#mental illness misconceptions
Text

By: Andy L.
Published: Apr 14, 2024
It has now been just little under a week since the publication of the long anticipated NHS independent review of gender identity services for children and young people, the Cass Review.
The review recommends sweeping changes to child services in the NHS, not least the abandonment of what is known as the “affirmation model” and the associated use of puberty blockers and, later, cross-sex hormones. The evidence base could not support the use of such drastic treatments, and this approach was failing to address the complexities of health problems in such children.
Many trans advocacy groups appear to be cautiously welcoming these recommendations. However, there are many who are not and have quickly tried to condemn the review. Within almost hours, “press releases“, tweets and commentaries tried to rubbish the report and included statements that were simply not true. An angry letter from many “academics”, including Andrew Wakefield, has been published. These myths have been subsequently spreading like wildfire.
Here I wish to tackle some of those myths and misrepresentations.
-
Myth 1: 98% of all studies in this area were ignored

Fact
A comprehensive search was performed for all studies addressing the clinical questions under investigation, and over 100 were discovered. All these studies were evaluated for their quality and risk of bias. Only 2% of the studies met the criteria for the highest quality rating, but all high and medium quality (50%+) studies were further analysed to synthesise overall conclusions.
Explanation
The Cass Review aimed to base its recommendations on the comprehensive body of evidence available. While individual studies may demonstrate positive outcomes for the use of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones in children, the quality of these studies may vary. Therefore, the review sought to assess not only the findings of each study but also the reliability of those findings.
Studies exhibit variability in quality. Quality impacts the reliability of any conclusions that can be drawn. Some may have small sample sizes, while others may involve cohorts that differ from the target patient population. For instance, if a study primarily involves men in their 30s, their experiences may differ significantly from those of teenage girls, who constitute the a primary patient group of interest. Numerous factors can contribute to poor study quality.
Bias is also a big factor. Many people view claims of a biased study as meaning the researchers had ideological or predetermined goals and so might misrepresent their work. That may be true. But that is not what bias means when we evaluate medical trials.
In this case we are interested in statistical bias. This is where the numbers can mislead us in some way. For example, if your study started with lots of patients but many dropped out then statistical bias may creep in as your drop-outs might be the ones with the worst experiences. Your study patients are not on average like all the possible patients.
If then we want to look at a lot papers to find out if a treatment works, we want to be sure that we pay much more attention to those papers that look like they may have less risk of bias or quality issues. The poor quality papers may have positive results that are due to poor study design or execution and not because the treatment works.
The Cass Review team commissioned researchers at York University to search for all relevant papers on childhood use of puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones for treating “gender dysphoria”. The researchers then graded each paper by established methods to determine quality, and then disregarded all low quality papers to help ensure they did not mislead.
The Review states,
The systematic review on interventions to suppress puberty (Taylor et al: Puberty suppression) provides an update to the NICE review (2020a). It identified 50 studies looking at different aspects of gender-related, psychosocial, physiological and cognitive outcomes of puberty suppression. Quality was assessed on a standardised scale. There was one high quality study, 25 moderate quality studies and 24 low quality studies. The low quality studies were excluded from the synthesis of results.
As can be seen, the conclusions that were based on the synthesis of studies only rejected 24 out of 50 studies – less than half. The myth has arisen that the synthesis only included the one high quality study. That is simply untrue.
There were two such literature reviews: the other was for cross-sex hormones. This study found 19 out of 53 studies were low quality and so were not used in synthesis. Only one study was classed as high quality – the rest medium quality and so were used in the analysis.
12 cohort, 9 cross-sectional and 32 pre–post studies were included (n=53). One cohort study was high-quality. Other studies were moderate (n=33) and low-quality (n=19). Synthesis of high and moderate-quality studies showed consistent evidence demonstrating induction of puberty, although with varying feminising/masculinising effects. There was limited evidence regarding gender dysphoria, body satisfaction, psychosocial and cognitive outcomes, and fertility.
Again, it is myth that 98% of studies were discarded. The truth is that over a hundred studies were read and appraised. About half of them were graded to be of too poor quality to reliably include in a synthesis of all the evidence. if you include low quality evidence, your over-all conclusions can be at risk from results that are very unreliable. As they say – GIGO – Garbage In Garbage Out.
Nonetheless, despite analysing the higher quality studies, there was no clear evidence that emerged that puberty blockers and cross-sex hormones were safe and effective. The BMJ editorial summed this up perfectly,
One emerging criticism of the Cass review is that it set the methodological bar too high for research to be included in its analysis and discarded too many studies on the basis of quality. In fact, the reality is different: studies in gender medicine fall woefully short in terms of methodological rigour; the methodological bar for gender medicine studies was set too low, generating research findings that are therefore hard to interpret. The methodological quality of research matters because a drug efficacy study in humans with an inappropriate or no control group is a potential breach of research ethics. Offering treatments without an adequate understanding of benefits and harms is unethical. All of this matters even more when the treatments are not trivial; puberty blockers and hormone therapies are major, life altering interventions. Yet this inconclusive and unacceptable evidence base was used to inform influential clinical guidelines, such as those of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH), which themselves were cascaded into the development of subsequent guidelines internationally.
-
Myth 2: Cass recommended no Trans Healthcare for Under 25s
Fact
The Cass Review does not contain any recommendation or suggestion advocating for the withholding of transgender healthcare until the age of 25, nor does it propose a prohibition on individuals transitioning.
Explanation
This myth appears to be a misreading of one of the recommendations.
The Cass Review expressed concerns regarding the necessity for children to transition to adult service provision at the age of 18, a critical phase in their development and potential treatment. Children were deemed particularly vulnerable during this period, facing potential discontinuity of care as they transitioned to other clinics and care providers. Furthermore, the transition made follow-up of patients more challenging.
Cass then says,
Taking account of all the above issues, a follow-through service continuing up to age 25 would remove the need for transition at this vulnerable time and benefit both this younger population and the adult population. This will have the added benefit in the longer-term of also increasing the capacity of adult provision across the country as more gender services are established.
Cass want to set up continuity of service provision by ensure they remain within the same clinical setting and with the same care providers until they are 25. This says nothing about withdrawing any form of treatment that may be appropriate in the adult care pathway. Cass is explicit in saying her report is making no recommendations as to what that care should look like for over 18s.
It looks the myth has arisen from a bizarre misreading of the phrase “remove the need for transition”. Activists appear to think this means that there should be no “gender transition” whereas it is obvious this is referring to “care transition”.
-
Myth 3: Cass is demanding only Double Blind Randomised Controlled Trials be used as evidence in “Trans Healthcare”
Fact
While it is acknowledged that conducting double-blind randomized controlled trials (DBRCT) for puberty blockers in children would present significant ethical and practical challenges, the Cass Review does not advocate solely for the use of DBRCT trials in making treatment recommendations, nor does it mandate that future trials adhere strictly to such protocols. Rather, the review extensively discusses the necessity for appropriate trial designs that are both ethical and practical, emphasizing the importance of maintaining high methodological quality.
Explanation
Cass goes into great detail explaining the nature of clinical evidence and how that can vary in quality depending on the trial design and how it is implemented and analysed. She sets out why Double Blind Randomised Controlled Trials are the ‘gold standard’ as they minimise the risks of confounding factors misleading you and helping to understand cause and effect, for example. (See Explanatory Box 1 in the Report).
Doctors rely on evidence to guide treatment decisions, which can be discussed with patients to facilitate informed choices considering the known benefits and risks of proposed treatments.
Evidence can range from a doctor’s personal experience to more formal sources. For instance, a doctor may draw on their own extensive experience treating patients, known as ‘Expert Opinion.’ While valuable, this method isn’t foolproof, as historical inaccuracies in medical beliefs have shown.
Consulting other doctors’ experiences, especially if documented in published case reports, can offer additional insight. However, these reports have limitations, such as their inability to establish causality between treatment and outcome. For example, if a patient with a bad back improves after swimming, it’s uncertain whether swimming directly caused the improvement or if the back would have healed naturally.
Further up the hierarchy of clinical evidence are papers that examine cohorts of patients, typically involving multiple case studies with statistical analysis. While offering better evidence, they still have potential biases and limitations.
This illustrates the ‘pyramid of clinical evidence,’ which categorises different types of evidence based on their quality and reliability in informing treatment decisions

The above diagram is published in the Cass Review as part of Explanatory Box 1.
We can see from the report and papers that Cass did not insist that only randomised controlled trials were used to assess the evidence. The York team that conducted the analyses chose a method to asses the quality of studies called the Newcastle Ottawa Scale. This is a method best suited for non RCT trials. Cass has selected an assessment method best suited for the nature of the available evidence rather than taken a dogmatic approach on the need for DBRCTs. The results of this method were discussed about countering Myth 1.
Explainer on the Newcastle Ottawa Scale
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) is a tool designed to assess the quality of non-randomized studies, particularly observational studies such as cohort and case-control studies. It provides a structured method for evaluating the risk of bias in these types of studies and has become widely used in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
The NOS consists of a set of criteria grouped into three main categories: selection of study groups, comparability of groups, and ascertainment of either the exposure or outcome of interest. Each category contains several items, and each item is scored based on predefined criteria. The total score indicates the overall quality of the study, with higher scores indicating lower risk of bias.
This scale is best applied when conducting systematic reviews or meta-analyses that include non-randomized studies. By using the NOS, researchers can objectively assess the quality of each study included in their review, allowing them to weigh the evidence appropriately and draw more reliable conclusions.
One of the strengths of the NOS is its flexibility and simplicity. It provides a standardized framework for evaluating study quality, yet it can be adapted to different study designs and research questions. Additionally, the NOS emphasizes key methodological aspects that are crucial for reducing bias in observational studies, such as appropriate selection of study participants and controlling for confounding factors.
Another advantage of the NOS is its widespread use and acceptance in the research community. Many systematic reviews and meta-analyses rely on the NOS to assess the quality of included studies, making it easier for researchers to compare and interpret findings across different studies.
As for future studies, Cass makes no demand only DBRCTs are conducted. What is highlighted is at the very least that service providers build a research capacity to fill in the evidence gaps.
The national infrastructure should be put in place to manage data collection and audit and this should be used to drive continuous quality improvement and research in an active learning environment.
-
Myth 4: There were less than 10 detransitioners out of 3499 patients in the Cass study.


Fact
Cass was unable to determine the detransition rate. Although the GIDS audit study recorded fewer than 10 detransitioners, clinics declined to provide information to the review that would have enabled linking a child’s treatment to their adult outcome. The low recorded rates must be due in part to insufficient data availability.
Explanation
Cass says, “The percentage of people treated with hormones who subsequently detransition remains unknown due to the lack of long-term follow-up studies, although there is suggestion that numbers are increasing.”
The reported number are going to be low for a number of reasons, as Cass describes:
Estimates of the percentage of individuals who embark on a medical pathway and subsequently have regrets or detransition are hard to determine from GDC clinic data alone.
There are several reasons for this:
Damningly, Cass describes the attempt by the review to establish “data linkage’ between records at the childhood gender clinics and adult services to look at longer term detransition and the clinics refused to cooperate with the Independent Review. The report notes the “…attempts to improve the evidence base have been thwarted by a lack of cooperation from the adult gender services”.
We know from other analyses of the data on detransitioning that the quality of data is exceptionally poor and the actual rates of detransition and regret are unknown. This is especially worrying when older data, such as reported in WPATH 7, suggest natural rates of decrease in dysphoria without treatment are very high.
Gender dysphoria during childhood does not inevitably continue into adulthood. Rather, in follow-up studies of prepubertal children (mainly boys) who were referred to clinics for assessment of gender dysphoria, the dysphoria persisted into adulthood for only 6–23% of children.
This suggests that active affirmative treatment may be locking in a trans identity into the majority of children who would otherwise desist with trans ideation and live unmedicated lives.
I shall add more myths as they become spread.
==
It's not so much "myths and misconceptions" as deliberate misinformation. Genderists are scrambling to prop up their faith-based beliefs the same way homeopaths do. Both are fraudulent.
#Andy L.#Cass Review#Cass Report#Dr. Hilary Cass#Hilary Cass#misinformation#myths#misconceptions#detrans#detransition#gender affirming healthcare#gender affirming care#gender affirmation#affirmation model#medical corruption#medical malpractice#medical scandal#systematic review#religion is a mental illness
380 notes
·
View notes
Text
did you guys know that social skills aren't fixed. these are something you can and should learn. even if you're already an adult. it is valuable to understand general social conventions, boundaries, etc. this is true regardless of your cultural context or neurodivergency or anxiety. that's all. xoxo gossip girl
#i am not vaguing anyone ftr#i just think there is a widespread misconception on this website that if you're ND or mentally ill#that it's a get out of jail free card for having good boundaries and ignoring social convention#i personally am both ND and mentally ill so if you were thinking of hassling me about this - don't :D
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
I can't stop thinking about how there are so few resources and information regarding impulsive thoughts. When you look it up, you get a bunch of information about intrusive thoughts. It's not even shocking to me, at this point, that people confuse these two concepts. The people actually dealing with fucked up impulsive thoughts have little to no resources, advice, or support. Google is an absolute joke when it comes to this. I am begging the field of psychology to actually give a shit about this.
An impulsive thought is not necessarily a personal desire. Many people have disturbing impulsive thoughts they do not truly want to do and would never act upon. It is a huge misconception that people always enjoy or want to act on their impulsive thoughts. I see this remark frequently popping up even when people try to distinguish intrusive and impulsive thoughts. An impulsive thought, in many cases, is not a desire or fantasy at all. Human brains are complicated things.
#mental illness#mental health#impulsive thoughts#intrusive thoughts#misconceptions#social stigma#trauma#ptsd#cptsd#cluster b#bpd thoughts#bpd problems#ocd#impulse control#actually cluster b#vent#aspd
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
regarding pretty privilege: when i lost weight people began emphasizing to me that i was conventionally attractive. only difference i noticed is that when i tried to speak about my issues like loneliness or my social struggles due to my autism people would dismiss me because apparently now that im conventionally attractive and all i need to do to solve my problems is bat my eyes at someone. i havent really noticed any actual benefits.
thank you for sharing your experience!
ive heard from other women who have lost significant amounts of weight that they felt they were treated better, like just in general that people were nicer and more attentive etc. interesting thats not a universal experience then, i guess mentall illness is a significant additional factor! additionally, a lot of beauty bias is subtle, for example you would not always know if someone offered you help or you got the job because someone else found you to be attractive. your experience tells me that mental illness and its consequences are not taken seriously because from what you say i assume people believed your alienation due to your weight/looks, not because they consider the issues autistic women face!
and this image of beautiful women getting whatever they want „with the bat of an eye“ is an obvious misogynistic myth. while attractiveness can impact your life its not the end all be all its made out to be to get women to compete and buy products.
#ask#beauty bias#if more people from wherever on the ‚spectrum‘ of perceived attractiveness want to share i will collect these in the hashtag!#this actually kind of confirms beauty bias… people make assumptions based on your attractiveness.#when you’re unattractive people think your life must be bad and when youre attractive people dont think your life can be bad#this also shows misconceptions about mental illness and how it develops - attractiveness can factor into it but is by far not the most#relevant factor
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
'Here's to the people whose trauma did not give them thick skin.
The ones who became more sensitive and insecure,
Who cry more easily,
Who get overwhelmed at the little things.
I'm so tired of the narrative that trauma makes you tough and untouchable.
We're survivors-
Not superheroes.'
-Anonymous
#new username#the story behind my username#complex post traumatic stress disorder#trauma survivor#the truth about trauma#trauma response#trauma recovery#childhood trauma#cptsd recovery#cptsd#cptsdsupport#writeblr#healing#self care#misconceptions#mental support#mental illness#mental disorder#ptsd#childhood ptsd#complex ptsd#cptsdsurvivor#cptsd coping#just cptsd things#writing#tumblr#brittbooks#writers of tumblr#mental heath support#mental heath awareness
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
I might not make it out of this year alive
#idk#its not really up to me#i think thats a common misconception abt suicidal people#its never really up to us there just isnt any other way#mental illness#sui ideation#sui#mentally ill
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
obsessed with how people call any critique or questioning of the big pharma industries surrounding meds for mental illness and neurodivergence “ableist med shaming”. we are never escaping this prison that society has crafted around us.
#these medications are . not great in many ways and conversations need to be had 😭#as someone who’s been on 4 diff ssris and is currently on them#I hate hate hate the way psychiatrists treat them and gps give them out to even mild depression cases#overprescribed with their negative side effects undermined just to get mental health treatment responsibility off your bac#efficacy of half these meds is questionable too in terms of their harm reduction but go off I guess#don’t even get me started on ssri polypharmacy and this concept of perpetually increasing doses + therefore adverse effects until ‘it works’#putting people on insane cocktails without even being in good therapy like you can’t make this shit up#personally I can’t wait to get off my meds#the idea that once you’re on them and stable you should never stop taking them#it’s just the drug companies trying to like their pockets 😭#some people may need meds forever but for that to be your aim from the onset of taking them ? :/#most mental illnesses aren’t even chemical imbalances that’s literally a medically proven misconception
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

"The most common misconception about evolution is that it did not happen.
Celebrate Darwin.”
Charles Darwin, born Feb 12, 1809.
#Charles Darwin#Darwin Day#evolution#Common Creationist Misconceptions#misconceptions#religion is a mental illness
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing anxiety into my characters is something that can and is very personal to me.
#shut up kdot#coming from a person with diagnosed general anxiety and OCD#with an emphasis on them still being generally happy#mentally ill people are not just sad/anxious all the time#we also have a full range of emotions! anger! happiness! excitement!#which i find is a misconception#sure some people may be struggling really hard where it’s hard to find happiness#but for me it’s different#this post is specifically about#niomi hansen (who has GAD and panic disorder)#and mina atsumi (OCD and depression)#mental health
0 notes
Text
Misconceptions about Mental Health | Solh Wellness
For a very long time, people have been embarrassed to talk about their challenges with mental diseases and mental health problems or to ask for treatment. Many of the myths and lies about mental diseases that resulted from it were fostered by exaggerated media coverage. The battle against stigma has made some progress, but there are still many prevalent beliefs about mental illnesses that may prevent individuals from getting the care they require.
These misconceptions may be detrimental in a number of different ways. They propagate unfounded beliefs that discourage people from seeking treatment because they fear being criticised. Because they have unrealistic expectations about the therapy they would receive, some people may opt not to seek therapy, leaving them to suffer alone and possibly making their problems worse.

Let's debunk some of these common mental health misconceptions:
Myth 1: Mental illnesses are not common. Contrary to popular belief, mental illnesses are relatively prevalent. A severe mental disorder affects one in every 25 Americans, and one in five people will encounter mental health concerns at some point in their lives. Anyone, including children, teenagers, and adults, can develop a mental disease, which can range in severity from moderate to severe.
Myth 2: Using willpower may help those who suffer from mental illnesses. It's a frequent misperception that mental health issues may be treated by effort and mental toughness alone. Despite their complexity, a number of factors, such as genetics, trauma, the environment, and neurological problems, can contribute to mental diseases. It is imperative to know that having a mental health issue does not signify frailty or weakness.
Myth 3: All mental diseases require medication. It's not necessary for everyone with a mental illness to use medication to manage their symptoms. The type of treatment will depend on the patient and how serious the problem is. While some individuals may discover that taking medication aids in the management of their mental health, others may discover that talking therapy, making lifestyle modifications, or turning to social support networks are adequate.
Myth 4: Those who have mental problems are unable to work. Another damaging myth is the notion that people with mental health issues cannot get or maintain employment. The reality is that many people who suffer from mental diseases are just as successful, trustworthy, and driven as those who do not. Even having a work could be advantageous since it offers structure and a sense of purpose.
Myth 5: Mentally ill individuals are more violent Contrary to what many people think, those who have mental health problems are not more violent. People who are displaying mental health symptoms conduct a relatively small percentage of violent crimes. In truth, those who suffer from mental diseases are more likely to become victims of crime than criminals.
Myth 6: It is impossible to recover from a mental disease. It is false to believe that mental health issues are enduring and unavoidable. If given the right support and care, people with mental illnesses can live happy, fulfilling lives. Many people recover from mental health conditions and go on to lead happy lives.
Conclusion
For the purpose of fostering a more welcoming and constructive approach towards mental health, it is essential to dispel these prejudices. In order to help people on their path to increased mental wellbeing, seeking care and treatment for mental illness should not be stigmatised; rather, it should be encouraged and supported.
Since we at Solh think that mental health is important, we have selected a variety of effective self-help techniques to improve your mental wellbeing. We provide a variety of services, including goal-setting, mood analysis, self-assessment tests, journaling, and access to a vast collection of educational materials. Utilise our extensive collection of self-help resources to take control of your path to greater mental health and personal growth.
#mental health misconceptions#misconceptions about mental illness#mental health myths#mental health treatment#mental health issues
0 notes
Text
Random Fact #6,430
People with severe mental illnesses are more than 10 times more likely to be victims of violent crime than the general population.

#mental illness#mental health#stigma#misconceptions#gun violence#did you know#random fact#random facts#social stigma#random factoids#random factoid#yes really#little known fact
1 note
·
View note
Text
Homicidal Ideation
homicidal ideation is the term for having active thoughts about murdering others. these thoughts can be intrusive, however they can also often be voluntary.
misconceptions:
‘people who have these thoughts either have killed someone or will kill someone in the future’ - this is false. most people who have these thoughts usually have disordered behaviours (most commonly as a result of personality disorders) and struggle to find healthy ways to cope with their emotions, therefore provocation and stress can easily cause thoughts of inflicting harm onto others. this doesn’t inherently mean these people are dangerous, nor does it mean that they’re going to act upon these thoughts. most people who experience homicidal ideation never act on it and use it more as a way to process their distress/frustration internally.
‘having these thoughts about people in your life means you can’t possibly care for them’ - also false. caring for someone doesn’t make them an exception to mental illness and it doesn’t stop your mental illnesses from existing. to think that someone’s love for you is only valid as long as they’re not displaying traits of mental illness is unfair and is hugely misinformed. to love and be loved by someone who is mentally ill is to accept that they will display symptoms of their mental illness. you are not the exception and they do not love you any less by showing traits of being unwell.
‘so you endorse murder’ - no. that’s not at all what this means and if you seriously think this then your grasp of severe mental health issues is too limited to be commenting on such topics.
‘you’re evil’ - for being unwell? don’t be a cunt. if you seriously think that having a disordered manner of processing emotions internally makes someone ‘evil’ then that sounds more like an issue with you being too sensitive and having a lack of understanding, not an issue with the mentally ill person experiencing these thoughts. don’t make your inability to understand mental illness into someone else’s problem.
as someone who does experience homicidal ideation, it’s also important to not make the mistake of assuming everyone who is mentally ill experiences these thoughts either. i had an anonymous ask earlier today that directly associated the fact i’m mentally unwell with murder and homicidal thoughts, to immediately make this assumption just because someone is mentally ill is disgusting.
#actually mentally ill#clusterb#actually aspd#actually npd#aspd#npd#cluster b#actuallynpd#actuallyaspd#actually bpd#bpd#actuallybpd#actually antisocial#actually narcissistic#actually borderline#antisocial personality disorder#borderline personality disorder#narcissistic sociopath#narcissistic personality disorder#cluster b personality disorder#psychopathy#homicidal ideation#homicidal thoughts#mental illness#personality disorder#narc abuse isnt real#stigma#stigmatised disorders#being ill doesn’t make you evil#ableism
736 notes
·
View notes
Text
My dear lgbt+ kids,
Someone requested some advice on whether to openly tell people you are mentally ill/neurodivergent/invisibly disabled or not.
There's some research that suggests that, for example, autistic people are more likely to identify as lgbt+ than their non-autistic peers - so this is absolutely a topic that belongs on a lgbt+ blog and I'm sure there are a lot of you who had to make that decision (and probably keep having to make it as coming-outs of any sort are rarely one-and-done!).
In fact, I had/have to make that decision myself! As an autistic person with depression and anxiety, I could tell you now why I personally decided to be open about all those diagnoses - but the right decision for me isn't necessarily the right decision for you as my life isn't yours.
So, what I'll do instead is to write down a general list with (potential) pros and cons, and I encourage you to nitpick it. Personalize it, take some time to decide how much, if at all, each point weighs in your own decision. There's no right or wrong answer here. It's all about your highly individual situation, about your safety and comfort.
Reasons not to be open about it:
It may put you at risk for various sorts of hate, discrimination, negative stigma and bad treatment
It may put a burden on you to educate others and discuss any misconceptions or myths they believe in, including potentially hurtful or disstressing ones (maybe even fruitlessly so which may cause frustrations or fights)
It may change the way people treat you, even in well-meant ways (babying you, pitying you, trying to "help" against your wishes etc.)
It may feel like a loss of privacy, make you feel "naked" or emotionally vulnerable, make you worry more about the way others perceive you etc.
Reasons to be open about it:
It may help others understand you or your behavior better, which may have positive effects on your relationships
It may allow you to ask for support and help more easily (either from friends and loved ones or in the workplace, school etc.)
It may make you feel empowered and help you accept/love yourself as a disabled person more
It may contribute to making your specific diagnosis more visible in society (which may also make you feel pride in breaking down stereotypes and supporting your community)
It may discourage people from assigning wrong or hurtful labels to you (either armchair-diagnosing you or labeling you as weird, crazy, lazy, gross etc.)
It's important to keep in mind that some people do not have the option to make this decision for themselves, for example because they have highly visible symptoms or they are in a position where their caretakers make the decision for them. This adds another layer to why we can't judge one decision as better or worse than the other - it's not always their own decision.
With all my love,
Your Tumblr Dad
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
[screams] its sooo weird telling ppl i have psychosis bc they like. usually treat me different love it <3
#doing my part to try and normalize it but also it sucks bc i alienate the ppl around me due to their misconceptions that i try to clear up#like though fr. so many ppl think that om gonna b violent bc of my mental illness. no bitch i just have a bad time!! not abt u!!!
1 note
·
View note
Text
"So, you wanna make them ace?"
Asexuality 101: Making your characters asexual
Indroduction: Ok, so, from what I've seen in fandom and in general, most people don't really know how to write an asexual character. Many just quit it and make them allosexual, others just struggle their way without having much of a guide. Prime example is Alastor from Hazbin Hotel, whom many people want to involve in sexual scenarios so they go with the "asexuality is a spectrum" route. Problem is, they don't understand how asexuality is a spectrum exactly and then they just end up writing their characters as allo. Now, how to avoid this? Teaching them!
If you're looking for a good way to get started with your own asexual oc, an ace headcanon or a media charater, I've got you! (i mention sex briefly here in some parts)
My credentials: I'm ace.
The basics
What is asexuality?
Asexuality is a sexual orientation that is generally defined by the lack of sexual attraction, or a very little amount of it. Sexual attraction is many times confused with libido, which is the sexual desire. Sexual attraction is more accurately, "the desire of having sex with this specific person." Therefore, some ace people do have a libido, and do want to have sex, but mostly are just not attracted to a person.
Myths and misconceptions
Asexuals can't have sex - as many shippers say, "asexuality is a spectrum", and while some aces don't have sex indeed, they can want it and have it as well. Person to person scenario
Asexuals don't know nothing about sex - unless the ace in question is a child, they probably may know, in fact, a lot. Many ace people like reading, watching or consuming smut, and by this and other means, even if they don't have sex themselves, they pretty much know how it is and how it works. Sex is everywhere, after all. Hard to miss
Asexuality is caused by trauma - it can be! Just not always, and most aces are simply born this way
Asexuality is a medical condition - much like homosexuality, asexuality is frequently treated as an illnes and many ace people are forced into conversion therapy. Some people also hold the belief that asexuality is caused by an anormality in a person's hormones, a mental illness, etc. But it is not true! Asexual people can obviously also be mentally ill in some way, but these are different things. It is just a sexual orientation like any other!
Asexuality is caused by HRT - hormone replacement therapy, ie. taking testosterone or estrogen, is one of the most common type of medical transition for trans people. Some hold the belief that taking hormones like those can "break" your sexuality (estrogen does sometimes decrease a person's libido, but it depends on the person's organism and it doesn't take your sexual attraction away from you), and turn you asexual
Asexuality is caused by autism - this myth may be originated from the fact that many autistic people are in fact asexual, or by the fact that both asexuals and autistic people tend to be infantilized a lot. However, as much as autistic people are very commonly also ace, asexuality is not, in fact, a symptom of autism
Basic terminology
Ace - short for "asexual".
Aro - short for "aromantic"; someone who experiences little to no romantic attraction, aka typically "doesn't fall in love".
Allo - somebody who does experience attraction. "Allosexual" is someone who is not asexual, and "alloromantic" is someone who is not aromantic.
Aspec - short for "a-spectrum". The a-spectrum is an umbrella term for anyone who is in any way ace, aro, aplatonic, afamilial, or other identities that fit here.
Acespec - short for "asexual spectrum/ace spectrum". It's a part of the a-spectrum and contemplates all asexuality.
Aesthetic attraction - finding someone pretty or beatiful, without necessarily wanting to have sex with them. Many ace people who didn't know they were ace report to having used to mistake it with sexual attraction.
Sensual attraction - similar to sexual attraction; the desire to touch someone, but without wanting to actuall have sex with them. Many ace people also confused this with sexual attraction.
Aphobia - discrimination against aspec people.
Amatonormativity- the belief that everybody is happier in a relationship, wether they want it or not, and should want and seek to be in one, and the general root of aphobia.
The Split Attraction Model
If you are looking on the ace community for a while, you might have heard of the split attraction model--if you haven't, here it is:
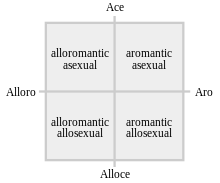
Image description: The Split Attraction Model, a cross chart inside a square, with four ends. The first end of the cross is labelled "ace", its opposite is labelled as "alloce", the third end is labelled as "alloro" and it's opposite is labelled as "aro". The section on the "alloro" and "ace" square is labelled "alloromantic asexual", the section in the "ace" and "aro" part is labelled "aromantic asexual", the section on the "alloro" and "alloce" square is labelled as "alloromantic allosexual" and the section on the "aro" and "alloce" section is labelled "aromantic allosexual". /end ID.
The split attraction model divides all orientations in four groups: The aroaces, the aroallos, the alloaces and the alloallos. It is usually shortened to "SAM".
Many people find this model useful, because it sorts your attraction into two groups: allo- and a-, and yes and no. It's simple and easy.
Many aces do not use this model to explain their attraction/lack thereof though! Hence the first distinction of aces we have here: SAM-aces and non-SAM-aces. Basically aces who use the Split Attraction Model and aces who prefer not to!
A non-SAM ace may define their asexuality as their romantic orientation as well, or label themselves differently altogether. While a SAM ace could call themselves an "asexual aromantic" or an "asexual alloromantic", a non-SAM ace could call themselves just "an asexual". In this case, they can be neither "alloro" nor "aro".
If your character is aware of their sexuality and identifies as ace, it's good to know wether they use the Split Attraction Model for themselves or not.
The spectrum
You may have heard that "asexuality is a spectrum" a thousand times, but what does it mean?
Just like "non-binary", "asexual" can be an identity on its own, but it is actually an umbrella term for a bunch of orientations. When we say that it is a spectrum, we are saying that there is Nuance. "Ace who doesn't date", "ace who dates", "ace who experiences just a little bit of sexual attraction", "aces who like sex" and so on. 'But Angel', you ask me, 'didn't you say that asexuality is when people don't have sexual attraction?' It can be! But there IS nuance, and that's what I am here to tell you.
There are two more factors beyond the SAM that you can consider:
"Are they sex repulsed, sex favorable, or sex neutral?"
Here is the "aces can still have sex" thing. A sex repulsed ace is probably what the majority of people think when they hear "asexual". It is an ace person who doesn't like sex. Doesn't want to have it, is disgusted by it, despises sexual intimacy, etc. They are the aces who tipically just don't want to have sex, and are very happy without it.
A sex favorable asexual is someone who likes it. Sure, they don't feel sexual attraction, but who's letting it stop them, right? They like sexual acts, they are fine and happy with having sex in general, and that's what the "aces can still have sex" point means. Yes, they can, if they want to! Maybe your character themself doesn't define themselves as neither repulsed nor favorable, but it's good to know what their instance on sex is.
Sex neutral asexuals are aces who are not repulsed by it, but are not really into it either. They may have sex, they may be fine with it, they may like it even, but they generally don't have a desire or strong feelings regarding it. It's just sex, after all.
Sex ambivalent asexuals are another thing I want to touch on. They are tipically aces whose instance on sex changes! Sometimes they may feel repulsed by it, sometimes they may want it, sometimes they may not care. They are neither strictly one, nor another. Their feelings change!
It's good to see where in this categorization your character or blorbo would be.
Inside the asexual spectrum, where do they stand?
If I were to represent the ace spectrum as a linear thing, I'd do it like this:
Image description: A linear representation of the asexual spectrum, in the shape of an arch. In one end, it is written "asexual", on the other, it is written "allosexual" and on the very middle, at the top of the arch, it is written "gray-asexual". /end ID.
or like this:
Image description: Another linear representation of the asexual spectrum. One of the ends is a black circle and the other is a white circle. Between them, a gradient goes from one circle to another, passing through different shades of gray. The black end is labelled as "asexual", the white end is labelled as "allosexual", and the gradient with shades of gray is labelled "different kinds of Gray-As". /end ID.
What is graysexual, you ask me? We all know that the world is not black-and-white, and as so, sexuality is also not. Grayace is a term for a person that is also asexual, but not strictly: that is, they are the "feels a little of sexual attraction" part of the spectrum. It is called like that because when we put asexual and allosexual in two ends of a spectrum, graysexuality stands in this gray area.
Gray sexuals may:
Experience sexual attraction only sometimes
Experience light sexual attraction
Experience sexual attraction under certain conditions in certain scenarios, for example, when they are already very intimate with a certain person
And many more! Graysexuality is on itself a spectrum, but having an idea of allosexual -> graysexual -> strictly asexual is already a good guide. Graysexuality can also be described as "having partial sexual attraction".
Fun fact about gray-aces: The asexual flag has four stripes; purple, white, gray and black. The purple stripe is meant to be a color signifier of the community, the white means allosexual, the gray means the gray aces and the black stripe represents people with strictly no sexual attraction. Hence the term "black stripe asexual" (which is not very popular but I personally like).
Micro-labels
You already have a basic understanding of the asexual spectrum and how it works, so you can think on where exactly in the spectrum your character/blorbo is. To help you out further, I present you the microlabels! Much like non binary is an umbrella term with many microlabels like genderqueer, xenogender and demigender, that help one explain their identity with more and more specific explanations, asexuals also have a lot of microlabels! Here are some:
Cupiosexual - asexual person that wishes to have a sexual relationship (example: i am cupioromantic person and i am basically a hopeless romantic and a yearner. cupiosexuality is similar, but with sex)
Gray sexual - asexual person with partial sexual attraction
Demisexual - asexual person who can only be attracted to people they already have a bond with
Abrosexual - person whose sexuality is fluid, and may be asexual at one time, bisexual at another, gay at another, etc.
Aceflux - asexual person whose sexuality changes, like abrosexual, but only between asexual identities
Aegosexual - asexual person who likes the idea of sex or fantasises about it, as long as it doesn't envolve them
Lythosexual - asexual person who is only sexually attracted to people they are not close with, and their sexual attraction fades out once the become closer
Myrsexual - asexual person that uses multiple asexual identities to describe their sexuality
Aroace - aromantic asexual person
Alloace - alloromantic asexual person
Apothisexual - sex-repulsed asexual person
These are not all micro labels in the asexual spectrum, but they are quite a lot. Maybe even if your charater is not sure if they are in a certain label or not, you may find them in some of these descriptions.
Links to resources with more microlabels: Tumblr post by @aroacesafeplaceforall (no images) /
/ A slightly longer list on asexuals.net (undescribed flags) /
/ Another guide for microlabels on lgbtqia.fandom.com (undescribed flags)
Bonus questions
Is it okay if I make my asexual character autistic? Is it not stereotyping? Yes, it's okay. There are actual asexual autistic people, and I'm sure they'd love to get represented as well!
Is it okay if I make my asexual character have sex? Is it not erasure? Yes, you can do that too! As long as it is where they stand in the spectrum (as explained in the topics above), you are doing a good thing by representing sex-favorable asexuals.
Do I have to make a romantic orientation for them too? No. Your character may be a non-sam ace, and identify as ace alone!
I heard that it is erasure if I make smut fanfic of ace character X. I don't get it how! While it is true many ace people have sex, many people when writing that just ignore their sexuality when writing/drawing smut of them! The spectrum is wide, so when you are doing that, remember where they stand on it.
Why can't I headcanon this ace character as allosexual? I headcanon straight characters as gay/bi/pan all the time and nobody says it's wrong! If people don't like my headcanon why can't they just look away? Because asexual people are a marginalized group, unlike straight people, so it is as okay to make them allo as it is to take an asian or black or jewish character and make them white. Because it is not just an individual headcanon; it's a part of a much bigger problem, and by avoiding headcanoning ace characters as allo, you are confronting your own internalized aphobia, which is a good thing! If you still want to make them have sex, well, that's what I made this guide for! So you can make them have sex as you wish without erasing their identity.
I am ace and am basing myself or my own experiences here. Is it okay if I...? The answer is generally yes. If you wanna write about a different ace experience than your own, a little bit of research won't hurt, though!
Is this enough for me to write my ace character? It is a start. This is a general guide, and there are some things I haven't touched on this guide (like aphobia) so I'd advice you to do more in-depth research on topics you want to focus more on, but this should get you pretty far.
Extra
"Is Alastor from Hazbin Hotel canonically ace or aroace?" (slightly related, because some people looking for this guide to write this guy might want to know this too)
Answer: link to a post clearing this up this with some sources. Short answer though, is that he is confirmed to be ace, not aroace.
"If I didn't understand something here, or I have more questions, can I ask you?"
Answer: Yes! You can reblog this post with questions, and my inbox is also open, and I make sure to always let anon on. I will be happy to help if I can.
"One of the image descriptions on this post was off or confusing, can you change it to X so it is better to understand it?"
Answer: Of course! I will need you to signal me in either the notes or in the inbox what I need to change, though.
"Are asexual people queer?"
Answer: Yes! Because the queer community, as the name suggests, is for people who are different, odd, and are not considered "normal" because of that. Asexual people are not a part of "the norm", because we don't feel sexual attraction, and therefore, we, and by extension your ace characters too, are queer.
<2
#writing advice#representation#writing tips#fanfiction#fandom#hazbin alastor#hazbin hotel alastor#radioapple#radiodust#radiohusk#alastor the radio demon#asexual#asexuality#asexual spectrum#non sam ace#aroace#alloace#ace#acespec#ace spectrum#character building#writing asexual characters#queer#writing queer characters#ace characters#asexual characters#shipping#ace alastor#described#angel's weird essay things
496 notes
·
View notes
Note
what are some common character misconceptions that you often see get thrown around in the fandom?
#homestuck#homestuck meta#homestuck analysis#homestuck fandom#homestuck polls#alpha trolls#alpha kids#beta trolls#beta kids#the exiles#nekro.sms
306 notes
·
View notes