box#dichotomy
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
wish the algorithm would push my post about Pr0t3st safety more than it was pushing my pspspspsps post go reblog it force it into the algorithm
#lesbian#trans lesbian#sapphic#wlw#butch lesbian#queer nsft#sapphic yearning#trans nsft#wlw post#free palestine#tumblr algorithm#algorithmic bias#fypシ
2 notes
·
View notes
Text









Read More Here: Substack
#algorithmic determinism#techcore#philosophy#quote#quotes#ethics#technology#anthony doerr#sociology#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writlbr#artificial intelligence#bias#prejudice#inequality#outcomes
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Does AI Use Impact Critical Thinking?
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/how-does-ai-use-impact-critical-thinking/
How Does AI Use Impact Critical Thinking?


Artificial intelligence (AI) can process hundreds of documents in seconds, identify imperceptible patterns in vast datasets and provide in-depth answers to virtually any question. It has the potential to solve common problems, increase efficiency across multiple industries and even free up time for individuals to spend with their loved ones by delegating repetitive tasks to machines.
However, critical thinking requires time and practice to develop properly. The more people rely on automated technology, the faster their metacognitive skills may decline. What are the consequences of relying on AI for critical thinking?
Study Finds AI Degrades Users’ Critical Thinking
The concern that AI will degrade users’ metacognitive skills is no longer hypothetical. Several studies suggest it diminishes people’s capacity to think critically, impacting their ability to question information, make judgments, analyze data or form counterarguments.
A 2025 Microsoft study surveyed 319 knowledge workers on 936 instances of AI use to determine how they perceive their critical thinking ability when using generative technology. Survey respondents reported decreased effort when using AI technology compared to relying on their own minds. Microsoft reported that in the majority of instances, the respondents felt that they used “much less effort” or “less effort” when using generative AI.
Knowledge, comprehension, analysis, synthesis and evaluation were all adversely affected by AI use. Although a fraction of respondents reported using some or much more effort, an overwhelming majority reported that tasks became easier and required less work.
If AI’s purpose is to streamline tasks, is there any harm in letting it do its job? It is a slippery slope. Many algorithms cannot think critically, reason or understand context. They are often prone to hallucinations and bias. Users who are unaware of the risks of relying on AI may contribute to skewed, inaccurate results.
How AI Adversely Affects Critical Thinking Skills
Overreliance on AI can diminish an individual’s ability to independently solve problems and think critically. Say someone is taking a test when they run into a complex question. Instead of taking the time to consider it, they plug it into a generative model and insert the algorithm’s response into the answer field.
In this scenario, the test-taker learned nothing. They didn’t improve their research skills or analytical abilities. If they pass the test, they advance to the next chapter. What if they were to do this for everything their teachers assign? They could graduate from high school or even college without refining fundamental cognitive abilities.
This outcome is bleak. However, students might not feel any immediate adverse effects. If their use of language models is rewarded with better test scores, they may lose their motivation to think critically altogether. Why should they bother justifying their arguments or evaluating others’ claims when it is easier to rely on AI?
The Impact of AI Use on Critical Thinking Skills
An advanced algorithm can automatically aggregate and analyze large datasets, streamlining problem-solving and task execution. Since its speed and accuracy often outperform humans, users are usually inclined to believe it is better than them at these tasks. When it presents them with answers and insights, they take that output at face value. Unquestioning acceptance of a generative model’s output leads to difficulty distinguishing between facts and falsehoods. Algorithms are trained to predict the next word in a string of words. No matter how good they get at that task, they aren’t really reasoning. Even if a machine makes a mistake, it won’t be able to fix it without context and memory, both of which it lacks.
The more users accept an algorithm’s answer as fact, the more their evaluation and judgment skew. Algorithmic models often struggle with overfitting. When they fit too closely to the information in their training dataset, their accuracy can plummet when they are presented with new information for analysis.
Populations Most Affected by Overreliance on AI
Generally, overreliance on generative technology can negatively impact humans’ ability to think critically. However, low confidence in AI-generated output is related to increased critical thinking ability, so strategic users may be able to use AI without harming these skills.
In 2023, around 27% of adults told the Pew Research Center they use AI technology multiple times a day. Some of the individuals in this population may retain their critical thinking skills if they have a healthy distrust of machine learning tools. The data must focus on populations with disproportionately high AI use and be more granular to determine the true impact of machine learning on critical thinking.
Critical thinking often isn’t taught until high school or college. It can be cultivated during early childhood development, but it typically takes years to grasp. For this reason, deploying generative technology in schools is particularly risky — even though it is common.
Today, most students use generative models. One study revealed that 90% have used ChatGPT to complete homework. This widespread use isn’t limited to high schools. About 75% of college students say they would continue using generative technology even if their professors disallowed it. Middle schoolers, teenagers and young adults are at an age where developing critical thinking is crucial. Missing this window could cause problems.
The Implications of Decreased Critical Thinking
Already, 60% of educators use AI in the classroom. If this trend continues, it may become a standard part of education. What happens when students begin to trust these tools more than themselves? As their critical thinking capabilities diminish, they may become increasingly susceptible to misinformation and manipulation. The effectiveness of scams, phishing and social engineering attacks could increase.
An AI-reliant generation may have to compete with automation technology in the workforce. Soft skills like problem-solving, judgment and communication are important for many careers. Lacking these skills or relying on generative tools to get good grades may make finding a job challenging.
Innovation and adaptation go hand in hand with decision-making. Knowing how to objectively reason without the use of AI is critical when confronted with high-stakes or unexpected situations. Leaning into assumptions and inaccurate data could adversely affect an individual’s personal or professional life.
Critical thinking is part of processing and analyzing complex — and even conflicting — information. A community made up of critical thinkers can counter extreme or biased viewpoints by carefully considering different perspectives and values.
AI Users Must Carefully Evaluate Algorithms’ Output
Generative models are tools, so whether their impact is positive or negative depends on their users and developers. So many variables exist. Whether you are an AI developer or user, strategically designing and interacting with generative technologies is an important part of ensuring they pave the way for societal advancements rather than hindering critical cognition.
#2023#2025#ai#AI technology#algorithm#Algorithms#Analysis#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#automation#Bias#Careers#chatGPT#cognition#cognitive abilities#college#communication#Community#comprehension#critical thinking#data#datasets#deploying#Developer#developers#development#education#effects#efficiency#engineering
2 notes
·
View notes