#inadequate sanitation
Text
We are facing a global #watercrisis.

Water is essential for human well-being, energy and food production, healthy ecosystems, gender equality, poverty reduction and more.
But we are currently facing a global water crisis. Billions of people around the world still lack access to water. It is estimated that more than 800,000 people die each year from diseases directly attributed to unsafe water, inadequate sanitation, and poor hygiene practices.
Demands for this precious resource continue to rise: about four billion people experience severe water scarcity for at least one month of the year. With water being so crucial to many aspects of life, it is important to ensure its protection and proper management to ensure that everyone has equitable access to this essential resource by 2030.
0 notes
Text

Cases of Skin Rash are increasing everyday because of bacterial , fungal or viral infections , on the other sides alot of insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas and flies, which act as vectors. What we are witnessing in shelter centers and displacement camps from the accumulation of stagnant water and inadequate management of waste and sanitation provides a fertile ground for disease vectors. Every day we see in our Medical point about 50 cases of multi-cause rash. 😥💔
Save our children from this war. Link for donation 👇🔗🍉
Verified by Operation Olive Branch line 395 master line
We still very far from the goal. I hope everyone will donate even a little. I am confident that you will stand with me and support me until I reach my goal and remove my family from the danger of war. Share my story. Pin my story to your page. Everything helps.
@stil-lindigo @riding-with-the-wild-hunt @palestinegenocide @communistchilchuck @palentonga @palms-upturned @commissions4aid-international @cherifaouachani @sayruq @sar-soor
#palestine#free gaza#gaza#gaza genocide#gaza strip#fuck israel#rafah#education#film#north gaza#human rights#humanity#humanization#save rafah#save palestine#save gaza#save rottmnt#save rise of the tmnt#saving#done
26K notes
·
View notes
Text
Achieving Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation for a Sustainable Future

Clean water and sanitation are fundamental human rights and essential for the well-being and prosperity of communities worldwide. Access to clean water is crucial for drinking, hygiene, agriculture, and industry. Sanitation facilities ensure the proper disposal of waste and prevent the spread of diseases. Recognizing the importance of water and sanitation, the United Nations has set Goal 6 as part of its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In this article, we will explore the significance of Goal 6, its targets, and the actions needed to achieve clean water and sanitation for all.
The Importance of Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Access to clean water and sanitation is not only a pressing global issue but also a matter of basic human rights. Shockingly, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF, a staggering 2.2 billion people worldwide lack access to safely managed drinking water, while an overwhelming 4.2 billion people do not have access to safely managed sanitation services. These numbers highlight the scale of the problem and the urgent need for action.
The consequences of inadequate water and sanitation are far-reaching and severe. One of the most significant impacts is the spread of waterborne diseases. Contaminated water sources and poor sanitation facilities create a breeding ground for diseases like cholera, typhoid, and dysentery. These illnesses disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, including children and the elderly, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates. Lack of access to clean water and sanitation perpetuates a cycle of poverty and ill-health, as communities struggle to break free from the burden of preventable diseases.
Child mortality is also closely linked to the absence of clean water and sanitation. Unsafe drinking water and inadequate sanitation facilities contribute to the deaths of hundreds of thousands of children each year. Diarrheal diseases, in particular, claim the lives of many young children, as their weakened immune systems make them more susceptible to the harmful effects of contaminated water. Furthermore, the time spent collecting water from distant sources and the lack of proper sanitation facilities affect children's education and overall development, perpetuating a cycle of disadvantage and limited opportunities.
In addition to the human toll, inadequate access to clean water and sanitation hinders economic development. Communities that lack reliable access to clean water face numerous challenges. For instance, the burden of water collection falls primarily on women and girls, who often spend hours each day walking long distances to fetch water. This time-consuming task takes away from opportunities for education, income generation, and other productive activities, reinforcing gender inequalities and limiting economic empowerment.
Moreover, industries and businesses also suffer when water and sanitation are compromised. Lack of clean water can impede agricultural production, affecting crop yields and food security. Industries that rely on water, such as manufacturing and tourism, face operational challenges and increased costs when they must rely on alternative, often expensive, water sources. Inadequate sanitation can lead to environmental pollution, further exacerbating health risks and harming ecosystems, which are essential for the well-being of communities and biodiversity.
The gravity of the water and sanitation crisis necessitates urgent action and a comprehensive approach. Goal 6 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) recognizes the importance of clean water and sanitation for all and sets targets to address these challenges. Governments, organizations, and individuals must prioritize investment in infrastructure development, education and awareness programs, sustainable practices, and innovative solutions.
By investing in infrastructure, such as water treatment plants, pipelines, and sanitation facilities, governments can improve access to clean water and proper waste management. Concurrently, education and awareness programs can promote proper hygiene practices, behavioral change, and the sustainable use of water resources. It is crucial to empower communities with knowledge and tools to protect their water sources and ensure sustainable practices are adopted at the individual and community levels.
Sustainable agriculture practices also play a significant role in achieving clean water and sanitation goals. Implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques, promoting organic farming, and reducing the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers can help conserve water resources and prevent pollution. By embracing technology and innovation, such as water purification systems, smart water management systems, and affordable sanitation technologies, we can bridge the gap in access to clean water and sanitation, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
Collaboration and partnerships among governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), businesses, and communities are crucial for progress. By joining forces, sharing expertise, and pooling resources, we can overcome financial constraints, leverage innovative solutions, and achieve more significant impact. International cooperation, aid, and support can also play a pivotal role in assisting countries with limited resources to improve their water and sanitation infrastructure and practices.
The lack of access to clean water and sanitation remains a global crisis with far-reaching consequences. The numbers are staggering, and the impacts on health, child mortality, and economic development are severe. Achieving Goal 6 of the SDGs requires concerted efforts, investment in infrastructure, education, sustainable practices, and innovative solutions. It is only through collaboration and a commitment to this fundamental human right that we can ensure a sustainable future where every individual has access to clean water and sanitation, leading to improved health, reduced poverty, and enhanced opportunities for all.
Targets for Goal 6
Goal 6 encompasses multiple targets that aim to address the water and sanitation challenges. These targets include:
Achieving universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.
Ensuring access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all.
Improving water quality by reducing pollution and increasing water treatment.
Increasing water-use efficiency and ensuring sustainable water withdrawals.
Implementing integrated water resources management at all levels.
Protecting and restoring water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, and lakes.
Actions to Achieve Goal 6
To achieve Goal 6 and ensure clean water and sanitation for all, various actions need to be undertaken at local, national, and global levels. Here are some key actions:
Infrastructure Development: Governments and organizations should invest in infrastructure development to improve water and sanitation systems. This includes building water treatment plants, pipelines, and sanitation facilities to ensure access to clean water and proper waste management.
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of clean water and sanitation is crucial. Education programs can help communities understand the benefits of proper hygiene practices and promote behavior change to prevent water pollution and ensure the sustainable use of water resources.
Sustainable Agriculture: Promoting sustainable agriculture practices can reduce water pollution from pesticides and fertilizers. Implementing efficient irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation, can also conserve water resources.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Addressing the water and sanitation challenges requires collaboration between governments, NGOs, businesses, and communities. Partnerships can bring together expertise, resources, and innovative solutions to overcome the barriers to clean water and sanitation.
Technology and Innovation: Embracing technological advancements can greatly contribute to achieving Goal 6. Innovative solutions, such as water purification systems, smart water management systems, and affordable sanitation technologies, can improve access to clean water and sanitation in remote areas.
Water Conservation: Encouraging water conservation practices at the individual and community levels is essential. Simple measures like fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, and harvesting rainwater can go a long way in reducing water wastage and ensuring the availability of clean water.
Success Stories and Best Practices
Several success stories demonstrate that progress can be made in achieving Goal 6. For instance, in Rwanda, the government's commitment to improving water and sanitation services has resulted in significant improvements in access to clean water, particularly in rural areas. The introduction of community-led total sanitation programs in Bangladesh has successfully improved sanitation practices and reduced open defecation.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the progress made, significant challenges remain in achieving Goal 6. Limited financial resources, inadequate infrastructure, climate change impacts, and conflicts are some of the obstacles that need to be overcome. However, there are opportunities to address these challenges. By increasing investments in water and sanitation, promoting sustainable practices, and strengthening partnerships, we can create a future where clean water and sanitation are accessible to all.
Conclusion
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation is a critical component of the Sustainable Development Goals, highlighting the significance of access to clean water and sanitation for all. Achieving this goal requires concerted efforts from governments, organizations, communities, and individuals. By implementing the targets and taking necessary actions, we can ensure a sustainable future with clean water and sanitation, improving health, reducing poverty, and fostering economic development worldwide. Let us work together to make Goal 6 a reality and create a world where no one is deprived of this basic human right.
#Importance of clean water and sanitation#Achieving Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation#Access to clean water and sanitation#Waterborne diseases and sanitation#Goal 6 and global water crisis#Sustainable Development Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation#Lack of access to clean water and sanitation#Water and sanitation challenges worldwide#Promoting clean water and sanitation for all#Impact of inadequate water and sanitation#Clean water and sanitation for a sustainable future#Achieving universal access to clean water#Improving sanitation facilities worldwide#Water quality and pollution reduction#Sustainable water management practices#Protecting water-related ecosystems#Infrastructure development for clean water#Education and awareness for water and sanitation#Innovative solutions for clean water access#Addressing water scarcity and sanitation issues#Achieving equitable access to clean water#Ensuring sustainable sanitation services#Water conservation for a better future#Economic benefits of clean water and sanitation#Overcoming water and sanitation challenges#Success stories in achieving Goal 6#Partnership for clean water and sanitation#Technology advancements in water management#Achieving clean water and sanitation in rural areas#Breaking the cycle of poverty through water and sanitation
0 notes
Text
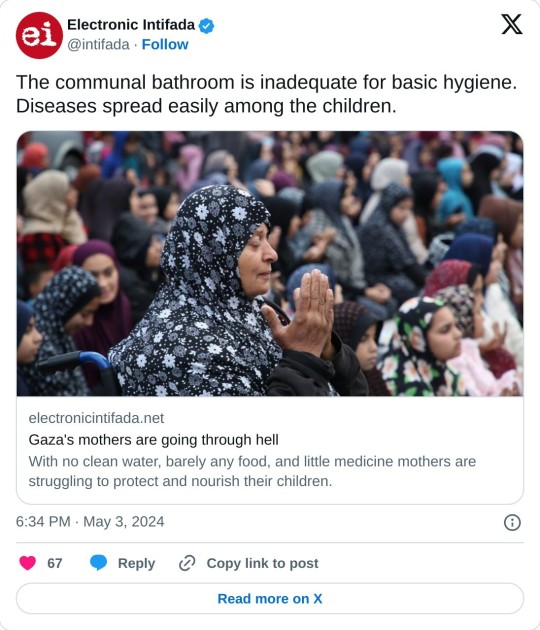
Amid Israel’s ongoing genocidal war on Gaza, maternal healthcare faces excruciating challenges.
Deliberate and systematic Israeli attacks on hospitals and medical centers, and critical shortages of humanitarian aid, including medicine, have created a crisis that is endangering the lives of both mothers and newborns.
The situation is critical. There are an estimated 50,000 pregnant women in Gaza and some 180 births every day.
Israel’s decision in October to prevent food, water, fuel and electricity from entering Gaza created a desperate situation.
Inadequate nutrition, exposure to cold and hot weather, the absence of clean water, and poor sanitation weigh heavily on the wellbeing of women and children.
The circumstances force them to consume contaminated water, heightening the peril of dehydration and waterborne diseases, particularly among vulnerable groups such as expectant mothers, new mothers and young children.
Fuel shortages and the constrained capacity of the few remaining medical facilities exacerbate the difficulty for women in labor to access hospitals.
Um Amin, a mother with a few children, confronted with the harsh reality of displacement, recounted her family’s struggles during Israel’s aggression. As bombs relentlessly fell on their neighborhood, reducing their home to rubble, Um Amin had to seek refuge at a school run by the UN agency for Palestine refugees (UNRWA) in the northern Gaza Strip taking only very few belongings.
She was pregnant. And in the school there was little by way of basic necessities such as clean water, food or even clothes for her children.
She considered moving south, where food might be a little more accessible. Her husband refused, causing conflict between them.He feared not being able to return. And while she believed that the Israeli army was attempting to force them to leave, she also felt it was a matter of life and death for her children.
“It was heart-wrenching to witness my kids fighting over scraps of bread. My 4-year-old started stashing away bread in his pocket for later. I was shocked. Before the war, I never slept without knowing my children were fed. Now, most of the time, I am certain they never feel satisfied.”
Her entire motivation to carry on became a matter of feeding her children She denied herself food for their sake, but had also to remind herself of the child within her.
“The baby inside me is also a priority, so I had to eat too.”
She found the balancing act incredibly challenging, an unbearable burden of motherhood.
“I am going to share something I’ve never told anyone I know: I contemplated suicide to escape the weight of this responsibility.”
After the Israeli army unexpectedly stormed al-Rimal, a Gaza City neighborhood, for a second time, Um Amin panicked and fled again, this time going from the UNRWA school to a relative’s house.
But her fear caused her to enter preterm labor. A doctor, at the nearby al-Sahaba medical center, had to resort to a cesarean section.
It was hell, Um Amin said. There was insufficient anesthesia and she could feel the scalpel cutting into her body.
There was no electricity; the doctor had to use a handheld flashlight to see.
Um Amin’s cries of pain could not drown out the crashing of shells around her.
The operation left her utterly drained. She couldn’t believe she was still alive.She needed nourishment to recover what she had lost during the bleeding and to breastfeed her son. But hunger was stalking Gaza.
Food was scarce, there was no white flour in the markets, and Israel was blocking aid trucks from entering the north.
“All I had to eat was bread made from animal feed and water. When I had my other children, I relied on foods rich in animal proteins, but it was impossible this time. The price of meat was five times higher than normal.”
Unable to adequately breastfeed her child, she had to find infant formula. But the price was multiple times higher than it used to be and more than she could afford.
Eventually, she was forced to buy formula that was past its expiry date.
“You might blame me, but there was literally no other option. I didn’t have enough money. It wasn’t clumped together, so the doctor told me it could still be used.”
She would never find out. Due to the lack of clean water, she prepared the milk with non-potable water from a well.
The baby refused to drink.
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#children of gaza#famine#gaza genocide#genocide#palestinian women#water scarcity
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

#Today#3.6 billion people are still living with poor quality toilets that ruin their health and pollute their environment. Inadequate sanitation s#lakes and soil#contaminating the water resources under our feet.#Everyone must have access to a toilet connected to a sanitation system that effectively removes and treats human waste. The link between sa#This World Toilet Day#let’s make the the invisible visible.#[src.: https://www.worldtoiletday.info/]#gemsartsjewellery#UN#UnitedNations#Lazimpat#kathmandu#kathmanduvalley#nepal#SanitationForAll#international#UNESCO#diamonds#gold#silver#gems#ring#earring#necklace#nosering#stud#anklet#bangles#bracelets
1 note
·
View note
Text
Increase Investment to reach the goal of a toilet for all by 2030.
"Without proper access, millions of people the world over are deprived of the dignity, safety and convenience of a decent toilet," Dr. Tedros.
#world health organisation (who)#Universal Sanitation Coverage#Toilets#latrines#access to toilets#access to latrines#sanitation#inadequate sanitation systems#proper sanitation
0 notes
Text

“In the coming year, I wish for a safer future for the children of Laos who are suffering from inadequate nutrition, contaminated water, and poor sanitation.” 🤍
#lee felix#lee yongbok#stray kids#people#unicef#i love all the pictures with the kids#he truly looks happy
513 notes
·
View notes
Note
Actually bathrooms shouldn't be gendered at all that's half the problem.
In communities that lack access to single-sex bathrooms, you witness an increase in the rate of sexual violence, physical health issues like incontinence, and mental health issues like PTSD. If women's health and safety aren't a problem to you, then by all means continue insisting that there's no need to provide them, but you should know these issues disproportionately affect poor women, disabled women, young women, and women from ethnically, linguistically, and racially diverse backgrounds (e.g. bathrooms in northern India are particularly unsafe for women).
I'll leave you with a quote from a book I read recently - Invisible Women, by Caroline Criado Perez:
According to the UN, one in three women lack access to safe toilets, and WaterAid reports that girls and women collectively spend 97 billion hours a year finding a safe space to relieve themselves [which affects their productivity, as women are more likely to be engaged in the informal economy, and their safety].
Local governments that fail to provide public toilets may believe that they are cutting costs, but a 2015 Yale study suggests that this is a false economy. [They linked] the ‘risk of sexual assault to the number of sanitation facilities and the time a woman must spend walking to a toilet, and calculated the tangible costs (lost earnings, medical, court, and prison expenses) and intangible costs (pain and suffering, risk of homicide) [against] the cost of installing and maintaining public toilets … [they found public toilets could save one town $5 million better off, which is a conservative estimate, as it doesn’t include the various health benefits saved from women having more regular and more private bowel movements (e.g. chronic constipation, cholera)].
Health problems arising from a lack of public sanitary provision are not restricted to low-income countries. Canadian and British studies have revealed that referrals for urinary-tract infection, problems with distended bladders, and a range of other uro-gynaeloogical problems have increased proportionately to [toilet inaccessibility].
Urban planning that fails to account for women’s risk of being sexually assaulted is a clear violation of women’s equal right to public spaces – and inadequate sanitary provision is only one of the many ways planners exclude women with this kind of gender-insensitive design.
...
For women who try to escape from war and disaster, the gender-neutral nightmare often continues in the refugee camps of the world … [although] international guidelines state that toilets in refugee camps should be sex-segregated, marked, and lockable, [sic] these requirements are often not enforced [and] research by the Women’s Refugee Commission has found that women and girls in accommodation centres in Germany and Sweden are vulnerable to rape, assault, and other violence…
248 notes
·
View notes
Text
As we see an increase in antisemitism I have reflected on my experiences how many years ago being the token Jew in my eighth grade English class and I have found some aspects about it which lead me to believe are the parts that Holocaust Education in the U.S. goes wrong
Being taught in English Classes
Often such as in my state, the Holocaust is taught as part of English curriculum. English teachers aren't history teachers and they may be lacking in the skills or knowledge required to teach in the necessary depth to discuss the Holocaust.
My mother used to teach English but she had a history degree as well. She would lecture in class about everything leading up to and during WWII. I remember reading handouts she had in her classroom while I was waiting after school about the history of antisemitism. I didn't have any of this in my English class unit, because to put it simply most English teachers aren't my mother who also has the prior knowledge of how to teach history.
Additionally, as it is part of English, there is often more focus on Holocaust literature rather than the topic itself
This is where I think it gets extremely flawed if a person's primary knowledge of a historical period is Anne Frank or the incredibly inaccurate boy in the striped pajamas. A single account or work of complete fiction shouldn't be your main lens to view any topic whether it's the Holocaust, Slavery, Civil Rights movement etc.
You're in short blurring fact and fiction when discussing these things in the context of literature.
Sense of Finality
I feel like in my classes at least there was this idea that was kind of implied that hatred of Jews began and ended with Hitler and the Holocaust. I think this leads to misconceptions about antisemitism.
I feel this is a problem as I remember mistakenly getting that takeaway in school regarding civil rights in America. It was taught that Slavery was a problem, emancipation proclamation, MLK said I have a dream, and the civil rights act was passed and bam no inequality or racism. Later on, I fortunately learned this was flawed for many reasons. But not everyone does.
Not teaching about how the Holocaust happened
If you aren't given the knowledge of how centuries of hatred lead up to the Holocaust, I feel the main takeaway becomes that it was almost a random occurrence.
Many learn the Holocaust is bad without learning the signs of thinking that can lead neighbors to kill neighbors.
So many people don't have the basic facts such as Hitler being elected rather than assuming power.
I think when you learn of an atrocity of such scale without learning the human beliefs that brought about it, you have learned nothing.
I had a girl in my college uni class who was shocked when I said that antisemitism didn't begin and end with Hitler. I can see where she would get this idea if I at ten figured that racism ended with MLK.
Using Simulation
Slavery and the Holocaust should probably not be taught using roleplay. It usually goes poorly and you can find dozens of examples of how this goes wrong.
Sanitizing History
Exactly what it sounds like. But it's a major problem in general with history education in the US. I think we downplay westward expansion, and slavery in the us. When we downplay those it's easy to see how some begin to downplay the Holocaust.
We had a kid faint on the trip to the Holocaust memorial at some of the images. I think it was because they were inadequately prepared to see the horrors in image, my teacher didn't show any pictures in class.
Final notes
I don't blame teachers. Teacher's jobs fucking suck from what I've seen and many don't have the skills or resources or experience. I guess for now I think it's good to recognize those holes in our education and fill them ourselves through self education and life long learning
With the current political atmosphere of education of the unpleasant or difficult to discuss parts of history, i can only see things getting worse if we don't change anything. But like I said in the absence of a solid education which discusses these topics, it's important to educate ourselves and confront our lack of knowledge.
#tw shoah#tw holocaust#jumblr#feel free to add on with your school experiences#especially if you're jewish
167 notes
·
View notes
Photo

On this day, 20 November 1969, a group of 78 Native Americans occupied Alcatraz Island demanding that it be returned to them, as well as demanding the establishment of a Native American university. In their declaration the occupiers noted that Alcatraz was "more than suitable for an Indian reservation, as determined by the white man’s own standards", as it had no "adequate means of transportation… no fresh running water, inadequate sanitation facilities… no oil or mineral rights… no health-care facilities… no educational facilities" and "The population has always been held as prisoners and kept dependent upon others." The occupiers dubbed themselves Indians of All Tribes, elected a council, set up a school and distributed tasks amongst the whole group, voting on all major decisions. Holding out until June 1971, authorities eventually evicted the protesters without agreeing to any of their demands. However, the action was reported around the world, and helped spark the growth of the modern Native American movement. Learn more about Indigenous resistance in the Americas in this book: https://shop.workingclasshistory.com/products/500-years-of-indigenous-resistance-gord-hill https://www.facebook.com/workingclasshistory/photos/a.296224173896073/2140335012818304/?type=3
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
ok that was fun now imagine i’m a broken little hand sanitizer dispenser and you’re desperately trying to jam a refill into my hopelessly inadequate insertion hole
78 notes
·
View notes
Text

UNICEF Laos posted on instagram
Vía @/uniceflaos
“"In the coming year, I wish for a safer future for the children of Laos who are suffering from inadequate nutrition, contaminated water, and poor sanitation." @yong.lixx, @realstraykids.
💦👧👦This #WorldWaterDay and every day,let's join Felix in supporting our cause of improving water and sanitation #ForEveryChild.”
#stray kids#lee felix#han jisung#changbin#hwang hyunjin#leeknow#bang chan#jeongin#seungmin#felix#felix skz#felix yongbok#felix stray kids#stray kids felix#skz felix#yongbokie#yong.lixx#skz yongbok#stray kids yongbok#lee yongbok#unicef#laos#instagram
106 notes
·
View notes
Text


Cases of Skin Rash are increasing everyday because of bacterial , fungal or viral infections , on the other sides alot of insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas and flies, which act as vectors. What we are witnessing in shelter centers and displacement camps from the accumulation of stagnant water and inadequate management of waste and sanitation provides a fertile ground for disease vectors. 💔💔
Help me save our children and reach my limit we are so far away from the goal. 😥🔗💔
Verified by Operation Olive Branch line 395 master line🔗👇
We still very far from the goal. I hope everyone will donate even a little. I am confident that you will stand with me and support me until I reach my goal and remove my family from the danger of war. Share my story. Pin my story to your page. Everything helps.
@stil-lindigo @riding-with-the-wild-hunt @communistchilchuck @palestinegenocide @fairuzfan @fallahifag @blackpearlblast
#palestine#free gaza#gaza#gaza genocide#gaza strip#fuck israel#rafah#education#north gaza#film#art#artists on tumblr#my art#advertising
558 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon and Water
Excerpt from the book Aaron Burr in Exile: A Pariah in Paris, 1810-1811, by Jane Merrill and John Endicott
Aaron Burr lived in Paris for 15 months, and this book goes into detail about those years living under Napoleon’s rule. This part focuses on Napoleon’s water related reforms.
———
Napoleon’s fountains gave drinking water to the population, that is, children drank water, not beer. The water was free, not purchased. And the apartment would have had a separate water closet equipped with squat toilets (adopted from the Turks) and a bucket to wash it after use. Some restaurants and cafes had W.C.s, even one for ladies and one for gents. These were hooked into the sewer system that branched under each important street.
Napoleon merits points for delivering fresh water to Paris. If serving Paris with water from the d'Ourcq River by canals was not be a consummate success, Paris gained 40 new fountains, and the emperor commanded that fountains run all day (instead of a few limited hours) and that the water be free of charge.
Perhaps the most laudable of Napoleon’s policies were utilitarian city works, especially bringing clean water and sanitation to Paris. The improvements to infrastructure included new quays to prevent floods, new gutters and pavement, new aqueducts and fountains, and relocating cemeteries and slaughterhouses to the outskirts of the city. This was also a way of keeping up employment. An Austrian aristocrat in town during Napoleon’s wedding to Marie-Louise wrote his mother, in Vienna: “Nothing can give an idea of the immense projects undertaken simultaneously in Paris. The incoherence of it is incredible; one cannot imagine that the life of a single man would be enough to finish them.”
It was a tall order. Previous rulers had been aware of the problems and one big engineering initiative, a failed marvel, had been the waterworks at Marly, located on the banks of the Seine about seven miles from Paris. Louis XIV had it constructed to pump water from the river to his chateaux of Versailles and Marly. This was the machine marvel of its age, with 250 pumps that forced river water up a 500-foot rise to an aqueduct, and it was a sight Burr mentions going to see. By 1817 the “Marly machine” had deteriorated because it was made of wood, and the waterworks were abandoned.
Charles-Augustin Sainte-Beuve, the prominent 19th century literary critic, wrote that there had been “ten years of anarchy, sedition and laxity, during which no useful work had been undertaken, not a street had been cleaned, not a residence repaired nothing improved or cleansed.” Postrevolutionary Paris was at a nadir in terms of both the inadequate, disease-ridden water supply and the filthy streets, which were basically open sewers, deep with black mud and refuse.
“Napoleon,” writes Alistair Horne, “was obsessed by the water of Paris, and everything to do with it.”
Parisians had mostly been getting their water directly from the Seine or lining up at the scant pay fountains. In 1806, nineteen new wells for fountains were dug that flowed day and night and were free. Napoleon had a canal built 60 miles from the River Ourcq, ordering 500 men to dig it, while still a consul in 1801. It brought water to the Bassin de la Villette, opening in 1808. Some doubted the wisdom of having such an abundance of water—an oriental luxury that might incur moral decay. Now the supply of water for firefighting was also much improved. The canal had light boats, as Napoleon tried to make back some of the huge expenditure by licensing navigation, and a circular aqueduct from which underground conduits went to the central city. In 1810, there were still many water porters wheeling barrels through the city.
Now Napoleon attacked the problem of the Seine as a catchall for pollution. Parisians were so used to it that men swam naked in the river and a contemporary guidebook advised merely that the water of the Seine had no ill effects on foreigners so long as they drank it mixed with wine or a drop of vinegar. Thus houses on bridges were demolished and an immense push began to clean and modernize the city sewers.
As this book is about Aaron Burr, here is section about Burr taking inspiration by a new water related invention during his time in Paris:
Remarkably for someone who was very aware of his health, he never complained of the water. He did, however, take an interest in an invention to make it easier to dig a well. When the inventor of a process to make vinegar from the sap of any tree was not in his shop, Burr and a friend, “Crede”, went to see another invention: “We went then to see Mons. Cagniard, and his new invention of raising water and performing any mechanical operation. His apparatus is a screw of Archimedes turned the reverse, air, water, and quick silver. Cagniard was abroad; but we saw a model, and worked it, and got the report of a committee of the Institute on the subject. If the thing performs what is said I will apply it to give water to Charleston.”
[Bold italics for quotations by me]
#Aaron Burr in Exile: A Pariah in Paris 1810-1811#Aaron Burr#Jane Merrill#John Endicott#napoleon#napoleonic era#napoleonic#napoleon bonaparte#first french empire#french empire#19th century#france#history#Paris#french history#water#water history#Napoleon’s reforms#social reforms#social history#reforms#napoleonic reforms
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
🇵🇸 🚨
DISEASE, ALONG WITH A LACK OF MEDICAL SUPPLIES AND SANITATION RISKS FURTHER DISASTER IN THE GAZA STRIP
📹 A Palestinian man shows green, algae-filled water buildup in the Gaza Strip as a result of Israel's ongoing bombing and shelling, describing how disease is spreading through the Palestinian population displaced by the Israeli genocide.
The Palestinian man describes the situation as an "environmental and health catastrophe" that risks spreading disease among the population of the Gaza Strip.
"The situation has reached a critical point after government and health authorities reported an outbreak affecting half a million people," the man tells the viewer.
"The outbreak is linked to a variety of diseases caused by parasites, bacteria, and other viral illnesses," he says, adding that "the crises in the Gaza Strip has been exacerbated by the occupation's targeting of intersections, streets, and large swaths of land, leading to the bursting of sewage lines that pass through these areas."
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the risk of disease is also being exacerbated by several other factors, including, "overcrowding, inadequate water and sanitation, disruption of routine healthcare services, and a dysfunctional health system" as a result of Israel's ongoing aggression.
The WHO emphasizes the importance of "ensuring ensuring access to safe water, sanitation, the importance of hand hygiene, the availability of [Infection Prevention and Control] IPC supplies, and the appropriate selection and use of personal protective equipment based on risk assessment," all of which is being hampered by continued bombing, shelling and blockade enforced by the Israeli occupation army.
#source
#videosource
@WorkerSolidarityNews
#gaza#disease in gaza#gaza strip#gaza news#gaza war#gaza genocide#genocide in gaza#genocide of palestinians#israeli war crimes#israeli genocide#war crimes#crimes against humanity#palestine#palestine news#palestinians#israel#israeli occupation forces#israeli occupation#middle east#war on gaza#israel palestine conflict#politics#news#geopolitics#world news#global news#international news#breaking news#current events#war
99 notes
·
View notes
Note
please help us we are dying. Help our children.

please help us please. please don't ignore us. we are from Gaza. we face death every single moment. I can approve anything you need to confirm about our siitiuation… I believe in your humanity please share our link with your followers. you can save innocent lives from death, yesterday they bombed us in Rafah, while we are sleeping.I don't want to die like this. I am a person like you dream to achieve a lot of goals. I dream to graduate from Dental school.
please help us…. please we lost everything home, family, collage, dreams, and memories. please ….
Cases of Skin Rash are increasing everyday because of bacterial, fungal or viral infections , on the other sides a lot of insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas and flies, which act as vectors. What we are witnessing in shelter centers and displacement camps from the accumulation of stagnant water and inadequate management of waste and sanitation provides a fertile ground for disease vectors. 😥💔
Save our children from this war. Link for donation in bio 👇🔗🍉
I hope this post reaches people who can help!
#palestine#this has been vetted for!!#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#gaza strip#gazaunderattack#gaza genocide#idk what other tags to use
20 notes
·
View notes