#structure tips
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Fantasy Guide to Political Structures

A Horse! A Horse! My X for a Horse!
Let's be honest, fantasy authors love their kingdoms and empires. You can throw a rock in a bookshop or a library in the fantasy section and you will 99.99999% hit a fantasy book that will be set in or mention either of those structures. But what are they really? What's the difference between them all? Are there any more examples of structures that would suit your WIP better? Are you using the right terms? Let's have a closer look.
Duchy

A Duchy is a small territory ruled by a Duke/Duchess. While Duchies can be found in kingdoms, some duchies were sovereign states in their own right. Duchies are usually small by land mass but some duchies such as Burgundy were extremely powerful and influential. Independent Duchies were usually apart of a kingdom but grew so powerful that they eventually broke away to become a sovereign state in their own right. An example would be modern day Luxembourg, historic Milan and Burgundy.
Principality

A principality is territory ruled by a Prince/Princess. A principality is typically smaller than a kingdom and in some instances, can be apart of a larger kingdom or be a sovereign state. Principalities have a history of having broken away from a larger kingdom or eventually becoming apart of a kingdom. A principality within a kingdom is ruled by a Prince/Princess, usually an heir of the monarch and can be used to train them up to assume the throne in the future. Examples include Monaco, Liechtenstein and Andorra.
Kingdom

A sovereign state/country that is ruled by ruling King or a Queen. A kingdom is much larger and more powerful than a principality. Kingdoms can be feudal, meaning they are ruled in a strict hierarchy or an autocracy where the monarch rules alone with minimal input from the government or constitutional where the monarch is more of a figurehead and the government has a good chunk of control. Examples include England, Thailand and modern day Spain.
Commonwealth

A Commonwealth isn't a popular choice in fantasy but it is an interesting structure. A Commonwealth in its most basic form is a collection of states that are linked by either a shared culture or history. A Commonwealth can be a politically power or an economic power, with every state allowed to participate as much as they like. Not one state leads the others, it is all one group of equals. A Commonwealth can be a good idea for a group of nations that are more powerful together with them keeping their own independence.
Federation

A Federation is a political structure that is made up of united states or countries that are under a single government but each state is still independent and rules itself. Each state can have different laws, different cultures and economies but they all answer to the single government. Examples include the United States of America.
Republic

A Republic is a territory that is ruled by leaders and heads of state that have been elected on merit and by choice of the people. Republics are not just countries but can also be much smaller areas such as cities. Republics are democratic in nature, with the people having a say in who leads them in accordance to a constitution. There are many kinds of Republic: presidential, parliamentary, federal, theocratic, unitary. Examples of Republics include the Republic of Ireland and the city of Florence.
Protectorate

A Protectorate is a country/region/territory that is independent but relies on a larger, more powerful state for protection either in a military or diplomatic sense. A Protectorate was often used by Empires in order to maintain control over an area without annexing it. There are many reasons a larger state and the protectorate would agree to this, mainly the protectorate is much smaller meaning it is far more vulnerable to attack or it has very little power when compared to other states. A Protectorate allows the territory some power to rule itself but the larger state may feel the need or desire to interfere in the dealings of the territory. Examples of protectorates include the client kingdoms of the Roman Empire like Egypt before its annexation and Puerto Rico.
Empire

An Empire is a collection of nations that are united under one sovereign head of state or government. An Empire is formed by one nation steadily taking control of other nations, either through straight invasion and colonization or acquiring them through marriage and other less violent ways. An Empire is powerful mainly because it can drum up more resources, more influence and more military power. An Empire might impose the traditions, beliefs and culture of its principal nation - the nation that started it all - onto its colonies for better control and feeling of uniformity. Empires never last, that is something to always remember. Empires will eventually fragment due to the vast size and sometimes revolt among the conquered states. Examples of empires include the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire, the Ottoman Empire.
#fantasy guide to political structures#kingdoms#empires#writeblr#writing reference#writing resources#writing#writing advice#writer#writer's problems#spilled words#writer's life#fantasy guide#creative writing#writing fantasy#writing community#writing inspiration#writing prompt#writing problems#on writing#writers#writing help#writing tips#wtwcommunity#writing guide
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Structure a Oneshot That Hits Like a Thunderclap
“A good oneshot is a single breath—sharp in, slow out.”
A oneshot isn’t just a short story. It’s a moment, a mood, a slice of intimacy that wouldn’t survive being stretched into a full-length fic. Here’s how to make it count.
Pick One Core Emotion
Build the whole thing around a single feeling. Obsession. Longing. Regret. Euphoria. Grief.
If a full-length fic is a symphony, your oneshot is a single piano note.
Ask: What should the reader feel when they finish?
Ex: “This oneshot is about the moment someone realizes they’ve already fallen in love.”
Limit the Timeline
Don’t span days. Or even hours, if you can help it. The strongest oneshots focus on a single scene or moment.
A kiss in a hallway.
A final goodbye at dawn.
A confession said too late.
Tight time = tight tension.
Start Late, End Early
Drop us into the scene already in motion—no lengthy set-up. And leave us just after the climax, not long after.
Don’t: “They met three years ago and…”
Do: “It’s raining the night he finally says it.”
Your oneshot should feel like eavesdropping on something private.
Structure Like This
ACT I: Setup (15–25%)
Who are we with? Where are we? What’s simmering under the surface?
ACT II: The Shift (50–70%)
Something changes. A kiss. A fight. A confession. A memory.
The mood deepens or flips—this is your emotional peak.
ACT III: The Fallout (15–25%)
How does it end? A single line. A final look. A choice not made.
Leave a lingering echo, not an epilogue.
Let Style Do the Heavy Lifting
A oneshot gives you space to lean into voice, imagery, and metaphor. Write like it’s the last thing you’ll ever write.
“He says her name like it’s a prayer, but the gods stopped listening hours ago.”
Mood. Matters.
#writeblr#writing community#writers of tumblr#writing tips#creative writing#vivsinkpot#amwriting#writing advice#oneshot#oneshot advice#fanfic writing#story structure#writing help#short fiction#fic writing#writing inspiration#writing resources#emotional writing#prose craft#oneshot writing#vivwrites
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
<div style="white-space:pre-wrap">
🧠 FREE WRITING LESSON — THE MOST POWERFUL CHARACTER DEPTH TRICK YOU’LL EVER READ.
Let’s say your character sucks.
She’s flat. Predictable. “Strong” in all the wrong ways. Let’s call her Nicolle. Or Carol. Or whatever name Hollywood gave her.
She’s a superhero. She’s got powers. She’s got sarcasm. She takes no shit. She leads the squad. She’s admired by everyone — and loved by no one.
You’ve seen this character before. Now watch what happens when you give her one secret she doesn’t brag about.
Nicolle has two sons.
She’s raising them alone — to become men like her late father: A man who sacrificed everything to raise her after her mother disappeared, broke, or gave up.
The world sees Nicolle as the apex of visual empowerment. But the world doesn’t see:
The arguments with her boys’ father — about what being a real dad means.
The prayers whispered in the dark over a fevered forehead.
The way she ghosted the only man she maybe wanted, not because she’s flaky — but because she doesn’t know if wanting love makes her a bad mother.
The nights she tucks her boys in, then collapses into her bed, staring at the ceiling, heart full of ache, because she gave the world her strength but kept no one to hold hers.
They don’t see the days her sons cry after watching her get slammed through buildings on TV.
Held by the throat. Left for dead. Motionless for seconds too long. Until she rises — because she has to.
They don’t see the breakdowns. They don’t see her flinch.
They assume she doesn’t feel fear. But the truth?
She feels it every single time.
She’s not fearless. She’s never been. But fear is a luxury she doesn’t have.
That’s a luxury for men. She is a god. And she will make any threat scream that truth — as she crushes it beneath her bleeding hands.
Because when demons invade, tyrants rise, and monsters descend, She suits up.
Not for hashtags. Not for feminism. Not for attention.
She suits up because the idea of her sons growing up in a world she could’ve fought for and didn’t — is more terrifying than death itself.
And she will not let the universe teach her boys that their mother ever cowered.
🔺 THE TRIFECTA THAT MAKES ANY SUPERHERO NEXT-LEVEL:
Intimacy. Contradiction. Duty.
Intimacy gives them a soul — something they protect more than their own body.
Contradiction gives them depth — because perfection is forgettable, but conflict creates memory.
Duty gives them immortality — because we remember those who bled for more than applause.
Give a character that trifecta — and suddenly:
She’s not annoying. She’s haunting. She’s not fanfiction. She’s canon. She’s not shallow. She’s legend.
✍️ That’s how you fix a weak character. You don’t soften her. You give her something to fight that fists can’t touch.
And suddenly?
She’s not a girlboss. She’s the last myth your enemies ever tell themselves before they die.
</div>
#writing tips#character development#blacksite literature™#scrolltrap#fiction writing#writers on tumblr#writing community#emotional writing#plot building#motherhood as power#writing advice#writing exercise#heroic narrative#feminine rage#masculine duty#superhero writing#literary structure#cadence weaponry
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to make your writing sound less stiff
Just a few suggestions. You shouldn’t have to compromise your writing style and voice with any of these, and some situations and scenes might demand some stiff or jerky writing to better convey emotion and immersion. I am not the first to come up with these, just circulating them again.
1. Vary sentence structure.
This is an example paragraph. You might see this generated from AI. I can’t help but read this in a robotic voice. It’s very flat and undynamic. No matter what the words are, it will be boring. It’s boring because you don’t think in stiff sentences. Comedians don’t tell jokes in stiff sentences. We don’t tell campfire stories in stiff sentences. These often lack flow between points, too.
So funnily enough, I had to sit through 87k words of a “romance” written just like this. It was stiff, janky, and very unpoetic. Which is fine, the author didn’t tell me it was erotica. It just felt like an old lady narrator, like Old Rose from Titanic telling the audience decades after the fact instead of living it right in the moment. It was in first person pov, too, which just made it worse. To be able to write something so explicit and yet so un-titillating was a talent. Like, beginner fanfic smut writers at least do it with enthusiasm.
2. Vary dialogue tag placement
You got three options, pre-, mid-, and post-tags.
Leader said, “this is a pre-dialogue tag.”
“This,” Lancer said, “is a mid-dialogue tag.”
“This is a post-dialogue tag,” Heart said.
Pre and Post have about the same effect but mid-tags do a lot of heavy lifting.
They help break up long paragraphs of dialogue that are jank to look at
They give you pauses for ~dramatic effect~
They prompt you to provide some other action, introspection, or scene descriptor with the tag. *don't forget that if you're continuing the sentence as if the tag wasn't there, not to capitalize the first word after the tag. Capitalize if the tag breaks up two complete sentences, not if it interrupts a single sentence.
It also looks better along the lefthand margin when you don’t start every paragraph with either the same character name, the same pronouns, or the same “ as it reads more natural and organic.
3. When the scene demands, get dynamic
General rule of thumb is that action scenes demand quick exchanges, short paragraphs, and very lean descriptors. Action scenes are where you put your juicy verbs to use and cut as many adverbs as you can. But regardless of if you’re in first person, second person, or third person limited, you can let the mood of the narrator bleed out into their narration.
Like, in horror, you can use a lot of onomatopoeia.
Drip Drip Drip
Or let the narration become jerky and unfocused and less strict in punctuation and maybe even a couple run-on sentences as your character struggles to think or catch their breath and is getting very overwhelmed.
You can toss out some grammar rules, too and get more poetic.
Warm breath tickles the back of her neck. It rattles, a quiet, soggy, rasp. She shivers. If she doesn’t look, it’s not there. If she doesn’t look, it’s not there. Sweat beads at her temple. Her heart thunders in her chest. Ba-bump-ba-bump-ba-bump-ba- It moves on, leaving a void of cold behind. She uncurls her fists, fingers achy and palms stinging from her nails. It’s gone.
4. Remember to balance dialogue, monologue, introspection, action, and descriptors.
The amount of times I have been faced with giant blocks of dialogue with zero tags, zero emotions, just speech on a page like they’re notecards to be read on a stage is higher than I expected. Don’t forget that though you may know exactly how your dialogue sounds in your head, your readers don’t. They need dialogue tags to pick up on things like tone, specifically for sarcasm and sincerity, whether a character is joking or hurt or happy.
If you’ve written a block of text (usually exposition or backstory stuff) that’s longer than 50 words, figure out a way to trim it. No matter what, break it up into multiple sections and fill in those breaks with important narrative that reflects the narrator’s feelings on what they’re saying and whoever they’re speaking to’s reaction to the words being said. Otherwise it’s meaningless.
—
Hope this helps anyone struggling! Now get writing.
#writing#writing advice#writing resources#writing a book#writing tools#writing tips#writeblr#for beginners#refresher#sentence structure#book formatting
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
🧩 How to Outline Without Feeling Like You’re Dying
(a non-suffering writer’s guide to structure, sanity, and staying mildly hydrated)
Hey besties. Let’s talk outlines. Specifically: how to do them without crawling into the floorboards and screaming like a Victorian ghost.
If just hearing the word “outline” sends your brain into chaos-mode, welcome. You’re not broken, you’re just a writer whose process has been hijacked by Very Serious Advice™ that doesn’t fit you. You don’t need to build a military-grade beat sheet. You don’t need a sixteen-tab spreadsheet. You don’t need to suffer to be legitimate. You just need a structure that feels like it’s helping you, not haunting you.
So. Here’s how to outline your book without losing your soul (or all your serotonin).
—
🍓 1. Stop thinking of it as “outlining.” That word is cursed. Try “story sketch.” “Narrative roadmap.” “Planning soup.” Whatever gets your brain to chill out. The goal here is to understand your story, not architect it to death.
Outlining isn’t predicting everything. It’s just building a scaffold so your plot doesn't fall over mid-draft.
—
🧠 2. Find your plot skeleton. There are lots of plot structures floating around: 3-Act. Save the Cat. Hero’s Journey. Take what helps, ignore the rest.
If all else fails, try this dirt-simple one I use when my brain is mush:
Act I: What’s the problem?
Act II: Why can’t we fix it?
Act III: What finally makes us change?
Ending: What does that change cost?
You don’t need to fill in every detail. You just need to know what’s driving your character, what’s blocking them, and what choices will change them.
—
🛒 3. Make a “scene bucket list.” Before you start plotting in order, write down a list of scenes you know you want: key vibes, emotional beats, dramatic reveals, whatever.
These are your anchors. Even if you don’t know where they go yet, they’re proof your story already exists, it just needs connecting tissue.
Bonus: when you inevitably get stuck later, one of these might be the scene that pulls you back in.
—
🧩 4. Start with 5 key scenes. That’s it. Here’s a minimalist approach that won’t kill your momentum:
Opening (what sucks about their world?)
Catalyst (what throws them off course?)
Midpoint (what makes them confront themselves?)
Climax (what breaks or remakes them?)
Ending (what’s changed?)
Plot the spaces between those after you’ve nailed these. Think of it like nailing down corners of a poster before smoothing the rest.
You’re not “doing it wrong” if you start messy. A messy start is a start.
—
🔧 5. Use the outline to ask questions, not just answer them. Every section of your outline should provoke a question that the scene must answer.
Instead of: — “Chapter 5: Sarah finds a journal.”
Try: — “Chapter 5: What truth does Sarah find that complicates her next move?”
This makes your story active, not just a list of stuff that happens. Outlines aren’t just there to record, they’re tools for curiosity.
—
🪤 6. Beware of the Perfectionist Trap™. You will not get the entire plot perfect before you write. Don’t stall your momentum waiting for a divine lightning bolt of Clarity. You get clarity by writing.
Think of your outline as a map drawn in pencil, not ink. It’s allowed to evolve. It should evolve.
You’re not building a museum exhibit. You’re making a prototype.
—
🧼 7. Clean up after you start drafting. Here’s the secret: the first draft will teach you what the story’s actually about. You can go back and revise the outline to fit that. It’s not wasted work, it’s evolving scaffolding.
You don’t have to build the house before you live in it. You can live in the mess while you figure out where the kitchen goes.
—
🛟 8. If you’re a discovery writer, hybrid it. A lot of “pantsers” aren’t anti-outline, they’re just anti-stiff-outline. That’s fair.
Try using “signposts,” not full scenes:
Here’s a secret someone’s hiding.
Here’s the emotional breakdown scene.
Here’s a betrayal. Maybe not sure by who yet.
Let the plot breathe. Let the characters argue with your outline. That tension is where the fun happens.
—
🪴 TL;DR but emotionally: You don’t need a flawless outline to write a good book. You just need a loose net of ideas, a couple of emotional anchors, and the willingness to pivot when your story teaches you something new.
Outlines should support you, not suffocate you.
Let yourself try. Let it be imperfect. That’s where the good stuff lives.
Go forth and outline like a gently chaotic legend 🧃
— written with snacks in hand by Rin T. @ thewriteadviceforwriters 🍓🧠✍️
Sometimes the problem isn’t your plot. It’s your first 5 pages. Fix it here → 🖤 Free eBook: 5 Opening Pages Mistakes to Stop Making:
#writing#writing advice#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writing tips#writing help#how to write#story structure#writing process#plotting tips#writing guide#writing blog#writing community#writing support#tumblr writing community#writing inspiration#storytelling tips#how to outline#writing resources#novel writing#outline tips#plotting a novel#writing craft#novel planning#write a book#drafting a novel#writing motivation#first draft advice#fiction writing#character arcs
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Quick Guide: Stay Safe While Downloading Sims 4 CC & Mods
I just published a quick guide to help you download Sims 4 CC & mods safely. ⚠️ From trusted sources to spotting red flags. Keep your game clean and secure! 😊
Read it now
#avoid malware in sims 4 mods#how to avoid malware sims 4 mods#how to download mods safely sims 4#patreon sims 4 cc download#safe sims 4 cc creators#safe sims 4 download sites#sims 4 cc best practices#sims 4 cc community guide#sims 4 cc download checklist#sims 4 cc education#sims 4 cc folder structure#sims 4 cc mod manager#sims 4 cc mod security tips#sims 4 cc mods support guide#sims 4 cc protection#sims 4 cc safe download#sims 4 cc safe hosting platforms#sims 4 cc safety guide#sims 4 cc safety tutorial#sims 4 cc virus warning#sims 4 cc zip file tips#sims 4 custom content security#sims 4 custom content tips#sims 4 mod folder organization#sims 4 mod malware prevention#sims 4 mod safety#sims 4 mod safety checklist#sims 4 modding guide#sims 4 mods antivirus#sims 4 script mod warning
281 notes
·
View notes
Text



#next to normal#next to normal uk#n2n#n2n proshot#next to normal proshot#musicals#musicalsedit#jack wolfe#gabe goodman#diana goodman#caissie levy#dan goodman#jamie parker#natalie goodman#eleanor worthington cox#my posts#hi it's me again:)#I really want to make a gif set about I'm alive but have no idea how to structure it#so if anyone has any ideas hit me up:)#hope you enjoy this one#I am still finding my way around lettering#so if you have any tips#they are also greatly appreciated:)
207 notes
·
View notes
Text
how I take notes on non fiction books
I recently made a post on my study method, and decided to make a whole separate post on my note taking method. The structure of the notes I write doesn't vary too much from my lecture notes to things I might have to read. A couple of useful informations you might want to know before I start actually talking about note writing is that I am mainly focused on studying history (tho I have had other humanities exams in my degrees), and that I study for oral exams in which the material is mainly composed of non fiction books, but sometimes include articles as well as lecture notes. Somehow I have also failed to mention that I am speaking about HANDWRITTEN NOTES. I only do handwritten notes, I don't work well digitally, so keep that in mind. And with this being said brace yourselves for a very long post. The bullet points I will be making are not really in a specific order and I will be including a few pictures too.
The first step when I am working on the materials for an exam is to figure out in which order I will be reading (and writing notes) the books. This hasn't really much to do with the notes themselves, but it's important to know which of your materials is more general and what other things go more in depth, so that you don't struggle too much while studying. Another plan related thing I always do is to write down each chapter of the book I have to study on my bullet journal and how many pages it is so I can plan my studying more comfortably. If the chapters are very long, and divided in subchapters I sometimes also write those down.
The goal of the notes I write is to fully take the place of the book, so they tend to be very detailed and long. I do this because the very act of writing is part of my study method, and working on things I have written down in my own words is just much better for the type of learner I am. So basically I read the book only once, then it goes back on the shelf and I work exclusively on the notes. This means my notes need to be detailed and well organized.
My method is to read a chapter, underlining important stuff as I am reading, and then right after I am done reading I work on the notes for that chapter before moving onto the next. I do this because it makes the note writing more effortless, I am fresh with informations I just read and I basically just need to skim over what I have underlined.
On underlining, since it is so important. I underline everything I will be including in my notes, it might seem much as sometimes it consists of full paragraphs, instead of key words. But this is okay because my notes I don't just copy and paste.
To create useful notes you need to be re-elaborating the informations. You need to read, understand what you read, and be able to write it down using your own words. That way the notes will be easier to review, they will often be composed of shorter sentences, and by doing so you are also actively making writing part of your studying and not just a mindless activity.
Personally I don't work well with full pages summaries, I need the text to be visually broken into sentences/small paragraphs, and I use a lot of symbols as well as abbreviations.
Symbols and abbreviations are in a way part of your very own language when you are writing notes, you tend to develop these with time, but they are so useful. I personally use different types of arrows, all caps words, position of the text in the page, different methods of highlighting and abbreviations (usually for words that come up often like country names, for example Italy becomes ita, France becomes fr, etc.).
Your notes need to be useful for you, they don't have to necessarily be comprehensible for another person (which means you can and will fuck up sentence structure because sometimes skipping a couple of words makes the notes shorter and still understandable), and they do not have to be pretty. They should be as tidy as possible, but again that might change from person to person, I have some very messy looking notes that make total sense to me. With time you'll learn what works best for you.
I have a visual memory so as I mentioned titles, highlighters, all caps, the placement on the page and other similar things are very important in my notes. I cannot fully exapain some of these things because some definitely only make sense to me in the moment (like the words I choose to write in all caps, or the way I highlight things).
I like to have a clear chapter and subchapter break (so that in case I need to refer back to the book it's super effortless). I like to write those with a red pen, usually the chapter title is in all caps and the subchapter in coursive, but it really depends.
I use only two highlighters in each set of notes yellow for dates, and the colour I associate with the book/the subject of the book (I have synesthesia I don't make the rules when it comes to colours). This of course might change depending your preferences and on the element of your notes you want to focus on. I like to have spacific colour for dates and time periods, because of course while studying history that is a fundamental element. If you are focusing on other subjects you might want to have a specific colour for names, or other elements.
I like to leave a big side margin to add either key words (especially in lecture notes since they might be messier and jump around informations more often), or additional information in a second time (sometimes it happens, after you read another book, or attended a particular lecture you have to add a couple of sentences and I rather have a blank space that never gets used rather than no space at all for emergencies).
I honestly mentioned everything that came to mind right away, but since note writing is now basically a mindless skill I have been practicing for years I surely forgot about something. I might end up adding to this post in the future or write another one. My note-writing method has also changed a lot thought the years from high school to university, it's a skill I have been perfecting for the past decade. This to say that depending on what you are working on things might change, and by experimenting with different things you might find out things that work very well for you. If you have any questions on specific things I didn't mention or that wen't clear my inbox is always open and I am more than happy to help.
Since this post is already very very long I am adding the pictures below the cut
Example of a page of notes before and after highlighting


Example of symbols and structure of the notes and the way I highlight things (in which you'll hopefully be able to understand my handwriting, and in which there might be some spelling errors but alas that often happens in my real notes as well so if there are any it's for the sake of accuracy lmao). If I end up adding informations on the margins I always use a pen of a different color so I can tell which informations I got from what source (ex. main notes from lecture, colorful notes from additional article).

Example of messier notes in which the main text in black are the notes I took during lectures and the additional colorful text was added while writing the materials (I rarely do this, it usually happens when the lectures follow a book precisely, which happens when we have to study books or summaries written by the professor). As you can see I often use post it notes to add more writing space, and sometime I even use them to create visually separated sections. If I end up adding some drawings I also usually like to have them on post it notes so they stand out more (and if you are wondering why the hell would an history student need drawings it's usually either because I need a map or a region/state to mark things out, or when studying for archaeology exams I often needed visual references, for example to identify different types of vases or decorations).


#this should be it#i was hoping on a more structured post but it was harder than i expected to write#both because so much of note writing is now a brainless activity for me and also bc it's really not easy to exaplain certain aspects#like the symbols i use#i really did my best and hope it will be useful#then again if y'all have questions the inbox is open and i will try my best to answer whatever your heart desires#studyblr#studyinspo#studying#study tips#study advice#note taking#hadwritten notes#my note taking method#how to take notes#non fiction books#academia#uniblr#university#booklr#study method#mine#the---hermit
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Dramatic Structure

Dramatic Structure - the framework that allows a story’s plot to unfold.
Aristotle’s ancient Greek text on dramatic theory, Poetics, was the first written work to examine story structure.
Since then, writers and readers have used various approaches to dramatic structure to organize and analyze the plots of plays, poems, short stories, and novels.
Dramatic structure is typically broken up into acts, scenes, and plot points. Examples of popular dramatic structures include the three-act structure and five-act structure.
During the 19th century, German playwright Gustav Freytag presented a plot diagram, commonly known as Freytag’s pyramid or Freytag’s triangle. Freytag's analysis of structure—which centers around a rising action, climax, and falling action—is now one of the most common tools for storytellers.
Key Elements of Dramatic Structure
Introduction: This early part of the story includes exposition—backstory information about the setting and the protagonist, or main character. After introducing the key elements of your story, present an inciting incident—also known as an exciting force—that disrupts the status quo of the story and sets the plot into motion.
Rising action: Following the inciting incident, the main character enters a new world and moves toward a clear goal. The action rises along with the stakes as the protagonist faces obstacles and trials.
Climax: The rising action culminates in a climax, or the turning point of the story arc. At this stage, the protagonist faces their main conflict head-on, opposing the antagonistic force of the story—typically a villain.
Falling action: Immediately following the climax, the conflict between the protagonist and the antagonist unravels, creating suspense about the final outcome. The falling action is often out of the protagonist’s control.
Resolution: Sometimes called the denouement, the resolution of a story concludes the plot, tying up loose ends and answering final questions.
How to Use Dramatic Structure to Write a Story
Although there is a vast variety of methods for structuring stories, consider these general tips for how to best structure your story.
Identify your theme. Before locking in a plot structure, find the central theme of your story. Integrate the central philosophical question of your theme throughout the dramatic arc of your story.
Develop your characters. Identify the goals, desires, needs, and weaknesses of your main character. The more you develop your protagonist, the clearer your story structure will become. Alongside the main plot of your story, create subplots that develop your secondary characters, including allies, mentors, and antagonists.
Experiment with genre. Different genres include different tropes when it comes to story structure. Depending on the genre of your story, choose a story structure that either confirms or subverts the expectations of that genre.
Choose a plot structure for your story. Dramatic structures can be linear, cyclical, or non-linear with flashbacks. The most common plot structure in films and television is a three-act structure with a clear first, second, and third act. Two-act stories often include a climactic midpoint where the stakes rise or the protagonist’s goal changes.
Adapt your structure when necessary. The possibilities for potential dramatic structures are nearly endless. Be prepared to change your dramatic structure based on how your story unfolds on the page. Stay open-minded during the writing process to determine whether your dramatic structure is organic and authentic to the story you’re telling.
Source ⚜ More: Writing Notes & References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
#plot#dramatic structure#writeblr#writing tips#literature#writers on tumblr#writing reference#dark academia#spilled ink#writing prompt#creative writing#writing advice#on writing#light academia#writing resources
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ways to Write a Meaningful AO3 Comment…
…or frankly, a comment on any writing or artwork where your primary goal is to encourage and appreciate the creator.
It occurs to me that comments are a mini writing task, I have been a writing tutor, and if I’m going to ramble about how not to form communities and have meaningful interactions on the internet, I could maybe also help make it a little easier.
This post is written on the assumption that people want to interact, but struggle for whatever reason: nervous, tired, didn’t realize comments meant that much, can’t think of what to say. I myself spent years at a time on ao3 not commenting on literally anything—something about stones in glass houses. But in my experience, while getting comments on my own fics is kind of my favourite, leaving the kind of comment I know I would cherish—and sometimes getting replies from authors replying to my comments and actually chatting with them—is pretty damn magical too.
In that spirit, this post is henceforth a how-to, not an argument, and I’m not going to address anything to do with bad faith comments. I’m gonna try and provide some structures and simple formats to start comments from. I cannot emphasise enough, these are all intended to be used from a place of sincerity. Tools for finding and formatting the appreciation which is already in your brain, just hiding from you.
That said, we’re gonna take this in stages—
1. The Chapter Kudos
“Chapter kudos,” a little “<3,” an “I loved this,” or similar simple expressions of warmth and enthusiasm, slapped on a oneshot or each chapter of a long fic. These are a nice small gesture that lets the author know you’re here and you’re still loving the fic. Not every author is in love with the these type of very short comments, but unless they have a specific note about it, they’re almost certainly glad for the knowledge you’re still reading. This is minimal—great for days or weeks when you’re tired, low effort, can’t think of shit to say about a particular chapter, and so on. Comments, like all tasks, must be allowed to vary in intensity with available energy and time.
2. The 1-2 sentences
A one or two sentence comment. Here, a combination of a general compliment: “this was amazing,” and a specific compliment: “character A’s dialogue felt so realistic” works really well.
General compliments are typically easier to come up with:
What an awesome chapter!
Wow ok I did not see that coming—
I fucking. Love. Your writing.
This was so exciting!
I screamed when I saw this updated
Maybe a little over the top, but you get the idea—it’s hard to go wrong with these.
Specific compliments are often a little harder to come up with, but they generally fall into two categories which are both wonderful: content and writing.
Content includes things like:
I love [character] so much, seeing them in [particular situation] was so fun
Wow there’s so little content for [niche fandom/character/ship/trope] it’s great to see it here
Your idea about [authors headcanon] is so smart—that makes [weird element of canon] make so much sense
I didn’t used to be into [trope/ship] but holy fuck am I convinced now
The point being you’re noting a particular element content of the fic—what and who it’s about—that you loved. These are great because getting really damn excited about a character/trope/headcanon etcetera, really is the heart of fandom.
Writing takes a slightly different tack, and talks about the author’s writing skills—what they do well:
You write such good dialogue, it feels really realistic
Your action scenes are so exciting!
The tone of this chapter was so perfectly creepy—the way you describe [setting/character] gave me the shivers
The spacing you used really fit the piece—it’s a neat way to show the character’s mindset there they’re struggling to think clearly
The combination of a general and specific compliment can make it easier to start writing your comment, while giving you a second to think of your specific thought. It’s simple, but it means a lot to get any kind of specific comment, because it shows the author that you are paying attention to their writing and that you appreciate or relate to them, specifically. These comments are fairly quick to write, but can mean so much.
3. The paragraph
Several sentences long, with a bit more room to explain what you loved. Everything from the 1-2 sentence section applies here too. A general compliment is still a great starting point, and specific compliments are still where we want to end up. The main difference is you’ve got a little more room to talk, and you can take that in a few different directions.
You can talk about one specific compliment for a bit:
I love the way you write dialogue—character A saying “[quote]” was exactly what they would say in that situation. And their banter with character B was incredible, i laughed out loud. The way they both use cursing, but in slightly different ways is fascinating. The way character B does it is…
Or you can go through several different ones quickly:
I love the way you write dialogue—character A saying “[quote]” was exactly what they would say in that situation. The fast dialogue kept the pace up and the whole chapter was so exciting—I loved that you brought up character B and character C’s relationship too, it gets so little attention but I love it…
There’s also room for wider observations and questions (these can also totally go in 1-2 sentence comments, it’s just easier to have a little more substance around them):
Your writing always makes me feel so [feelings]
Wait I’m a little confused did [event] happen the way I think it did, or am I being silly?
Your ideas about [character] are awesome, I love everything you’ve written about them.
I’m so curious, what’s your specific lore on [character/event]?
4. Multiparagraph
Several paragraphs, or a very long paragraph. Hot damn, the author is in love with you now. Either you’ve got a whole lot to say about one specific topic of writing or content, or you’ve got a couple of different topics you want to pay some attention to—as you start writing your comment, you’ll probably discover a few more. Let yourself ramble, make bullet points, just get your thoughts out, if you have this many. All the principles from before apply: general compliments, specific compliments, wider observations, questions—all of these can easily feature in a long comment.
5. Fuck Formating
Write comments in whatever format works for you. Bullet points, google translated into the necessary language, rambling, well organized, short, long, emojis, copy-pasting your favorite quote from the fic with an exclamation point, pre-formatted general compliments, whatever will get your thoughts and enthusiasm down.
If you are communicating, the format doesn’t matter all that much. The same information from a multi paragraph comment can be done in bullet points or by quoting. Whatever communication you do will be meaningful to the author.
It’s hard to go wrong—
Like most writing, making meaningful comments and picking out those specific compliments gets easier with practice. There’s no need to write multiparagraph comments all the time. Those 1-2 sentence ones can be full of so much love, and chapter kudos are sometimes all there’s energy for.
The most important writing advice ever in my opinion is this: you have interesting things to say. About yourself, about the world, about writing, about that damn fanfic.
Go forth and use the structures above, or come up with comments I couldn’t even dream of. Whatever you do, you will find fic authors are probably the most willing and grateful audience in the whole world.
192 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's talk about story structure.
Fabricating the narrative structure of your story can be difficult, and it can be helpful to use already known and well-established story structures as a sort of blueprint to guide you along the way. Before we delve into a few of the more popular ones, however, what exactly does this term entail?
Story structure refers to the framework or organization of a narrative. It is typically divided into key elements such as exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, and serves as the skeleton upon which the plot, characters, and themes are built. It provides a roadmap of sorts for the progression of events and emotional arcs within a story.
Freytag's Pyramid:
Also known as a five-act structure, this is pretty much your standard story structure that you likely learned in English class at some point. It looks something like this:
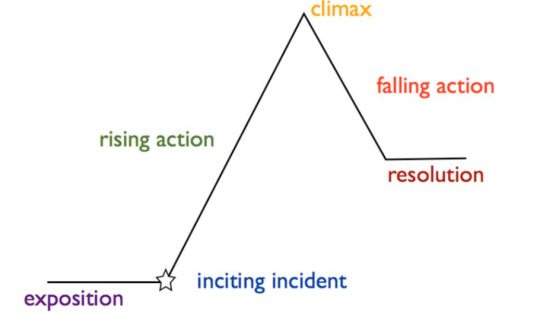
Exposition: Introduces the characters, setting, and basic situation of the story.
Inciting incident: The event that sets the main conflict of the story in motion, often disrupting the status quo for the protagonist.
Rising action: Series of events that build tension and escalate the conflict, leading toward the story's climax.
Climax: The highest point of tension or the turning point in the story, where the conflict reaches its peak and the outcome is decided.
Falling action: Events that occur as a result of the climax, leading towards the resolution and tying up loose ends.
Resolution (or denouement): The final outcome of the story, where the conflict is resolved, and any remaining questions or conflicts are addressed, providing closure for the audience.
Though the overuse of this story structure may be seen as a downside, it's used so much for a reason. Its intuitive structure provides a reliable framework for writers to build upon, ensuring clear progression and emotional resonance in their stories and drawing everything to a resolution that is satisfactory for the readers.
The Fichtean Curve:
The Fichtean Curve is characterised by a gradual rise in tension and conflict, leading to a climactic peak, followed by a swift resolution. It emphasises the building of suspense and intensity throughout the narrative, following a pattern of escalating crises leading to a climax representing the peak of the protagonist's struggle, then a swift resolution.
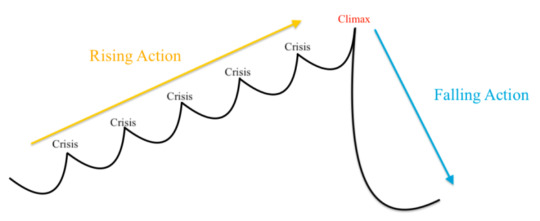
Initial crisis: The story begins with a significant event or problem that immediately grabs the audience's attention, setting the plot in motion.
Escalating crises: Additional challenges or complications arise, intensifying the protagonist's struggles and increasing the stakes.
Climax: The tension reaches its peak as the protagonist confronts the central obstacle or makes a crucial decision.
Falling action: Following the climax, conflicts are rapidly resolved, often with a sudden shift or revelation, bringing closure to the narrative. Note that all loose ends may not be tied by the end, and that's completely fine as long as it works in your story—leaving some room for speculation or suspense can be intriguing.
The Hero’s Journey:
The Hero's Journey follows a protagonist through a transformative adventure. It outlines their journey from ordinary life into the unknown, encountering challenges, allies, and adversaries along the way, ultimately leading to personal growth and a return to the familiar world with newfound wisdom or treasures.
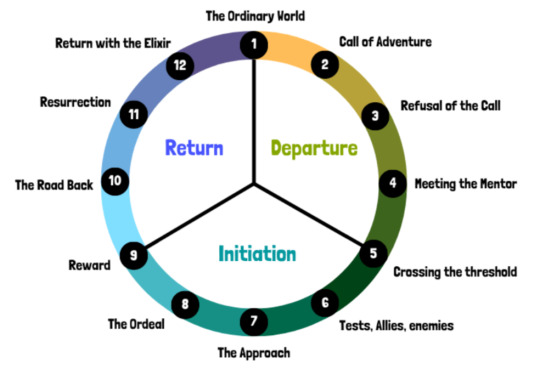
Call of adventure: The hero receives a summons or challenge that disrupts their ordinary life.
Refusal of the call: Initially, the hero may resist or hesitate in accepting the adventure.
Meeting the mentor: The hero encounters a wise mentor who provides guidance and assistance.
Crossing the threshold: The hero leaves their familiar world and enters the unknown, facing the challenges of the journey.
Tests, allies, enemies: Along the journey, the hero faces various obstacles and adversaries that test their skills and resolve.
The approach: The hero approaches the central conflict or their deepest fears.
The ordeal: The hero faces their greatest challenge, often confronting the main antagonist or undergoing a significant transformation.
Reward: After overcoming the ordeal, the hero receives a reward, such as treasure, knowledge, or inner growth.
The road back: The hero begins the journey back to their ordinary world, encountering final obstacles or confrontations.
Resurrection: The hero faces one final test or ordeal that solidifies their transformation.
Return with the elixir: The hero returns to the ordinary world, bringing back the lessons learned or treasures gained to benefit themselves or others.
Exploring these different story structures reveals the intricate paths characters traverse in their journeys. Each framework provides a blueprint for crafting engaging narratives that captivate audiences. Understanding these underlying structures can help gain an array of tools to create unforgettable tales that resonate with audiences of all kind.
Happy writing! Hope this was helpful ❤
Previous | Next
#writeblr#writing#writing tips#writing advice#writing help#writing resources#creative writing#story writing#storytelling#story structure#plot development#outlining#plot structure
500 notes
·
View notes
Text
Micro-tip: How to make emotional scenes hit harder
Don’t put the emotional payoff in the confrontation itself.
Put it two scenes later. Quiet. Off-guard. Uncontrolled.
Let your character hold it together when it matters.
Then let it fall apart in the silence that follows.
Not when they’re being watched.
When the door sticks.
When someone looks away.
When they forget the wine.
When they ask if anyone’s hungry just to fill the space.
Readers don’t cry when the character explodes.
They cry when the damage surfaces — quiet, and far too late.
#ao3 writer#writers on writing#fic writing#writing tips#writeblr#ao3 author#ao3 fanfic#ao3fic#writers on tumblr#female writers#character driven stories#writing#writing advice#character writing#character development#emotional tension#emotional writing#writing process#fiction writing#writing blog#narrative structure#character arcs#writting#writer on tumblr#writer tumblr#writer blog#writerblr#sub text#Quillver#creative writing
106 notes
·
View notes
Text
12 year old tim realizing robin’s not coming back to gotham and deciding that it’s Batman’s fault so he has to ruin the little bit of sanity and peace of mind Bruce has managed (read: struggled) to keep in his grasp:

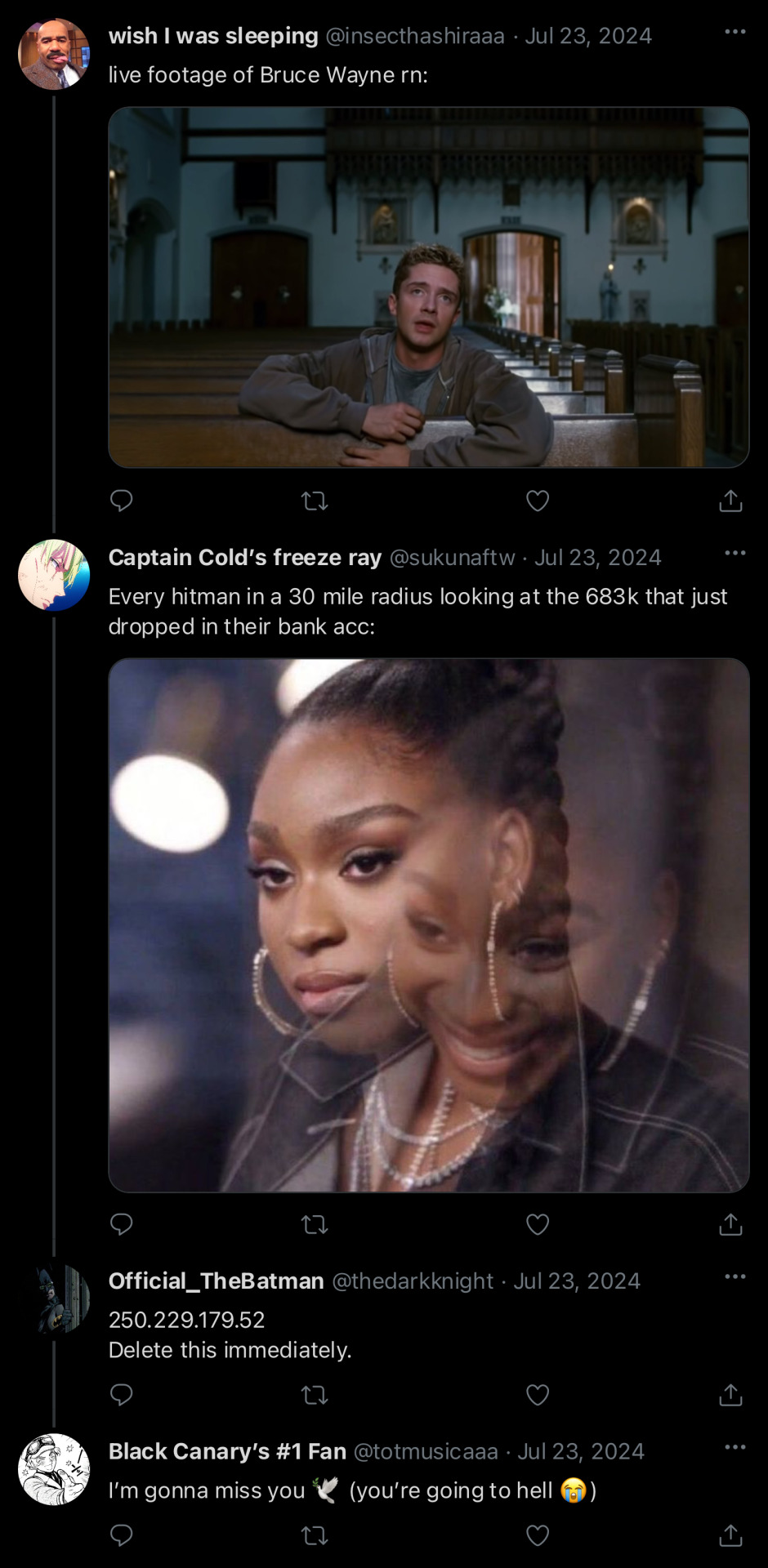
#tim drake#dick grayson#robin#dc robin#bruce wayne#batman#tim drake is a menace#tim drake was and still is a die hard Robin fan before anything else#so he 100% thinks Damian’s funny when he’s not the one being targeted#there’s mission reports with comments in the margin like ‘nice 👍🏾 do it again’ and ‘650000000/10 🎉’ and Bruce hates it sm#it starts with a mild explosion and psychological fuckery and ends with a prank war with city wide structural damage#Bruce sees Tim and Damian getting along and starts sobbing in the batcave#It was 12 year old Tim Drake and his 67 alt twitter accs against the world (Batman) when dick left#For the two years dick refused to stay in Gotham I promise you batman’s anonymous tip line was just 325 ruthless insults from tim everyday#Imagine bruce trying to figure out which of his rogues keeps photoshopping terrible .5s of Batman then mailing it to the gcpd#just to find out it’s some fucking middle schooler with a bowlcut from bristol#Tim drake is unhinged and petty#Like it gets so bad that gothamites (even the rogues) have picked a side in this mostly one sided beef between a middle schooler and batman#I want internet beef between a middle schooler and a 29 year old med school dropout bruce ‘I am the night’ wayne#Bruce is foaming at the mouth whenever someone opens Twitter next to him#and batman is breaking your clavicle if you mention twitter in his hearing range 😭#Batman showing up at Tim’s windowsill: take down all your accounts rn and im calling your parents 😡🦇#Tim pulling out a ouija board: let’s see if your parents answer before mine 🤨#I made yj on the sims so they could fight the jl and I was like middle school!tim drake w/ a twitter acc???
346 notes
·
View notes
Text
Plotting vs Discovery Writing: Should You Plan Your Story or Wing It?
Ah, the age-old writer’s dilemma:
Do you map every scene like a tactician drawing battle plans — or dive in with nothing but vibes and a chaotic sense of adventure?
Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of both approaches — and why the real magic might lie somewhere in between. 🖋️
Plotting (Outlining / Planning)
Pros:
✔️ Clear direction – You know where you’re going. No getting lost in the woods.
✔️ Foreshadowing magic – You can plant clues, callbacks, and payoff arcs with confidence.
✔️ Fewer plot holes – A roadmap helps spot inconsistencies early.
✔️ Less panic during writing – You’ve already solved some of the hardest narrative problems.
Cons:
✖️ It can feel rigid – The story may resist your outline or outgrow it.
✖️ Planning fatigue – You might lose momentum before the writing even begins.
✖️ Less room for surprise – Characters can feel boxed in by pre-decided fates.
✖️ Too much structure can kill discovery – Sometimes the magic is in what you didn’t see coming.
Discovery Writing (Pantsing / Writing as You Go)
Pros:
✔️ Creative freedom – You’re exploring in real time. Characters can surprise you.
✔️ Organic pacing – The story flows from instinct and mood.
✔️ Emotional authenticity – Moments feel raw, fresh, and true to how they unfolded.
✔️ Writing is more exciting – You’re discovering the story as a reader would.
Cons:
✖️ You might write into a corner – Plot knots are harder to untangle without a plan.
✖️ Revision may be intense – You’ll likely need more editing to fix structure, foreshadowing, and pacing.
✖️ Themes may be muddled – Without direction, your story can lose its core.
✖️ Momentum stalls – Getting stuck is common if you don’t know what happens next.
The Hybrid Approach (A Little Bit of Both)
Plot the skeleton. Discover the heart.
Many writers outline broad strokes (major beats, ending, key twists), but leave space to discover the emotional or interpersonal journey as they write.
You might:
Write a chapter, then outline the next.
Plan major events, but improvise how characters get there.
Start as a pantser, then reverse-outline what you’ve done.
There’s no “right” way — just the one that keeps you writing and enjoying your craft.
Final Thought:
Plotting is a compass.
Pantsing is a storm.
Every writer’s ship sails differently — but the goal is the same: reach the end, and love the journey.
#writeblr#writing community#writers of tumblr#writing tips#creative writing#amwriting#writing advice#tumblrs writers#writing resources#story structure#plotting#pantsing#plotter vs pantser#writing process#story planning#narrative craft#writing methods#writing style#outlining your novel#writing motivation#vivsinkpot#vivwrites
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Make Your Writing Less Stiff Part 3
Crazy how one impulsive post has quickly outshined every other post I have made on this blog. Anyway here’s more to consider. Once again, I am recirculating tried-and-true writing advice that shouldn’t have to compromise your author voice and isn’t always applicable when the narrative demands otherwise.
Part 1
Part 2
1. Eliminating to-be verbs (passive voice)
Am/is/are/was/were are another type of filler that doesn’t add anything to your sentences.
There were fireworks in the sky tonight. /// Fireworks glittered in the sky tonight.
My cat was chirping at the lights on the ceiling. /// My cat chirped at the lights on the ceiling.
She was standing /// She stood
He was running /// He ran
Also applicable in present tense, of which I’ve been stuck writing lately.
There are two fish-net goals on either end of the improvised field. /// Two fish-net goals mark either end of the improvised field.
For once, it’s a cloudless night. /// For once, the stars shine clear.
Sometimes the sentence needs a little finagling to remove the bad verb and sometimes you can let a couple remain if it sounds better with the cadence or syntax. Generally, they’re not necessary and you won’t realize how strange it looks until you go back and delete them (it also helps shave off your word count).
Sometimes the to-be verb is necessary. You're writing in past-tense and must convey that.
He was running out of time does not have the same meaning as He ran out of time, and are not interchangeable. You'd have to change the entire sentence to something probably a lot wordier to escape the 'was'. To-be verbs are not the end of the world.
2. Putting character descriptors in the wrong place
I made a post already about motivated exposition, specifically about character descriptions and the mirror trope, saying character details in the wrong place can look odd and screw with the flow of the paragraph, especially if you throw in too many.
She ties her long, curly, brown tresses up in a messy bun. /// She ties her curls up in a messy brown bun. (bonus alliteration too)
Generally, I see this most often with hair, a terrible rule of threes. Eyes less so, but eyes have their own issue. Eye color gets repeated at an exhausting frequency. Whatever you have in your manuscript, you could probably delete 30-40% of the reminders that the love interest has baby blues and readers would be happy, especially if you use the same metaphor over and over again, like gemstones.
He rolled his bright, emerald eyes. /// He rolled his eyes, a vibrant green in the lamplight.
To me, one reads like you want to get the character description out as fast as possible, so the hand of the author comes in to wave and stop the story to give you the details. Fixing it, my way or another way, stands out less as exposition, which is what character descriptions boil down to—something the audience needs to know to appreciate and/or understand the story.
3. Lacking flow between sentences
Much like sentences that are all about the same length with little variety in syntax, sentences that follow each other like a grocery list or instruction manual instead of a proper narrative are difficult to find gripping.
Jack gets out a stock pot from the cupboard. He fills it with the tap and sets it on the stove. Then, he grabs russet potatoes and butter from the fridge. He leaves the butter out to soften, and sets the pot to boil. He then adds salt to the water.
From the cupboard, Jack drags a hefty stockpot. He fills it with the tap, adds salt to taste, and sets it on the stove.
Russet potatoes or yukon gold? Jack drums his fingers on the fridge door in thought. Russet—that’s what the recipe calls for. He tosses the bag on the counter and the butter beside it to soften.
This is just one version of a possible edit to the first paragraph, not the end-all, be-all perfect reconstruction. It’s not just about having transitions, like ‘then’, it’s about how one sentence flows into the next, and you can accomplish better flow in many different ways.
4. Getting too specific with movement.
I don’t see this super often, but when it happens, it tends to be pretty bad. I think it happens because writers feel the need to overcompensate and over-clarify on what’s happening. Remember: The more specific you get, the more your readers are going to wonder what’s so important about these details. This is fiction, so every detail matters.
A ridiculous example:
Jack walks over to his closet. He kneels down at the shoe rack and tugs his running shoes free. He walks back to his desk chair, sits down, and ties the laces.
Unless tying his shoes is a monumental achievement for this character, all readers would need is:
Jack shoves on his running shoes.
*quick note: Do not add "down" after the following: Kneels, stoops, crouches, squats. The "down" is already implied in the verb.
This also happens with multiple movements in succession.
Beth enters the room and steps on her shoelace, nearly causing her to trip. She kneels and ties her shoes. She stands upright and keeps moving.
Or
Beth walks in and nearly trips over her shoelace. She sighs, reties it, and keeps moving.
Even then, unless Beth is a chronically clumsy character or this near-trip is a side effect of her being late or tired (i.e. meaningful), tripping over a shoelace is kind of boring if it does nothing for her character. Miles Morales’ untied shoelaces are thematically part of his story.
Sometimes, over-describing a character’s movement is meant to show how nervous they are—overthinking everything they’re doing, second-guessing themselves ad nauseam. Or they’re autistic coded and this is how this character normally thinks as deeply methodical. Or, you’re trying to emphasize some mundanity about their life and doing it on purpose.
If you’re not writing something where the extra details service the character or the story at large, consider trimming it.
—
These are *suggestions* and writing is highly subjective. Hope this helps!
#writing#writing resources#writing advice#writing tips#writing a book#writing tools#writeblr#for beginners#story structure#book formatting
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
📊 How to Use Tropes Without Turning Your Story into a YA Checklist
You can tell when a book was written by vibes and TVTropes alone.
It’s got: ☑️ the reluctant chosen one ☑️ the love triangle ☑️ the mysterious brooding boy™ ☑️ the sassy best friend ☑️ the dead parents ☑️ the villain with daddy issues ☑️ the scene where someone says “you don’t know what I’m capable of” and walks away dramatically
And like… that’s fine.
Tropes are tools. But here’s the thing: they are starting points, not story goals.
If your plot reads like it was drafted by a checklist in a Pinterest caption, it might be time to recalibrate. Here's how to actually use tropes without turning your book into a YA Mad Libs generator:
─────── ✦ ───────
🧩 Tropes Are Patterns--Not Presets
A trope is a pattern, not a requirement. It’s not a law. It’s not a plug-and-play feature. And it’s definitely not your plot.
The “enemies-to-lovers” arc? That’s a container. What you put inside it, that’s where the originality lives.
The goal isn’t to avoid tropes. It’s to do something interesting with them.
→ Why are they enemies? → What does the “love” cost them? → What happens if they fail to become lovers?
Tropes don’t carry the story. The conflict does.
─────── ✦ ───────
⚔️ Complicate the Familiar
Here’s a trick: if a trope feels too easy, break it in half.
Examples: → “Reluctant chosen one” → okay, but what if they wanted it, and then hated it once they got it? → “The mentor dies” → cool, but what if the mentor fakes their death to manipulate the protagonist? → “Sassy best friend” → no. Make them real. Give them pain. Give them depth. No more walking punchlines.
Tropes are scaffolding, not shortcuts. Add weight. Add doubt. Add betrayal.
─────── ✦ ───────
🕳️ Interrogate Why You’re Using It
Ask yourself: → Do I love this trope or do I feel like I have to include it? → Am I doing this because I’ve seen it done… or because it serves my story? → Is this trope the only interesting thing about this scene?
If your answer is “because that’s what YA stories do,” delete it. Go deeper.
─────── ✦ ───────
💔 Tropes Aren’t Substitutes for Character Arcs
You can’t use “grumpy x sunshine” and call it development. Tropes are flavors, not meals.
Give us: → Choices with consequences. → Conflicting values. → Character growth that costs something.
Otherwise? Your grumpy guy is just a Pinterest moodboard with a pulse.
─────── ✦ ───────
🧨 Use Reader Expectations Against Them
You want to use a trope and not make it predictable? Weaponize it.
Example: → Start with a love triangle. Let the MC fall hard. Then have both love interests realize they’re in love with each other. → Use the “chosen one” trope… but make it about dismantling that myth entirely. → Introduce the “villain redemption arc” and let them choose to stay bad because it makes more sense for them.
Set up the pattern. Then snap it in half. That’s how you surprise a jaded reader.
─────── ✦ ───────
Final thoughts from your local trope goblin:
→ Tropes aren’t the problem. It’s treating them like a checklist instead of a narrative engine. → A good trope doesn’t make your story good. How you twist it does. → If a story reads like it was built from Tumblr quotes and nothing else—it’s gonna flop.
So go ahead. Use the trope. Then ruin it. Make it weird. Make it hurt. Make it yours.
—rin t. // story mechanic. trope thief. YA bingo card burner. // thewriteadviceforwriters
Sometimes the problem isn’t your plot. It’s your first 5 pages. Fix it here → 🖤 Free eBook: 5 Opening Pages Mistakes to Stop Making:
🕯️ download the pack & write something cursed:
#writing#writing advice#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writing tips#writing help#how to write#story structure#writing process#plotting tips#writing guide#writing blog#writing community#writing support#tumblr writing community#writing inspiration#storytelling tips#how to outline#writing resources#novel writing#outline tips#plotting a novel#writing craft#novel planning#write a book#drafting a novel#writing motivation#first draft advice#fiction writing#character arcs
243 notes
·
View notes